Abstract
RCAS1 is involved in generating the suppressive profile of the tumor microenvironment that helps cancer cells evade immune surveillance. The status of the cells surrounding the cancer nest may affect both the progression of the cancer and the development of metastases. In cases of ovarian cancer, a large number of patients do not respond to the applied therapy. The patient’s response to the applied therapy is directly linked to the status of the tumor microenvironment and the intensity of its suppressive profile. We analyzed the immunoreactivity of RCAS1 on the cells present in the ovarian cancer microenvironment in patients with the disease; these cells included macrophages and carcinoma-associated fibroblasts. Later we analyzed the immunoreactivity levels within these cells, taking into consideration the clinical stage of the cancer and the therapeutic strategy applied, such as the number of chemotherapy regiments, primary cytoreductive surgery, or the presence of advanced ascites. In the patients who did not respond to the therapy we observed significantly higher immunoreactivity levels of RCAS1 within the cancer nest than in those patients who did respond; moreover, in the non-responsive patients we found RCAS1 within both macrophages and carcinoma-associated fibroblasts. RCAS1 staining may provide information about the intensity of the immuno-suppressive microenvironment profile found in cases of ovarian cancer and its intensity may directly relate to the clinical outcome of the disease.
Keywords: RCAS1, Ovarian cancer, RCAS1 positive macrophages, CAF
Introduction
Cancer cells must evade immune surveillance. Many molecular mechanisms present within both the cancer milieu and the cancer microenvironment participate in this process of evasion. RCAS1 is a well-known membrane protein that was discovered in 1996 by Sonoda (1996). More specifically, it is a membrane II protein that is expressed on various types of cancer cells, including those of ovarian cancer. The presence of RCAS1 expression correlates with a poor prognosis (Akahira et al. 2004; Sonoda et al. 2008; Enjoji et al. 2005) for the case. This is because this protein is able to suppress cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK cells (Nakashima et al. 1999; Yoshida et al. 2008) and it may evoke apoptosis of these mononuclear immune cells as well as trough activation of FADD in its cytoplasm (Matsushima et al. 2001). Some recent research papers have revealed that RCAS1 expression is not limited to the cancer milieu but can also be detected within cells derived from the cancer microenvironment, such as macrophages or stromal cells (Adamek et al. 2009; Dutsch-Wicherek 2010; Dutsch-Wicherek et al. 2009; Enjoji et al. 2006). Moreover, the presence of RCAS1 within the cancer microenvironment seems to be related to the escape of the cancer cells from immune surveillance (Sonoda et al. 1996; 2005a; b; Giaginis et al. 2008; Enjoji et al. 2004a). In a similar way, the function of RCAS1 is related to the soluble form of RCAS1 (Sonoda et al. 1996; Giaginis et al. 2008; Enjoji et al. 2004a; b; Dutsch-Wicherek and Wicherek 2008; Sonoda et al. 2010). The soluble form of RCAS1, or sRCAS1, has been detected in the blood sera of patients with various types of carcinomas and, moreover, the level of sRCAS1 correlated inversely with the response to applied anti-cancer therapy (Dutsch-Wicherek and Wicherek 2008; Sonoda et al. 2006). It is well known that the status of the tumor microenvironment is crucial for the development of the cancer nest. Both stromal cells and even immune cells present within the tumor microenvironment may help the cancer to progress. The macrophages from the tumor microenvironment, called tumor-associated macrophages (TAM), may suppress the activity of cytotoxic immune cells. Most likely, this process is realized by the expression of various proteins present on the cell membrane of the macrophages, including B7H4 and RCAS1 (Adamek et al. 2009; Dutsch-Wicherek 2010; Dutsch-Wicherek et al. 2009; Kryczek et al. 2007; Kryczek et al. 2006). As immune cells are able to suppress the activity of CTLs and NK cells, RCAS1-positive macrophages probably participate in generating the suppressive profile of the tumor microenvironment (Yoshida et al. 2008). The cellular profile of the tumor microenvironment is important for the clinical outcome of the cancer patient treatment. Not only do the macrophages surrounding the tumor affect its homeostasis but recently carcinoma-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) have been identified as a cellular population important for tumor growth. Furthermore, tumor growth does not proceed uniformly (Wu et al. 2011; Dutsch-Wicherek et al. 2010; Dutsch-Wicherek et al. 2011). Consequently, in advanced carcinoma it is possible to distinguish different zones within the tumor. For instance, one part of the tumor may be typified by strongly matched proliferation while another zone may be typified by apoptosis, necrosis, or hyalinization of the stroma. The development of metastases is linked with changes not only within the same tumor (e.g., the grading of cancer cells) but also in the cancer microenvironment itself. Most likely, the zones of the microenvironment associated with strong tumor growth (highly matched proliferation) differ from those zones in which there is highly marked hyalinization of the stroma. For this reason we decided to focus on RCAS1 immunoreactivity levels in the different parts of the tumor as well as in the different parts of its microenvironment. Since RCAS1 has been identified as a protein involved in the regulation of cytotoxic immune cells within the tumor microenvironment in patients with ovarian and cervical cancer, we selected RCAS1 for a planned immunohistochemical analysis that would examine the different zones in both the cancer milieu and in the cancer microenvironment.
In his study, Sonoda demonstrated that, while on the one hand, the intensity of the RCAS1 immunoreactivity in ovarian cancer cells was related to a poor prognosis for the case (Sonoda et al. 2009), on the other hand, the presence of RCAS1 expression within the cervical cancer microenvironment was associated with the potential to develop metastases (Sonoda et al. 2005a; 2007). The participation of RCAS1 in the development of metastases was also found in other types of adenocarcinoma (Dutsch-Wicherek et al. 2009; Iwasaki et al. 2000; Nakabayashi et al. 2007). Recently, RCAS1 has been proposed as a clinically useful marker for detecting various kinds of adenocarcinoma (Ali-Fehmi et al. 2010; Giaginis et al. 2009). We therefore decided to analyze the RCAS1 immunoreactivity levels precisely, measuring them in a large group of patients treated for ovarian cancer with both surgery and subsequent chemotherapy. We detected the same kind of RCAS1 immunoreactivity profile within both the cancer milieu and the cancer microenvironment. The differences in RCAS1 immunoreactivity were analyzed according to different clinical parameters, including the kind of surgery performed and the response to the chemotherapy applied.
Methods
Patients
The patients included in the study were treated surgically for ovarian cancer between December 2006 and January 2010 in the Department of Gynecology and Oncology of the Lukaszczyk Oncological Center, Bydgoszcz, Poland. All of the 74 patients involved underwent optimal cytoreductive surgery either during the primary surgical procedure or following neoadjuvant chemotherapy. The histological characteristics of the tumors are able presented in Table 1: grading, histological type and FIGO stage (Table 1). The patients were divided according to the therapeutic strategy applied: These data are also presented in Table 1 (Table 1). The patients included in our study were observed after the surgical procedure and chemotherapy in the Out-patient Unit of the Lukaszczyk Oncological Center, Bydgoszcz, Poland. The period of the follow up observation was from 1 to 5 years.
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of the patient and RCAS1 immunoreactivity changes correlating with different parts of the tumor and various clinico-pathological features (a precise description of these relationships was presented in the results section of chapters 2 and 3)
| Data | N (%) | Significant RCAS1 immunoreactivity correlating with different clinicopathological features |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 54 (8) | No |
| Grading | Yes | |
| G1 | 1 (1.3%) | |
| G2 | 25 (33.8%) | |
| G3 | 48 (64.9%) | |
| FIGO | Yes | |
| I | 20 (27.0%) | |
| II | 10 (13.5%) | |
| III | 44 (59.5%) | |
| IV | 0 | |
| Ca125 before surgery | 1823.36 | No |
| Surgery | Yes | |
| primary cytoreductive surgery - optimally debulked | 55 (74.3%) | |
| neoadjuvant chemotherapy - secondary cytoreductive surgery | 19 (25.7%) | |
| Ascites | Yes | |
| 0 | 42 (57.3%) | |
| 1 | 32 (42.7%) | |
| Histology | No | |
| Serous adenocarcinoma (ACS) | 31 (41.9%) | |
| Mucinous adenocarcinoma ( ACM) | 14 (18.9%) | |
| Endometrioid adenocarcinoma (ACE) | 7 (9.4%) | |
| Male differentiated (MD) | 10 (13.5%) | |
| Clear cell carcinoma (ACC) | 4 (5.4%) | |
| Granulosa cell tumors (GCTs) | 8 (10.9%) | |
| Number of chemotherapy regimens | Yes | |
| 1 | 59 (79.7%) | |
| More than 1 | 15 (20.3%) |
The patient’s consent was obtained in each case. Prior to the present study we also obtained the approval of the Jagiellonian University Ethical Committee for our research program (DK/KB/CM/0031/447/2010).
Immunohistochemistry
The RCAS1 immunoreactivity levels were evaluated in samples obtained from 74 patients with primary ovarian cancer treated at the Lukaszczyk Oncology Center, Bydgoszcz, Poland. Formalin-fixed paraffin embedded 4 μm sections were de-waxed, hydrated gradually and incubated with an anti-RCAS1 antibody (ready to use; Medical & Biological Laboratories Co, Ltd, Japan) overnight at 4°C. The sections were then rinsed and incubated for 30 minutes with the EnVision peroxidase labeled polymer conjugated to anti-mouse secondary antibody (Dako, Carpinteria, CA). After washing the sections, the reaction product was developed for 5 minutes using 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) (Dako, Carpinteria, CA), counterstained with hematoxylin and then dehydrated and mounted in a permanent medium (Consul Mount; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. Waltham, MA, USA). As a positive control breast cancer sections were used. The sections were viewed through the Nikon Eclipse 80i (Nikon Instruments Europe BV, Badhoevedorp, the Netherlands).
The intensity of the staining of both the cytoplasm and membrane was evaluated. The percentage of stained cells was also evaluated using the subjective method of the succeeding approximations we previously described (Jozwicki et al. 2005). Staining intensity was evaluated as negative (0) or positive with a grade of 1+ (pale brown), 2+ (brown) or 3+ (dark brown).
Ki67 immunostaining was performed using consecutive sections. After deparaffinization, rehydration and antigen retrieval using PT Link and high pH buffer (Dako, Carpinteria, CA), the endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched with a 3% solution of H2O2. Anti-Ki67 primary monoclonal mouse antibody, clone MIB-1 (Dako), at dilution 1:100 with EnVision™ FLEX Antibody Diluent (Dako, Carpinteria, CA) was then applied for 30 minutes. Next, the subsequent steps of immunostaining were performed as in RCAS1 labeling. Finally, the percentage of Ki67-positive cancer cells was evaluated in both the high and low proliferative areas.
Definitions used methodologically: CI (Cytoplasmatic Immunoreactivity) – the staining level of cytoplasmatic structures of the cancer cell; MI (Membrane Immunoreactivity) – the staining level of the cell membrane of the cancer cell; CP (Central Part) – the older part of the tumor, without signs of dynamic growth; BP (Border Part) – the younger part of the tumor, with signs of dynamic growth (e.g., the presence of small nests of tumor cells, expressions of stromal reactivity, as inflammatory infiltration and/or types of stromal modeling pattern).
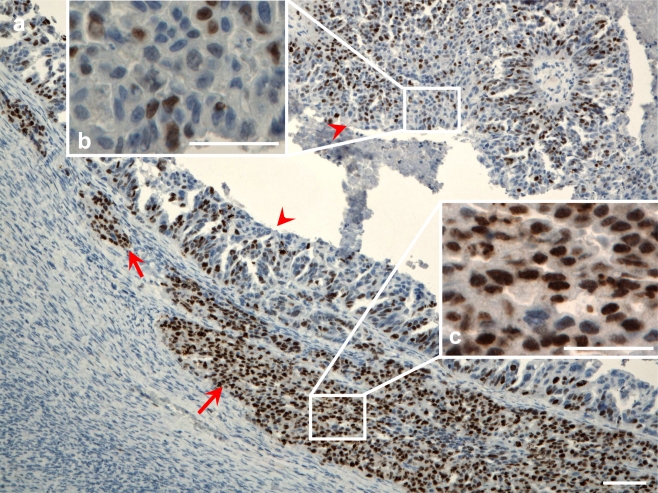
The categorization of the central and border parts of the tumors was carried out by means of morphological assessment. Later, Ki67 immunostaining was performed in order to evaluate the rate of proliferation in given areas. We determined the 40%-cutoff point based on the percentage of Ki67-positive cancer cells (calculated as follows: mean percentage of Ki67-positive cells for central parts +1SD). The proliferation rate in the areas of the tumors initially defined as central parts was significantly a lower when compared to the rate in the areas defined as border parts (p < 0.0001). In the central parts of the tumors, 22.75% of the cells were Ki67-positive while in the border parts 53.70% were Ki67-positive. The areas showing a higher proliferation rate than the cutoff point were classified as border parts while the areas with a proliferation rate below this point were classified as central parts Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
Ki67 immunostaining in ovarian cancer. a) The arrow indicates the area with a high proliferation rate of the border part of the tumor with a newly invasive ovarian cancer cell group. The arrow heads indicate areas of the central part of the tumor showing a lower percentage of the Ki67-positive cells. Scale bar 100 μm. b) The enlarged area of the central part of the tumor. Scale bar = 50 μm. c) The enlarged area of the newly invasive ovarian cancer cell group. Scale bar = 50 μm
Statistical analysis
The distribution of variables in the study groups of women checked with the use of the Shapiro-Wilk test showed that each of the women was different from normal. The statistical significance between the groups was determined by the Kruskal-Wallis test, one-way analysis of variance by ranks. The Mann-Whitney U test was then used as applicable. All statistical analyses were carried out with the Statistica 8.0 software program. A p value < 0.05 was considered indicative of statistical significance.
Results
The characteristic of RCAS1 immunoreactivity
RCAS1 immunoreactivity within the cancer milieu
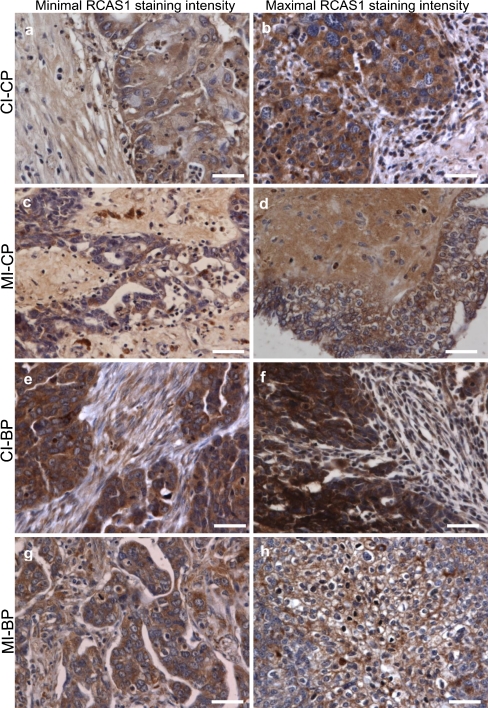
The levels of RCAS1 immunoreactivity within the cancer nest were not uniform; the chief differences that we found were between the levels in the central and border parts of the tumor. Many apoptotic cells were seen in the central part of the tumor, which was characterized by high stromal hyalinization, a small number of fibroblasts, either absence or presence of single macrophages and little or no inflammatory reactivity in the tumor microenvironment. In the border portion of the cancer nest, by contrast, the proliferation was distinct. For this reason, we decided to distinguish two parts of the cancer nest, the central part and the border part and to analyze the RCAS1 immunoreactivity levels independently as CP versus BP. Nevertheless, as the ovarian cancer cells were typified by cytoplasmatic and membrane expression of RCAS1, we analysed the RCAS1 immunoreactivity in the cytoplasm independently of the membrane RCAS1 expression as CI vs MI Fig. 2 Table 2.
Fig. 2.
RCAS1 immunoreactivity within the ovarian cancer nest. Scale bars = 50 μm. a) Cytoplasmatic RCAS1 immunoreactivity (CI) within the ovarian cancer cells derived from the central part of the tumor (CP) with predominant minimal staining expression 1+. b) Cytoplasmatic RCAS1 immunoreactivity (CI) within the ovarian cancer cells derived from the central part of the tumor (CP) with predominant maximal staining expression 2+. c) Membrane RCAS1 immunoreactivity (MI) within the ovarian cancer cells derived from the central part of the tumor (CP) with predominant minimal staining expression 0. d) Membrane RCAS1 immunoreactivity (MI) within the ovarian cancer cells derived from the central part of the tumor (CP) with predominant maximal staining expression 1+. e) Cytoplasmatic RCAS1 immunoreactivity (CI) within the ovarian cancer cells derived from the border part of the tumor (BP) with predominant minimal staining expression 2+. f) Cytoplasmatic RCAS1 immunoreactivity (CI) within the ovarian cancer cells derived from the border part of the tumor (BP) with predominant maximal staining expression 3+. g) Membrane RCAS1 immunoreactivity (MI) within the ovarian cancer cells derived from the border part of the tumor (BP) with predominant minimal staining expression 0. h) Membrane RCAS1 immunoreactivity (MI) within the ovarian cancer cells derived from the border part of the tumor (BP) with predominant maximal staining expression 2+
Table 2.
RCAS1 immunoreactivity levels (cytoplasmatic and membrane immunoreactivity of RCAS1) within the ovarian cancer milieu
| Immunostaining Intensity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | 11 | 21 | 31 | |
| CP-cytoplasm | 4 (5.4) | 42 (56.8) | 27 (36.5) | 1 (1.3) |
| CP-membrane | 58 (78.4) | 12 (16.2) | 4 (5.4) | 0 (0.0) |
| BP-cytoplasm | 0 (0.0) | 3 (4.1) | 41 (55.4) | 30 (40.5) |
| BP-membrane | 38 (51.4) | 12 (16.2) | 16 (21.6) | 8 (10.8) |
1 – Number of samples (percentage of samples)
RCAS1 immunoreactivity within the ovarian cancer microenvironment
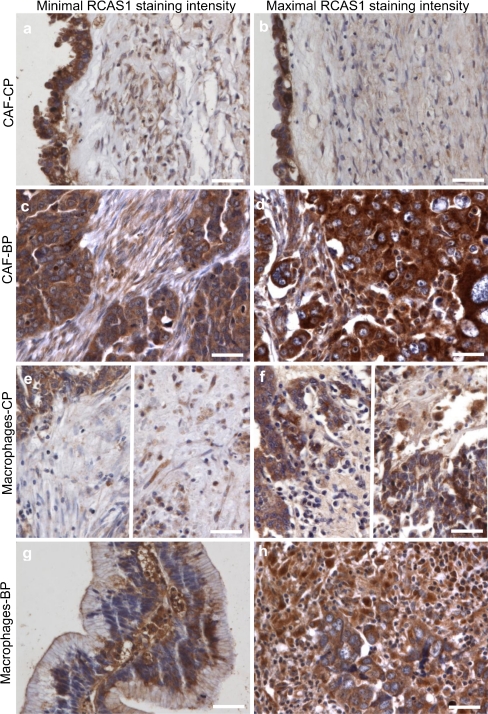
The level of RCAS1 immunoreactivity was detected within the cells surrounding the cancer nest, namely, macrophages (TAM) and carcinoma-associated fibroblasts (CAF). We observed significant differences in RCAS1 immunoreactivity levels between the cells infiltrating the cancer nest microenvironment and those surrounding the central part of the tumor Fig. 3 Table 3.
Fig. 3.
RCAS1 immunoreactivity within cells infiltrating the ovarian cancer microenvironment. Scale bars = 50 μm. a) Predominant minimal RCAS1 immunoreactivity within CAF in the central part of the tumor (CP) (staining expression 0). b) Predominant maximal RCAS1 immunoreactivity within CAF in the central part of the tumor (CP) (staining expression 1+) c) Predominant minimal RCAS1 immunoreactivity within CAF in the border part of the tumor (BP) (staining expression 1+). d) Predominant maximal RCAS1 immunoreactivity within CAF in the border part of the tumor (BP) (staining expression 2+). e) Predominant minimal RCAS1 immunoreactivity within the macrophages infiltrating the central part of the tumor (CP) (staining expression 0). Two regions of the tissue section are showed. f) Predominant maximal RCAS1 immunoreactivity within the macrophages infiltrating the central part of the tumor (CP) (staining expression 2+). ). Two regions of the tissue section are shown. g) Predominant minimal RCAS1 immunoreactivity within the macrophages in the border part of the tumor (BP) (staining expression 2+). h) Predominant maximal RCAS1 immunoreactivity within the macrophages in the border part of the tumor (BP) (staining expression 3+)
Table 3.
RCAS1 immunoreactivity levels in macrophages and fibroblasts (CAF) within the ovarian cancer microenvironment
| Immunostaining Intensity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | 11 | 21 | 31 | |
| CP-macrophages2 | 39 (52.7) | 10 (13.5) | 15 (20.3) | 6 (8.1) |
| CP-CAF | 20 (27.0) | 44 (59.5) | 10 (13.5) | 0 (0.0) |
| BP-macrophages3 | 10 (13.5) | 4 (5.4) | 31 (41.9) | 27 (36.5) |
| BP-CAF | 3 (4.1) | 43 (58.1) | 24 (32.4) | 4 (5.4) |
1 – Number of samples (percentage of samples), 2 – In 4 of the samples there were no macrophages, 3 – In 2 of the samples there were no macrophages
RCAS1 immunoreactivity relative to the clinicopathological features
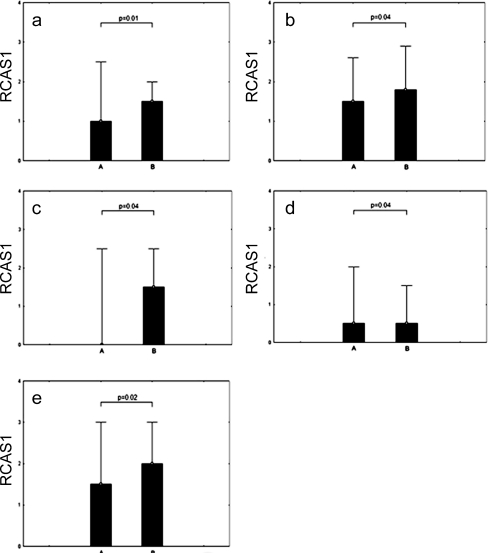
We found statistically significant differences in RCAS1 immunoreactivity within both macrophages and CAFs and these differences corresponded to either the presence or absence of lymph node metastases. The RCAS1 immunoreactivity levels were higher in the patients with lymph node metastases (FIGO IIIc) in comparison to those patients without lymph node metastases. The cases in which the differences were statistically significant are presented in Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.
Comparison of RCAS1 immunoreactivity according to the presence of lymph node metastases: A) without or B) with. a) Cytoplasmatic RCAS1 immunoreactivity (CI) within the ovarian cancer cells derived from the central part of the tumor (CP) b) Membrane RCAS1 immunoreactivity (MI) within the ovarian cancer cells derived from the central part of the tumor (CP) c) Membrane RCAS1 immunoreactivity (MI) within the ovarian cancer cells derived from the border part of the tumor (BP) d) RCAS1 immunoreactivity within CAFs derived from the central part of the tumor (CP) e) RCAS1 immunoreactivity within macrophages derived from the central part of the tumor (CP)
In the BP of the tumor, both the RCAS1 cytoplasmatic immunoreactivity (CI) and RCAS1 immunoreactivity within CAF and macrophages were higher in the cases with lymph node metastases than in those without lymph node metatases; the differences, however, were not statistically significant.
The differences in RCAS1 relative to the grade of the tumor were observed only in the cytoplasm (CI) of ovarian cancer cells derived from the central part of the tumor.
RCAS1 immunoreactivity relative to the applied therapy
We have observed significantly lower RCAS1 cytoplasmatic immunoreactivity levels in the border parts of the tumors derived from patients for whom first-line chemotherapy was sufficient in comparison to the levels in those patients who required second-line chemotherapy (p = 001). In addition, we observed statistically significantly higher levels of RCAS1 immunoreactivity within the macrophages in the central part of the tumor derived from those patients on whom neoadjuvant chemotherapy was applied before cytoreductive surgery in comparison to the levels found in the macrophages within the tissue samples derived from patients on whom primary cytoreductive surgery was performed (p = 0.01). Similarly, the level of membrane RCAS1 immunoreactvity in the central part of the tumor was significantly higher in those patients who underwent neoadjuvant chemotherapy but these differences were not statistically significant (p = 0.08). Furthermore, there was a significantly higher infiltration of RCAS1 positive macrophages in the central part of the tumor in patients with malignant ascites in comparison to those patients without ascites but this difference was, again, not statistically significant (p = 0.09)
Discussion
The suppressive profile of the tumor microenvironment differs according to the tumor zone and may be related to the development of metastases since a tumor depends on its microenvironment for its growth. Most likely, the proliferating zones of the tumor have different microenvironments and this can be detected by the RCAS1 immunoreactivity level. The cancer cells from proliferating zones may develop metastases because the surrounding cells create the conditions favorable for tumor progression. The tumor grows within the stroma that is prepared to support this growth. The presence of an increased number of fibroblasts demonstrating different types of histological dynamic mutual arrangements with cancer nests (modeling pattern: Fig. 1C) along with an increased number of inflammatory cells (e.g., macrophages) may indicate that a proper environment for the growth of the tumor has been established. This is especially true if there is also an increased expression of RCAS1 (Fig. 1). The stronger expression of RCAS1 on macrophages is likely connected with the presence of the M2 macrophage phenotype (Basta et al. 2011). While M1 macrophages are associated with an anti-cancer response and are able to increase the activation of T lymphocytes and NK cell trough secretion of such cytokines as interleukin-12 or TNF alfa, M2 macrophages seem to cooperate with cancer cells and constitute the main part of the suppressive profile that surrounds the tumor. M2 macrophages produce mainly IL-10 and their increased infiltration is linked with a poorer prognosis for the case in various types of carcinomas (Nagamatsu and Schust 2010). RCAS1-positive macrophages were observed in various types of cancer, including salivary gland carcinoma or brain tumors (Adamek et al. 2009; Dutsch-Wicherek 2010; Dutsch-Wicherek et al. 2009). The infiltration of these cells corresponds to cancer progression (Dutsch-Wicherek et al. 2009). RCAS1-positive macrophages were not detected in the ovarian cancer microenvironment, although RCAS1 was observed in both the cytoplasm and membrane of ovarian cancer cells within the cancer nest (Akahira et al. 2004; Sonoda et al. 2008; 2009). Moreover, RCAS1 expression in the cancer nest was higher in those patients who had advanced ovarian cancer (Akahira et al. 2004). Similarly, Sonoda et al. have observed that patients with advanced ovarian cancer have higher RCAS1 blood serum concentration levels (Sonoda et al. 2008). The different structures of these different microenvironments may be reflected in their different RCAS1 expression profiles and changes in RCAS1 immunoreactivity may indicate different functional potential. Certainly, RCAS1 may support the development of the suppressive profile of the tumor microenvironment. Recently, Sonoda et al. found that the level of RCAS1 correlates inversely with the number of Vimentin positive cells within the microenvironment of the ovarian cancer (Sonoda et al. 2009). These cells participate in connective tissue remodeling, which is in turn directly linked with overall survival rates. Thus patients with higher RCAS1 expression (and so lower Vimentin positive cells) have statistically significantly lower survival rates (Sonoda et al. 2009). In our study we did not assess survival rates relative to the level of RCAS1 immunoreactivity but we did observe higher RCAS1 immunoreactivity levels in patients who had lymph node metastases. These data may suggest a relationship between RCAS1 expression and poor prognosis. Clearly it cannot be ignored that as RCAS1 increases, an inhibition of infiltrating cytotoxic T lymphocytes and NK cells comes into play that allows cancer cells to evade immune surveillance and the tumor to grow. In our study we compared various clinical parameters associated with the outcome of applied therapy, such as the number of required chemotherapy regiments, the need for neo-adjuvant chemotherapy application and the primary cytoreductive surgery application. Additionally, we observed alterations in RCAS1 immunoreactivity levels in cases where there was a response to applied therapy in comparison to those typified by resistance to the applied therapy. In cases where resistance to therapy was observed, it was generally linked with a poor prognosis. Therefore, alteration in the microenvironment profile, as measured by the level of RCAS1 immunoreactivity, may help to predict resistance to therapy and such resistance indicates a higher biological potential for the tumor to disseminate.
Conclusion
RCAS1 immunoreactivity is diffuse and not homogeneous and so the levels of RCAS1 immunoreactivity detected in the various parts of the tumor differ. RCAS1 staining may provide information about the intensity of the immune-suppressive microenvironment profile of ovarian cancer; the intensity of this suppressive profile may in turn be related to the clinical outcome of the disease treatment.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Z. Pawlowicz for generating the conditions advantageous for our research. We wish also to thank Professors B. Spiewankiewicz, J. Stelmachow and Z Kojs, for their advice, helpful discussions and friendly words of support. Lastly, we would like to thank Christine Maisto for her assistance.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License, which permits any noncommercial use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
References
- Adamek D, Radwańska E, Gajda M. Expression of RCAS1 protein in microglia/macrophages accompanying brain tumours An immunofluorescence study. Folia Neuropathol. 2009;47(3):240–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akahira JI, Aoki M, Suzuki T, Moriya T, Niikura H, Ito K, Inoue S, Okamura K, Sasano H, Yaegashi N. Expression of EBAG9/RCAS1 is associated with advanced disease in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer. 2004;90:2197–2202. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali-Fehmi R, Chatterjee M, Ionan A, Levin NK, Arabi H, Bandyopadhyay S, Shah JP, Bryant CS, Hewitt SM, O'Rand MG, Alekseev OM, Morris R, Munkarah A, Abrams J, Tainsky MA. Analysis of the expression of human tumor antigens in ovarian cancer tissues. Cancer Biomark. 2010;6(1):33–48. doi: 10.3233/CBM-2009-0117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basta P, Galazka K, Mach P, Jozwicki W, Walentowicz M, Wicherek L. The immunohistochemical analysis of RCAS1, HLA-G, and B7H4-positive macrophages in partial and complete hydatidiform mole in both applied therapeutic surgery and surgery followed by chemotherapy. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2011;65:164–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2010.00897.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutsch-Wicherek M. RCAS1, MT, and vimentin as potential markers of tumor microenvironment remodeling. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2010;63:181–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2009.00803.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutsch-Wicherek M, Wicherek Ł. The Association of RCAS1 Serum Concentration with the Reversibility or Irreversibility of the Process of Immune Cytotoxic Activity Restriction during Normal Menstrual Cycle, Cancer Relapse, and Surgical Treatment for Various Types of Squamous Cell Carcinomas and Adenocarcinomas. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2008;59:266–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2007.00575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutsch-Wicherek M, Tomaszewska R, Lazar A, Wicherek L, Skladzien J. The association between RCAS1 expression in laryngeal and pharyngeal cancer and its healthy stroma with cancer relapse. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:35. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutsch-Wicherek M, Tomaszewska R, Lazar A, Strek P, Wicherek Ł, Piekutowski K, Jóźwicki W. The evaluation of metallothionein expression in nasal polyps with respect to immune cell presence and activity. BMC Immunol. 2010;11:10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-11-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutsch-Wicherek M, Lazar A, Tomaszewska R (2011) The potential role of MT and vimentin immunoreactivity in the remodeling of the microenvironment of parotid adenocarcinoma. 4:105–113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Enjoji M, Yamaguchi K, Nakashima M, Ohta S, Kotoh K, Fukushima M, Kuniyoshi M, Tanaka M, Nakamuta M, Watanabe T, Nawata H. Serum levels of soluble molecules associated with evasion of immune surveillance: a study in biliary disease. Liver Int. 2004;24:330–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2004.0931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enjoji M, Yamaguchi K, Nakamuta M, Nakashima M, Kotoh K, Tanaka M, Nawata H, Watanabe T. Movement of a novel serum tumour marker, RCAS1, in patients with biliary diseases. Dig Liver Dis. 2004;36:622–627. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2004.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enjoji M, Nakashima M, Yamaguchi K, Kotoh K, Nakamuta M. Significance of RCAS1 antigen in hepatocellular, cholangiocellular and pancreatic carcinomas. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;20:1143–1148. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2005.03840.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enjoji M, Kotoh K, Nakashima M, Yoshimoto T, Miyagi Y, Kohjima M, Nakamuta M. RCAS1-expressing macrophages in inflammatory liver diseases. Liver Int. 2006;26:385–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2005.01223.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaginis C, Davides D, Zarros A, Noussia O, Zizi-Serbetzoglou A, Kouraklis G, Theocharis S. Clinical significance of tumor-associated antigen RCAS1 expression in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53:1728–1734. doi: 10.1007/s10620-007-0035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaginis C, Giagini A, Theocharis S. Receptor-binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells (RCAS1): a novel biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis of human neoplasia. Histol Histopathol. 2009;24:761–776. doi: 10.14670/HH-24.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki T, Nakashima M, Watanabe T, Yamamoto S, Inoue Y, Yamanaka H, Matsumura A, Iuchi K, Mori T, Okada M. Expression and prognostic significance in lung cancer of human tumor-associated antigen RCAS1. Int J Cancer. 2000;89:488–493. doi: 10.1002/1097-0215(20001120)89:6<488::AID-IJC4>3.0.CO;2-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jozwicki W, Domaniewski J, Skok Z, Wolski Z, Domanowska E, Jozwicka G. Usefulness of histologic homogeneity estimation of muscle-invasive urinary bladder cancer in an individual prognosis: a mapping study. Urology. 2005;66:1122–1126. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2005.06.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kryczek I, Zou L, Rodriguez P, Zhu G, Wei S, Mottram P, Brumlik M, Cheng P, Curiel T, Myers L, Lackner A, Alvarez X, Ochoa A, Chen L, Zou W. B7-H4 expression identifies a novel suppressive macrophage population in human ovarian carcinoma. J Exp Med. 2006;203:871–881. doi: 10.1084/jem.20050930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kryczek I, Wei S, Zhu G, Myers L, Mottram P, Cheng P, Chen L, Coukos G, Zou W. Relationship between B7-H4, regulatory T cells, and patient outcome in human ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2007;67:8900–8905. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima T, Nakashima M, Oshima K, Abe Y, Nishimura J, Nawata H, Watanabe T, Muta K. Receptor binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells, a novel regulator of apoptosis of erythroid progenitor cells. Blood. 2001;98:313–321. doi: 10.1182/blood.V98.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamatsu T, Schust DJ. The Immunomodulatory Roles of Macrophages at the Maternal—Fetal Interface. Reprod Science. 2010;17:209–218. doi: 10.1177/1933719109349962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi H, Nakashima M, Hara M, Toyonaga S, Yamada SM, Park KC, Shimizu K. Clinico-pathological significance of RCAS1 expression in gliomas: a potential mechanism of tumor immune escape. Cancer Lett. 2007;246:182–189. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2006.02.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima M, Sonoda K, Watanabe T. Inhibition of cell growth and induction of apoptotic cell death by the human tumor-associated antigen RCAS1. Nat Med. 1999;5:938–942. doi: 10.1038/11383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda K, Nakashima M, Kaku T, Kamura T, Nakano H, Watanabe T. A novel tumor-associated antigen expressed in human uterine and ovarian carcinomas. Cancer. 1996;77:1501–1509. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960415)77:8<1501::AID-CNCR12>3.0.CO;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda K, Miyamoto S, Hirakawa T, Yagi H, Yotsumoto F, Nakashima M, Watanabe T, Nakano H. Association between RCAS1 expression and microenvironmental immune cell death in uterine cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2005;97:772–779. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2005.02.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda K, Miyamoto S, Hirakawa T, Yagi H, Yotsumoto F, Nakashima M, Watanabe T, Nakano H. Invasive potency related to RCAS1 expression in uterine cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2005;99:189–198. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2005.06.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda K, Miyamoto S, Hirakawa T, Yagi H, Yotsumoto F, Nakashima M, Watanabe T, Nakano H. Clinical significance of RCAS1 as a biomarker of uterine cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2006;103:924–931. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2006.05.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda K, Miyamoto S, Yamazaki A, Kobayashi H, Nakashima M, Mekada E, Wake N. Biologic significance of receptor-binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells (RCAS1) as a pivotal regulator of tumor growth through angiogenesis in human uterine cancer. Cancer. 2007;110:1979–1990. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda K, Miyamoto S, Nakashima M, Wake N. The biological role of the unique molecule RCAS1: a bioactive marker that induces connective tissue remodeling and lymphocyte apoptosis. Front Biosci. 2008;13:1106–1116. doi: 10.2741/2748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda K, Miyamoto S, Kobayashi H, Ogawa S, Okugawa K, Taniguchi S, Wake N. The level of RCAS1 expression is inversely correlated with the number of vimentin-positive stromal cells in epithelial ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2009;19:838–843. doi: 10.1111/IGC.0b013e3181a5ff6a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda K, Miyamoto S, Nakashima M, Wake N. Receptor-binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells induces apoptosis via ectodomain shedding. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316:1795–1803. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu MH, Hong HC, Hong TM, Chiang WF, Jin YT, Chen YL (2011) Targeting Galectin-1 in Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblasts Inhibits Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis by Downregulating MCP-1/CCL2 Expression. Clin Cancer Res. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Yoshida S, Higuchi F, Ishibashi Y, Goto M, Sugita Y, Nomura Y, Karube K, Shimizu K, Aoki R, Komatani H, Hashikawa K, Kimura Y, Nakashima M, Nagata K, Ohshima K. Downregulation of RCAS1 and upregulation of cytotoxic T cells affects synovial proliferation and apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2008;35:1716–1722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]