Abstract
Aldol reaction is one of the most important methods for the formation of carbon-carbon bonds. Because of its significance and usefulness, asymmetric versions of this reaction have been realized with different approaches in the past. Over the last decade, the area of organocatalysis has made significant progresses. As one of most studied reactions in organocatalyses, organocatalyzed aldol reaction has emerged as a powerful tool for the synthesis of a large number of useful products in optically enriched forms. In this review, we summarize our efforts on the development of novel organocatalyzed aldol reactions for the enantioselective synthesis of biological active molecules. Literatures closely related to our studies are also covered.
Keywords: aldol reaction, carbonyl compounds, proline, cinchona alkaloid thioureas, organocatalysis
1 Introduction
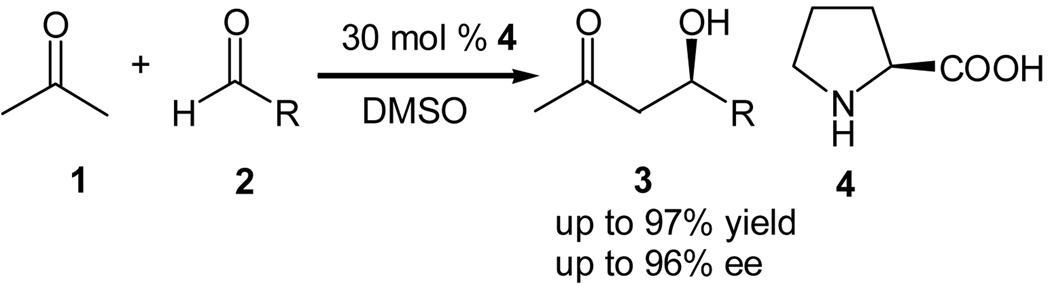
Since its discovery in 1872,1 the aldol reaction has been shown to be an important method for the construction of carbon-carbon bond.2 The reaction involves the addition of an enolizable carbonyl compound with itself or another carbonyl compound to afford the corresponding β-hydroxy carbonyl derivatives, which are key building blocks for the syntheses of poly functional compounds and natural products.3 Apart from the formation of a new carbon-carbon bond, a new stereogenic center is created in the process, which allows potential asymmetric induction in this reaction for the synthesis of optically enriched aldol products. Owing to the numerous applications of optically active β-hydroxy carbonyl compounds and the abundant presence of this moiety in biologically active compounds, such as, carbonyhydrates, antibiodies, alkaloids, and terpenes, their asymmetric synthesis has attracted a lot of attentions.4 Conventionally, the asymmetric aldol reaction was performed using a chiral enolate and a prochiral carbonyl compound as the starting materials. Although the aldol products may be obtained in excellent enantioselectivities using this method, stoichiometric amount of chiral auxillaries have to be employed in these reactions.5 Asymmetric Mukaiyama-aldol reaction catalyzed by chiral Lewis acids represents a convenient method for the preparation of enantioenriched aldol compounds in excellent stereoselectivities.6 However, preformed silyl enol ethers have to be employed in the reaction as the substrates, and therefore, it is less convenient than a direct aldol reaction. Moreover, due to the loss of the silyl group in the products, the atom economy of this reaction is affected.6 The catalytic asymmetric direct aldol reaction reported independently by Shibasaki7 and List8 offers a direct access to β-hydroxy carbonyl compounds using unmodified ketones as the nucleophiles. Shibasaki`s approach was based upon class II aldolases that use a metal co-factor.7 Although the proline mediated intramolecular aldol reaction were reported in the 1970`s,9 List, Lerner and Barbas reported the first intermolecular variant of this reaction using L-proline (4) as the catalyst (Scheme 1).8 The best result obtained was from the reaction of acetone (1) with isobutyraldehyde (2, R= i-Pr), which gave the aldol product 3 in 97% yield and 96% ee.8 The high enantioselectivity obtained in the reaction was explained by a class I aldolase-like enamine mechanism, where proline acts as a “micro-aldolase”.8
Scheme 1.
Proline catalyzed intermolecular asymmetric aldol reaction
Following the rediscovery of this small molecule-catalyzed intermolecular aldol reaction by List, Lerner and Barbas,8 the field of asymmetric organocatalysis has become a intensively studied field of organic chemistry over the last decade. In general, these organocatalysts are derivatives that can be easily synthesized from the chiral pool, such as, amino acids and cinchona alkaloids, or even are commercially available.10 Additionally, organocatalysts usually have better substrate tolerance than enzymes. Therefore, by now these research efforts have led to a greener and general approach for conducting the asymmetric direct aldol reactions as compared to the traditional transition metal-catalysis and enzyme catalysis. The development of this fast-growing field of asymmetric organocatalysis is constantly reviewed.11 In this current account, we will summarize the efforts of our group in the past a few years in developing novel asymmetric aldol reactions for the enantioselective synthesis of biologically active compounds. Studies that are closely related to our research are also covered.
2 Enamine-mediated aldol reaction
In contrast to the catalytic cycles proposed by Hajos and Parrish, which involves a carbinol amine intermediate,9 or by Agami, which involves a two proline molecules in the transition state,12 an enamine mechanism involving a single proline molecule was proposed for the proline-catalyzed intermolecular asymmetric aldol reaction.8 This mechanism is supported by the experimental data and computational results.13 Recently, List group has reported the crystal structures of various proline derived enamines that lend further supports to this mechanism.10c
Although the results obtained in the proline-catalyzed direct aldol reaction represent a breakthrough in this field, high catalyst loading, long reaction times, and highly polar solvents have to be used in this reaction (since proline is insoluble in many organic solvents). Most important of all, the ee values obtained with proline were not that high for most of the substrates.8 These facts indicate that there are still rooms for optimizations. Consequently, many efforts have been directed towards the design and synthesis of new proline derivatives that are more reactive and selective. Expanding the substrate scope of this reaction is another goal in these researches.14 Our journey in this area started in 2005, with the goal of designing and synthesis of more reactive proline-derived catalysts for the aldol reaction in mind.
2.1 Design and synthesis of C2-symmetric bisprolinamindes for asymmetric aldol reaction
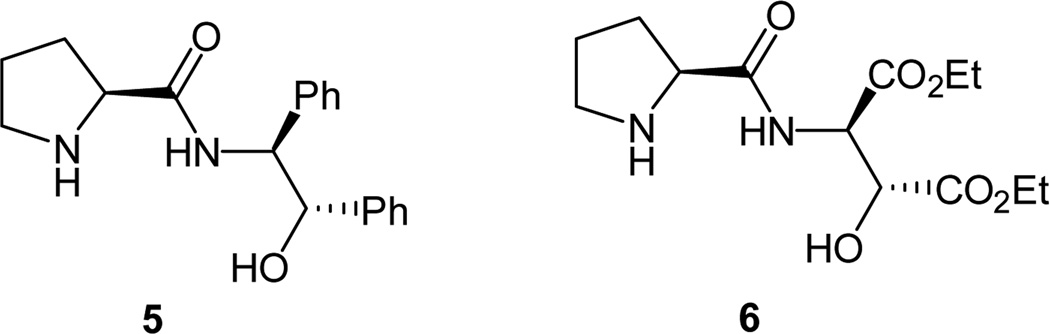
Because of the significance of the optically enriched β-hydroxy carbonyl derivatives in the synthesis of many natural products and biologically active molecules, the proline-catalyzed aldol reaction immediately became a hot research area right after List and Barbas published their seminal results. Before our efforts, several novel proline derivatives that can achieve high enantioselectivities in organocatalytic asymmetric aldol reaction of linear and cyclic ketones with aldehydes have been reported.15 For example, Gong and co-workers reported a prolinamide derivative 5 (Figure 1) as high enantioselective catalysts for the asymmetric aldol reaction.15d However, a high loading of 20 mol % of the catalyst has to be used in order to obtain good reactivities.15d Through fine tuning of the electronic effects, they obtained catalyst 6, which shows both excellent enantioselectivity and high reactivity in asymmetric aldol reactions.16
Figure 1.
Gong’s prolinamide catalysts.
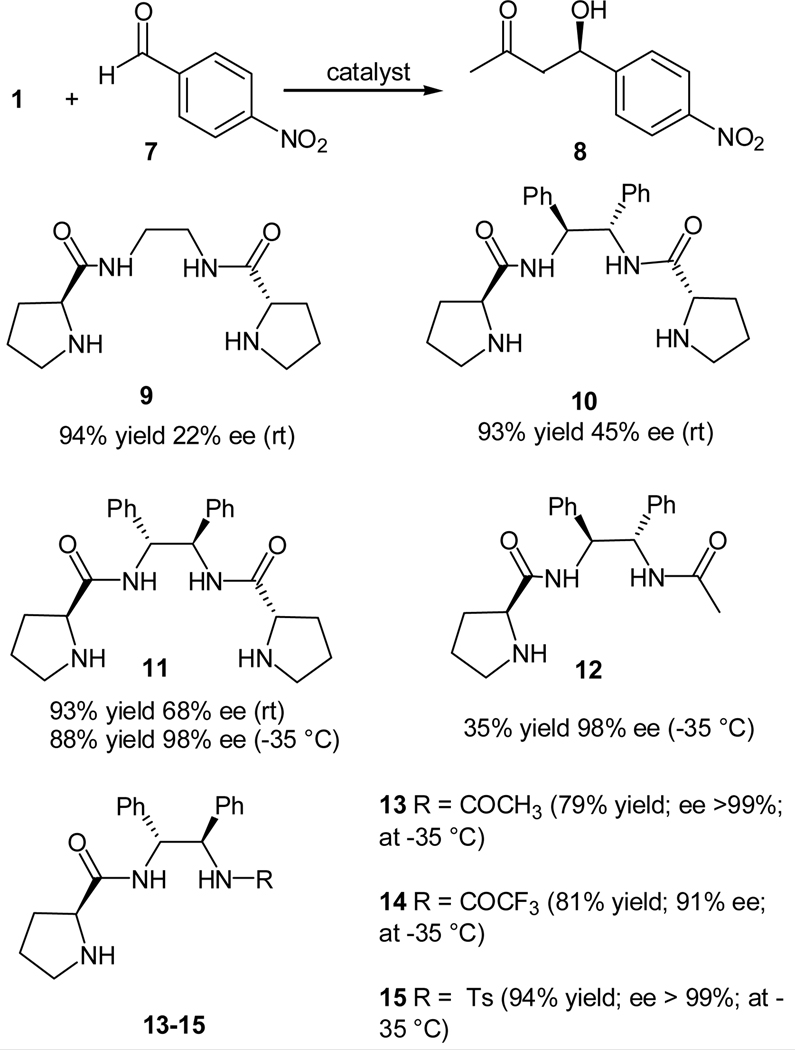
We believe the reactivity prolinamide catalyst may be improved by introducing more reaction center moieties into the catalyst structure, because intuitively more reaction centers should increase the chances for substrate to meet with the reaction center and, therefore, lead to higher reactivity. Thus, we designed and synthesized some prolinamide catalysts that containing two prolinamide moieties (9–11). C2-symmetry was introduced to achieve uniformity in stereocontrol of these two reaction centers. The aldol reaction of acetone (1) with 4-nitrobenzaldehyde (7) was adopted to evaluate these catalysts (Scheme 2).17 Some similar catalysts with only one reaction center, such as 12, were also synthesized and evaluated for comparison purpose (Scheme 2).17
Scheme 2.
Aldol reaction of acetone and 4-nitrobenzaldehyde using C2-symmteric bisprolinamide 9–12 and monoprolinamides 13–15
Indeed, all these C2-symmetric catalysts showed high reactivity at ambient temperature, and among them catalyst 11 yielded the aldol adduct in 93% yield with the highest ee value (68% ee). Through optimization of the reaction temperature, an ee value of 98% with 88% yields may be obtained at −35 °C. For comparison, although catalyst 12, which contain only one prolinamide moiety, also gave high ee value of the product at this temperature, the reactivity is much less since less product yield was obtained. The less reactivity of catalyst 12 as compared to 11 can be attributed to the fact that the catalyst 12 has less reaction center. After the optimization of reaction conditions, the scope of this reaction was examined with catalyst 11.17 Aromatic aldeyhdes bearing both electron-donating and an electron-withdrawing group gave the desired aldol product in moderate to good yields and high ee values. Catalyst 11 also catalyzes the aldol addition of acetone with aliphatic aldehydes in excellent stereoselectivities. The reaction of cyclic ketones and acetol was also investigated; however only cyclohexanone furnished with an excellent dr of 97:3 with an ee value of 93% for the major anti dastereomer. Cyclopenatanone and acetol gave a mixture of diastereomers in moderate selectivities.
During this study, we also discovered this reactivity of this type of catalyst may also be improved through tuning the acidity of the remote hydrogen atom, a concept originally proposed by Gong and co-workers.16 For example, catalysts 13–15 (Scheme 2) having a remote acidic amide proton. Through tuning the electron with-drawing ability of the substituent, high enantioselectivities and low catalyst loadings (down to 5 mol %) were achieved with these catalysts.17b
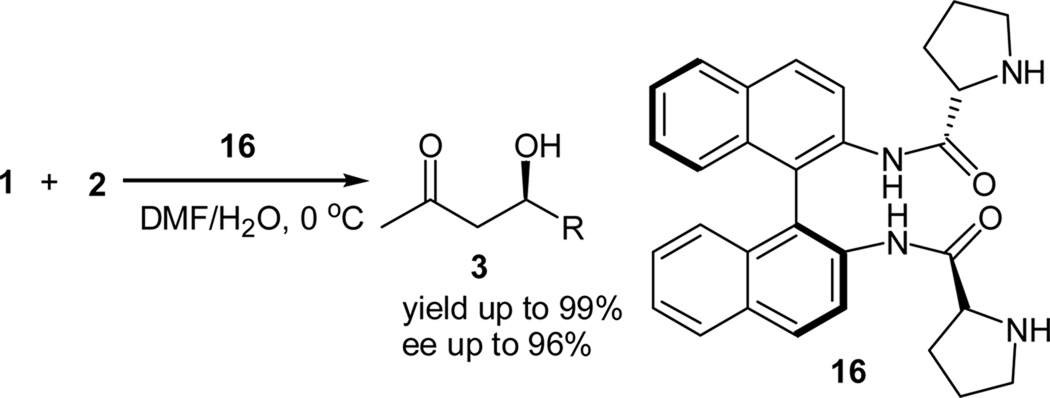
Several other C2-symmetric prolinamide-based organocatalysts have been reported since then. For example, Guillena et al. reported C2-symmetric BINAM-prolinamide catalyst 16 for the direct enantioselective aldol reaction (Scheme 3).18 The reaction employed a mixture of DMF and water as the solvent and the catalyst could be easily recovered after the reaction and reused with no significant decrease in the yields and ee values of the products. The same group later on reported a significant rate enhancement of this reaction using benzoic acid as an additive. The acceleration of the reaction rate was explained on the basis of the improvement in the formation of the enamine intermediate.19
Scheme 3.
Aldol reactionsof ketones with aldehydes catalyzed by a BINAM-prolinamide
2.2 Aldol reaction of 1,2-diketones and glyoxylates
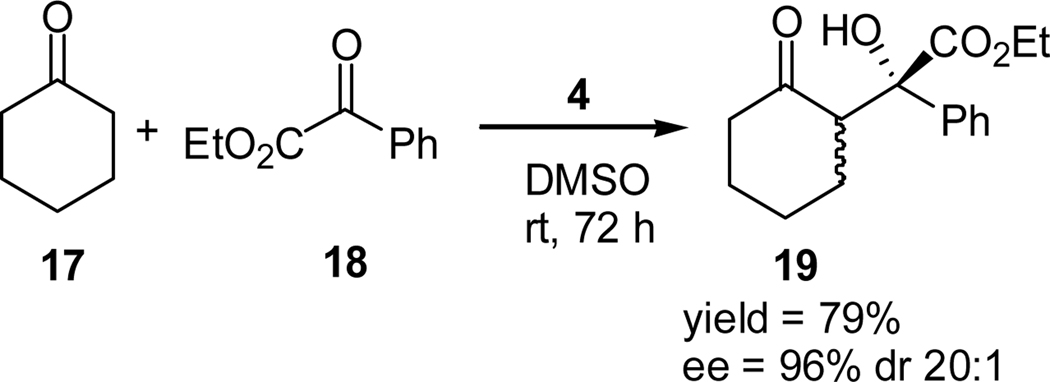
We are interested in developing asymmetric synthesis of biological active molecules using the enamine-mediated asymmetric aldol reaction. For this purpose, the scope of this proline derivative-catalyzed aldol reaction has to be widened to include enamine acceptors other than simple aldehydes. Since normal ketones are poor enamine acceptors in direct aldol reactions, we focused our attention on the use of activated ketones as the enamine acceptors. Before our work, only a few such examples are known in the literature.20 For example: Maruoka and co-workers reported a practical synthesis of (S)-oxybutynin, in which the key step is the L-proline-catalyzed cross aldol reaction of cyclohexanone (17) and ethyl phenylglyoxylate (18) that affords the α-hydroxycarboxylate intermediate 19 in high ee values and excellent dr value (Scheme 4).20d
Scheme 4.
Cross-aldol reaction of cyclohexanone with ethyl phenylglyoxylate
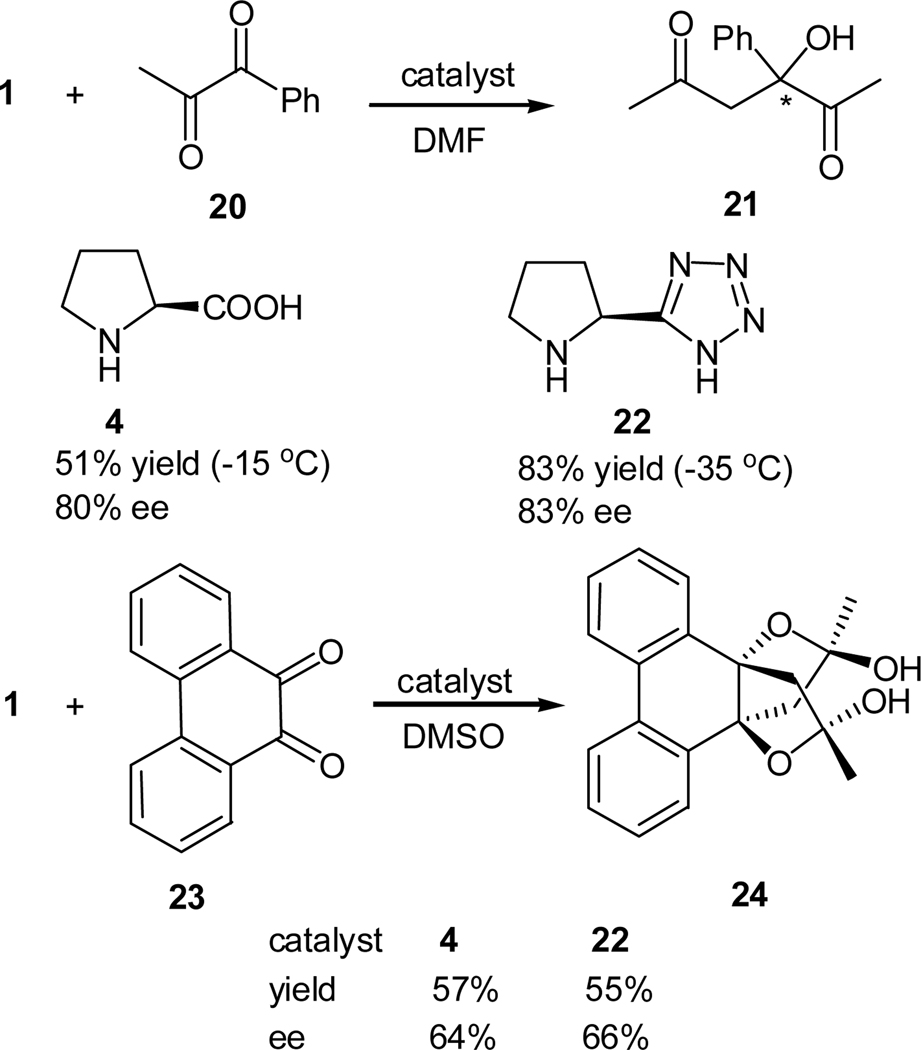
In our initial study, 1,2-diketones were chosen as the representative substrates of activated carbonyl compounds since the two carbonyl are activating each other through inductive effects. Using L-proline (4) and L-proline tetrazole (22) as the catalysts, we studied the cross aldol reaction of 1,2-diketones and ketones, such as acetone and cyclohexanone, and developed an enantioselective synthesis of 2-hydroxy-1,4-diketones (Scheme 5).21 Both catalysts were found to exhibit good reactivity and enantioselectivity. For example, the reaction of 1-phenyl-1,2-propanedione (20) and acetone (1) with L-proline (4) as a catalyst afforded the expected aldol product in 51% yield and 80% ee at −15 °C. Similar reaction with L-proline tetrazole (22) at −35 °C gave a yield of 89% with an ee value of 83% for the product. Cyclic ketones such as cyclohexanone gave only one diastereomer with an enantioselectivity of 80%, whereas cyclopentanone afforded a diastereomeric ratio of 95:5 and an ee value of 99% for the major enantiomer, albeit with lower reactivity.21 In contrast, the reaction of benzil and acetone leads to low reactivity and stereoselectivity. The reaction of cyclic 9,10-phenanthrenequinone (23) with acetone generated a dialdolized product in 86% ee that formed a dihemiacteal in situ.
Scheme 5.
Cross aldol reaction of acetone and 1,2-diketones catalyzed by L-proline and L-proline tetrazole
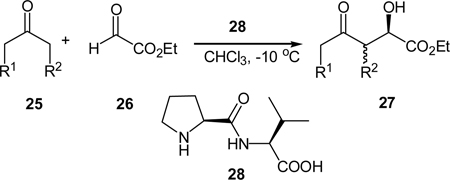
α-Hydroxycarboxylate moiety may be found in many biologically active molecules.22 These compounds may also be regarded as analogues of α-amino acids. Although the asymmetric synthesis of tertiary α-hydroxycarboxylates was well documented,23 the enantioselective synthesis of secondary α-hydroxycarboxylates was not reported. On the basis of proline derivative-catalyzed aldol reaction of activated carbonyl compounds,20,21 we envisioned that secondary α-hydroxycarboxylates should be accessible from the cross aldol reaction of ketones and with glyoxylates. Several novel L-proline derived peptide catalysts were synthesized and evaluated for the cross-aldol reaction of acetone with ethyl glyoxylate (26), and the desired secondary α-hydroxycarboxylate was obtained in 90% yield and 91% ee of under the optimal conditions (Table 1).24 The reaction scope was explored by reacting linear and cyclic ketones with ethyl glyoxylate. Good to excellent diastereo- and enantioselectivities were accomplished with cyclic ketones. Although linear ketones tend to yield a mixture of regioisomers, the ee values of these products are usually high. Moreover, the peptide catalyst 28 may be easily synthesized in just three steps from N-CBZ-L-proline.
Table 1.
Cross-aldol reaction of ketones with ethyl glyoxylate
 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | R1 | R2 | Yield (%) | dr | Ee |
| 1 | H | H | 90 | 91 | |
| 2 | H | Me | 42 | 95:5 | 98 |
| Me | H | 28 | 84 | ||
| 3 | Et | H | 62 | 74 | |
| 4 | i-Pr | H | 35 | 86 | |
| 5 | OMe | H | 56 | 70:30 | 89 (57) |
| 6 | -(CH2)2- | 72 | 60:40 | 95 (85) | |
| 7 | -(CH2)3- | 70 | 90:10 | 88 | |
| 8 | -(CH2OCH3)- | 74 | 80:20 | 80 (26) | |
| 9 | -(CH2SCH3)- | 75 | 90:10 | 81 | |
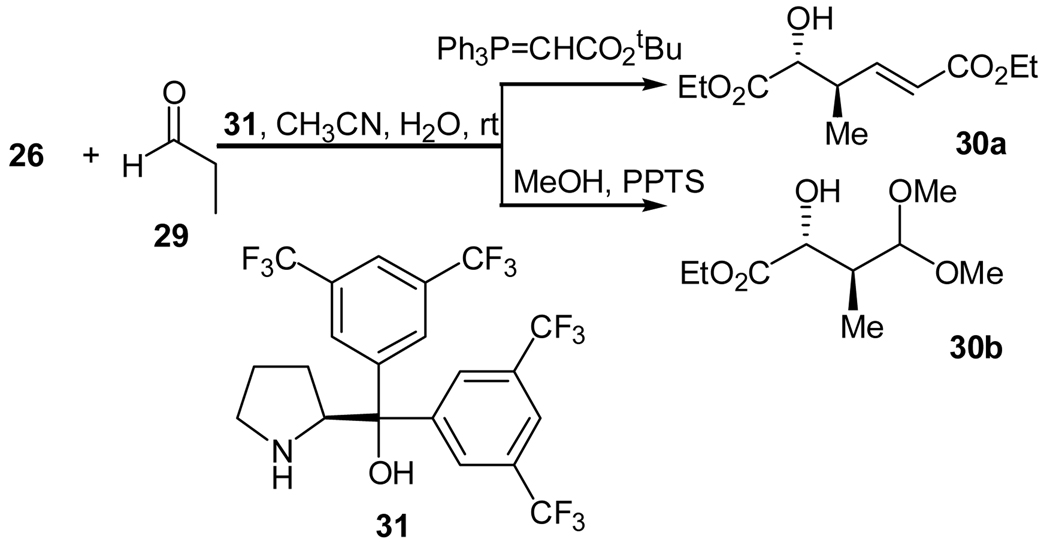
Most recently, Hayashi and co-workers reported a highly enantioselective synthesis of secondary α-hydroxycarboxylates using the cross aldol reaction of aldehydes and polymeric ethyl glyoxylate (Scheme 6).25 Diaryl prolinol 31 was found to be an efficient catalyst for this cross aldol reaction. Using acetonitrile as the solvent and 3 equivalents of water as the additive, the best reactivity was achieved. Excellent diastereo- and enantioselectivities of the desired aldol products were obtained in almost all cases when different aldehydes were used. To facilitate the analysis, the primary aldol products were further converted to homoallylic alcohols 30a using a Wittig reaction or as acetals 30b.25 On the basis of the determined absolute configuration of the product, a reaction mechanism was also proposed.
Scheme 6.
Cross aldol reaction of aldehydes with polymeric ethyl glyoxylate catalyzed by a diarylprolinol
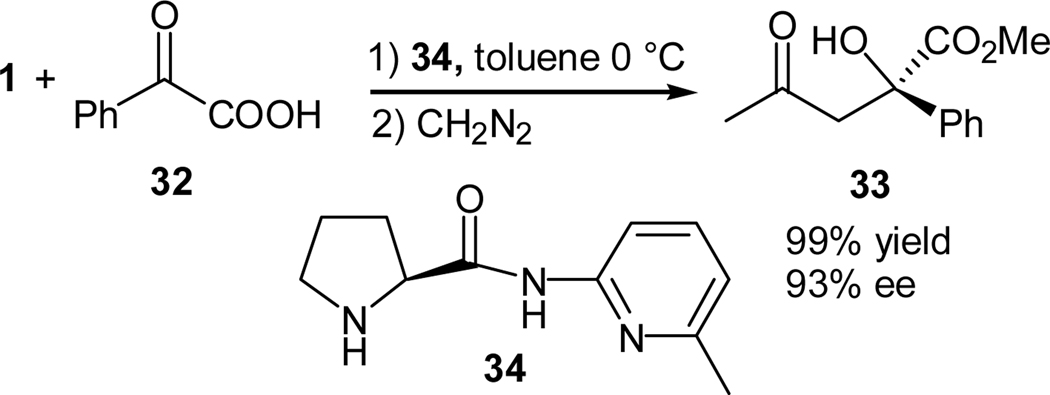
Gong and coworkers also reported a direct aldol addition of ketones to α-ketoacids (32) using a novel prolinamide catalyst 33 designed on the basis of molecular recognition (Scheme 7).26 This asymmetric aldol reaction offers a direct synthesis of α-hydroxycarboxylic acids. The reaction tolerates different types of α-ketoacids and the corresponding products, after in situ protection as their methyl esters 33, were obtained in good yields and excellent ee values. The absolute configuration of the product was determined and a mechanism was proposed to account for the formation of the major stereoisomer. The catalyst may also be reused for at least 2 cycles with no significant loss in reactivity and stereoselectivity. 26
Scheme 7.
Cross aldol reaction of acetone with α-ketoacids promoted by a prolinamide catalyst
2.3 Syntheses of α-hydroxyphosphonates and phosphinates
In recent decades chiral α-hydroxyphosphonates have gained considerable attention due to their antibacterial, antiviral, and anti-cancer properties.27 As structural analogues of α-amino acids, α-hydroxyphosphonates are very good enzyme inhibitors. For examples, some of these derivatives are found to display good inhibitory potency against renin.28 They also act as autotaxin inhibitors and, therefore, are useful in preventing or treating cancer.29 These compounds are also very useful in organic synthesis. For example, they may used as the precursors for the synthesis of α and γ-substituted phosphonates.30 Several enzymatic and chemical methods for the asymmetric synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates have been developed.31 Enantioselective reduction of α-ketophosphonates, enantioselective α-hydroxylation of alkylphosphonates, enantioselective and diastereoselective addition of trialkylphosphites or dialkylphosphites to aldehydes (the Pudovik reaction) are among those reported chemical methods. Most of these methods involve the use of stoichiometric amount of chiral reagents or a kinetic resolution of the racemic starting materials. The chiral Lewis acid-catalyzed dialkylphosphite addition to aldehydes (phospho-aldol reaction) is one of the most convenient method for the synthesis of these compounds.32
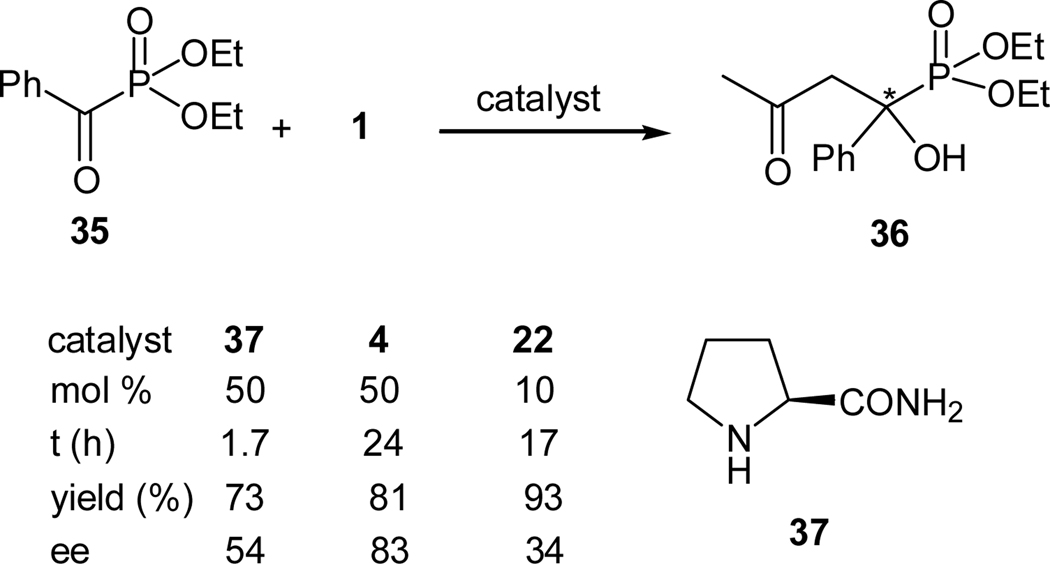
As summarized above, we and others have demonstrated that activated ketones may also be used as the enamine acceptors in the proline derivative-catalyzed asymmetric aldol reactions. Since α-ketophosphonates may be regarded as activated carbonyl compounds due to the strong electron-withdrawing effects of the phosphonate group, we envisioned that α-hydroxphosphonates may be obtained via a direct aldol reaction of α-ketophosphonates and ketones. Thus, the aldol reaction between acetone (1) and benzoylphosphonate 35 was tested with several proline derivatives as the catalysts (Scheme 8).33
Scheme 8.
Organocatalyzed asymmetric cross aldol reaction of acetone and diethyl benzoylphosphonate using different catalysts
Indeed, several proline-based catalysts (4, 22, and 37) catalyze the desired cross aldol reaction between 1 and 35. L-prolinamide (37) was found to be the most reactive catalyst, although it is less enantioselective. On the other hand, L-proline (4) was found to the most efficient catalyst, providing the desired aldol product 36 in 83% ee with a good yield of 81%. After further optimization of the catalyst loading (20 mol %), the reaction temperature (−30 °C), and the solvent (acetone), the desired α-hydroxyphosphonate 36 may be obtained in 67% yield and 87% ee. Thus, a highly efficient organocatalyzed asymmetric synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates was realized for the first time. The scope of this reaction is summarized in Table 2.33
Table 2.
Proline catalyzed asymmetric synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates
 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | R | R1 |
T (°C) |
Time (h) |
Yield (%) |
ee (%) |
| 1 | Ph | Et | −30 | 96 | 65 | 87 |
| 2 | Ph | Me | −30 | 96 | 66 | 95 |
| 3 | Ph | i-Pr | −30 | 120 | 60 | 96 |
| 4 | p-Cl-C6H4 | Et | −30 | 96 | 68 | 91 |
| 5 | p-Cl-C6H4 | i-Pr | −30 | 96 | 63 | 95 |
| 6 | p-F-C6H4 | Et | −30 | 120 | 47 | 80 |
| 7 | p-F-C6H4 | i-Pr | −30 | 120 | 68 | 96 |
| 8 | p-Br-C6H4 | Et | −30 | 96 | 66 | 99 |
| 9 | p-I-C6H4 | Et | −30 | 96 | 67 | 94 |
| 10 | p-Me-C6H4 | Et | −30 | 96 | 63 | 85 |
| 11 | p-OMe-C6H4 | Et | −30 | 96 | 32 | 86 |
| 12 | Me | Et | 0 | 72 | 91 | 97 |
| 13 | PhCH2 | Et | rt | 24 | 86 | 92 |
| 14 | trans-CH3CH=CH | Et | −30 | 108 | 67 | 98 |
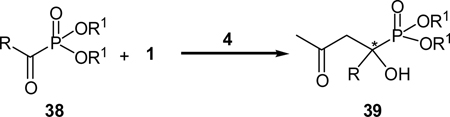
Diethyl benzoylphosphonates (38, R = Ar, R1 = Et) with an electron-withdrawing halogen substituent on the phenyl ring all give good yields of the products with ee values up to 99%, whereas as those with an electron-donating substituent react more sluggishly and require higher catalyst loading. Nevertheless, the desired α-hydroxyphosphonates may still be obtained in good enantioselectivities. Changing the ester functionality of the benzoylketophosphonates (from methyl to isopropyl) enhances the enantioselectivity while the reactivity of the reaction is maintained. Aliphatic and β,γ-unstaurated α-ketophosphonates are highly reactive in this reaction, too. For example, diethyl acetylphosphonate afford the desired adduct in 91% yield and 96% ee. If L-prolinamide (37) is used as the catalyst, the protocol is also applicable for the aldol addition of 2-butanone and methoxy acetone, which provides only a single regioisomer in moderate ee value.33 Thus, with proline derivatives as the catalyst, a versatile catalytic method for the enantioselective synthesis of substituted tertiary α-hydroxyphosphonates was developed.
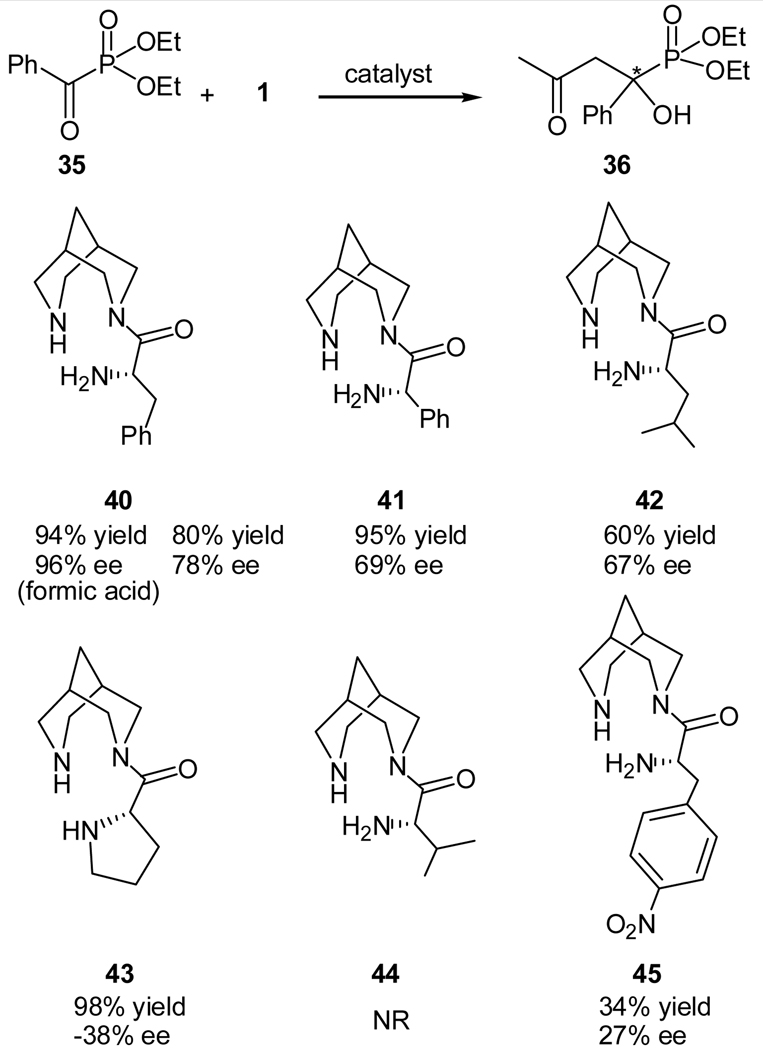
Later Hu and co-workers reported a new class of bispidine-based catalysts for the direct asymmetric synthesis of chiral tertiary α-hydroxyphosphonates (36).34 Various amino acids, such as, L-phenyl alanine, L-phenyl glycine, L-leucine, L-proline, L-valine, and L-4-nitrophenyl alanine were introduced into the bispidine backbone to yield the desired catalysts (40–45) and they were employed in the enantioselective aldol reaction of acetone (1) and diethyl benzoylphosphonate (35, Scheme 9).34
Scheme 9.
Bispidine-derived amines as the catalyst for the enantioselective aldol reaction of acetone and diethyl benzoylphosphonate
The best result was obtained by using the L-phenyl alanine-derived bispidine catalyst 40 (80% yield and 78% ee). The reactivity and enantioselectivity of this catalytic system was further enhanced by adding an acid additive to the reaction mixture, and formic acid was found to be the best acid additive. Under these optimized conditions, the desired α-hydroxyphosphonate 36 was obtained in 94% yield and 96% ee (Scheme 9). The reaction has been show to have a broad substrate scope.
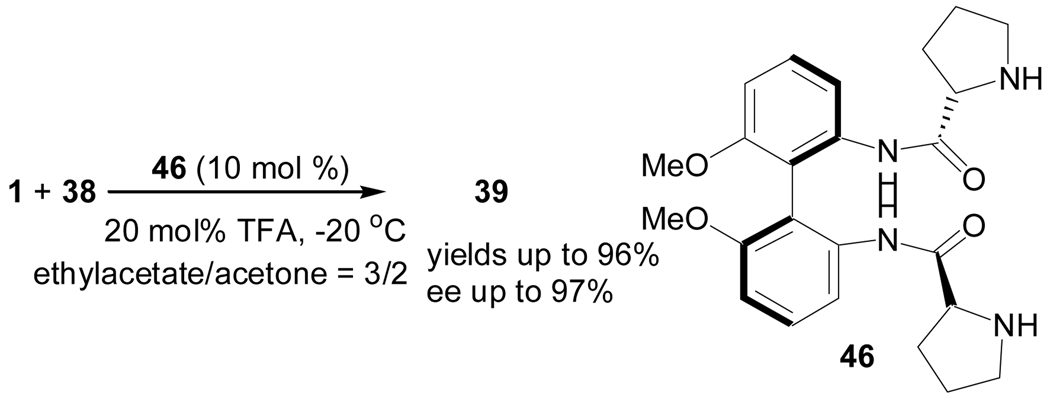
Most recently, Feng and coworkers also reported a biphenyl-derived C2–symmetric bisprolinamide catalyst 46 for the enantioselective aldol reaction of 1 and 38 for the synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates 39 (Scheme 10).35 The presence of an acid additive, such as, trifluoroacetic acid, was found to enhance the reactivity and enantioselectivity of the reaction.35
Scheme 10.
Enantioselective synthesis of α-hydroxy phosphonates catalyzed by a biphenyl-derived C2–symmetric bisprolinamide catalyst
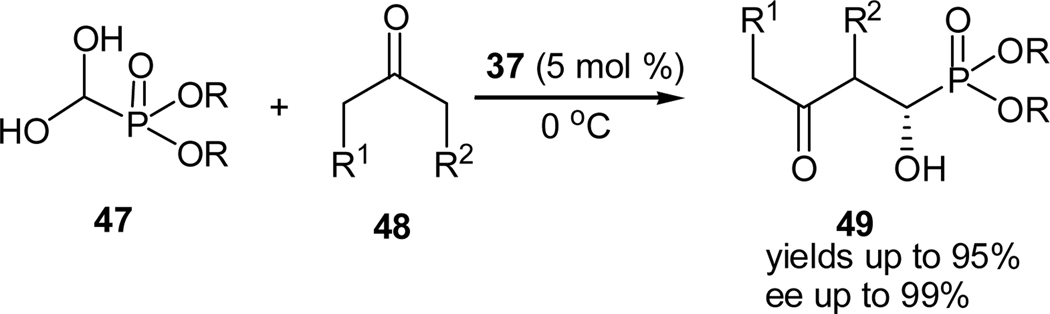
By using diethyl formylphosphonate hydrate (47) as the starting material, we also achieved the first organocatalytic enantioselective synthesis of secondary α-hydroxyphoshphonates using a similar aldol reaction (Scheme 11).36 Readily available proline derivatives, such as, L-proline (4), L-prolinamide (37) and L-proline tetrazole (22), were originally screened as the catalyst, and among them, L-prolinamide (37) was found to be best catalyst for this reaction. Surprisingly, L-proline (4), which proves to be the best catalyst for the aldol reaction of α-ketophosphonates and acetone, completely failed in this case. Most likely because the formylphosphonate hydrate is labile towards the more acidic L-proline (4). Nevertheless, with L-prolinamide (4) and L-proline tetrazole (22) as the catalysts, the desired secondary α-hydroxyphosphonate 49 (R1 = R2 = H) was obtained in 93% yields and 84% ee, and in 46% yield and 72% ee, respectively. The ee value of the product may be further enhanced to 94% by conducting the reaction at 0 °C with L-prolinamide (37). The reaction scope was investigated by reacting formylphosphonate hydrates with a variety of ketones, such as, linear, α-substituted, and cyclic ketones (Table 3). High enantioselectivities were universally obtained with the exception of hydroxyacetone, which gave only 43% ee for the corresponding product. Linear ketone and cyclopentanone also lead to high diastereoselectivities for the products, while cyclohexanone derivatives yield low diastereoselectivities. Linear ketones also tend to a yield a mixture of regioisomers.
Scheme 11.
Prolinamide- catalyzed enantioselective aldol reaction of α-formylphosphonate hydrates and ketones
Table 3.
Enantioselective cross aldol reaction of diethylformyl phosphonate and ketones
| Entry | R1 | R2 | Yield (%) | dr | ee (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | H | 95 | 94 | |
| 2 | Me | H | 62 | 93 | |
| H | Me | 20 | 95:5 | 99 | |
| 3 | Et | H | 58 | 97 | |
| H | Et | 5 | >95:5 | 99 | |
| 4 | Cl | H | 65 | 90 | |
| 5 | OH | H | 75 | 43 | |
| 6 | OMe | H | 77 | 85 | |
| 7 | AcCH2 | H | 60 | 86 | |
| 8 | -(CH2)2- | 94 | 95:5 | >99 | |
| 9 | -(CH2)3- | 82 | 65:35 | 93 | |
| 10 | -CH2OCH2- | 85 | 70:30 | 97 | |
| 11 | -CH2SCH2- | 88 | 70:30 | 93 | |
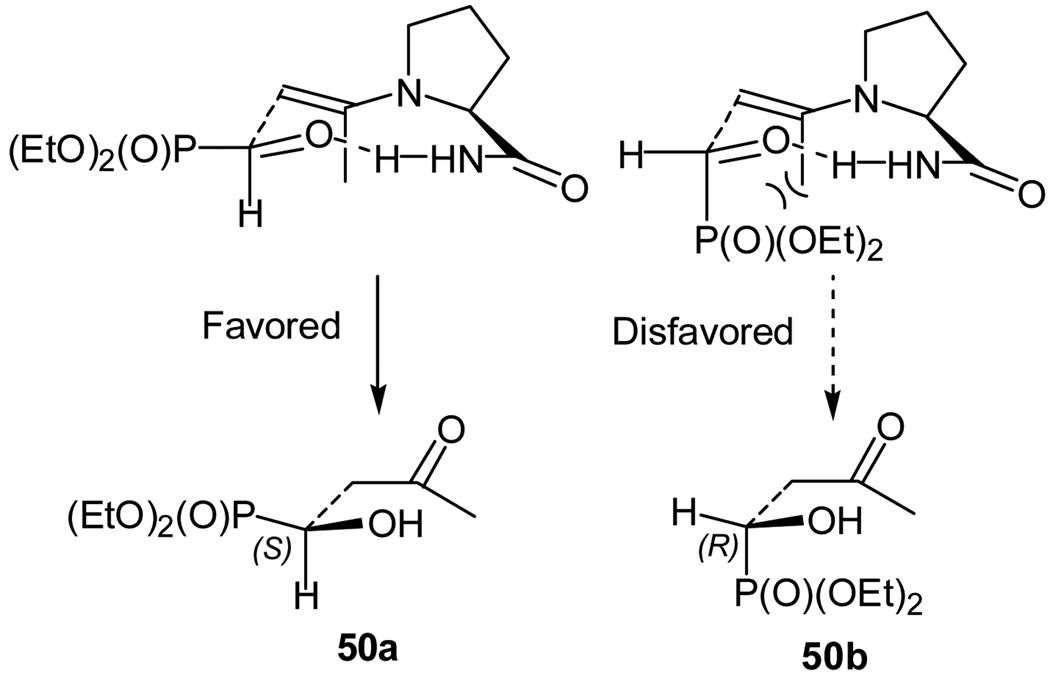
The absolute configuration of the product was determined to be S-configured by converting the primary product obtained in the reaction into a compound of known stereochemistry.36 On the basis of the absolute configuration of the major enantiomer obtained in the reaction and the previously proposed mechanisms for similar proline derivative-catalyzed aldol reactions, plausible transition states of this reaction were proposed (Figure 2).36 As show in Figure 2, the re face approach of the enamine onto the formyl group is disfavored as a result of the steric interactions between the large axial phosphonate group and the axial methyl group. The favored si face attack leads to the observed S-configured major enantiomer.
Figure 2.
Proposed transition state structures for the aldol reaction of acetone and diethyl formylphosphonate
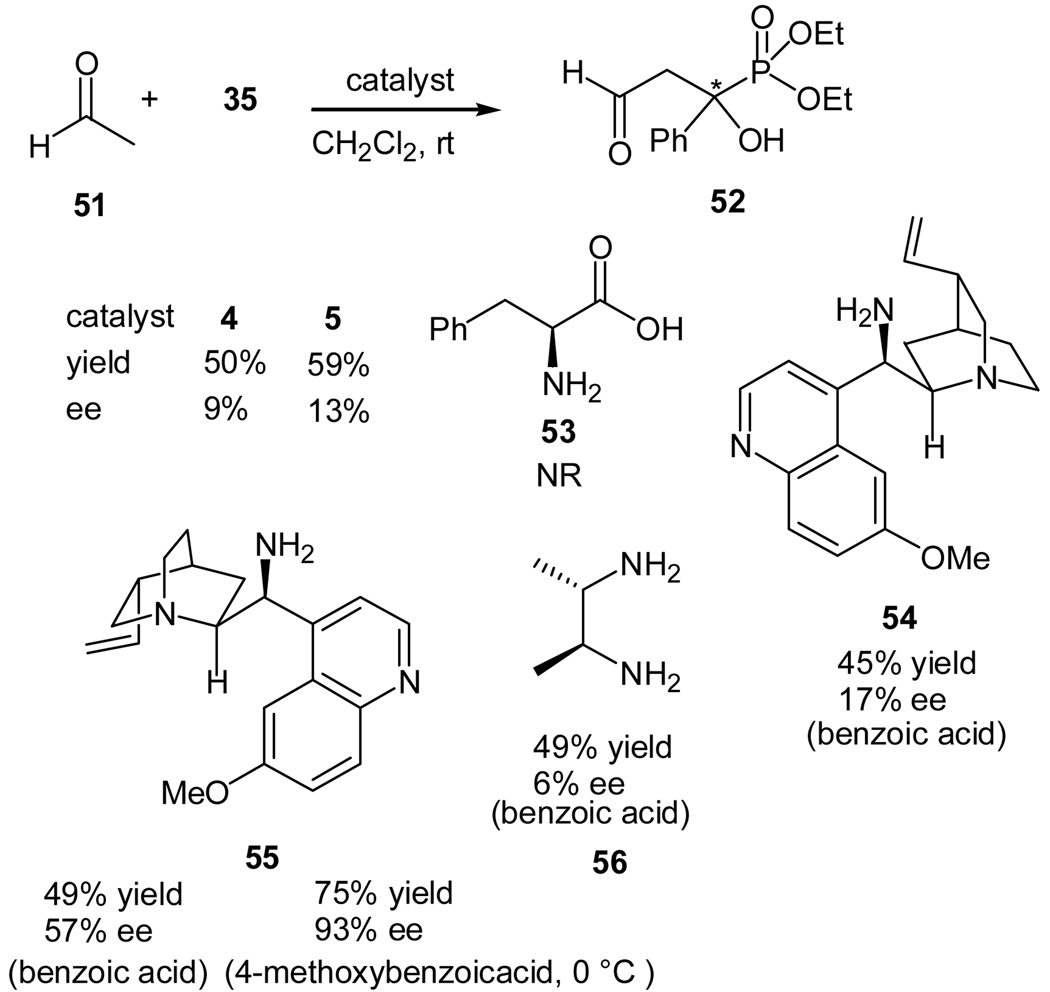
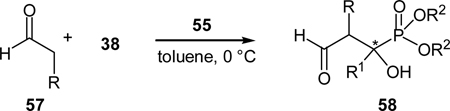
Most recently, we also realized a highly enantioselective synthesis of β-formyl-α-hydroxyphosphonates using a cross aldol reaction of enolizable aldehydes to α-ketophosphonates with a quinine-derived amine as the organocatalyst (Scheme 12).37 Previously we reported such an aldol reaction was not feasible if a secondary amine (such as proline) was used as the catalyst.38 After careful evaluation of the proposed reaction transition states, we believe that steric interaction between the enamine and the α-ketophosphonate is the culprit for the failure. By using less hindered aldehyde, such as acetaldehyde, and/or primary amines as the catalysts,39 the aldol reaction may be realized. For example, L-proline and L-prolinamide catalyzed the aldol reaction of acetaldehyde (51) and α-ketophosphonate 35 to give the expected product 32 in moderate yields and low ee values. Better results may be obtained with chiral primary amine catalysts, and the best results was obtained with quinine-derived primary amine catalyst 55 in presence of benzoic acid, which afforded the desired product in 49% yield with an ee value of 57%.37 Further optimization of reaction conditions led to the finding of a better co-catalyst, 4-methoxy benzoic acid. Under the optimized conditions, the expected aldol product was obtained in 75% yield and 93% ee.
Scheme 12.
Cross aldol reaction of acetaldehyde with benzoylphosphonates
The quinine amine-catalyzed cross aldol reaction was applicable for the synthesis of a series of β-formyl-α-hydroxyphosphonates (Table 4). α-Ketophosphonates bearing an electron-donating and an electron-withdrawing groups were well tolerated in the reaction and in general high ee values of the products were obtained. The reaction of diisopropyl benzoylphosphonate with acetaldehyde under the optimal conditions yielded the desired product in 67% yield and 96% ee. The reaction of propionaldehyde was also found to proceed under these conditions and provided a diastereomeric ratio of 7:5 with an ee value of 68% and 73% for the two diastereomers, respectively. Preliminary screening of these compounds indicates that they can the proliferation of human and murine tumour cells, while are mild against immortalized cells (HFF).37
Table 4.
Quinine amine-catalyzed asymmetric synthesis of β-formyl-α-hydroxyphosphonates
 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | R | R1 | R2 | t (d) | Yield (%) |
ee (%) |
| 1 | H | Ph | Me | 8 | 67 | 96 |
| 2 | H | Ph | Et | 7 | 75 | 93 |
| 3 | H | Ph | i-Pr | 5 | 67 | 96 |
| 4 | H | 4-FC6H4 | Et | 7 | 61 | 99 |
| 5 | H | 4-ClC6H4 | Et | 7 | 62 | 94 |
| 6 | H | 4-BrC6H4 | Et | 7 | 55 | 99 |
| 7 | H | 4-IC6H4 | Et | 7 | 54 | 95 |
| 8 | H | 4-MeC6H4 | Et | 6 | 67 | 96 |
| 9 | H | 4-OMeC6H4 | Et | 7 | 66 | 92 |
| 10 | H | 2-ClC6H4 | Et | 5 | 35 | 96 |
| 11 | H | 3-ClC6H4 | Me | 7 | 60 | 97 |
| 12 | H | Me | Et | 9 | 44 | 68 |
Like α-hydroxyphosphonates, α-hydroxy phosphinates are also biological active compounds. They may act as enzyme inhibitors and have found applications in anti-cancer studies.27,40 However, unlike α-hydroxyphosphonates, the phosphinate group in α-hydroxyphosphinates has intrinsic chirality. Such phosphorus chirality makes the enantioselective synthesis of these compounds even more complicated because the starting materials, such as α-ketophosphinates, are now chiral molecules. Although optically active α-hydroxyphosphinates have been synthesized in good enantioselectivities using various strategies,41 none of these methods addressed the stereochemistry of the phosphinate group. Based on our previously proposed transition states, we hypothesized that the stereochemistry of the phosphorous atom should not affect the enantiofacial selectivity of the cross aldol reaction of racemic α-ketophosphinates with ketones since the phosphinate group should be pointing away from the reaction center in the favored transition state (cf. Figure 2). This would allow the synthesis of both diastereomers of α-hydroxyphosphinates in good enantioselectivities simultaneously.42
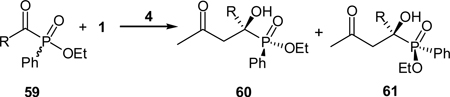
The aldol reaction of ethyl benzoylphenylphosphinate (59a, R = Ph) and acetone was studied with proline-derived catalysts, such as, L-proline (4), L-prolinamide (37), L-proline tetrazole (22), and (S)-N-tosylprolinamide (Table 5).42 All the catalyst exhibited high reactivity and led to the formation of the expected diastereomeric mixture of 60a and 61a (due to the phosphorus chirality) in roughly 50:50 ratio and good yields. Although moderate enantioselectivities were obtained for the rest of these catalysts, L-proline (4) was found to yield good enantioselectivities for both diastereomers. Further optimization of the reaction conditions, such as solvent and reaction temperature, resulted in enantioselectivities of 99% and 91% for the two diastereomers with a diastereomeric ratio of 52:48. This L-proline-catalyzed cross aldol reaction between acetone and α-ketophosphinate was applicable for the synthesis of various substituted α-hydroxyphosphinates in moderate to good yields and high enantioselectivities (Table 5). In all the cases, diastereomeric ratios around 50:50 were obtained, which indicates both enantiomers of the racemic 59 reacts efficiently under the reaction conditions, which is different from normal kinetic resolutions.
Table 5.
L-proline-catalyzed aldol reaction of racemic α-ketophos-phinates and acetone
 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | R | T (°C) |
t (h) |
yield (%) |
ee (%) | Dr | |
| 60 | 61 | ||||||
| 1 | Ph | −30 | 96 | 58 | 99 | 91 | 52:48 |
| 2 | 4-FC6H4 | −30 | 120 | 67 | 98 | 91 | 50:50 |
| 3 | 3-FC6H4 | 0 | 36 | 89 | 96 | 80 | 52:48 |
| 4 | 4-BrC6H4 | −30 | 120 | 70 | 97 | 87 | 54:46 |
| 5 | 4-ClC6H4 | −30 | 120 | 65 | 94 | 73 | 52:48 |
| 6 | 3-ClC6H4 | 0 | 36 | 92 | 99 | 89 | 53:47 |
| 7 | 4-MeC6H4 | −30 | 120 | 45 | 90 | 80 | 54:46 |
| 8 | 4-OMeC6H4 | rt | 40 | 87 | 93 | 71 | 56:44 |
| 9 | rt | 48 | 85 | 84 | 62 | 46:54 | |
| 10 | Me | rt | 24 | 88 | 95 | 87 | 44:56 |
| 11 | Et | rt | 40 | 90 | 87 | 61 | 45:55 |
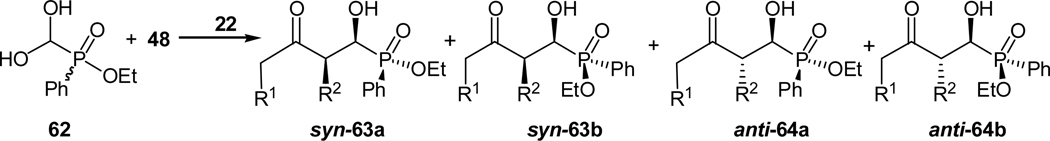
The cross aldol reaction of acetone and ethyl formylphenylphosphinate hydrate (62) was also realized (Scheme 13, R1 = R2 =H).42 And again, L-prolinamide was found to be the best catalyst for this reaction, which gave 90% yield of desired adduct with ee values of 90% and 79% for the two diastereomers. These two diastereomers were also obtained in equal amount. Performing the reaction at 0 °C further enhanced the ee values to 93% and 87% with no loss in reactivity. Cyclopentanone [R1,R2 =(CH2)2] is also a good substrate for this reaction, and complete syn selectivity (referring to the relative stereochemistry of the two carbon stereogenic centers) was observed. The two syn diastereomers (syn-63a and syn-63b) were obtained in enantioselectivities of 96% and 87%, respectively. However, the reaction of cyclohexanone [R1,R2 =(CH2)3] gave lower diastereoselectivities and the four diastereomers were obtained with good to excellent enantioselectivities.42
Scheme 13.
Prolinamide-catalyzed cross aldol reaction of ketones with formylphenylphosphinate hydrate
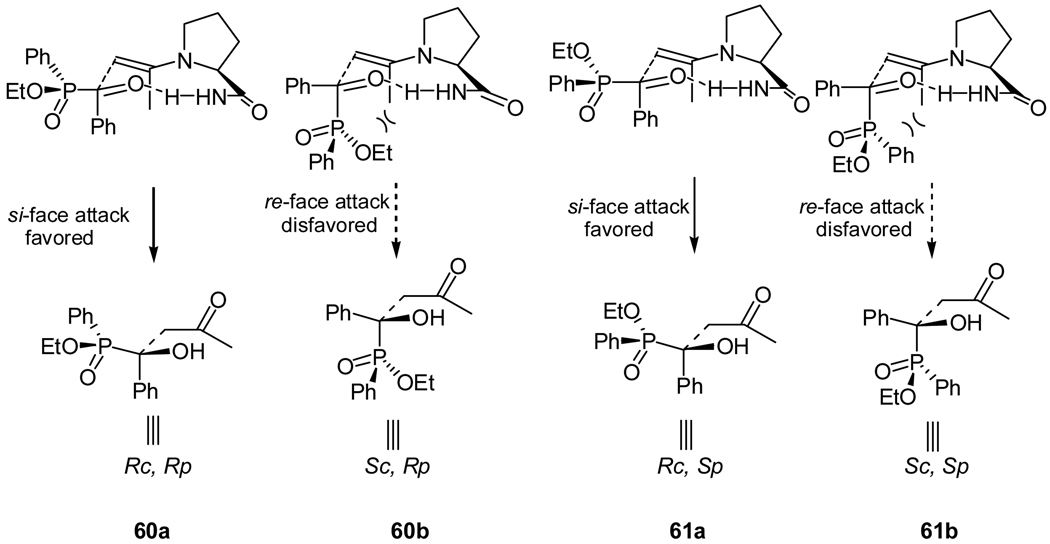
The absolute configuration of the products was determined using X-ray crystallographic analysis of the separated diastereomer.42 With that information, a reaction mechanism was proposed (Figure 3). As in the α-ketophosphonate case, irrespective of the phosphinate group chirality, the attack of the enamine on the si face of the substrate was always favored, because the unfavorable steric interactions between the large axial phosphinate group and the axial enamine methyl group are avoided in such an approach. The favored transition states lead to the expected RCRP (60a), and RCSP (60b) diastereomers as the major products.42
Figure 3.
Proposed transition states for the cross aldol reaction of acetone to acylphosphinate
3. Enolate- and enol-mediated aldol reactions of unactivated ketones
The primary/secondary amine-catalyzed aldol reaction of unactivated ketones via the enamine pathway is well documented; however, the reports on organocatalyzed asymmetric aldol reactions of unactivated ketones via an enolate or enol pathway are rare. Organocatalytic asymmetric aldol reaction of unactivated ketones via the enolate intermediate is difficult because the acidity of the α-proton of these substrates is very low, while the basicity of organocatalysts is limited. The enol pathway is also not easy since the acidity of organocatalysts (a Brønsted acid) is not comparable to that of Lewis acids. Nevertheless, the enolate- and enol-mediated aldol reactions may potentially offer some synthetic advantages over the enamine-mediated aldol reactions. For example, the enolate-mediated aldol is mainly affected by the acidity of the α-proton. It is not sensitive towards the electrophilicity of the carbonyl group of the ketone substrate like the enamine mechanism. These facts allow some tough substrates for the enamine mechanism to be adopted in the enolate-mediated aldol reactions.
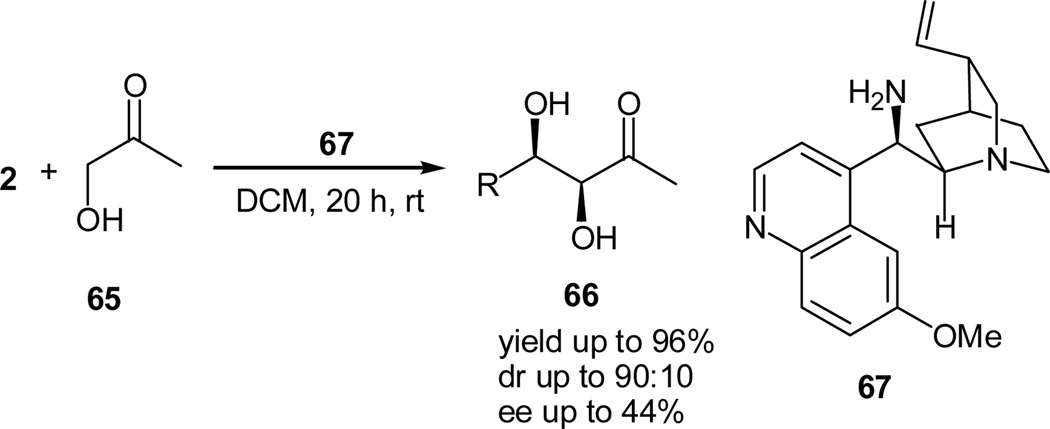
There are very few reports on tertiary amine-catalyzed aldol reactions of activated ketones.43–47 For examples, Mahrwald and coworkers reported a 1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]-undec-7-ene (DBU)-catalyzed diastereoselective addition of hydroxyacetone to aldehydes.44 Shing and coworkers utilizes a similar intramolecular aldol reaction in sugar synthesis.45 An asymmetric version of the Mahrward aldol reaction was reported recently by Mlynarski and coworkers,46 who employed cinchona alkaloids as the organocatalyst for the enantioselective addition of hydroxyacetone (66) to aldehydes (2) (Scheme 14).46 However, the diastereo- and enantioselectivities obtained in this reaction were low. The stereochemistry of the products was determined and based on that, a reaction mechanism was proposed. The hydroxy group of the quinidine catalyst activates the aldehyde electrophile while the tertiary nitrogen on the quinuclidine backbone deprotonates the hydroxyacetone, resulting in a hydrogen bond- stabilized enolate nucleophile.46 On the other hand, Shi and Zhang also reported that the reaction of cyclopenten-2-one with methyl benzoylformate afforded an aldol product in 64% yield using DBU as a catalyst.47
Scheme 14.
Quinidine-catalyzed aldol addition of hydroxyacetone to aldehydes
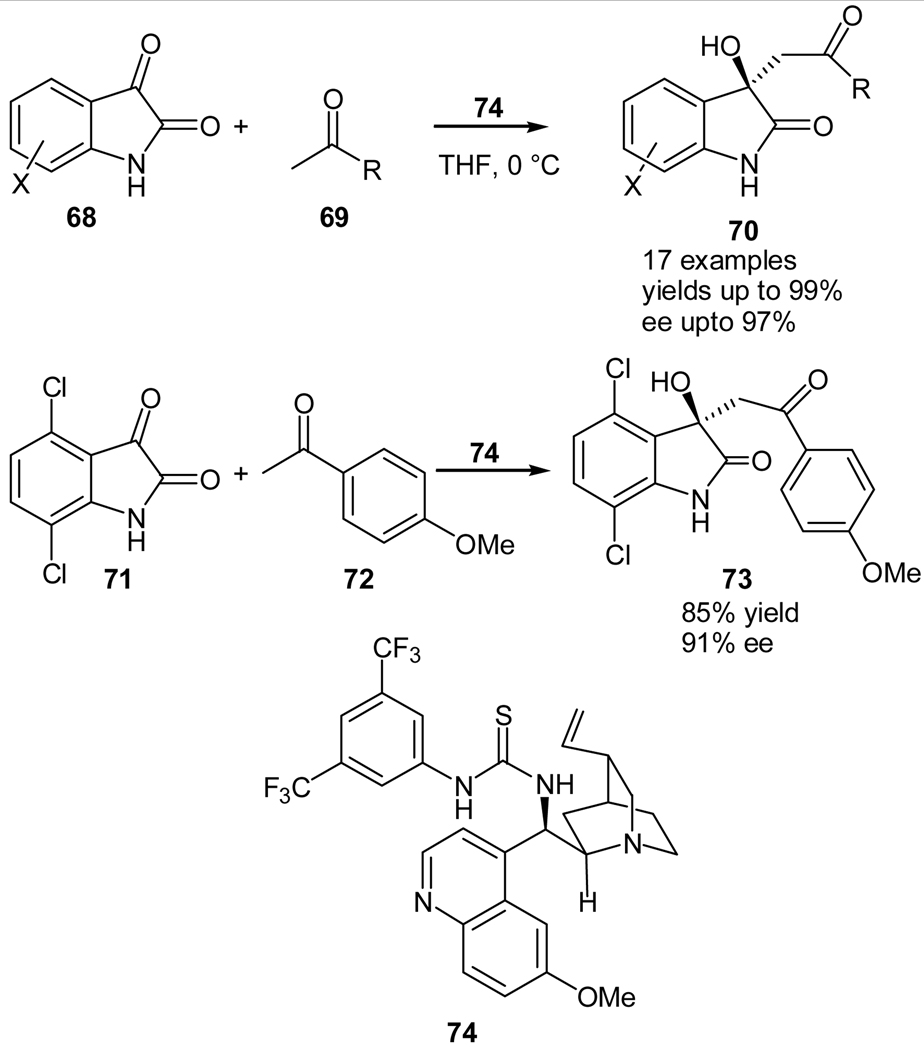
During our study of using activated carbonyl compounds as the enamine acceptors for the organocatalyzed direct aldol reactions, we envisioned such an organocatalyzed enolate-mediated aldol reaction of unactivated ketones should be possible if the enolate acceptor is sufficiently activated, because with such a substrate the equilibrium favors the formation of the aldol product. Since isatin contains an activated ketone group, we studied the asymmetric aldol reaction of isatins (68)48 and unactivated ketones (69) using a quinidine-derived thiourea 74 as the catalyst (Scheme 15).49 The reaction was shown to undergo an enolate-mediated aldol reaction.49 Moreover, the reaction products, 3-alkyl-3-hydroxyindolin-2-ones (70) are biologically active natural products and medicinal compounds.50 This was the first report on an organocatalyzed direct aldol reaction of unactivated ketones following an enolate pathway. The protocol allowed the synthesis of various 3-hydroxy-indolin-2-one derivatives in high enantioselectivity (Table 6). Besides acetone, acetophenone and α,β-unsaturated ketones, which are otherwise unreactive for the enamine-mediated asymmetric aldol reactions due to their low electrophilicity, react efficiently and high yields and enantioselectivities of the corresponding aldol products may be obtained. We also demonstrated that our protocol is useful for the high enantioselective synthesis of compound 73 (Scheme 15), which has been recently chosen as the lead compound for treating Erwings Sarcoma.51
Scheme 15.
Quinidine thiourea-catalyzed aldol reaction of unactivated ketones with isatins
Table 6.
Cross aldol reaction of isatins and ketones
| Entry | R1 | R2 | t (d) | Yield (%) |
ee (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | Me | 6 | 97 | 85 |
| 2 | 4-Cl | Me | 4 | 98 | 87 |
| 3 | 4-Br | Me | 4 | 99 | 91 |
| 4 | 5-F | Me | 5 | 99 | 85 |
| 5 | 6-Br | Me | 4 | 99 | 79 |
| 6 | 5,7-Br2 | Me | 5 | 99 | 83 |
| 7 | H | Ph | 6 | 75 | 90 |
| 8 | 4-Cl | Ph | 5 | 98 | 95 |
| 9 | 4-Br | Ph | 5 | 98 | 97 |
| 10 | 5-F | Ph | 4 | 99 | 86 |
| 11 | 6-Br | Ph | 5 | 98 | 84 |
| 12 | 4,7-Cl2 | Ph | 5 | 98 | 92 |
| 13 | H | Np | 6 | 70 | 86 |
| 14 | H | Np | 5 | 98 | 90 |
| 15 | H | E-Me-CH=CH | 6 | 76 | 87 |
| 16 | H | E-Me-CH=CH | 4 | 98 | 91 |
| 17 | H | H | 3 | 82 | 73 |
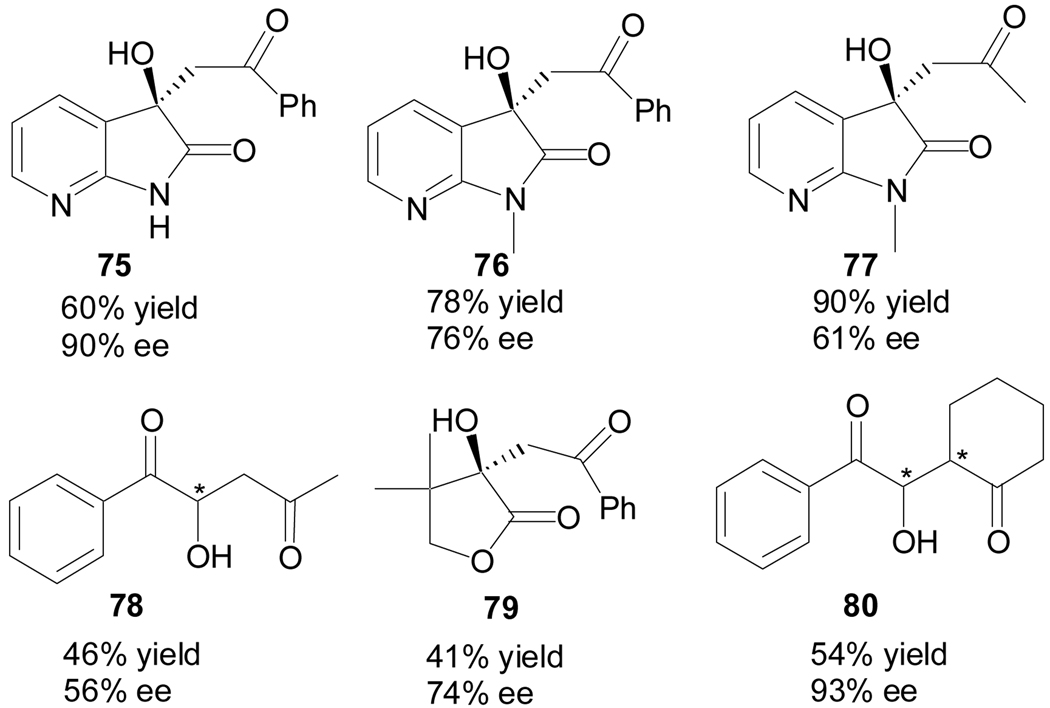
This enolate-mediated aldol reaction may also be applied to other activated carbonyl compounds, such as 7-azaisatins, dihydrofuran-2,3-dione, and phenylglyoxal hydrate, and good enantioselectivities and diastereoselectivities were obtained (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
Quinidine thiourea-catalyzed cross-aldol reaction products of activated carbonyl compounds with unactivated ketones
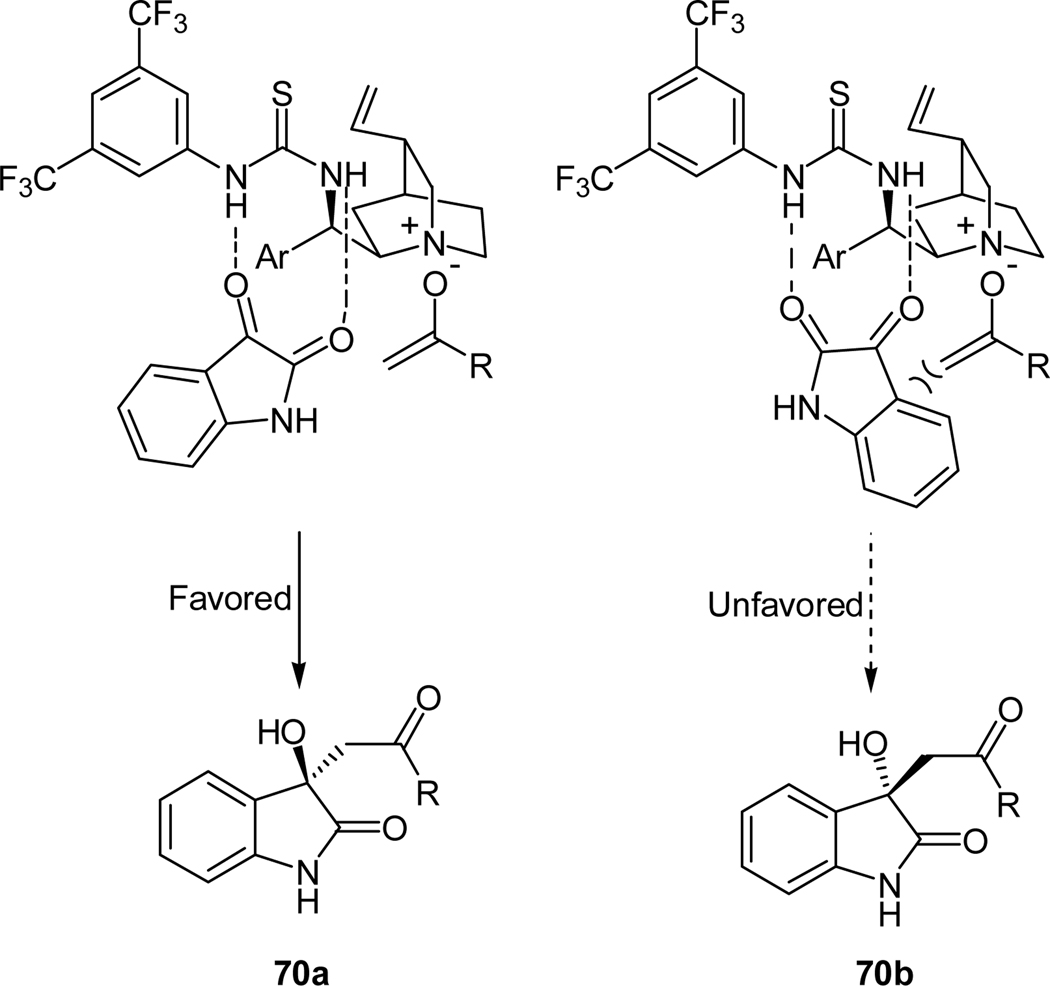
Base on the stereochemistry of the obtained major enantiomer of this reaction, a plausible reaction mechanism was proposed (Figure 5).49 Deprotonation of acetone by the tetriary nitrogen of the quinuclidine moiety of the catalyst results in the formation of an enolate that is bound to the catalyst via ionic interactions. Simultaneously, the carbonyl groups of isatin interact with the thiourea moiety of the catalyst via the hydrogen bonds, which directs the isatin’s approach and activate its carbonyl group for nucleophilic attack. The favored si face attack of the enolate on the isatin group leads to the observed major ‘R’ enantiomer.
Figure 5.
Proposed mechanism for quinidine thiourea-catalyzed aldol reaction of acetone with isatin
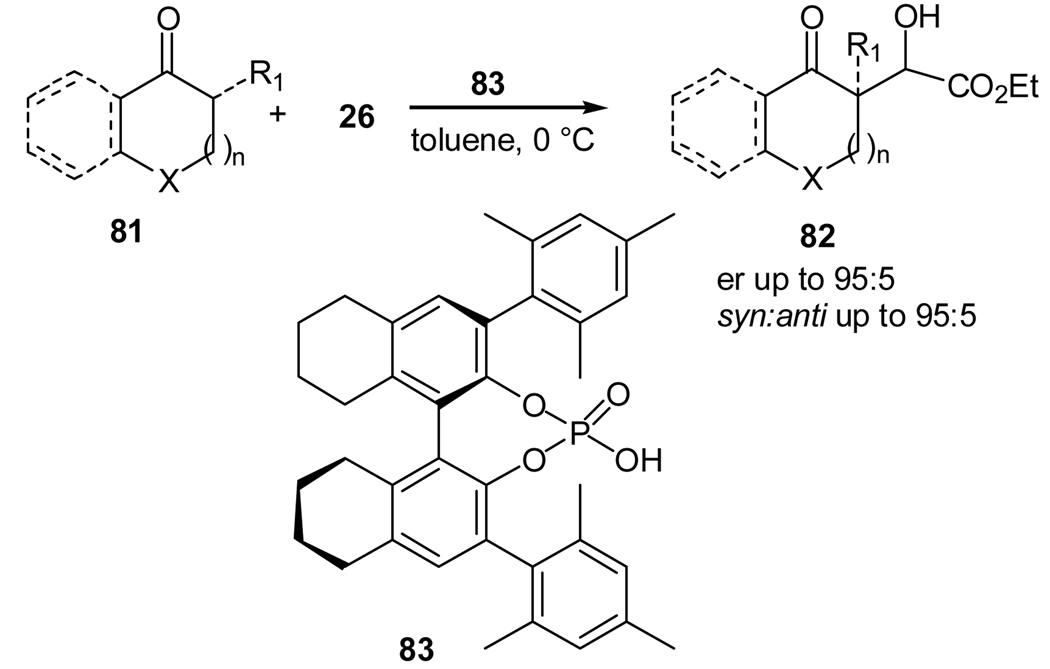
As mentioned above, organocatalyzed enol-mediated aldol reaction is difficult, too. Nevertheless, Blanchet and co-workers achieved a chiral Brønsted acid-catalyzed asymmetric aldol reaction recently (Scheme 16).52 The reaction also utilizes an activated carbonyl compound as the enol acceptor.52 With the chiral phosphoric acid 83 as the acid catalyst, the aldol reaction of various cyclic unactivated ketones 81 with ethyl glyoxylate (26) gave the desired aldol products in moderate syn selectivity and good enantioselectivities. This aldol reaction may also be applied to α, β-unsaturated compounds, which are poor enamine precursors. Although no mechanism of reaction has been proposed, it most likely follows an enol pathway since an acidic catalyst is used.
Scheme 16.
A chiral phosphoric acid-catalyzed aldol reaction of carbonyl compounds with ethyl glyoxylate
4. Organocatalytic tandem reactions
The realm of organocatalysis has been extended to reactions that allow the formation of complex compounds starting from simple substrates in a single transformation consisting of several steps. Such reactions are called tandem or domino or cascade reactions. Molecules with complex structure features containing one or more stereogenic centers may be easily generated during the course of these reactions from simple starting materials. They are particularly useful in the asymmetric synthesis of bioactive compounds. Numerous reports of organocatalytic tandem reactions are available and are reviewed elsewhere.53 We are particularly interested in synthesizing molecules of potential biological activities using the tandem reactions containing an aldol reaction step.
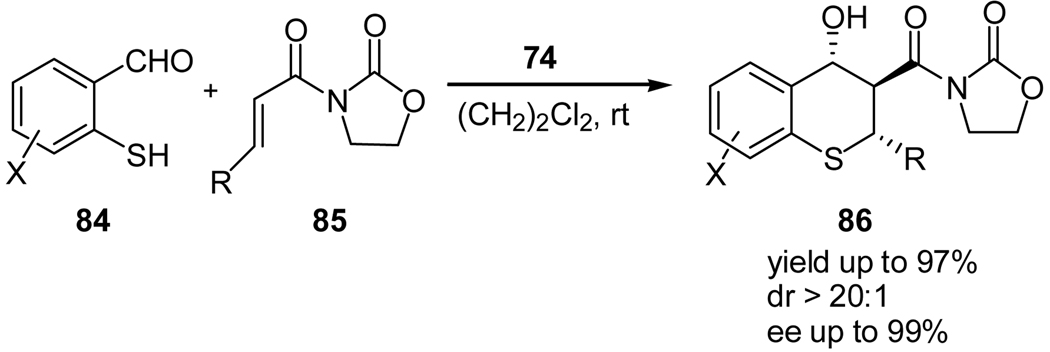
Thiochromane derivatives have been demonstrated to possess many biological activities54 and their asymmetric synthesis has attracted a lot attention in recent years. For example, Wang and co-workers developed an asymmetric synthesis of thiochromanes via a tandem Michael-aldol reaction of mercaptobenzaldehyde (84) with 3-cinnamoyloxazolidin-2-one derivatives (85) (Scheme 17).55 Employing quinidine thiourea (74) as the catalyst, excellent diastereoselectivities and enantioselectivities were obtained for the desired products.
Scheme 17.
Quinidine thiourea-catalyzed cascade reaction of 2-mercaptobenzaldehyde with α, β-unsaturated oxazilidinone
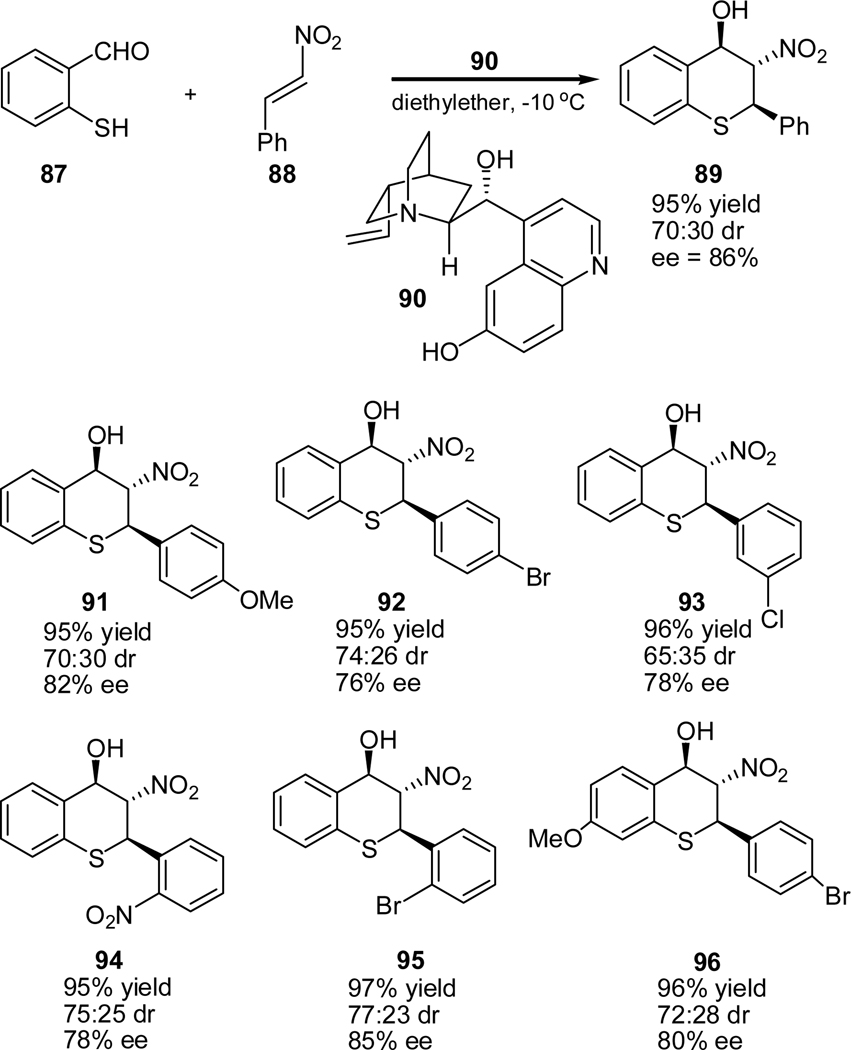
In 2008, we developed an efficient synthesis of 2, 3, 4-trisubsituted thiochromanes using an tandem Michael-Henry reaction of 2-mercaptobenzaldehydes (87) with trans-β-nitrostyrenes catalyzed by cupriene (89).56 For example, the reaction of 2-mercaptobenzaldehyde (87) with trans-β-nitrostyrenes (88) afforded the corresponding thiochromane in 95% yield and 86% ee (Scheme 18). A series of 2-mercaptoaldehydes and nitrostyrenes with substituents of different electronic properties reacted smoothly to furnish the desired thiochromanes in moderate diastereoselectivities and good enantioselectivities (Scheme 18). The major diastereomers and enantiomers obtained in this study may be further enriched through recrystalization. The nitro-substituted thiochromanes may also be further reduced to aminothiochromanes with no loss in enantioselectivity. The latter products are also biologically active compounds.
Scheme 18.
Cupriene-catalyzed tandem Michael-aldol reaction of 2-mercaptobenzaldehyde with trans-β-nitrostyrene
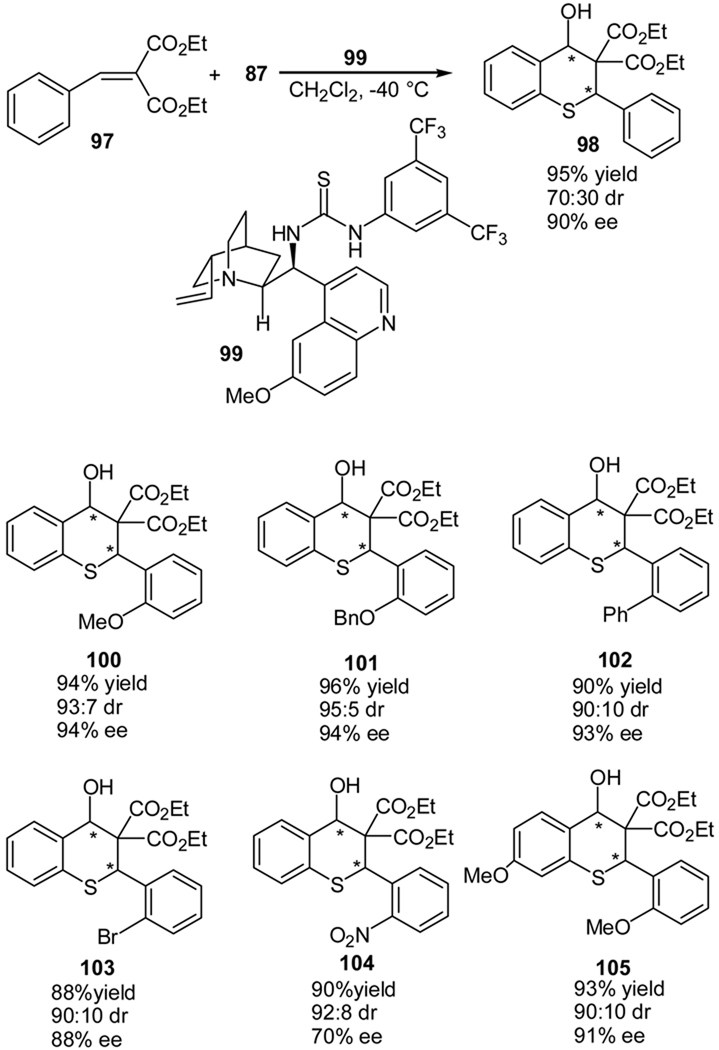
We also developed an organocatalytic Michael-Knoevenagel reaction between 2-mercaptobenzaldehydes (87) and benzylidenemalonates (97) for the high enantioselective and diastereoselective synthesis of the corresponding thiochromanes (98) (Scheme 19).57 When quinine thiourea (99) was used as the catalyst, the desired thiochromanes was obtained in high ee values if the reaction was conducted at −40 °C. Other alkaloid-derived catalysts, such as quinine and cupreine, provided lower enantioselectivities. The diastereoselectivities of this reaction remain around 70:30, irrespective of the catalyst used. However, when o-substituted benzylidenemalonates are used as the substrates, excellent diastereoselectivities are obtained (Scheme 19). The reaction of aliphatic benzylidene malonates was also investigated; however, lower ee value of the product was obtained.57
Scheme 19.
Quinine thiourea catalyzed cascade reaction of 2-mercaptobenzaldehyde with benzyl malonates
In the above approaches, the catalyst activates the nucleophile through deprotonation of the thiol group, and the enantioselectivities are achieved mainly through controlling the approaches of the electrophilic substrates using the hydrogen bonding between the substrates and the catalysts.
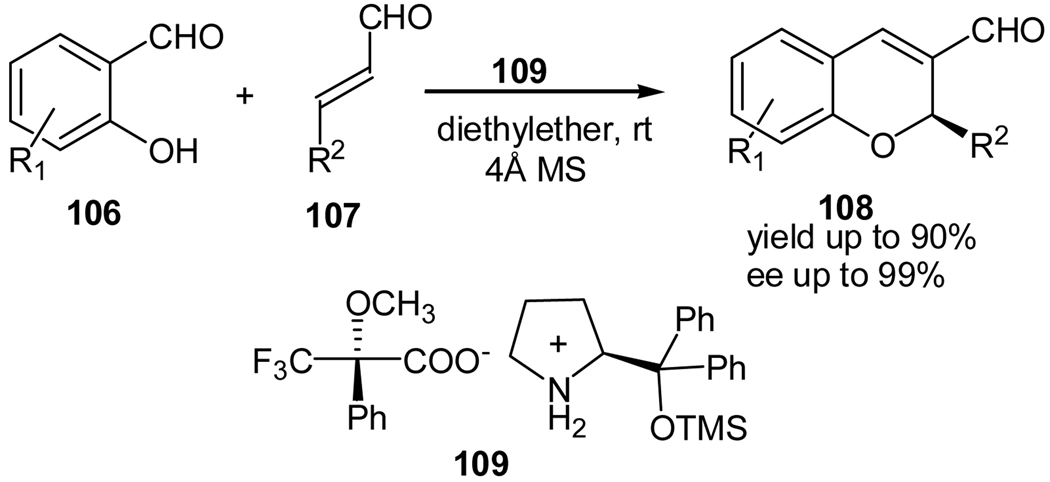
Most recently, Luo and coworkers reported a tandem oxa-Michael-aldol reaction of salicaldehydes (106) and cinnamaldehydes (107) for the enantioselective synthesis of chromene derivatives using a diphenylprolinol TMS ether as the organocatalyst in the presence of chiral acid as the co-catalyst (Scheme 20).58 However, unlike Wang’s and our syntheses, this reaction is achieved through the formation an iminium intermediate and the stereoselectivity is mainly controlled by steric factors.
Scheme 20.
Tandem oxa-Michael-aldol reaction catalyzed by a chiral amine catalyst in the presence of a chiral acid co-catalyst
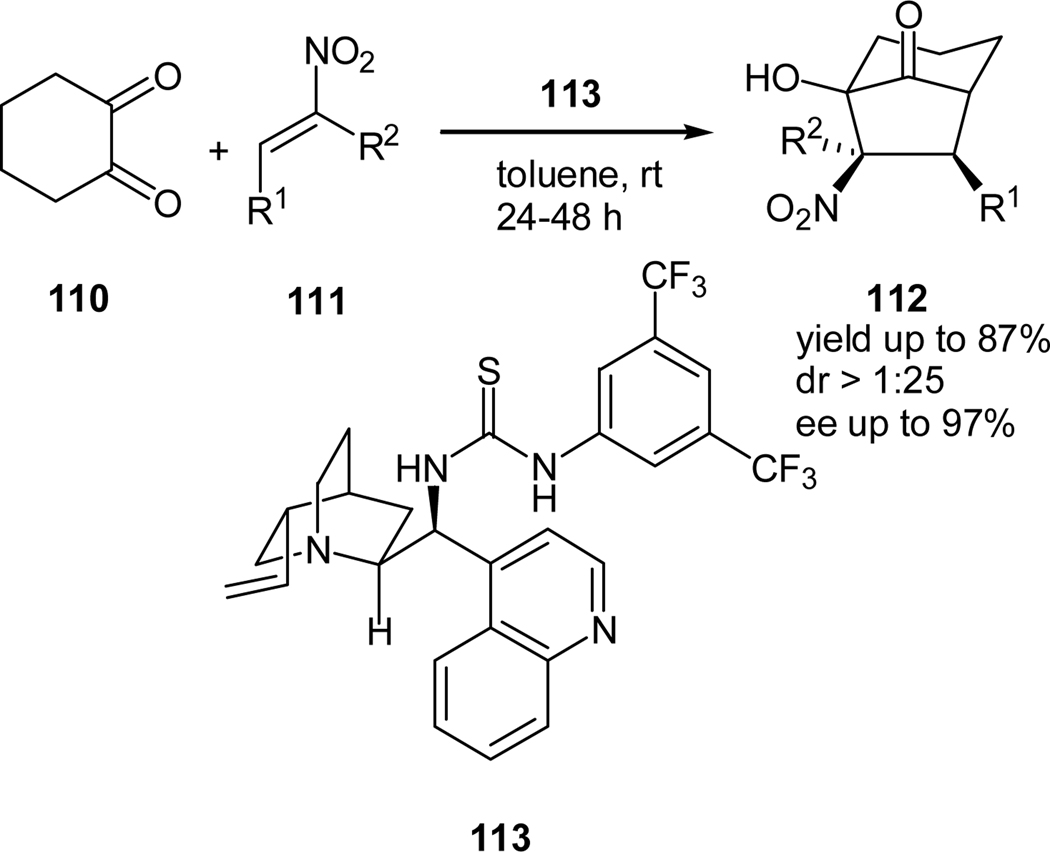
Most recently, Rueping and co-workers and our group independently developed a tandem Michael-Henry reaction of cyclohexane-1,2-dione (110) and β-nitro styrenes (111) using bifunctional cinchona-derived thiourea catalysts. Rueping and co-workers used cinchonidine thiourea (113) as the catalyst to afford the corresponding polyfunctionalized bicyclo[3.2.1]octane-8-ones (112) in good diastereoselectivities and excellent enantioselectivities (Scheme 21).59
Scheme 21.
Cinchonidine thiourea-catalyzed tandem Michael-Henry reaction of cyclohexan-1,2-dione and β-nitro styrenes
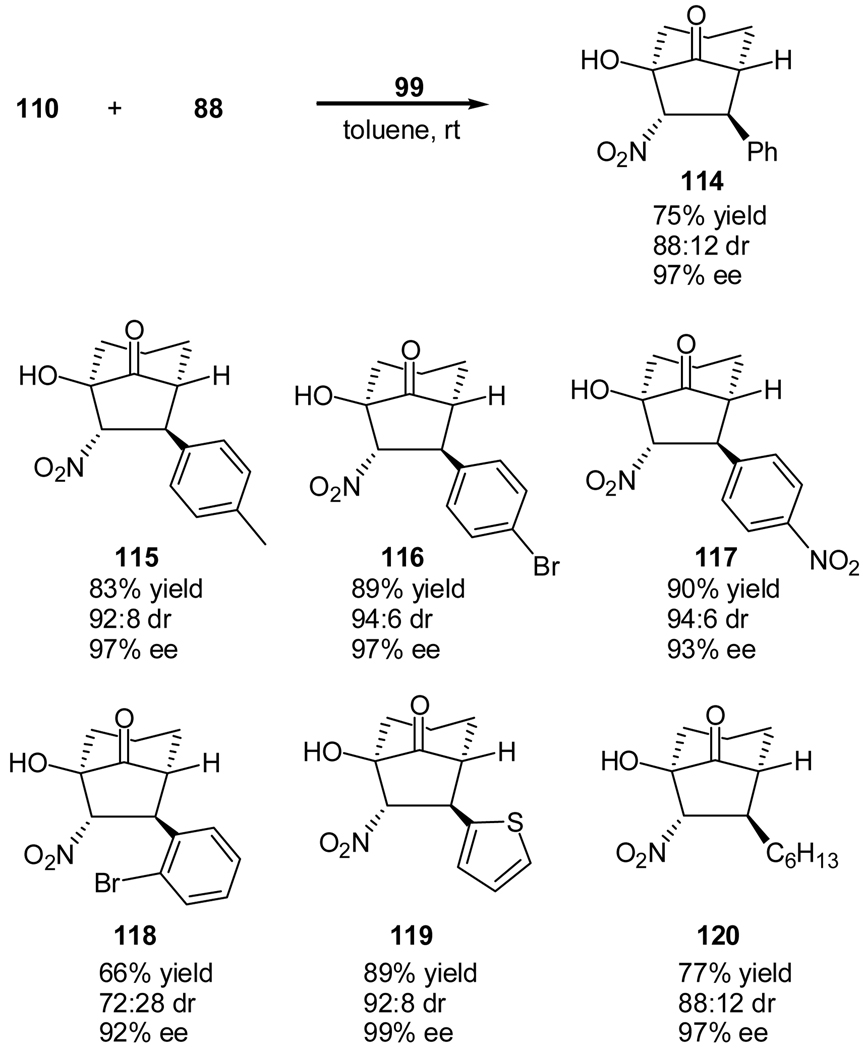
We instead used quinine thiourea (99) as the catalyst. The reaction of cyclohexane-1,2-dione (110) with β-nitrostyrene (88) gave a different diastereomer (the 1R, 5R, 6S, 7S–diastereomer) as the major product (Scheme 22).60 After optimization of the reaction conditions, the quinine thiourea- catalyzed tandem Michael-Henry reaction provides the corresponding bicylco[3.2.1]octan-8-ones in good diastereoselectivities (up to 95:5) and excellent enantioselectivities (up to 99%). The reaction is applicable for a variety of substituted β-nitrostyrenes with different steric and electronic properties. Excellent ee value (97%) and good dr value (88:12) were also obtained for the product of aliphatic nitrostyrene (120). However, the protocol is not applicable for the open-chain 1,2-diones, such as, butane-2,3-dione, and cyclopentane-1,2-dione.
Scheme 22.
Quinine thiourea-catalyzed tandem Michael-Henry reaction for the synthesis of bicylco[3.2.1]octan-8-ones
5. Conclusion
The field of organocatalysis has grown tremendously since its advent and the asymmetric aldol reaction has been one of the most studied reactions in organocatalysis. Significant advances have been achieved both in terms of reactivity and selectivity in the organocatalyzed aldol reaction via the enamine mechanism. Most recently, asymmetric aldol reactions of substrates that are less reactive for the enamine pathway have been made possible by using the complementary enolate/enol pathways. While the organocatalyzed enamine-mediated aldol reactions are well established by now, the organocatalyzed enolate/enol-mediated aldol reactions are still in its infancy. Future work should be directed particularly to the development of new organocatalysts that can enhance of reaction rate and improve the substrate scope so that unactivated enolate/enol acceptors may be used in these reactions. Taking the advantages of these developments in the organocatalyzed aldol reactions, we have synthesized many useful organic molecules that have or potentially have interesting biological activities, such as, α-hydroxy carboxylate, α-hydroxyphosphonate, α-hydroxyphosphinate, 3-hydroxy-indolin-2-one, and thiochromane derivatives in good to high enantioselectivities.
6. Acknowledgment
Our research in this field is impossible without the generous financial support from the NIH-NIGMS (grant No. S06GM 08194; SC1GM082718), the Welch Foundation (grant No. AX-1593), and the NSF (grant No. CHE-0909954), for which the authors are very grateful. We are also very grateful for the efforts and the contributions of our current and former coworkers.
Biographies

Mayur Bhanushali received his PhD degree in September 2008 from the Institute of Chemical Technology Mumbai, India under the supervision of Professor. B. M. Bhanage. After that he spent one year working in medicinal chemistry at GVK Biosciences Pvt Ltd. Hyderabad, India, he joined the Department of Chemistry, University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA) in 2009 as a postdoctoral fellow with Professor C.-G. Zhao. He is currently working the area of organocatalysis.

Cong-Gui Zhao received his MS degree from the Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, China in 1995. He received his PhD degree in 1999 from the University of Würzburg, Germany under the supervision of Professor Waldemar Adam. From 2000 to 2001, he was a postdoctoral fellow at UTSA with Professor George Negrete. He was a Visiting Assistant Professor at the Department of Chemistry, UTSA from 2001–2002. He joined the Department of Chemistry, UTSA as a tenure-track Assistant Professor in September 2002, where he was promoted to a Full Professor recently. His current research interests include asymmetric catalysis and green chemistry, medicinal chemistry, and organophosphorus compounds.
7. References
- 1.Wurtz A. Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. 1872;17:436. [Google Scholar]
- 2.For reviews, see: Mukaiyama T. Org. React. 1982;28:303.; (b) Kim BM, Williams SF, Masamune S. In: Comprehensive Organic Synthesis. Trost BM, Fleming I, Heathcock CH, editors. Oxford: Pergamon; 1991. p. 229. [Google Scholar]; (c) Mahrwald R, editor. Modern Aldol Reactions. Vols. 1–2 Weinheim: Wiley-VCH; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 3.(a) Schetter B, Mahrwald R. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2006;45:7506. doi: 10.1002/anie.200602780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Paterson I, Mansuri MM. Tetrahedron. 1985;41:3569. [Google Scholar]; (c) Masamune S, Bates GS, Corcoran JW. Angew. Chem. 1977;89:602. doi: 10.1002/anie.197705851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1977;16:585. [Google Scholar]
- 4.For reviews on asymmetric aldol reaction, see: Trost BM, Brindle CS. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010;39:1600. doi: 10.1039/b923537j.; (b) Geary LM, Hultin PG. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 2009;20:131. [Google Scholar]; (c) Saito S, Yamamoto H. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004;37:570. doi: 10.1021/ar030064p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Machajewski TD, Wong C-H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000;39:1352. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1521-3773(20000417)39:8<1352::aid-anie1352>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. For reviews, see: Evans DA, Nelson JV, Taber TR. In: Topics in Stereochemistry. Eliel EL, Wilen SH, editors. Vol. 13. New York: Wiley-Interscience; 1982. pp. 1–116. Braun M. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1987;26:24.
- 6.(a) Mukaiyama T, Banno K, Narasaka K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1974;96:7503. [Google Scholar]; (b) Kobayashi S, Murakami M, Mukaiyama T. Chem. Lett. 1985:1535. [Google Scholar]; (c) Mahrwald R. Chem. Rev. 1999;99:1095. doi: 10.1021/cr980415r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Johnson JS, Evans DA. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000;33:325. doi: 10.1021/ar960062n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.(a) Yamada YMA, Yoshikawa N, Sasai H, Shibasaki M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 1997;36:1871. [Google Scholar]; (b) Yamada YMA, Shibasaki M. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998;39:5561. [Google Scholar]; (c) Yoshikawa N, Yamada YMA, Das J, Sasai H, Shibasaki M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999;121:4168. [Google Scholar]
- 8.List B, Lerner RA, Barbas CF., III J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000;122:2395. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hajos ZG, Parrish DR. J. Org. Chem. 1974;39:1615. [Google Scholar]
- 10.(a) Takemoto Y. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010;58:593. doi: 10.1248/cpb.58.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Dondoni A, Massi A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008;47:4638. doi: 10.1002/anie.200704684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Enders D, Grondal C, Huttl MRH. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2007;46:1570. doi: 10.1002/anie.200603129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Seayad J, List B. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005;3:719. doi: 10.1039/b415217b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.For selected reviews on organocatalysis, see: Dalko PI, Moisan L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001;40:3726. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20011015)40:20<3726::aid-anie3726>3.0.co;2-d.; (b) Schreiner PR. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2003;32:289. doi: 10.1039/b107298f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Dalko PI, Moisan L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004;43:5138. doi: 10.1002/anie.200400650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Houk KN, List B. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004;37:487. doi: 10.1021/ar0300571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Ouellet SG, Walji AM, MacMillan DWC. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007;40:1327. doi: 10.1021/ar7001864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Connon SJ. Chem. Eur. J. 2006;12:5419. doi: 10.1002/chem.200501076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (g) MacMillan DWC. Nature. 2008;455:304. doi: 10.1038/nature07367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (h) Enders D, Narine AA. J. Org. Chem. 2008;73:7857. doi: 10.1021/jo801374j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (i) Dondoni A, Massi A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008;47:4638. doi: 10.1002/anie.200704684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (j) Bertelsen S, Jorgensen KA. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009;38:2178. doi: 10.1039/b903816g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (k) Jacobsen EN, MacMillan DWC. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 2010;107:20618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1016087107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (l) Erkkilӓ A, Majander I, Pihko PM. Chem. Rev. 2007;107:5416. doi: 10.1021/cr068388p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.(a) Agami C, Meynier F, Puchot C, Guilhem J, Pascard C. Tetrahedron. 1984;40:1031. [Google Scholar]; (b) Agami C, Puchot C, Sevestre H. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986;27:1501. [Google Scholar]
- 13.(a) Schmid MB, Zeitler K, Gschwind RM. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2010;49:4997. doi: 10.1002/anie.200906629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) List B, Hoang L, Martin HJ. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 2004;101:5839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307979101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Bock DA, Lehmann CW, List B. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 2010;107:20636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1006509107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.For reviews on asymmetric organocatalyzed aldol reactions see: Chen X-H, Yu J, Gong L-Z. Chem. Commun. 2010;46:6437. doi: 10.1039/c0cc00754d.; (b) Zlotin SG, Kucherenko AS, Beletskaya IP. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2009;78:737. [Google Scholar]; (c) Gabriela G, Carmen N, Diego RJ. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 2007;18:2249. [Google Scholar]; (d) Mukherjee S, Yang JW, Hoffmann S, List B. Chem. Rev. 2007;107:5471–5569. doi: 10.1021/cr0684016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Notz W, Tanaka F, Barbas CF., III Acc. Chem. Res. 2004;37:580. doi: 10.1021/ar0300468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.(a) Sakthivel K, Notz W, Bui T, Barbas CF., III J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001;123:5260. doi: 10.1021/ja010037z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Cordova A, Notz W, Barbas CF., III Chem. Comm. 2002:3024. doi: 10.1039/b207664k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Martin HJ, List B. Synlett. 2003:1901. [Google Scholar]; (d) Tang Z, Jiang F, Yu L-T, Gong L-Z, Mi A-Q, Jiang Y-Z, Wu Y-D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:5262. doi: 10.1021/ja034528q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Tang Z, Yang Z-H, Cun L-F, Gong L-Z, Mi A-Q, Jiang Y-Z. Org. Lett. 2004;6:2285. doi: 10.1021/ol049141m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Tang Z, Jiang F, Cui X, Gong L-Z, Mi A-Q, Jiang Y-Z, Wu Y-D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2004;101:5755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307176101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (g) Guo H-M, Cun L-F, Gong L-Z, Mi A-Q, Jiang Y-Z. Chem. Commun. 2005:1450. doi: 10.1039/b417267a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (h) Kano T, Takai J, Tokuda O, Maruoka K. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005;44:3055. doi: 10.1002/anie.200500408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tang Z, Yang Z-H, Chen X-H, Cun L-F, Mi A-Q, Jiang Y-Z, Gong L-Z. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005;127:9285. doi: 10.1021/ja0510156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.(a) Samanta S, Liu J, Dodda R, Zhao C-G. Org. Lett. 2005;7:5321. doi: 10.1021/ol052277f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Dodda R, Samanta S, Zhao CG. Unpublished results [Google Scholar]
- 18.Guillena G, Hita MC, Najera C. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 2006;17:729. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Guillena G, Hita MC, Najera C. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 2006;17:1493. [Google Scholar]
- 20.(a) Luppi G, Cozzi PG, Monari M, Kaptein B, Broxterman QB, Tomasini C. J. Org. Chem. 2005;70:7418. doi: 10.1021/jo050257l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Shen Z, Li B, Wang L, Zhang Y. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005;46:8785. [Google Scholar]; (c) Enders D, Grondal C. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005;44:1210. doi: 10.1002/anie.200462428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Tokuda O, Kano T, Gao W-G, Ikemoto T, Maruoka K. Org. Lett. 2005;7:5103. doi: 10.1021/ol052164w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Samanta S, Zhao C-G. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006;47:3383. [Google Scholar]
- 22.For a review see: Coppola GM, Schuster HF, editors. α-Hydroxy Acids in Enantioselective Synthesis. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH; 1997.
- 23.Bøgevig A, Kumaragurubaran N, Jørgensen KA. Chem. Commun. 2002:620. doi: 10.1039/b200681b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dodda R, Zhao C-G. Synlett. 2007:1605. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Urushima T, Yasui Y, Ishikawa H, Hayashi Y. Org. Lett. 2010;12:2966. doi: 10.1021/ol1009812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tang Z, Cun L-F, Cui X, M. i. AQ, Jiang Y-Z, Gong L-Z. Org. Lett. 2006;8:1263. doi: 10.1021/ol0529391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.For reviews, see: Kuhkar VP, Hudson HR, editors. Aminophosphonic and Aminophosphinic Acids. Chichester, UK: John Wiley; 2000. ; (b) Kafarski P, Lejczak B. Curr. Med. Chem.: Anti-Cancer Agents. 2001;1:301–312. doi: 10.2174/1568011013354543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Berlicki L, Kafarski P. Curr. Org. Chem. 2005;9:1829–1850. [Google Scholar]; (d) Redmore DIn. In: Topics in Phosphorus Chemistry. Griffith EJ, Grayson M, editors. Vol. 8. New York: John Wiley; 1976. pp. 515–585. [Google Scholar]; (e) Kolodiazhnyi OI. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 2005;16:3295. [Google Scholar]; (f) Stawinski J, Kraszewski A. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002;35:952. doi: 10.1021/ar010049p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (g) Snoeck R, Holy A, Dewolf-Peeters C, Van Den Oord J, De Clercq E, Andrei G. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002;46:3356. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.11.3356-3361.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (h) Kategaonkara AH, Pokalwara RU, Sonara SS, Gawalib VU, Shingatea BB, Shingare MS. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010;45:1128. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2009.12.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.(a) Patel DV, Rielly-Gauvin K, Ryono DE, Free CA, Rogers WL, Smith SA, DeForrest JM, Oehl RS, Petrillo EW., Jr J. Med. Chem. 1995;38:4557. doi: 10.1021/jm00022a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Tao M, Bihovsky R, Wells GJ, Mallamo JP. J. Med. Chem. 1998;41:3912. doi: 10.1021/jm980325e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Dellaria JF, Jr, Maki RG, Stein HH, Cohen J, Whittern D, Marsh K, Hoffman DJ, Plattner JJ, Perun TJ. J. Med. Chem. 1990;33:534. doi: 10.1021/jm00164a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lynch, Kevin R, MacDonald, Timothy L. U.S. Pat. 2010 US 20100016258. [Google Scholar]
- 30.(a) Peters ML, Leonard M, Licata AA. Clev. Clin. J. Med. 2001;68:945. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.68.11.945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Lee MV, Fong EM, Singere FR, Guenette RS. Cancer Res. 2001;61:2602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Leder BZ, Kronenberg HM. Gastroenterology. 2000;119:866. doi: 10.1053/gast.2000.17841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Cui P, McCalmont WF, Tomsig JL, Lynch KR, Macdonald TL. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008;16:2212. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2007.11.078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.(a) Wiemer DF. Tetrahedron. 1997;53:16609. [Google Scholar]; (b) Davies SR, Mitchell MC, Cain CP, Devitt PG, Taylor RJ, Kee TP. J. Organomet. Chem. 1998;550:29. [Google Scholar]
- 32.(a) Merino P, Lopez-Marques E, Herrera RP. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008;350:1195. [Google Scholar]; (b) Huang J, Wang J, Chen X, Wen Y, Liu X, Feng X. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008;350:287. [Google Scholar]; (c) Groger H, Hammer B. Chem. Eur. J. 2000;6:943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Samanta S, Zhao C-G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:7442. doi: 10.1021/ja062091r. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Liu J, Yang Z, Wang Z, Wang F, Chen X, Liu X, Feng X, Su Z, Hu C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:5654. doi: 10.1021/ja800839w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jiang J, Chen X, Wang J, Hui Y, Liu X, Lin L, Feng X. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009;7:4355. doi: 10.1039/b917554g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Dodda R, Zhao C-G. Org. Lett. 2006;8:4911. doi: 10.1021/ol062005s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Perera S, Naganaboina V, Wang L, Zhang B, Guo Q, Rout L, Zhao CG. Adv. Syn. Catal. doi: 10.1002/adsc.201000835. under revision. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Samanta S, Krause J, Mandal T, Zhao C-G. Org. Lett. 2007;9:2745. doi: 10.1021/ol071097y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.For reviews on primary amine-catalyzed aldol reactions, see: Xu L-W, Luo J, Lu Y. Chem. Comm. 2009:1807. doi: 10.1039/b821070e.; (b) Peng F, Shao Z. J. Mol. Catal. A. 2008;285:1. [Google Scholar]; (c) Chen Y-C. Synlett. 2008:1919. [Google Scholar]
- 40.(a) Stowasser B, Budt K-H, Li J-Q, Peyman A, Ruppert D. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992;33:6625. [Google Scholar]; (b) Patel DV, Rielly-Gauvin K, Ryono DE, Free CA, Rogers WL, Smith SA, DeForrest JM, Oehl RS, Petrillo EW., Jr J. Med. Chem. 1995;38:4557. doi: 10.1021/jm00022a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Froestl W, Mickel SJ, Hall RG, von Sprecher G, Strub D, Baumann PA, Brugger F, Gentsch C, Jaekel J, Olpe H-R, Rihs G, Vassout A, Waldmeier PC, Bittiger H. J. Med. Chem. 1995;38:3297. doi: 10.1021/jm00017a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Froestl W, Mickel SJ, von Sprecher G, Diel PJ, Hall RG, Maier Lu, Strub D, Melillo V, Baumann PA, Bernasconi R, Gentsch C, Hauser K, Jaekel J, Karlsson’s G, Klebs K, Maitre L, Marescaux C, Pozza MF, Schmutz M, Steinmann MW, van Riezen H, Vassout A, Mondadori C, Olpe H-R, Waldmeier PC, Bittiger H. J. Med. Chem. 1995;38:3313. doi: 10.1021/jm00017a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Rosen RE, Weaver DG, Cornille JW, Spangler LA. 5,500,405. U.S. Patent. 1996; (f) Spangler LA, Mikołajczyk M, Burdge EL, Kiełbasiński P, Smith HC, Łyzwa P, Fisher JD, Omelańczuk J. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999;47:318. doi: 10.1021/jf980527j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.(a) Yamagishi T, Miyamae T, Yokomatsu T, Shibuya S. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004;45:6713. [Google Scholar]; (b) Patel DV, Rielly-Gauvin K, Ryono DE. Tetrahedron Lett. 1990;31:5591. [Google Scholar]; (c) Yamagishi T, Suemune K, Yokomatsu T, Shibuya S. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001;42:5033. [Google Scholar]; (d) Cai J, Zhou Z, Zhao G, Tang C. Heteroatom Chem. 2003;14:312. [Google Scholar]; (e) Yamagishi T, Yokomatsu T, Suemune K, Shibuya S. Tetrahedron. 1999;55:12125–12136. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Samanta S, Perera S, Zhao C-G. J. Org. Chem. 2010;75:1101. doi: 10.1021/jo9022099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.For amine thiourea-catalyzed tandem aldol cyclization reaction of α-isothiocyanatoketones, see: Li L, Klauber EG, Seidel D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:12248. doi: 10.1021/ja804838y.; (b) Misaki T, Takimoto G, Sugimura T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010;132:6286. doi: 10.1021/ja101216x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Jiang X, Zhang G, Fu D, Cao Y, Shen F, Wang R. Org. Lett. 2010;12:1544. doi: 10.1021/ol1002829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Vecchione MK, Li L, Seidel D. Chem. Commun. 2010;46:4604. doi: 10.1039/c0cc00556h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Jiang X, Cao Y, Wang Y, Liu L, Shen F, Wang R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010;132:15328. doi: 10.1021/ja106349m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Guang J, Zhao C-G. J. Org. Chem. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Markert M, Mulzer M, Schetter B, Mahrwald R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:7258. doi: 10.1021/ja071926a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Shing TKM, Cheng HM. Org. Lett. 2008;10:4137. doi: 10.1021/ol801889n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Paradowska J, Rogozinska M, Mlynarski J. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009;50:1639. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Shi M, Zhang W. Tetrahedron. 2005;61:11887. [Google Scholar]
- 48.For aldol reaction of isatin and acetone, mediated by achiral amines or K2CO3, see: Garden SJ, da Silva RB, Pinto AC. Tetrahedron. 2002;58:8399.; (b) Garden SJ, Torres JC, Ferreira AA, da Silva RB, Pinto AC. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997;38:1501. [Google Scholar]; (c) Braude F, Lindwall HG. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1933;55:325. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Guo Q, Bhanushali M, Zhao C-G. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010;49:9460. doi: 10.1002/anie.201004161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.For examples, see: Goehring RR, Sachdeva YP, Pisipati JS, Sleevi MC, Wolfe JF. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985;107:435.; (b) Labroo RB, Cohen LA. J. Org. Chem. 1990;55:4901. [Google Scholar]; (c) Rasmussen HB, MacLeod JK. J. Nat. Prod. 1997;60:1152. doi: 10.1021/np970006a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Jimenez J, Huber U, Moore R, Patterson G. J. Nat. Prod. 1999;62:569. doi: 10.1021/np980485t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Tokunaga T, Hume WE, Umezome T, Okazaki K, Ueki Y, Kumagai K, Hourai S, Nagamine J, Seki H, Taiji M, Noguchi H, Nagata R. J. Med. Chem. 2001;44:4641. doi: 10.1021/jm0103763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Tokunaga T, Hume WE, Nagamine J, Kawamura T, Taiji M, Nagata R. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005;15:1789. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.02.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Erkizan HV, Kong Y, Merchant M, Schlottmann S, Barber-Rotenberg JS, Yuan L, Abaan OD, Chou T-h, Dakshanamurthy S, Brown ML, Üren A, Toretsky JA. Nature Med. 2009;15:750. doi: 10.1038/nm.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Pousse G, Cavelier F, Humphreys L, Jacques Rouden, Blanchet J. Org. Lett. 2010;12:3582. doi: 10.1021/ol101176j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.For reviews, see: Westermann B, Ayaz M, van Berkel SS. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010;49:846. doi: 10.1002/anie.200904638.; (b) Alba A-N, Companyo X, Viciano M, Rios R. Curr. Org. Chem. 2009;13:1432. [Google Scholar]; (c) Yu X, Wang W. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008;6:2037. doi: 10.1039/b800245m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Grondal1 C, Jeanty M, Enders D. Nature Chem. 2010;2:167. doi: 10.1038/nchem.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Enders D, Grondal C, Hüttl MRM. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007;46:1570. doi: 10.1002/anie.200603129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Foe examples see: Castro ME, Harrison PJ, Pazos A, Sharp T. J. Neurochem. 2000;75:755. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0750755.x.; (b) Lejuene F, Rivet J-M, Gobert A, Canton H, Millan MJ. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1993;240:307. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90915-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Bolognesi ML, Bortolini M, Cavalli A, Andrisano V, Rosini M, Minarini A, Melchiorre CJ. J. Med Chem. 2004;47:5945. doi: 10.1021/jm049782n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Vliet LAV, Rodenhuis N, Dijkstra D, Wikstrom H, Pugsley TA, Serpa KA, Meltzer LT, Heffner TG, Wise LD, Lajiness ME, Huff RM, Svensson K, Sundell S, Lundmark M. J. Med. Chem. 2000;43:2871. doi: 10.1021/jm0000113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Chen Y, Zhang Q, Zhang B, Xia P, Xia Y, Yang Z-Y, Kilgore N, Wild C, Morris-Natschka SL, Lee K-H. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004;12:6383. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2004.09.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Zu L, Wang J, Li H, Xie H, Jiang W, Wang W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:1036. doi: 10.1021/ja067781+. Wang W, Li H, Wang J, Zu L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:10354. doi: 10.1021/ja063328m.See also: Rios R, Sunden H, Ibrahem I, Zhao G-L, Cordova A. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006;47:8679.
- 56.Dodda R, Goldman JJ, Mandal T, Zhao C-G, Broker GA, Tiekink ERT. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008;350:537. doi: 10.1002/adsc.200700331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Dodda R, Mandal T, Zhao C-G. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008;49:1899. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2008.01.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Luo S-P, Li Z-B, Wang L-P, Guo Y, Xia AB, Xu D-Q. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009;7:4539. doi: 10.1039/b910835a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Rueping M, Kuenkel A, Fröhlich R. Chem. Eur. J. 2010;16:4173. doi: 10.1002/chem.201000237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ding D, Zhao C-G, Guo Q, Arman H. Tetrahedron. 2010;66:4423. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2010.04.044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]