Abstract
We analyze the stochastic dynamics of genetic regulatory networks using a system of nonlinear differential equations. The system of  -functions is applied to capture the role of RNA polymerase in the transcription-translation mechanism. Using probabilistic properties of chemical rate equations, we derive a system of stochastic differential equations which are analytically tractable despite the high dimension of the regulatory network. Using stationary solutions of these equations, we explain the apparently paradoxical results of some recent time-course microarray experiments where mRNA transcription levels are found to only weakly correlate with the corresponding transcription rates. Combining analytical and simulation approaches, we determine the set of relationships between the size of the regulatory network, its structural complexity, chemical variability, and spectrum of oscillations. In particular, we show that temporal variability of chemical constituents may decrease while complexity of the network is increasing. This finding provides an insight into the nature of "functional determinism" of such an inherently stochastic system as genetic regulatory network.
-functions is applied to capture the role of RNA polymerase in the transcription-translation mechanism. Using probabilistic properties of chemical rate equations, we derive a system of stochastic differential equations which are analytically tractable despite the high dimension of the regulatory network. Using stationary solutions of these equations, we explain the apparently paradoxical results of some recent time-course microarray experiments where mRNA transcription levels are found to only weakly correlate with the corresponding transcription rates. Combining analytical and simulation approaches, we determine the set of relationships between the size of the regulatory network, its structural complexity, chemical variability, and spectrum of oscillations. In particular, we show that temporal variability of chemical constituents may decrease while complexity of the network is increasing. This finding provides an insight into the nature of "functional determinism" of such an inherently stochastic system as genetic regulatory network.
[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38]
References
- Bower JM, Bolouri H, editor. Computational Modeling of Genetic and Biochemical Networks. MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass, USA; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Boxler P. A stochastic version of center manifold theory. Probability Theory and Related Fields. 1989;83(4):509–545. doi: 10.1007/BF01845701. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley R. Basic properties of strong mixing conditions. A survey and some open questions. Probability Surveys. 2005;2:107–144. [Google Scholar]
- Bressan A. Tutorial on the Center Manifold Theory. 2003. SISSA, Trieste, Italy, http://www.math.psu.edu/bressan/PSPDF.
- Cai L, Friedman N, Xie XS. Stochastic protein expression in individual cells at the single molecule level. Nature. 2006;440(7082):358–362. doi: 10.1038/nature04599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr J. Applications of Center Manifold Theory. Springer, New York, NY, USA; 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Chen F. Introduction to Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion. Plenum Press, New York, NY, USA; 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Chen T, He HL, Church GM. Modeling gene expression with differential equations. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing (PSB '99), Mauna Lani, Hawaii, USA, January 1999. pp. 29–40. [PubMed]
- De Jong H. Modeling and simulation of genetic regulatory systems: a literature review. Journal of Computational Biology. 2002;9(1):67–103. doi: 10.1089/10665270252833208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elf J, Ehrenberg M. Fast evaluation of fluctuations in biochemical networks with the linear noise approximation. Genome Research. 2003;13(11):2475–2484. doi: 10.1101/gr.1196503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Martínez J, Aranda A, Pérez-Ortín JE. Genomic run-on evaluates transcription rates for all yeast genes and identifies gene regulatory mechanisms. Molecular Cell. 2004;15(2):303–313. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner CW. Handbook of Stochastic Methods for Physics, Chemistry and the Natural Sciences. Springer, New York, NY, USA; 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D. Exact stochastic simulation of coupled chemical reactions. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. 1977;81(25):2340–2361. doi: 10.1021/j100540a008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman S, Peterson C, Samuelsson B, Troein C. Random Boolean network models and the yeast transcriptional network. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2003;100(25):14796–14799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2036429100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim JT, Martinetz T, Polani D. Bioinformatic principles underlying the information content of transcription factor binding sites. Journal of Theoretical Biology. 2003;220(4):529–544. doi: 10.1006/jtbi.2003.3153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon B, Tjian R. Orchestrated response: a symphony of transcription factors for gene control. Genes & Development. 2000;14(20):2551–2569. doi: 10.1101/gad.831000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Genes VIII. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. In: Canonical Nonlinear Modeling. S-System Approach to Understanding Complexity. Voit E, editor. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, NY, USA; 1991. A qualitative analysis of S-systems: Hopf bifurcation; pp. 304–344. [Google Scholar]
- Loeve M. Probability Theory, The University Series in Higher Mathematics. Van Nostrand, New York, NY, USA; 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz EN. Deterministic nonperiodic flow. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences. 1963;20(2):130–141. doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1963)020<0130:DNF>2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lotka AJ. Elements of Physical Biology. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, Md, USA; 1925. [Google Scholar]
- Maquat LE. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in mammals. Journal of Cell Science. 2005;118(9):1773–1776. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdams HH, Arkin A. Stochastic mechanisms in gene expression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1997;94(3):814–819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.3.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdams HH, Arkin A. It's a noisy business! Genetic regulation at the nanomolar scale. Trends in Genetics. 1999;15(2):65–69. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(98)01659-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Review. 2003;45(2):167–256. doi: 10.1137/S003614450342480. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Parr RG, Yang W. Density Functional Theory of Atoms and Molecules. Oxford University Press, New York, NY, USA; 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Perko L. Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems. 3. Springer, New York, NY, USA; 2001. [Google Scholar]
-
Peytavi R, Raymond FR, Gagné D. et al. Microfluidic device for rapid (
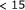 min) automated microarray hybridization. Clinical Chemistry. 2005;51(10):1836–1844. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2005.052845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
min) automated microarray hybridization. Clinical Chemistry. 2005;51(10):1836–1844. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2005.052845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] - Ptashne M. Regulated recruitment and cooperativity in the design of biological regulatory systems. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A. 2003;361(1807):1223–1234. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2003.1195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld N, Young JW, Alon U, Swain PS, Elowitz MB. Gene regulation at the single-cell level. Science. 2005;307(5717):1962–1965. doi: 10.1126/science.1106914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savageau M, Voit E. Recasting nonlinear differential equations as S-systems: a canonical nonlinear form. Mathematical Biosciences. 1987;87:83–115. doi: 10.1016/0025-5564(87)90035-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sorribas A, Savageau MA. Strategies for representing metabolic pathways within biochemical systems theory: reversible pathways. Mathematical Biosciences. 1989;94(2):239–269. doi: 10.1016/0025-5564(89)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voit E, editor. Canonical Nonlinear Modeling. S-System Approach to Understanding Complexity. Van Norstand Reinhold, New York, NY, USA; 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Wang W, Cherry JM, Botstein D, Li H. A systematic approach to reconstructing transcription networks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2002;99(26):16893–16898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.252638199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R, Jing Z, Chen L. Modelling periodic oscillation in gene regulatory networks by cyclic feedback systems. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology. 2005;67(2):339–367. doi: 10.1016/j.bulm.2004.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuensche A. Genomic regulation modeled as a network with basins of attraction. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing (PSB '98), Maui, Hawaii, USA, January 1998. pp. 89–102. [PubMed]
- Zhang D, Gyorgyi L, Peltier WR. Deterministic chaos in the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction: experiments and simulations. Chaos. 1993;3(4):723–745. doi: 10.1063/1.165933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumdahl S. Chemical Principles. Houghton Mifflin, New York, NY, USA; 2005. [Google Scholar]


