Abstract
A Boolean network is a model used to study the interactions between different genes in genetic regulatory networks. In this paper, we present several algorithms using gene ordering and feedback vertex sets to identify singleton attractors and small attractors in Boolean networks. We analyze the average case time complexities of some of the proposed algorithms. For instance, it is shown that the outdegree-based ordering algorithm for finding singleton attractors works in 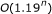 time for
time for 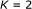 , which is much faster than the naive
, which is much faster than the naive 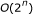 time algorithm, where
time algorithm, where  is the number of genes and
is the number of genes and  is the maximum indegree. We performed extensive computational experiments on these algorithms, which resulted in good agreement with theoretical results. In contrast, we give a simple and complete proof for showing that finding an attractor with the shortest period is NP-hard.
is the maximum indegree. We performed extensive computational experiments on these algorithms, which resulted in good agreement with theoretical results. In contrast, we give a simple and complete proof for showing that finding an attractor with the shortest period is NP-hard.
[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32]
Contributor Information
Shu-Qin Zhang, Email: sqzhang@hkusua.hku.hk.
Morihiro Hayashida, Email: morihiro@kuicr.kyoto-u.ac.jp.
Tatsuya Akutsu, Email: takutsu@kuicr.kyoto-u.ac.jp.
Wai-Ki Ching, Email: wkc@maths.hku.hk.
Michael K Ng, Email: mng@math.hkbu.edu.hk.
References
- Celis JE, Kruhøffer M, Gromova I. et al. Gene expression profiling: monitoring transcription and translation products using DNA microarrays and proteomics. FEBS Letters. 2000;480(1):2–16. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01771-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes TR, Mao M, Jones AR. et al. Expression profiling using microarrays fabricated by an ink-jet oligonucleotide synthesizer. Nature Biotechnology. 2001;19(4):342–347. doi: 10.1038/86730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipshutz RJ, Fodor SPA, Gingeras TR, Lockhart DJ. High density synthetic oligonucleotide arrays. Nature Genetics. 1999;21(supplement 1):20–24. doi: 10.1038/4447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockhart DJ, Winzeler EA. Genomics, gene expression and DNA arrays. Nature. 2000;405(6788):827–836. doi: 10.1038/35015701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jong HD. Modeling and simulation of genetic regulatory systems: a literature review. Journal of Computational Biology. 2002;9(1):67–103. doi: 10.1089/10665270252833208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass K, Kauffman SA. The logical analysis of continuous, nonlinear biochemical control networks. Journal of Theoretical Biology. 1973;39(1):103–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(73)90208-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman SA. Metabolic stability and epigenesis in randomly constructed genetic nets. Journal of Theoretical Biology. 1969;22(3):437–467. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(69)90015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman SA. Homeostasis and differentiation in random genetic control networks. Nature. 1969;224(215):177–178. doi: 10.1038/224177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman SA. The large scale structure and dynamics of genetic control circuits: an ensemble approach. Journal of Theoretical Biology. 1974;44(1):167–190. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5193(74)80037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. Gene expression profiling, genetic networks, and cellular states: an integrating concept for tumorigenesis and drug discovery. Journal of Molecular Medicine. 1999;77(6):469–480. doi: 10.1007/s001099900023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman SA. The Origins of Order: Self-Organization and Selection in Evolution. Oxford University Press, New York, NY, USA; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi R, Sniegoski C. Modeling the complexity of genetic networks: understanding multigenic and pleiotropic regulation. Complexity. 1996;1(6):45–63. [Google Scholar]
- Shmulevich I, Zhang W. Binary analysis and optimization-based normalization of gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 2002;18(4):555–565. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.4.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thieffry D, Huerta AM, Pérez-Rueda E, Collado-Vides J. From specific gene regulation to genomic networks: a global analysis of transcriptional regulation in Escherichia coli. BioEssays. 1998;20(5):433–440. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199805)20:5<433::AID-BIES10>3.0.CO;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. Cell state dynamics and tumorigenesis in Boolean regulatory networks. InterJournal Genetics. http://www.interjournal.org/ http://www.interjournal.org/ MS: 416.
- Drossel B. Number of attractors in random Boolean networks. Physical Review E. 2005;72(1) doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.72.016110. 5 pages. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drossel B, Mihaljev T, Greil F. Number and length of attractors in a critical Kauffman model with connectivity one. Physical Review Letters. 2005;94(8) doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.088701. 4 pages. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B, Troein C. Superpolynomial growth in the number of attractors in Kauffman networks. Physical Review Letters. 2003;90(9) doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.90.098701. 4 pages. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socolar JES, Kauffman SA. Scaling in ordered and critical random Boolean networks. Physical Review Letters. 2003;90(6) doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.90.068702. 4 pages. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devloo V, Hansen P, Labbé M. Identification of all steady states in large networks by logical analysis. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology. 2003;65(6):1025–1051. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8240(03)00061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki A. An analytical study of the number of steady states in gene regulatory networks. Journal of Theoretical Biology. 2005;236(3):291–310. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2005.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal R, Ivanov I, Datta A, Bittner ML, Dougherty ER. Generating Boolean networks with a prescribed attractor structure. Bioinformatics. 2005;21(21):4021–4025. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou X, Wang X, Pal R, Ivanov I, Bittner M, Dougherty ER. A Bayesian connectivity-based approach to constructing probabilistic gene regulatory networks. Bioinformatics. 2004;20(17):2918–2927. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bth318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akutsu T, Kuhara S, Maruyama O, Miyano S. A system for identifying genetic networks from gene expression patterns produced by gene disruptions and overexpressions. Genome Informatics. 1998;9:151–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milano M, Roli A. Solving the satisfiability problem through Boolean networks. Proceedings of the 6th Congress of the Italian Association for Artificial Intelligence on Advances in Artificial Intelligence, Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence, Springer, Bologna, Italy, September 1999. pp. 72–83.
- Garey MR, Johnson DS. Computers and Intractability: A Guide to the Theory of NP-Completeness. W.H. Freeman, New York, NY, USA; 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Even G, Naor J, Schieber B, Sudan M. Approximating minimum feedback sets and multicuts in directed graphs. Algorithmica. 1998;20(2):151–174. doi: 10.1007/PL00009191. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Barabási A-L, Albert R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science. 1999;286(5439):509–512. doi: 10.1126/science.286.5439.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guelzim N, Bottani S, Bourgine P, Képès F. Topological and causal structure of the yeast transcriptional regulatory network. Nature Genetics. 2002;31(1):60–63. doi: 10.1038/ng873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akutsu T, Miyano S, Kuhara S. Identification of genetic networks from a small number of gene expression patterns under the Boolean network model. Proceedings of the 4th Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing (PSB '99), Big Island of Hawaii, Hawaii, USA, January 1999. pp. 17–28. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Akutsu T, Kuhara S, Maruyama O, Miyano S. Identification of genetic networks by strategic gene disruptions and gene overexpressions under a Boolean model. Theoretical Computer Science. 2003;298(1):235–251. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3975(02)00425-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Akutsu T, Hayashida M, Ching W-K, Ng MK. Control of Boolean networks: hardness results and algorithms for tree structured networks. Journal of Theoretical Biology. 2007;244(4):670–679. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2006.09.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


