Abstract
Small, non-coding RNAs are a distinct class of regulatory RNAs in plants and animals that control a variety of biological processes. In plants, several classes of small RNAs with specific sizes and dedicated functions have evolved through a series of pathways. The major classes of small RNAs include microRNAs (miRNAs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), which differ in their biogenesis. miRNAs control the expression of cognate target genes by binding to reverse complementary sequences, resulting in cleavage or translational inhibition of the target RNAs. siRNAs have a similar structure, function, and biogenesis as miRNAs but are derived from long double-stranded RNAs and can often direct DNA methylation at target sequences. Besides their roles in growth and development and maintenance of genome integrity, small RNAs are also important components in plant stress responses. One way in which plants respond to environmental stress is by modifying their gene expression through the activity of small RNAs. Thus, understanding how small RNAs regulate gene expression will enable researchers to explore the role of small RNAs in biotic and abiotic stress responses. This review focuses on the regulatory roles of plant small RNAs in the adaptive response to stresses.
Keywords: small RNA, miRNA, siRNA, biotic, abiotic, stress responses, plant
1 Introduction
Small non-coding RNAs, which consist of 20–24 nucleotides (nt), have been increasingly investigated as important regulators of protein-coding gene expression; these small RNAs function by causing either transcriptional gene silencing (TGS) or post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS) [1]. They were first reported in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans [2] and are responsible for the phenomenon known as RNA interference (RNAi), co-suppression, gene silencing, or quelling [3–6]. Shortly after these reports were published, researchers demonstrated that PTGS in plants is correlated with the activity of small RNAs [7]. These small RNAs regulate various biological processes, often by interfering with mRNA translation. In plants, two main categories of small regulatory RNAs are distinguished based on their biogenesis and function: microRNAs (miRNAs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). Recently, miRNAs and siRNAs have been shown to be highly conserved, important regulators of gene expression in both plants and animals [8, 9]. The modes of action by which small RNAs control gene expression at the transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels are now being developed into tools for molecular biology research. One important goal of this research is to determine how a stress affects small RNAs and how small RNAs in turn regulate plant responses to a stress.
Plants have evolved sophisticated mechanisms to cope with a variety of environmental stresses. Many plant genes are regulated by stresses such as drought, salt, cold, heat, light, and oxidative stress [10, 11]. Recent evidence indicates that plant miRNAs and siRNAs play a role in biotic and abiotic stress responses [12–14]. The first indication for such roles came from bioinformatics/in silica analysis of miRNAs and their target genes, and cloning of miRNAs from stress-treated Arabidopsis thaliana plants, which revealed new miRNAs that had not been previously cloned from plants grown in unstressed conditions [15, 16]. Understanding small RNA-guided stress regulatory networks can provide new insights for the genetic improvement of plant-stress tolerance. Many studies have also revealed complexity and overlap in plant responses to different stresses, and understanding this complexity and overlay will likely lead to new ways to enhance crop tolerance to diseases and environmental stresses. Researchers recently demonstrated that manipulation of miRNA/siRNA-guided gene regulation can help in the engineering of stress-resistant plants [17–19]. In this review, we consider what are currently known and unknown about roles of miRNAs and siRNAs in plant responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. The responses of small RNAs to different types of stresses are discussed in detail.
2 Classes of small RNAs
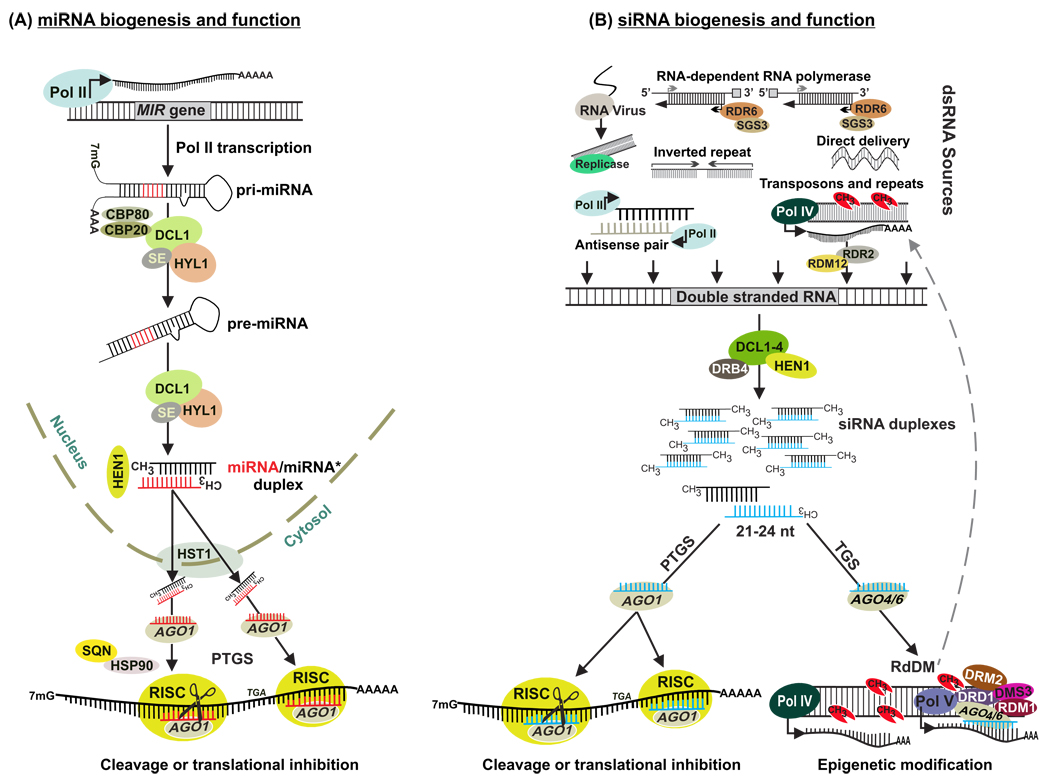
Independent approaches combining traditional cloning, computational prediction, and high throughput sequencing of small RNA libraries have identified several classes of small RNAs with specific sizes and functions in plants. These classes of small RNAs include miRNAs, repeat-associated small interfering RNAs (ra-siRNAs), natural antisense transcript-derived small interfering RNAs (nat-siRNAs), trans-acting small interfering RNAs (ta-siRNAs), heterochromatic small interfering RNAs (hc-siRNAs), secondary transitive siRNA, primary siRNAs, and long small interfering RNAs (lsiRNAs) [20–22]. The biogenesis and functions of most of these small RNA classes have been well characterized in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. In general, small RNAs are generated from at least partially double-stranded RNA precursors by the action of ribonuclease III-like Dicer proteins (DCL) [23]. The small RNA duplexes generated by DCL activity have a characteristic 2-nucleotide overhang at the 3’ end because of an offset cutting of the DCLs. In plants, these 3’ overhangs are stabilized by 2’-O-methylation [24]. Generation of lsiRNAs depends on the DCL and ARGONAUTE (AGO) subfamily protein AGO7. This differs from the generation of the 25-to 31-nt animal PIWI interacting RNAs, which are independent of the Dicer and AGO subfamily protein. Only one strand of the processed small RNA duplex subsequently associates with an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) that scans for nucleic acids complementary to the loaded small RNA to execute its function [25, 26]. In plants, small RNAs act in gene silencing by mediating RNA slicing [27], translational repression [28], and histone modification and DNA methylation [29, 30]. The first two mechanisms control gene expression posttranscriptionally, whereas the latter two affect gene expression at the transcriptional level (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Biogenesis and function of miRNAs and siRNAs. (A) MIR genes are initially transcribed by Pol II into a single-stranded RNA that folds back to form a hairpin structure (also called pri-miRNA) thought to be stabilized by the RNA-binding protein DAWDLE (DDL) [138]. Splicing and further processing in nuclear dicing bodies involves the interactive functions of HYL1 and SE and of the cap-binding proteins (CBP) CBP20 and CBP80 [139, 140]. Pri-miRNAs and pre-miRNAs are generally thought to be processed from the free-end opposite to the loop by DCL1 to yield one or several phased miRNA/miRNA* duplexes. These are then methylated by HEN1 and transported to the cytoplasm by HST1. The miRNA guide strand is selected, incorporated, and stabilized in dedicated AGO1 protein. miRNA-guided AGO1-containing RISC directs mRNA cleavage or translation inhibition of the target transcript. miRNA-guided AGO1 functions are promoted by SQUINT (SQN) and HSP90 [22, 141]. (B) Various sources of dsRNA, its processing into siRNAs by one of four DCLs proteins assisted by dsRNA-binding proteins, HEN1-mediated siRNA stabilization, and selected strands of siRNA duplexes guide AGO-containing RISC to target RNAs for endonucleolytic cleavage and for translation repression, or these siRNAs can then guide AGO4 or AGO6 to function in RNA-directed DNA Methylation (RdDM) pathway involving Pol IV and Pol V. Cytosine methylation at these specific sites involves different effectors like the de novo methyltransferase DOMAINS REARRANGED METHYLTRANSFERASE 2 (DRM2); DEFECTIVE IN RNADIRECTED DNA METHYLATION 1 (DRD1), a member of the SWI2-SNF2 chromatin remodeling protein family; and DEFECTIVE IN MERISTEM SILENCING 3 (DMS3), a structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) protein.
2.1 miRNAs
2.1.1 Biogenesis of miRNAs
miRNAs are small regulatory RNAs of 20–22 nt that are encoded by endogenous MIR genes. Their primary transcripts form precursor RNAs, which have a partially double-stranded stem-loop structure and which are processed by DCL proteins to release mature miRNAs [26]. In the miRNA biogenesis pathway, primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs) are transcribed from nuclear-encoded MIR genes by RNA polymerase II (Pol II) [31] leading to precursor transcripts with a characteristic hairpin structure (Fig. 1A). In plants, the processing of these pri-miRNAs into pre-miRNAs is catalyzed by DCL1 and assisted byHYPONASTIC LEAVES 1 (HYL1) and SERRATE (SE)proteins [26]. The pre-miRNA hairpin precursor is finally converted into 20- to 22-nt miRNA/miRNA* duplexes by DCL1, HYL1, and SE. The duplex is then methylated at the 3’ terminus by HUA ENHANCER 1 (HEN1) and exported into the cytoplasm by HASTY (HST1), an exportin protein [32, 33]. In the cytoplasm, one strand of the duplex (the miRNA) is incorporated into an AGO protein, the catalytic component of RISC, and guides RISC to bind to cognate target transcripts by sequence complementarity (Fig. 1A). In addition to the control of targets at the posttranscriptional level, miRNAs regulate gene expression by causing epigenetic changes such as DNA and histone methylation [29, 34, 35].
Functional analysis of conserved miRNAs revealed their involvement in multiple biological and metabolic processes in plants. They regulate various aspects of developmental programs including auxin signaling, meristem boundary formation and organ separation, leaf development and polarity, lateral root formation, transition from juvenile-to-adult vegetative phase and from vegetative-to-flowering phase, floral organ identity, and reproduction. They also regulate plant responses to biotic and abiotic stresses, and the miRNA pathway itself (Table 1).
Table 1.
Role of conserved plant miRNAs
| Role | miRNA family | Target families/genes | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Auxin signaling | miR160 | ARF10 | [122, 123] |
| miR164 | NAC1 | [130] | |
| miR167 | ARF8 | [122] | |
| miR390 | ARF | [114] | |
| miR393 | TIR1/F-box AFB | [15, 124] | |
| Leaf development | miR159 | MYB | [48, 127, 128] |
| miR164 | NAC1 | [132] | |
| miR166 | HD-ZIPIII | [131] | |
| miR172 | AP2 | [127] | |
| miR319 | TCP | [128] | |
| Leaf polarity | miR166 | HD-ZIPIII | [121, 131] |
| miR168 | AGO1 | [120] | |
| miR390 | ARF | [114] | |
| Floral organ identity | miR160 | ARF10 | [122, 123, 127, 128] |
| miR164 | NAC1 | [132, 133] | |
| miR172 | AP2 | [134] | |
| miR319 | TCP | [127, 128] | |
| Flowering time | miR156 | SBP | [125–127] |
| miR159 | MYB | [48, 127, 128] | |
| miR172 | AP2 | [127, 135] | |
| miR319 | TCP | [127, 128] | |
| Adaptive responses to stress | miR156 | SBP | [37, 43, 44, 103] |
| miR159 | MYB | [16, 37, 43, 48, 49] | |
| miR160 | ARF10 | [37, 50, 100] | |
| miR167 | ARF8 | [37, 42, 43] | |
| miR168 | AGO1 | [37] | |
| miR169 | NFY/MtHAP2-1 | [37, 43, 52, 110, 136] | |
| miR171 | SCL | [37, 43] | |
| miR319 | TCP | [16, 37, 43] | |
| miR393 | TIR1/F-box AFB | [15, 16, 37, 42, 43] | |
| miR395 | APS/AST | [15, 16, 37] | |
| miR396 | GRF | [16, 37] | |
| miR397 | Laccases, Beta-6-tubulin | [15, 16, 37] | |
| miR398 | CSD | [15, 19, 37, 43, 53, 72] | |
| miR399 | UBC24/PHO2 | [36, 37, 75, 76] | |
| miR408 | Plastocyanin | [16, 37, 44] | |
| Regulation of miRNA | miR162 | DCL1 | [137] |
| miR168 | AGO1 | [120] | |
| miR403 | AGO2 | [114] | |
| Others | miR158 | At1g64100 | |
| miR161 | PPR | ||
| miR163 | At1g66700, At1g66690 | ||
| miR173 | At3g28460 | ||
| miR174 | At1g17050 | ||
| miR175 | At5g18040, At3g43200, At1g51670 |
||
| miR394 | F-box |
2.1.2 Role of miRNAs in plant stress responses
Environmental stress causes plants to over- or under-express certain miRNAs or to synthesize new miRNAs to cope with stress. Several stress-regulated miRNAs have been identified in model plants under various biotic and abiotic stress conditions, including nutrient deficiency [36], drought [37–39], cold [40], salinity [37, 41], bacterial infection [42], UV-B radiation [43], and mechanical stress [44]. Although stress regulation may imply a potential function of the regulated miRNA in stress responses, it is obvious that the fact that a miRNA is differentially regulated in response to an environmental stress does not necessarily mean that the miRNA is involved in stress adaptation responses.
In a recent report, the levels of 117 miRNAs under salinity, drought, and low-temperature conditions were analyzed using miRNA chips representing nearly all known miRNAs identified in Arabidopsis [37]. Seventeen stress-inducible miRNAs were detected, and the results were confirmed by detecting their expression patterns and analyzing the cis-regulatory elements in their promoter sequences [37]. Jones-Rhoades and Bartel [15] identified novel Arabidopsis miRNAs that were predicted to target genes such as superoxide dismutases, laccases, and ATP sulfurylases (APS). The expression of one particular miRNA (miR395) was increased upon sulphate starvation, showing that miRNAs can be induced by environmental factors and not only by developmental processes. miR395 targets the genes that encode ATP sulfurylases APS1, APS3, and APS4. These enzymes catalyze the first step of inorganic sulfate assimilation [15, 16]. Sunkar and Zhu [16] constructed a library of small RNAs from Arabidopsis seedlings exposed to different abiotic stresses including cold, dehydration, high salt, and abscisic acid (ABA), and identified several new miRNAs that are responsive to abiotic stress [16]. For example, miR393 was upregulated by cold, dehydration, salinity, and ABA treatments; miR397b and miR402 were slightly upregulated by general stress treatments while miR319c was induced by cold but not by the other treatments; miR389a, however, was downregulated by all of the stress treatments. The results indicated that stress-induced miRNAs target negative regulators of stress responses or positive regulators of processes that are inhibited by stresses and that several of the newly identified miRNAs exhibit tissue- or developmental stage-specific expression patterns. More recently, genome-wide profiling and analysis of miRNAs was carried out in drought-challenged rice [39]. Lu et al. [44] also identified 48 miRNA sequences from the Populus genome and found that most of these Populus miRNAs target developmental and stress/defense-related genes. The authors also found that plant miRNAs can be induced by mechanical stress and may function in critical defense systems for structural and mechanical fitness [44].
A number of miRNAs have been linked to biotic stress responses in plants, and the role of these miRNAs in plants infected by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, nematodes, and fungi has been reported [12, 45]. Moreover, miRNAs are also important in regulating plant–microbe interactions during nitrogen (N) fixation by Rhizobium and tumor formation by Agrobacterium [45]. Additionally, Mishra et al. [46] observed a significant increase in the GC content of stress-regulated miRNA sequences, which further supports the view that miRNAs act as ubiquitous regulators under stress conditions. GC content may also be considered a critical parameter for predicting stress-regulated miRNAs in plants [46].
It is noteworthy that some of the regulations were seen from only a single species and may not be applicable to other species. In fact, it remains to be seen whether some of the observations may even be confirmed by an independent method or reproducible from independent experiments with the same species.
2.1.2.1 miRNAs involved in ABA-mediated stress responses
The phytohormone ABA is involved in plant responses to environmental stresses. The first indication that miRNAs may be involved in ABA-mediated responses came from observations of ABA hypersensitivity in an Arabidopsis mutant containing a “pleiotropic recessive Arabidopsis transposon insertion mutation,” hyl1 [47]. Recently, two research groups independently found that either ABA or gibberellin (GA) treatment regulated miR159 expression [16, 48] and controlled floral organ development [48]. In germinating Arabidopsis seeds, miR159 was upregulated in ABA-treated seedlings [49]. Sunkar and Zhu [16] reported that the expression of miR393, miR397b and miR402 was upregulated by ABA treatment. In contrast, miR389a appears to be downregulated by ABA [16]. Other studies in Arabidopsis have also reported upregulation of miR160 [50] and miR417 [51] and downregulation of miR169 [52] and miR398 [53] in response to ABA. In rice, miR319 was upregulated, whereas miR167 and miR169 were downregulated in ABA-mediated responses [54]. In Phaseolus vulgaris, miR159.2, miR393, and miR2118 were induced under ABA treatments whereas miRS1, miR1514, and miR2119 were moderately upregulated in response to ABA (Fig. 2) [55]. The dependence of DNA methylation on miRNA levels was also shown for an ABA-responsive PpbHLH-miR1026 regulon in Physcomitrella patens. ABA application caused an increase of miR1026 and a decrease of its PpbHLH target RNA [29].
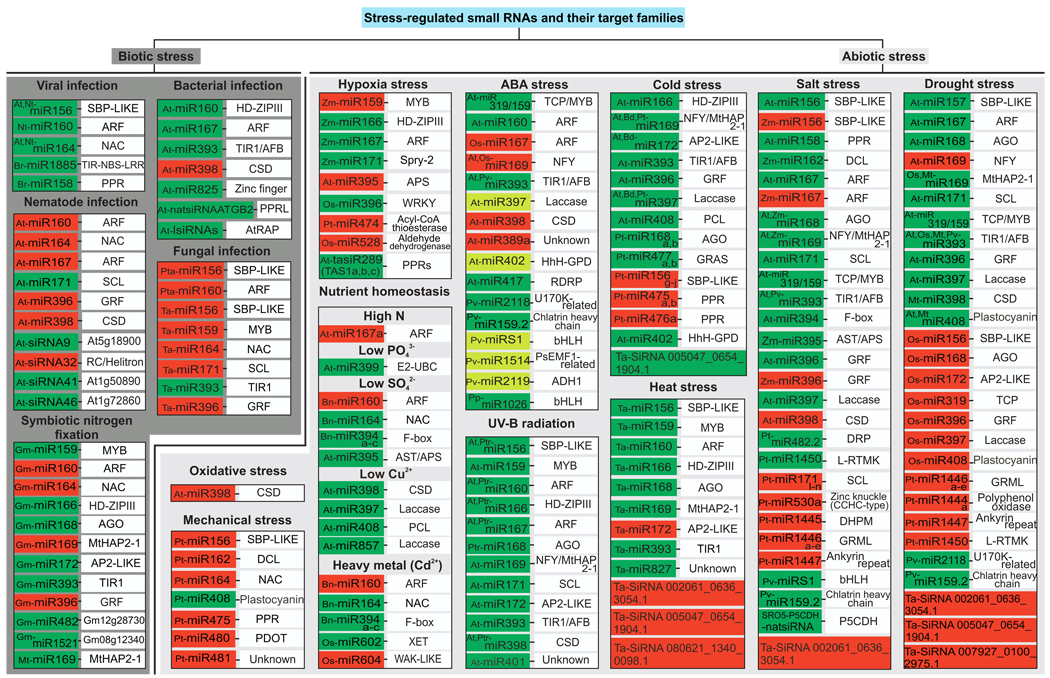
Fig. 2.
Summary of stress-regulated small RNAs and their target families. Small RNAs are categorized based on the stress that they respond to. Grey box: abiotic stress, dark grey: biotic stress, green boxes: up-regulated small RNA, light green boxes: slightly up-regulated small RNA, and red boxes: down-regulated small RNA. At (Arabidopsis thaliana), Bd (Brachypodium distachyon), Bn (Brassica napus), Br (Brassica rapa), Gm (Glycine max), Mt (Medicago truncatula), Nt (Nicotiana tabacum), Os (Oryza sativa), Pt (Populus trichocarpa), Pta (Pinus taeda), Ptr (Populus tremula), Pp (Physcomitrella patens), Pv (Phaseolus vulgaris), Ta (Triticum aestivum), Zm (Zea mays). See the text for references.
2.1.2.2 miRNAs in response to drought and salt stress
Studies with Arabidopsis have revealed a general role for miRNAs in drought and salt responses (Fig. 2). Several stress-related miRNAs were identified based on the sequencing of a library of small RNAs isolated from Arabidopsis seedlings exposed to various stresses [16]. Recently, miRNAs such as miR168, miR171, and miR396 were found to be responsive to high salinity, drought, and cold stress in Arabidopsis, thus supporting the hypothesis of a role for miRNAs in the adaptive response to abiotic stress [37]. miRNA-expression profiling under drought stress has now been performed in Arabidopsis, rice, and Populus trichocarpa. In Arabidopsis, miR396, miR168, miR167, miR165, miR319, miR159, miR394, miR156, miR393, miR171, miR158, and miR169 were shown to be drought responsive [37]. The upregulation of miR393, miR319, and miR397 in response to dehydration in Arabidopsis has been reported [16]. In rice, miR169g was strongly upregulated by drought while miR393 was transiently induced by drought [38]. Genome-wide profiling and analysis of miRNAs were carried out in drought-challenged rice across a wide range of developmental stages, from tillering to inflorescence formation, using a microarray platform [39]. The results indicated that 16 miRNAs (miR156, miR159, miR168, miR170, miR171, miR172, miR319, miR396, miR397, miR408, miR529, miR896, miR1030, miR1035, miR1050, miR1088, and miR1126) were significantly downregulated in response to drought stress. Conversely, 14 miRNAs (miR159, miR169, miR171, miR319, miR395, miR474, miR845, miR851, miR854, miR896, miR901, miR903, miR1026, and miR1125) were significantly upregulated under drought stress. Some miRNA gene families, such as miR171, miR319, and miR896, were identified in both down-and upregulated groups, and nine miRNAs (miR156, miR168, miR170, miR171, miR172, miR319, miR396, miR397, and miR408) showed opposite expression to that observed in drought-stressed Arabidopsis [39]. In Populus, miR171l-n, miR1445, miR1446a-e, and miR1447 were found to be drought-responsive [56]. In Phaseolus vulgaris, miRS1, miR1514a, and miR2119 showed a moderate but clear increase in accumulation upon drought treatment, while the accumulation was greater for miR159.2, miR393, and miR2118 in response to the same treatment [55]. In Medicago truncatula, miR169 was downregulated only in the roots, and miR398a,b and miR408 were strongly upregulated in both shoots and roots under drought stress [57]. More recently, miRNA expression patterns of drought-resistant wild emmer wheat (Triticum turgidum ssp. Dicoccoides) in response to drought stress were investigated using a plant miRNA microarray platform [58]. Expression levels were detected for 205 miRNAs in control and 438 miRNAs in drought-stressed leaf and root tissues. The following 13 miRNAs were found to be differentially regulated in response to drought stress: miR1867, miR896, miR398, miR528, miR474, miR1450, miR396, miR1881, miR894, miR156, miR1432, miR166, and miR171 [58]. Similarly, miR474, which targets proline dehydrogenase (PDH), was recently shown to be upregulated during drought stress in maize [59].
Approximately 6% of the total arable land is affected by excess salt [60]. Numerous genes and pathways in plants are affected by salt stress [11]. Several differentially regulated miRNAs have been identified in salt-stressed plants. In Arabidopsis, miR156, miR158, miR159, miR165, miR167, miR168, miR169, miR171, miR319, miR393, miR394, miR396, and miR397 were upregulated in response to salt stress (Fig. 2), while the accumulation of miR398 was decreased [37]. In Phaseolus vulgaris, Arenas-Huertero et al. [55] observed increased accumulation of miRS1 and miR159.2 in response to NaCl addition (Fig. 2). In Populus trichocarpa, miR530a, miR1445, miR1446a-e, miR1447, and miR171l-n were downregulated, whereas miR482.2 and miR1450 were upregulated during salt stress [56]. Later, miR169g and another member of the miR169 family, miR169n, were reported to be induced by high salinity [61]. The authors found a cis-acting ABA-responsive element (ABRE) in the upstream region of miR169n, which suggested that miR169n may be ABA-regulated. Both miR169g and miR169n targeted Nuclear factor Y subunit A (NF-YA), a factor that was previously shown to be downregulated in drought-affected wheat leaves [62]. Recently, a report used microarray experiments to explore the miRNA profile in a salt-tolerant and a salt-sensitive line of maize (Zea mays) [63]; the results indicated that members of the miR156, miR164, miR167, and miR396 families were downregulated, while miR162, miR168, miR395, and miR474 families were upregulated in salt-shocked maize roots (Fig. 2).
2.1.2.3 miRNAs in response to cold and heat stress
The expression of miRNAs in cold stress has been examined in Arabidopsis [16, 37], Populus [56], and Brachypodium [64]. miR397 and miR169 were upregulated in all three species, and miR172 was upregulated in Arabidopsis and Brachypodium. In addition to these miRNAs, several miRNAs (miR165/166, miR393, miR396, and miR408) were induced under cold stress in Arabidopsis (Fig. 2), while other miRNAs (miR156/157, miR159/319, miR164, miR394, and miR398) showed either transient or mild regulation under cold stress [16, 37]. In Populus, miR168a,b and miR477a,b were upregulated while miR156g-j, miR475a,b, and miR476a were downregulated under cold stress (Fig. 2) [56]. Wheat miRNAs showed differential expression in response to heat stress; by using Solexa high-throughput sequencing, Xin et al. [65] cloned the small RNAs from wheat leaves treated by heat stress. Among the 32 miRNA families detected in wheat, nine conserved miRNAs were putatively heat responsive. For example, miR172 was significantly decreased, and miRNAs (including miR156, miR159, miR160, miR166, miR168, miR169, miR393 and miR827) were upregulated under heat stress (Fig. 2).
2.1.2.4 miRNAs in response to hypoxia and oxidative stress
Anaerobic or low-oxygen stress (hypoxia) interferes with mitochondrial respiration [66]. Hypoxia induces massive changes in the transcriptome and a switch from aerobic respiration to anaerobic respiration [67]. Recent studies suggested that miRNAs are involved in plant responses to hypoxia [68, 69]. Several miRNAs were differentially regulated in seedlings that were submerged; early during submergence, Zm-miR166, Zm-miR167, Zm-miR171, Os-miR396, and Zm-miR399 were induced but Zm-miR159, At-miR395, Pt-miR474, and Os-miR528 were downregulated (Fig. 2) [69]. Similarly, high-throughput sequencing was carried out on small RNA libraries from hypoxia-treated and control root tissues in Arabidopsis [68]. The abundances of 19 miRNAs families significantly changed in response to hypoxia, and their abundances were inversely correlated with those of their specific mRNA targets [68]. Expression levels of miR156g, miR157d, miR158a, miR159a, miR172a,b, miR391, and miR775 increased under hypoxia. The involvement of miRNAs in plant response to hypoxia was further confirmed in experiments with a chemical that inhibits mitochondrial respiration and therefore mimics hypoxia [68].
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are inherent to plants because ROS are constantly produced by aerobic processes in chloroplasts, mitochondria, and peroxisomes [70]. Elevated levels of ROS are often associated with plant stress such as high intensity light, UV radiation, temperature extremes, heavy metals, drought stress, salt stress, and mechanical stress [70]. Superoxide in plants are converted into molecular oxygen and hydrogen peroxide by superoxide dismutases (SODs). Cu-Zn SODs are encoded by CSD1, CSD2, and CSD3 in Arabidopsis [19]. miR398 was predicted to target CSD1 and CSD2 [15, 71], and Sunkar et al. [19] confirmed these targets and discovered that miR398 is downregulated under oxidative stress. Downregulation of miR398 is accompanied by an accumulation of CSD1 and CSD2 transcripts [19]. This accumulation did not result from stress-related transcriptional induction of the Cu/Zn SOD genes, but rather resulted from the relaxation of miR398-directed cleavage [19]. Furthermore, transgenic Arabidopsis plants overexpressing a miR398-resistant form of CSD2 accumulated more CSD2 mRNA than plants overexpressing a regular CSD2 and were consequently much more tolerant to high intensity light, heavy metals, and other oxidative stressors [19]. Under stress conditions, the negative regulation of CSD1 and CSD2 by miR398 is relieved, which leads to the increased expression of CSD1 and CSD2 and therefore reduced accumulation of the highly toxic superoxide free radicals [19]. miR398 was induced under Cu2+-limited conditions to relocate the Cu2+ ion from CSD1 and CSD2 for synthesis of more essential proteins and processes [72]. A genome-wide study of H2O2-regulated miRNAs from rice seedlings indicated that expression of some miRNAs is regulated in response to oxidative stress [73]. The authors identified seven H2O2-responsive miRNAs (miR169, miR397, miR528, miR827, miR1425, miR319a.2, and miR408-5p), i.e., miRNAs that were expressed differentially in H2O2-treated and control samples; miR169, miR397, miR827, and miR1425 were upregulated while miR528 was downregulated by H2O2-treatments [73].
2.1.2.5 miRNAs in response to UV-B radiation
A computational approach was used to identify Arabidopsis miRNAs induced by UV-B radiation [43]. Of the 21 miRNAs belonging to 11 miRNA families identified in that study, the following were predicted to be upregulated under UV-B stress: miR156/157, miR159/319, miR160, miR165/166, miR167, miR169, miR170/171, miR172, miR393, miR398, and miR401 [43]. Some of the same miRNA families that were predicted to be upregulated by UV-B radiation in Arabidopsis (miR156, miR160, miR165/166, miR167, miR398, and miR168) were found to be upregulated by UV-B radiation in Populus tremula (Fig. 2) [74]. Interestingly, three families (miR159, miR169, and miR393) that were predicted to be upregulated in Arabidopsis were downregulated in Populus tremula, suggesting that some responses to UV-B radiation stress may be species specific [74].
2.1.2.6 miRNAs and nutrient homeostasis
miRNAs are involved in plant responses to nutrient stress. According to recent studies with Arabidopsis, miR399, miR395, and miR398 are induced in response to phosphate-, sulfate-, and copper-deprived conditions, respectively [15, 19, 72, 75, 76]. Phosphate is required for the synthesis of nucleic acids and membrane lipids and is frequently a limiting nutrient for plant growth. Phosphate homeostasis is partially controlled through miR399, which targets a gene encoding a putative ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (UBC24) [15, 16]. miR399 is upregulated in low phosphate-stressed plants (Fig. 2) [36, 76, 77] and is not induced by other common stresses, whereas its target, UBC24 mRNA, was reduced primarily in roots of plants exposed to low-phosphate stress. It is likely that an MYB transcription factor, PHOSPHATE STARVATION RESPONSE 1 (PHR1), is involved in miR399 expression. PHR1 is expressed in response to phosphate starvation and positively regulates a group of phosphate-responsive genes by binding to GNATATNC cis-elements [78–80]. This cis-element has been found upstream of all known miR399 genes in Arabidopsis [76, 78]. Furthermore, phr1 mutants show a significant decline in miR399 induction under phosphate stress [76, 78]. miR399 has been isolated from phloem, and its abundance in phloem increases upon phosphate starvation [81, 82]. These studies strongly suggest that miR399 acts as a phosphate starvation signal that is translocated from shoot to root where it promotes phosphate uptake by downregulating PHO2, which encodes E2-UBC24 [75, 76]. miRNAs themselves can be subject to posttranscriptional regulation, as revealed by the discovery of the INDUCED BY PHOSPHATE STARVATION1 (IPS1) gene, which acts as a target mimic to control miR399 action [83]. IPS1 has imperfect sequence complementarity to miR399. The complementarity is interrupted by a mismatched loop at the expected miRNA cleavage site. Because of this complementarity interruption, the IPS1 RNA sequesters miR399 and prevents it from causing degradation of PHO2 mRNA [83].
Sulfur (S) is one of the essential macronutrients and is available in the form of sulfate in the soil. miR395 targets both ATP sulfurylases (APSs) and the sulfate transporter AST68 [9, 15]. Sulfate deprivation induces the expression of miR395 (Fig. 2), with a concomitant decrease in transcript levels of APS1 [15]. The abundance of miR395 in the phloem increases for Brassica plants deprived of S, and the increase was much stronger in the phloem than in the root, stem, or leaf tissue [81, 84].
The plant micronutrient copper (Cu) is essential for photosynthesis, oxidative responses, and other physiological processes [85]. miR398 is a key regulator of Cu homeostasis. When Cu is limiting, the level of miR398 increases (Fig. 2), and this reduces the allocation of Cu to CSDs (CSD1 and CSD2) and therefore makes Cu available for other essential processes [72, 86]. In higher plants, the Cu/Zn-SODs are replaced by Fe-SODs [87]. In Brassica under Cu deprivation, miR398 is upregulated not only in leaf, stem, and root tissue but also in phloem sap [84]. According to more recent research, Brassica phloem sap contains a specific set of small RNAs that are distinct from those in leaves and roots, and the phloem responds specifically to stress [81]. Upon S and Cu deficiencies, the phloem sap reacts with an increase of the same miRNAs that were earlier characterized in other tissues, while no clear positive response to iron was observed. However, iron led to a reduction of copper- and phosphate-responsive miRNAs. Grafting experiments also indicated that miR395 and miR399 are phloem-mobile, suggesting that such translocatable miRNAs might be candidates for information-transmitting molecules [81].
Cadmium (Cd) is one of the most toxic metals in agricultural soils. Under high concentrations of Cd or other heavy metals, plants encounter cation imbalances that result in many physiological and biochemical disorders. Recent studies identified a set of conserved and non-conserved miRNAs that are differentially regulated in response to heavy metals in rice [88], Medicago truncatula [89], Brassica napus [90], and Arabidopsis [91]. These results suggest that miRNAs help regulate plant responses to heavy metal stress in addition to other abiotic stresses. In Brassica napus, expression of miRNAs shows different responses to sulfate deficiency and Cd exposure (Fig. 2) [90]. miR160 was transcriptionally downregulated by sulphate deficiency and by Cd exposure but miR164b and miR394a,b,c in roots and stems were upregulated by sulfate deficiency. Similarly, treatment with Cd induced expression of miR164b and miR394a,b,c in all tissues (Fig. 2), except that miR164b was downregulated in leaves [90]. miR156a and miR167b in roots and miR156a and miR167c in leaves were upregulated under sulfate deficiency. In contrast, miR167a and miR168 in roots and miR167a, miR167b, and miR168 in leaves were downregulated [90]. Under Cd stress, most B. napus miRNAs were induced. Notably, miR156a, miR167a, and miR167c in roots and miR167a and miR167c in leaves were strongly upregulated. miR393 expression in leaves was also upregulated by Cd exposure [90]. Xie et al. [92] reported that Cd exposure increased the expression of miR156, miR171, miR393, and miR396a in B. napus roots but the accumulation of the transcripts for these miRNAs was suppressed [92].
Huang et al. [88] constructed a library of small RNAs from rice seedlings that were exposed to toxic levels of Cd. In most cases, the rice miRNAs showed different patterns of expression in leaves and roots. miR601, miR602, and miR603 in roots were upregulated while miR602 and miR606 in leaves and miR604 in roots were downregulated by Cd exposure (Fig. 2). The rest of rice miRNAs, such as miR601 in leaves and miR605 and miR606 in roots, do not appear to be regulated by Cd stress [88]. Cd, mercury (Hg), and aluminum (Al) also regulated the expression of miRNAs in Medicago truncatula [89]. In that study, miR171, miR319, miR393, and miR529 were upregulated in response to Hg, Cd, and Al, and miR319 showed weak constitutive expression in leaves; it was upregulated by Cd and Al but was not affected by Hg. Similarly, expression of miR393 was not affected by Al but was slightly upregulated by Hg and Cd. In contrast, miR166 and miR398 were downregulated by Hg, Cd, and Al exposure [89].
Rice miR1432 and miR444d, which were identified by high throughput sequencing, are predicted to target a calmodulin-binding protein and an EF-hand protein, respectively, which suggests a role for these miRNAs in calcium signaling [93]. miRNAs also affect the growth of specific cells in roots under N-limiting conditions [94]. In the presence of N, miR167a was repressed (Fig. 2) and its target, ARF8, was induced in the pericycle, resulting in the initiation of many lateral roots. When N is limiting, lateral root extension is stimulated, and this permits roots to search for N in the soil further from the plant [94]. The Arabidopsis miR169 was strongly downregulated, whereas its targets, NFYA was strongly induced by nitrogen N starvation. Analysis of the expression of miR169 precursors showed that miR169a was substantially downregulated in both roots and shoots by N starvation. Accumulation of the NFYA family members was suppressed in transgenic Arabidopsis with constitutive expression of miR169a [95]. Several pri-miR169 species as well as pri-miR398a were found to be repressed during N limitation, whereas during P limitation, pri-miR778, pri-miR827, and pri-miR399 species were induced and pri-miR398a was repressed [96]. Bioinformatic analysis of small RNA sequences with a modified miRDeep algorithm led to the identification of the novel P limitation-induced miR2111, which is encoded by two loci in the Arabidopsis genome. Furthermore, miR2111, miR169, a miR827-like sequence, and the abundances of several miR star strands were found to be strongly dependent on P or N status in rapeseed (Brassica napus) phloem sap, flagging them as candidate systemic signals [96].
Expression of miRNAs also are affected by Fe deficiency, in Arabidopsis miR169b, miR169c, miR172c, miR172d, miR173 and miR394b in roots and miR169c, miR172c, miR172d, miR173, miR394a and miR394b in shoots was initially up-regulated and then down-regulated during the period of Fe deficiency. These results indicate that the cloned miRNAs respond to Fe deficiency [97].
2.1.2.7 miRNAs and mechanical stress
Plants experience mechanical stress, which is also referred to as static and dynamical stress when branches or stems are bent by wind, gravity, or other external forces. In a study of Populus trichocarpa, Pt-miRNA transcript levels were compared in tension-stressed or compression-stressed xylem with those in unstressed xylem [44]. miR156, miR162, miR164, miR475, miR480, and miR481 were downregulated but miR408 was upregulated by tension and compression (Fig. 2). miR160 and miR172 were downregulated only in compressed tissue while miR168 was upregulated only in tissue under tension stress. These results show that plant miRNAs can be regulated by mechanical stress and may function in one of the critical defense systems for structural and mechanical fitness [44].
2.1.2.8 miRNAs and biotic stress
In mammals, several examples of miRNA-mediated inhibition or enhancement of viral infection have been reported [98]. In plants, Arabidopsis miR393 was the first miRNA reported to play a role in plant antibacterial PTI (pattern triggered immunity) by regulating the auxin signaling pathway. miR393 was induced by a bacterial PAMP (pattern associated molecular pattern) peptide flg22 post-treatment [42]. Using small RNA-expression profiling on Arabidopsis leaves collected at 1 and 3 h post-inoculation (hpi) with Pst DC3000 hrcC, Fahlgren et al. [99] identified three miRNAs (miR160, miR167, andmiR393) that were highly induced and one that was downregulated (miR825) after infection (Fig. 2). The role of miRNAs in plant basal defense was further supported by the finding that Arabidopsis miRNA-deficient mutants dcl1 and hen1 showed enhanced growth of the bacterium Pst DC3000 hrcC and several bacteria strains that are non-pathogenic to Arabidopsis, including Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola, P. fluorescens, and E. coli [100]. Navarro et al. [100] showed that the induction of flg22-responsive pri-miR393 and pri-miR396 in Arabidopsis was suppressed by the virulent strain Pst DC3000 but not by the TTSS mutant strain Pst DC3000 hrcC. miR398 in Arabidopsis was downregulated by infection of with Pst (avrRpm1) and Pst (avrRpt2) but was unaffected by Pst DC3000 infiltration [101]. Also in Arabidopsis, miR156 and miR164 were induced by infection with the virus TYMV p69 and were induced in transgenic Arabidopsis plants expressing the viral silencing suppressor P1/HC-Pro [102]. In tobacco, miR156, miR160, and miR164 were induced after virus infection [100]. Upon virus infection, new miRNAs (miR158 and miR1885) were identified in Brassica; miR158 and miR1885 were specifically induced by turnip mosaic virus but not by cucumber mosaic virus or tobacco mosaic virus [104].
Various miRNA families were differentially expressed in response to infection by the rust fungus Cronartium quercuum f. sp. fusiforme, which causes fusiform rust disease in pines; 10 of 11 miRNA families were downregulated, including seven that were pine specific [102]. For example, miR156 and miR160 were repressed in pine stems infected with the rust fungus (Fig. 2) [105]. More recent data indicate that miRNAs may affect the response of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to powdery mildew infection; some of the conserved miRNAs showed differential expression patterns in response to powdery mildew infection: miR156, miR159, miR164, miR171, and miR396, were downregulated and miR393, miR444, and miR827, were upregulated, respectively[65]. In addition, a negative correlation between miRNA abundance and their targets was observed in roots infected by the plant-parasitic nematode Heterodera schachtii, which confirmed that miRNAs are involved in plant–nematode interactions [103]. In response to H. schachtii infection, miR161, miR164, miR167a, miR172c, miR396a,b, and miR398a were downregulated (Fig. 2). Expression of miR156 and miR160 was substantially repressed in the galled stem (Fig. 2).
miRNAs also play critical and diverse roles in symbiotic N fixation. To identify potential regulators early in nodule development, Subramanian et al. [107] inoculated soybean (Glycine max) roots with Bradyrhizobium japonicum and identified differentially expressed miRNAs. For example, miR168 and miR172 were upregulated at 1 or 3 hpi but returned to basal levels by 12 hpi; miR159 and miR393 were upregulated by 3 hpi and continued to maintain these levels to 12 hpi; miR160 and miR169 were downregulated in response to rhizobia. Also, rhizobial infection changed the levels of miR160, miR393, miR164, and miR168, which target ARFs (ARF10, ARF16, and ARF17), TIR1, NAC1, and AGO1, respectively (Fig. 2). Li et al. [108] examined the gene expression levels of six families of novel miRNAs and investigated their functions in nodule development in soybean. The results suggested that miR482, miR1512, and miR1515 might have specific and important functions during soybean nodulation [108]. Cloning and sequencing of miRNAs from functional nodules of soybean revealed conserved miRNAs (miR167, miR172, miR396, and miR399), whereas four other families had sequences homologous to Gm-miR1507, Gm-miR1508, Gm-miR1509, and Gm-miR1510, which play a role in N fixation [109]. In Medicago truncatula, the functions during nodulation have been studied for two conserved miRNAs; miR169 regulated MtHAP2-1, which altered nodule development [110], while overexpression of miR166 reduced the number of symbiotic nodules and lateral roots [111].
2.2 siRNAs
2.2.1 Biogenesis of siRNAs
siRNAs are generated from perfectly double-stranded RNAs that can originate from different sources such as RNAs transcribed from inverted repeats, natural cis-antisense transcript pairs, the action of RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RDRs) which convert single-stranded RNA into dsRNA, the replication of RNA viruses, and regions of the genome rich in retroelements (Fig. 1B). The dsRNA is cleaved into 21- to 24-nt siRNAs by DCLs proteins, and the size of the released siRNAs depends on the specific catalytic activity of the respective DCL protein. dsRNA is usually cleaved by multiple DCL proteins, thereby generating siRNA classes with different sizes. Like miRNAs, siRNAs are loaded into AGO protein-containing RISC that guides target regulation at the posttranscriptional level or at the transcriptional level through a pathway termed RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) (Fig. 1B).
2.2.2 Role of siRNAs in plant stress responses
2.2.2.1 siRNAs and abiotic stress
The first evidence that siRNAs are involved in abiotic stress responses in plants was provided by Sunkar and Zhu [16]. Work on the founding member of nat-siRNAs, which is derived from a natural cis-antisense transcript pairs of SRO5 and P5CDH genes, demonstrated an important role of nat-siRNAs in osmoprotection and oxidative stress management under salt stress in Arabidopsis [112]. P5CDH is constitutively expressed, whereas SRO5 is induced by salt stress. Under high salt stress, the 24-nt nat-siRNA corresponding to the SRO5 mRNA is produced; this nat-siRNA targets the P5CDH mRNA for degradation and leads to the production of a population of 21-nt nat-siRNAs. Downregulation of P5CDH leads to proline accumulation, which is an important step contributing to the plant’s ability to tolerate excess salt [112]. However, reduced P5CDH activity also leads to the accumulation of P5C (a toxic metabolic intermediate) and ROS; that accumulation is probably countered by the SRO5 protein through direct detoxification activity in the mitochondria [112]. The initial induction of SRO5 mRNA by salt stress may be mediated by oxidative stress that is an inevitable consequence of salt stress. Thus, the SRO5-P5CDH nat-siRNAs together with the P5CDH and SRO5 proteins are key components of a regulatory loop controlling ROS production and salt stress response [112].
Abiotic stress responsiveness has also been observed in a pool of Triticum aestivum small noncoding RNAs [113]. In wheat seedlings, cold, heat, salt, or drought stresses substantially change the expression of four siRNAs: siRNA002061_0636_3054.1 is strongly downregulated by heat, salt, and drought; siRNA 005047_0654_1904.1 is greatly upregulated by cold stress and downregulated by heat, salt, and drought; siRNA080621_1340_0098.1 is slightly upregulated by cold and downregulated by heat but not by salt and drought; and siRNA007927_0100_2975.1 is downregulated by cold, salt, and drought but not by heat stress [113].
TasiRNAs are a specialized class of siRNAs that are generated by miRNA processing of a TAS gene transcript, resulting in the production of 21-nt RNAs that are phased with respect to the miRNA cleavage site. Four families of TAS genes have been identified in Arabidopsis, with TAS1 and TAS2 transcripts recognized by miR173, TAS3 recognized by miR390, and TAS4 targeted by miR828 [114]. TAS1, TAS2, and TAS3 tasiRNAs all showed increased expression in hypoxia-treated samples in Arabidopsis [68]. These changes in tasiRNA levels are reflected in the changes to TAS-targeting miRNAs; both miR173 and miR390 showed increased expression [68]. Most pentatricopeptide (PPR) repeat-containing proteins (PPRs) targeted by hypoxia-responsive small RNAs are from the P subfamily, which is predicted to localize to the mitochondria [68]. It is likely that some of the observed changes in tasiRNAs are the result of decreased mitochondrial function during hypoxia because TAS1 is induced by chemical inhibition of the cytochrome and alternative oxidase respiration pathways in the mitochondria. The downregulation of these PPR genes may either protect mitochondria during hypoxia or simply reflect a decreased requirement for these gene transcripts.
Stress responses in plants also involve novel long non-protein coding RNAs (npcRNA). In Arabidopsis, salt stress resulted in a dramatic increase in npcRNA60 and npcRNA536 and a decrease in npcRNA72 and npcRNA82 accumulation [115]. In the same study, phosphate deprivation caused substantial upregulation of npcRNA43 and npcRNA536, substantial downregulation of npcRNA33, slight upregulation of npcRNA60, and slight downregulation of npcRNA311 [115]. In Craterostigma plantagineum, an endogenous siRNA has been identified that is induced during dehydration and that may contribute to desiccation tolerance [116]. The authors describe the T-DNA tagging of a Craterostigma gene that induces desiccation tolerance by activating ABA-inducible genes. Activation tagging was used to identify constitutively desiccation tolerant (CDT) callus lines, and this led to the identification of CDT-1 (constitutively desiccation tolerant-1) callus lines. In wild-type C. plantagineum, the transcript levels of CDT-1 were upregulated by ABA and dehydration treatments but repressed when rehydrated. Interestingly, sense and antisense siRNAs corresponding to the CDT-1 locus were detected, suggesting that during stress (ABA or dehydration) the locus generates small RNAs that may confer stress tolerance through induction of stress-responsive genes [116].
2.2.2.2 siRNAs and biotic stress
The first plant-endogenous siRNA that was found to be involved in plant biotic stress was nat-siRNAATGB2, which regulates R-gene mediated ETI (effector triggered immunity) [18]. This siRNA is specifically induced by Pst DC3000 carrying effector avrRpt2 (Fig. 2). Induction of nat-siRNAATGB2 represses the expression of its antisense target PPRL, a negative regulator of RPS2-mediated ETI against Pst (avrRpt2). A novel class of endogenous siRNA, the lsiRNAs, are 30–40 nt long and are induced by bacterial infection or specific growth conditions, such as cell suspension culture [17]. AtlsiRNA1 is strongly induced by Pst (avrRpt2), whereas AtlsiRNA2, AtlsiRNA3, and AtlsiRNA4 are moderately induced by infection with various Pst strains and/or mock treatment. siRNAs also differentially accumulate in response to H. schachtii infection; infection by this nematode caused a substantial increase in expression of siRNA9, siRNA41, and siRNA46 but a decrease in expression of siRNA32 (Fig. 2) [106].
3 Stress-miRNA networks
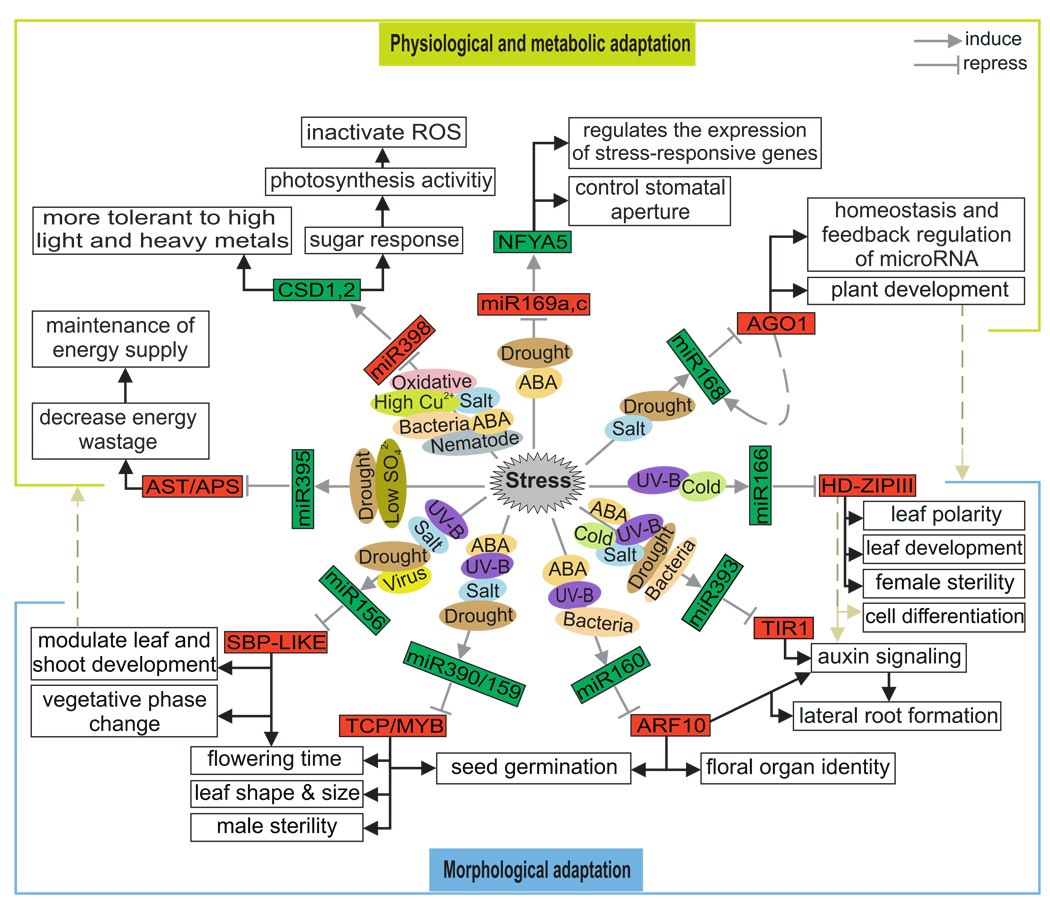
The spectrum of action by miRNAs seems to be extremely wide and includes various aspects of development, adaptive responses to stresses, and the regulation of the miRNA pathway itself. Most miRNAs do not function independently but rather are involved in overlapping regulatory networks (Table 1). One obvious feature of the adaptation to stress is change in gene expression profiles for genes involved in a broad spectrum of biochemical, cellular, and physiological processes [117]. Under optimal conditions, all resources are used for supporting plant growth and development. Under stress, however, growth and development are stalled, and the resources are mobilized toward adaptive responses to stress. Most conserved miRNAs target mRNAs encoding diverse families of transcription factors. For example, miR156, miR159/319, miR160, miR166, and miR169 target SBPs, MYBs/TCPs, ARFs, HD-ZIPs, and the NFY subunit, respectively, but miR168, miR393, miR395, and miR398 target mRNAs encoding AGO1, TIR1, ATS/APS, and CSD1/2, respectively [9, 21]. The level of those conserved miRNAs appears to be regulated during stress, and their target genes appear to be stress regulated as well (Fig. 3), suggesting that plant growth and development are modulated during stress.
Fig. 3.
Regulatory network of stress-responsive miRNAs in Arabidopsis. A network is proposed that describes the molecular mechanisms underlying the response of Arabidopsis plants to different biotic and abiotic stresses. The network is based on the changes in expression profiles of miRNA and subsequent target transcripts in plants under stress. Green boxes: up-regulated RNAs; red boxes: down-regulated RNAs.
The stress-responsive miRNAs could be involved in many pathways that reprogram complex processes of metabolism and physiology. For example, upregulation of miR395 is involved in sulfur metabolism (Fig. 3); miR395 targets ATP sulfurylases (APS1, APS3, and APS4), which catalyze the first step of the sulfur assimilation pathway [118]. miR395 also targets AST68, a low-affinity sulfate transporter [114]. AST68 is implicated in the internal translocation of sulfate from roots to shoots [119]. Thus, miR395 potentially coordinates changes in sulfate translocation and assimilation. In addition, downregulation of miR398 during stress enables the mRNA levels of both targets (CSD1 and CSD2) to increase and detoxify ROS (Fig. 3). miR398 also targets the gene cytochrome C oxidase subunit V [15, 16]; further studies are required to determine whether this gene is also part of the oxidative stress network in plants. Downregulation of miR169a and miR169c allows expression of the mRNA of NFYA5, which is important for drought responses in Arabidopsis [52]. Researchers have hypothesized that NFYA5 expressed in guard cells controls stomatal aperture, whereas NFYA5 expressed in other cells may contribute to the expression of stress-associated genes (Fig. 3). Because AGO1 is a key miRNA pathway regulator, the difference in AGO1 mRNA expression under salt and drought stress may induce further changes of numerous miRNA activities (Fig. 3). In addition, AGO1 and miR168 seem to be transcriptionally coregulated, allowing AGO1/miR168 homeostasis to be maintained in every cell where the miRNA pathway is functioning [120]. Data also indicate that AGO1 is required for stem cell function and organ polarity [120].
The accumulation of miR166 and miR160 together with miR393 could modulate morphological and hormone homeostasis by regulating transcripts of HD-ZIPIII, ARF10, and TIR1 (Fig. 3). HD-ZIPIII was found to regulate the pattern of vasculature and the establishment and maintenance of abaxial-adaxial polarity in lateral organs [121]. ARFs regulate the expression of auxin-inducible genes, such as GH3 and auxin/indole-3-acetic acid (Aux/IAA), by binding auxin-responsive promoters (ARPs) [122, 123]. In related studies, increased or decreased levels of ARF10 altered GH3-like gene expression and led to severe developmental defects, miR160-resistant ARF plants were found to have dramatic developmental abnormalities, and ARF10 was found to regulate floral organ identity and to be involved in seed germination [50, 122, 123]. The auxin receptor TIR1 is an important SCF E3 ubiquitin ligase that functions in degrading Aux/IAA proteins in response to auxin [121] and then triggers adventitious root formation and lateral root development. miR393-mediated inhibition of TIR1 would downregulate auxin signaling and seedling growth under biotic- and abiotic-stress conditions. Also, the upregulation of miR156 and miR319/159 could help the plant adapt to stress by modulating plant morphological characteristics via regulation of transcripts of SBPs and MYBs/TCPs transcription factors (Fig. 3). SBP-LIKE is involved in floral transition and regulation of flowering [125, 126]. Recent results indicate that overexpression of miR156 affects phase transition from vegetative growth to reproductive growth by causing a rapid initiation of rosette leaves, a severe decrease in apical dominance, and a moderate delay in flowering [125–127]. TCP transcription factors direct the developmental processes determining leaf size, leaf form, and flower symmetry [127, 128]. Overexpression of miR319, which specifically downregulates TCP mRNAs, results in uneven leaf shape and delayed flowering [128]. Overexpression of miR159a specifically reduces MYB mRNA accumulation and results in male sterility, whereas plants that express miR159-resistant MYB33 have upwardly curled leaves, reduced stature, and shortened petioles [128, 129]. Reyes and Chua [49] demonstrated how ABA induces the accumulation of miR159 in association with the seed-specific transcription factor ABI3. In turn, miR159 mediates cleavage of MYB101 and MYB33 transcripts, which encode positive regulators of ABA responses.
4 Conclusions and outlook
A complete understanding of the actions of small RNAs depends on the identification of the target genes. Identification of entire sets of miRNAs and siRNAs and their targets will lay the foundation that is needed to unravel the complex miRNA- and siRNA-mediated regulatory networks controlling development and other physiological processes. Given that miRNAs and siRNAs are crucial components of in gene regulatory networks, we believe that a complete understanding of the functions of miRNAs and siRNAs will greatly increase our understanding of plant tolerance to biotic and abiotic stresses.
Analysis of the DNA methylation profiles and the small RNA profiles will identify genes or regions that are regulated by miRNA/siRNA-mediated DNA methylation, which may contribute to epigenetic inheritance of stress effects. Also, the artificial microRNA (amiRNA)-mediated approach should have broad applicability for engineering multiple stress-responsive genes in crop plants.
Research Highlights.
Small RNAs are important regulators of gene expression in plants and animals.
Plant small RNAs play a role in biotic and abiotic stress responses.
The expression of many miRNAs is responsive to various stresses.
Stress-responsive small RNAs are crucial components in gene regulatory networks.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by USDA and NIH grants to J.-K. Zhu and by National Science Foundation grants IOS0919745 and MCB0950242 to J. Zhu.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Baulcombe D. RNA silencing in plants. Nature. 2004;431:356–363. doi: 10.1038/nature02874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–854. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90529-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.de Carvalho F, Gheysen G, Kushnir S, Van Montagu M, Inze D, Castresana C. Suppression of beta-1,3-glucanase transgene expression in homozygous plants. EMBO J. 1992;11:2595–2602. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hannon GJ. RNA interference. Nature. 2002;418:244–251. doi: 10.1038/418244a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Napoli C, Lemieux C, Jorgensen R. Introduction of a Chimeric Chalcone Synthase Gene into Petunia Results in Reversible Co-Suppression of Homologous Genes in trans. Plant Cell. 1990;2:279–289. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.4.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Romano N, Macino G. Quelling: transient inactivation of gene expression in Neurospora crassa by transformation with homologous sequences. Mol. Microbiol. 1992;6:3343–3353. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hamilton AJ, Baulcombe DC. A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science. 1999;286:950–952. doi: 10.1126/science.286.5441.950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Axtell MJ, Bowman JL. Evolution of plant microRNAs and their targets. Trends Plant Sci. 2008;13:343–349. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2008.03.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Bartel B. MicroRNAS and their regulatory roles in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006;57:19–53. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Seki M, Narusaka M, Ishida J, Nanjo T, Fujita M, Oono Y, Kamiya A, Nakajima M, Enju A, Sakurai T. Monitoring the expression profiles of 7000 Arabidopsis genes under drought, cold and high-salinity stresses using a full-length cDNA microarray. Plant J. 2002;31:279–292. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhu J-K. Salt and Drought Stress Signal Transduction in Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2002;53:247–273. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.53.091401.143329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ruiz-Ferrer V, Voinnet O. Roles of Plant Small RNAs in Biotic Stress Responses. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009;60:485–510. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.043008.092111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shukla LI, Chinnusamy V, Sunkar R. The role of microRNAs and other endogenous small RNAs in plant stress responses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2008;1779:743–748. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sunkar R, Chinnusamy V, Zhu JH, Zhu JK. Small RNAs as big players in plant abiotic stress responses and nutrient deprivation. Trends Plant Sci. 2007;12:301–309. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2007.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP. Computational Identification of Plant MicroRNAs Their Targets, Including a Stress-Induced miRNA. Mol. cell. 2004;14:787–799. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.05.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sunkar R, Zhu JK. Novel and stress-regulated microRNAs and other small RNAs from Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2004;16:2001–2019. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.022830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Katiyar-Agarwal S, Gao S, Vivian-Smith A, Jin H. A novel class of bacteria-induced small RNAs in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 2007;21:3123–3134. doi: 10.1101/gad.1595107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Katiyar-Agarwal S, Morgan R, Dahlbeck D, Borsani O, Villegas A, Zhu J-K, Staskawicz BJ, Jin H. A pathogen-inducible endogenous siRNA in plant immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2006;103:18002–18007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608258103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sunkar R, Kapoor A, Zhu JK. Posttranscriptional induction of two Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase genes in Arabidopsis is mediated by downregulation of miR398 and important for oxidative stress tolerance. Plant Cell. 2006;18:2051–2065. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.041673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chapman EJ, Carrington JC. Specialization and evolution of endogenous small RNA pathways. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007;8:884–896. doi: 10.1038/nrg2179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chen X. Small RNAs and Their Roles in Plant Development. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2009;25:21–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.042308.113417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Vazquez F, Legrand S, Windels D. The biosynthetic pathways and biological scopes of plant small RNAs. Trends Plant Sci. 2010;15:337–345. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2010.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature. 2001;409:363–366. doi: 10.1038/35053110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yang Z, Ebright YW, Yu B, Chen X. HEN1 recognizes 21–24 nt small RNA duplexes and deposits a methyl group onto the 2' OH of the 3' terminal nucleotide. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:667–675. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hutvagner G, Simard MJ. Argonaute proteins: key players in RNA silencing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008;9:22–32. doi: 10.1038/nrm2321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Voinnet O, Origin biogenesis. and activity of plant microRNAs. Cell. 2009;136:669–687. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Baumberger N, Baulcombe DC. Arabidopsis ARGONAUTE1 is an RNA Slicer that selectively recruits microRNAs and short interfering RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2005;102:11928–11933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0505461102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lanet E, Delannoy E, Sormani R, Floris M, Brodersen P, Crete P, Voinnet O, Robaglia C. Biochemical evidence for translational repression by Arabidopsis microRNAs. Plant Cell. 2009;21:1762–1768. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.063412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Khraiwesh B, Arif MA, Seumel GI, Ossowski S, Weigel D, Reski R, Frank W. Transcriptional control of gene expression by microRNAs. Cell. 2010;140:111–122. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.12.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Schramke V, Allshire R. Those interfering little RNAs! Silencing and eliminating chromatin. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2004;14:174–180. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2004.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lee Y, Kim M, Han J, Yeom KH, Lee S, Baek SH, Kim VN. MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. EMBO J. 2004;23:4051–4060. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kim VN. MicroRNA precursors in motion: exportin-5 mediates their nuclear export. Trends Cell Biol. 2004;14:156–159. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2004.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Park MY, Wu G, Gonzalez-Sulser A, Vaucheret H, Poethig RS. Nuclear processing and export of microRNAs in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2005;102:3691–3696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405570102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bao N, Lye KW, Barton MK. MicroRNA binding sites in Arabidopsis class III HD-ZIP mRNAs are required for methylation of the template chromosome. Dev. Cell. 2004;7:653–662. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2004.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wu L, Zhou H, Zhang Q, Zhang J, Ni F, Liu C, Qi Y. DNA methylation mediated by a microRNA pathway. Mol. Cell. 2010;38:465–475. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.03.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Fujii H, Chiou T-J, Lin S-I, Aung K, Zhu J-K. A miRNA Involved in Phosphate-Starvation Response in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2005;15:2038–2043. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.10.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Liu H-H, Tian X, Li Y-J, Wu C-A, Zheng C-C. Microarray-based analysis of stress-regulated microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. RNA. 2008;14:836–843. doi: 10.1261/rna.895308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zhao B, Liang R, Ge L, Li W, Xiao H, Lin H, Ruan K, Jin Y. Identification of drought-induced microRNAs in rice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007;354:585–590. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zhou L, Liu Y, Liu Z, Kong D, Duan M, Luo L. Genome-wide identification and analysis of drought-responsive microRNAs in Oryza sativa. J. Exp. Bot. 2010;61:4157–4168. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zhou X, Wang G, Sutoh K, Zhu J-K, Zhang W. Identification of cold-inducible microRNAs in plants by transcriptome analysis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2008;1779:780–788. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sunkar R, Zhou X, Zheng Y, Zhang W, Zhu J-K. Identification of novel and candidate miRNAs in rice by high throughput sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 2008;8:25. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-8-25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Navarro L, Dunoyer P, Jay F, Arnold B, Dharmasiri N, Estelle M, Voinnet O, Jones JD. A plant miRNA contributes to antibacterial resistance by repressing auxin signaling. Science. 2006;312:436–439. doi: 10.1126/science.1126088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhou X, Wang G, Zhang W. UV-B responsive microRNA genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2007;3:103. doi: 10.1038/msb4100143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lu SF, Sun YH, Shi R, Clark C, Li LG, Chiang VL. Novel and mechanical stress-responsive microRNAs in Populus trichocarpa that are absent from Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2005;17:2186–2203. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.033456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Katiyar-Agarwal S, Jin H. Role of Small RNAs in Host-Microbe Interactions. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2010;48:225–246. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-073009-114457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Mishra AK, Agarwal S, Jain CK, Rani V. High GC content: critical parameter for predicting stress regulated miRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Bioinformation. 2009;4:151–154. doi: 10.6026/97320630004151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lu C, Fedoroff N. A Mutation in the Arabidopsis HYL1 Gene Encoding a dsRNA Binding Protein Affects Responses to Abscisic Acid, Auxin, and Cytokinin. Plant Cell. 2000;12:2351–2366. doi: 10.1105/tpc.12.12.2351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Achard P, Herr A, Baulcombe DC, Harberd NP. Modulation of floral development by a gibberellin-regulated microRNA. Development. 2004;131:3357–3365. doi: 10.1242/dev.01206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Reyes JL, Chua NH. ABA induction of miR159 controls transcript levels of two MYB factors during Arabidopsis seed germination. Plant J. 2007;49:592–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Liu PP, Montgomery TA, Fahlgren N, Kasschau KD, Nonogaki H, Carrington JC. Repression of AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR10 by microRNA160 is critical for seed germination and post-germination stages. Plant J. 2007;52:133–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Jung HJ, Kang H. Expression and functional analyses of microRNA417 in Arabidopsis thaliana under stress conditions. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2007;45:805–811. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2007.07.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Li W-X, Oono Y, Zhu J, He X-J, Wu J-M, Iida K, Lu X-Y, Cui X, Jin H, Zhu J-K. The Arabidopsis NFYA5 Transcription Factor Is Regulated Transcriptionally and Posttranscriptionally to Promote Drought Resistance. Plant Cell. 2008;20:2238–2251. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.059444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Jia X, Wang W-X, Ren L, Chen Q-J, Mendu V, Willcut B, Dinkins R, Tang X, Tang G. Differential and dynamic regulation of miR398 in response to ABA and salt stress in Populus tremula and Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009;71:51–59. doi: 10.1007/s11103-009-9508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Liu Q, Zhang Y-C, Wang C-Y, Luo Y-C, Huang Q-J, Chen S-Y, Zhou H, Qu L-H, Chen Y-Q. Expression analysis of phytohormone-regulated microRNAs in rice, implying their regulation roles in plant hormone signaling. FEBS Lett. 2009;583:723–728. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Arenas-Huertero C, Pérez B, Rabanal F, Blanco-Melo D, De la Rosa C, Estrada-Navarrete G, Sanchez F, Covarrubias A, Reyes J. Conserved and novel miRNAs in the legume Phaseolus vulgaris in response to stress. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009;70:385–401. doi: 10.1007/s11103-009-9480-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lu SF, Sun YH, Chiang VL. Stress-responsive microRNAs in Populus. Plant J. 2008;55:131–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Trindade I, Capitão C, Dalmay T, Fevereiro M, Santos D. miR398 and miR408 are up-regulated in response to water deficit in Medicago truncatula. Planta. 2010;231:705–716. doi: 10.1007/s00425-009-1078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kantar M, Lucas S, Budak H. miRNA expression patterns of Triticum dicoccoides in response to shock drought stress. Planta. 2010 doi: 10.1007/s00425-010-1309-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Wei L, Zhang D, Xiang F, Zhang Z. Differentially Expressed miRNAs Potentially Involved in the Regulation of Defense Mechanism to Drought Stress in Maize Seedlings. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2009;170:979–989. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Munns R, Tester M. Mechanisms of Salinity Tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008;59:651–681. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Zhou X, Sunkar R, Jin H, Zhu JK, Zhang W. Genome-wide identification and analysis of small RNAs originated from natural antisense transcripts in Oryza sativa. Genome Res. 2009;19:70–78. doi: 10.1101/gr.084806.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Stephenson T, McIntyre C, Collet C, Xue G-P. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the NF-Y family of transcription factors in Triticum aestivum. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007;65:77–92. doi: 10.1007/s11103-007-9200-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Ding D, Zhang L, Wang H, Liu Z, Zhang Z, Zheng Y. Differential expression of miRNAs in response to salt stress in maize roots. Ann. Bot. 2009;103:29–38. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcn205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Zhang J, Xu Y, Huan Q, Chong K. Deep sequencing of Brachypodium small RNAs at the global genome level identifies microRNAs involved in cold stress response. BMC Genomics. 2009;10:449. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Xin M, Wang Y, Yao Y, Xie C, Peng H, Ni Z, Sun Q. Diverse set of microRNAs are responsive to powdery mildew infection and heat stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) BMC Plant Biol. 2010;10:123. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Agarwal S, Grover A, Molecular Biology. Biotechnology and Genomics of Flooding-Associated Low O2 Stress Response in Plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2006;25:1–21. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Bailey-Serres J, Voesenek LACJ. Flooding Stress: Acclimations and Genetic Diversity. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008;59:313–339. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Moldovan D, Spriggs A, Yang J, Pogson BJ, Dennis ES, Wilson IW. Hypoxia-responsive microRNAs and trans-acting small interfering RNAs in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2009;61:165–177. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erp296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Zhang Z, Wei L, Zou X, Tao Y, Liu Z, Zheng Y. Submergence-responsive MicroRNAs are Potentially Involved in the Regulation of Morphological and Metabolic Adaptations in Maize Root Cells. Ann. Bot. 2008;102:509–519. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcn129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Van Breusegem F. Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2004;9:490–498. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2004.08.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Bonnet E, Wuyts J, Rouze P, Van de PY. Detection of 91 potential conserved plant microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa identifies important target genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2004;101:11511–11516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0404025101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Yamasaki H, Abdel-Ghany SE, Cohu CM, Kobayashi Y, Shikanai T, Pilon M. Regulation of copper homeostasis by microRNA in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:16369–16378. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M700138200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Li T, Li H, Zhang Y-X, Liu J-Y. Identification and analysis of seven H2O2-responsive miRNAs and 32 new miRNAs in the seedlings of rice (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica) Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Jia X, Ren L, Chen Q-J, Li R, Tang G. UV-B-responsive microRNAs in Populus tremula. J. Plant Physiol. 2009;166:2046–2057. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2009.06.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Aung K, Lin SI, Wu CC, Huang YT, Su CL, Chiou TJ. pho2, a phosphate overaccumulator, is caused by a nonsense mutation in a microRNA399 target gene. Plant Physiol. 2006;141:1000–1011. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.078063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Bari R, Datt Pant B, Stitt M, Scheible W-R, PHO2 MicroRNA399. and PHR1 Define a Phosphate-Signaling Pathway in Plants. Plant Physiol. 2006;141:988–999. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.079707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Chiou T, Aung K, Lin S, Wu C, Chiang S, Su C. Regulation of phosphate homeostasis by microRNA in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2006;18:412–421. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.038943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Chiou T-J. The role of microRNAs in sensing nutrient stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2007;30:323–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Franco-Zorrilla JM, González E, Bustos R, Linhares F, Leyva A, Paz-Ares J. The transcriptional control of plant responses to phosphate limitation. J. Exp. Bot. 2004;55:285–293. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erh009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Rubio V, Linhares F, Solano R, Martin AC, Iglesias J, Leyva A, Paz-Ares J. A conserved MYB transcription factor involved in phosphate starvation signaling both in vascular plants and in unicellular algae. Genes Dev. 2001;15:2122–2133. doi: 10.1101/gad.204401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Buhtz A, Pieritz J, Springer F, Kehr J. Phloem small RNAs, nutrient stress responses, and systemic mobility. BMC Plant Biol. 2010;10:64. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Pant BD, Buhtz A, Kehr J, Scheible WR. MicroRNA399 is a long-distance signal for the regulation of plant phosphate homeostasis. Plant J. 2008;53:731–738. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Franco-Zorrilla JM, Valli A, Todesco M, Mateos I, Puga MI, Rubio-Somoza I, Leyva A, Weigel D, Garcia JA, Paz-Ares J. Target mimicry provides a new mechanism for regulation of microRNA activity. Nat. Genet. 2007;39:1033–1037. doi: 10.1038/ng2079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Buhtz A, Springer F, Chappell L, Baulcombe DC, Kehr J. Identification and characterization of small RNAs from the phloem of Brassica napus. Plant J. 2008;53:739–749. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03368.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Marschner H. Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. second ed. London: Academic Press; 1995. [Google Scholar]
- 86.Abdel-Ghany SE, Pilon M. MicroRNA-mediated systemic down-regulation of copper protein expression in response to low copper availability in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. chem. 2008;283:15932–15945. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801406200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Quinn JM, Merchant S. Two Copper-Responsive Elements Associated with the Chlamydomonas Cyc6 Gene Function as Targets for Transcriptional Activators. Plant Cell. 1995;7:623–638. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.5.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Huang SQ, Peng J, Qiu CX, Yang ZM. Heavy metal-regulated new microRNAs from rice. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2009;103:282–287. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2008.10.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Zhou ZS, Huang SQ, Yang ZM. Bioinformatic identification and expression analysis of new microRNAs from Medicago truncatula. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008;374:538–542. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.07.083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Huang SQ, Xiang AL, Che LL, Chen S, Li H, Song JB, Yang ZM. A set of miRNAs from Brassica napus in response to sulphate deficiency and cadmium stress. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2010;8:887–899. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2010.00517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Ding Y-F, Zhu C. The role of microRNAs in copper and cadmium homeostasis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009;386:6–10. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.05.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Xie FL, Huang SQ, Guo K, Xiang AL, Zhu YY, Nie L, Yang ZM. Computational identification of novel microRNAs and targets in Brassica napus. FEBS Lett. 2007;581:1464–1474. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.02.074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Sunkar R, Girke T, Jain PK, Zhu JK. Cloning and characterization of microRNAs from rice. Plant Cell. 2005;17:1397–1411. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.031682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Gifford ML, Dean A, Gutierrez RA, Coruzzi GM, Birnbaum KD. Cell-specific nitrogen responses mediate developmental plasticity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2008;105:803–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709559105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Zhao M, Ding H, Zhu J-K, Zhang F, Li W-X. Involvement of miR169 in the nitrogen-starvation responses in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2011 doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03647.x. no-no. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Pant BD, Musialak-Lange M, Nuc P, May P, Buhtz A, Kehr J, Walther D, Scheible WRd. Identification of Nutrient-Responsive Arabidopsis and Rapeseed MicroRNAs by Comprehensive Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Profiling and Small RNA Sequencing. Plant Physiol. 2009;150:1541–1555. doi: 10.1104/pp.109.139139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Kong WW, Yang ZM. Identification of iron-deficiency responsive microRNA genes and cis-elements in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010;48:153–159. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2009.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Lecellier C-H, Dunoyer P, Arar K, Lehmann-Che J, Eyquem S, Himber C, Saib A, Voinnet O. A Cellular MicroRNA Mediates Antiviral Defense in Human Cells. Science. 2005;308:557–560. doi: 10.1126/science.1108784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Fahlgren N, Howell MD, Kasschau KD, Chapman EJ, Sullivan CM, Cumbie JS, Givan SA, Law TF, Grant SR, Dangl JL, Carrington JC. High-throughput sequencing of Arabidopsis microRNAs: evidence for frequent birth and death of MIRNA genes. PLoS ONE. 2007;2:e219. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Navarro L, Jay F, Nomura K, He SY, Voinnet O. Suppression of the MicroRNA Pathway by Bacterial Effector Proteins. Science. 2008;321:964–967. doi: 10.1126/science.1159505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Jagadeeswaran G, Saini A, Sunkar R. Biotic and abiotic stress down-regulate miR398 expression in Arabidopsis. Planta. 2009;229:1009–1014. doi: 10.1007/s00425-009-0889-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Kasschau KD, Xie Z, Allen E, Llave C, Chapman EJ, Krizan KA, Carrington JC. P1/HC-Pro, a viral suppressor of RNA silencing, interferes with Arabidopsis development and miRNA unction. Dev. Cell. 2003;4:205–217. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(03)00025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Bazzini AA, Hopp HE, Beachy RN, Asurmendi S. Infection coaccumulation of tobacco mosaic virus proteins alter microRNA levels, correlating with symptom and plant development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007;104:12157–12162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705114104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.He X-F, Fang Y-Y, Feng L, Guo H-S. Characterization of conserved novel microRNAs and their targets, including a TuMV-induced TIR-NBS-LRR class R gene-derived novel miRNA in Brassica. FEBS Lett. 2008;582:2445–2452. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2008.06.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Lu S, Sun Y-H, Amerson H, Chiang VL. MicroRNAs in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) and their association with fusiform rust gall development. Plant J. 2007;51:1077–1098. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Hewezi T, Howe P, Maier TR, Baum TJ. Arabidopsis Small RNAs and Their Targets During Cyst Nematode Parasitism. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2008;21:1622–1634. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-21-12-1622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Subramanian S, Fu Y, Sunkar R, Barbazuk WB, Zhu JK, Yu O. Novel and nodulation-regulated microRNAs in soybean roots. BMC Genomics. 2008;9:160. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Li H, Deng Y, Wu T, Subramanian S, Yu O. Mis-expression of miR482, miR1512, and miR1515 Increases Soybean Nodulation. Plant Physiol. 2010;153:1759–1770. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.156950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Wang Y, Li P, Cao X, Wang X, Zhang A, Li X. Identification and expression analysis of miRNAs from nitrogen-fixing soybean nodules. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009;378:799–803. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.11.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Combier J-P, Frugier F, de Billy F, Boualem A, El-Yahyaoui F, Moreau S, Vernié T, Ott T, Gamas P, Crespi M, Niebel A. MtHAP2-1 is a key transcriptional regulator of symbiotic nodule development regulated by microRNA169 in Medicago truncatula. Genes Dev. 2006;20:3084–3088. doi: 10.1101/gad.402806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Boualem A, Laporte P, Jovanovic M, Laffont C, Plet J, Combier J-P, Niebel A, Crespi M, Frugier F. MicroRNA166 controls root and nodule development in Medicago truncatula. Plant J. 2008;54:876–887. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Borsani O, Zhu J, Verslues PE, Sunkar R, Zhu JK. Endogenous siRNAs derived from a pair of natural cis-antisense transcripts regulate salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Cell. 2005;123:1279–1291. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.11.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Yao Y, Ni Z, Peng H, Sun F, Xin M, Sunkar R, Zhu JK, Sun Q. Non-coding small RNAs responsive to abiotic stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Funct. Integr. Genomics. 2010;10:187–190. doi: 10.1007/s10142-010-0163-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Allen E, Xie Z, Gustafson AM, Carrington JC. microRNA-directed phasing during trans-acting siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell. 2005;121:207–221. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Ben Amor B, Wirth S, Merchan F, Laporte P, d’Aubenton-Carafa Y, Hirsch J, Maizel A, Mallory A, Lucas A, Deragon JM, Vaucheret H, Thermes C, Crespi M. Novel long non-protein coding RNAs involved in Arabidopsis differentiation and stress responses. Genome Res. 2009;19:57–69. doi: 10.1101/gr.080275.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Furini A, Koncz C, Salamini F, Bartels D. High level transcription of a member of a repeated gene family confers dehydration tolerance to callus tissue of Craterostigma plantagineum. EMBO J. 1997;16:3599–3608. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.12.3599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Vinocur B, Altman A. Recent advances in engineering plant tolerance to abiotic stress: achievements and limitations. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2005;16:123–132. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2005.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Lappartient AG, Vidmar JJ, Leustek T, Glass ADM, Touraine B. Inter-organ signaling in plants: regulation of ATP sulfurylase and sulfate transporter genes expression in roots mediated by phloem-translocated compound. Plant J. 1999;18:89–95. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1999.00416.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Takahashi H, Yamazaki M, Sasakura N, Watanabe A, Leustek T, Engler JdA, Engler G, Van Montagu M, Saito K. Regulation of sulfur assimilation in higher plants: A sulfate transporter induced in sulfate-starved roots plays a central role in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1997;94:11102–11107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.20.11102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Vaucheret H, Vazquez F, Crete P, Bartel DP. The action of ARGONAUTE1 in the miRNA pathway and its regulation by the miRNA pathway are crucial for plant development. Genes Dev. 2004;18:1187–1197. doi: 10.1101/gad.1201404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Williams L, Grigg SP, Xie M, Christensen S, Fletcher JC. Regulation of Arabidopsis shoot apical meristem and lateral organ formation by microRNA miR166g and its AtHD-ZIP target genes. Development. 2005;132:3657–3668. doi: 10.1242/dev.01942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Mallory AC, Bartel DP, Bartel B. MicroRNA-directed regulation of Arabidopsis AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR17 is essential for proper development and modulates expression of early auxin response genes. Plant Cell. 2005;17:1360–1375. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.031716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Wang J, Wang L, Mao Y, Cai W, Xue H, Chen X. Control of root cap formation by microRNA-targeted auxin response factors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2005;17:2204–2216. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.033076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Dharmasiri N, Dharmasiri S, Estelle M. The F-box protein TIR1 is an auxin receptor. Nature. 2005;435:441–445. doi: 10.1038/nature03543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Wang JW, Schwab R, Czech B, Mica E, Weigel D. Dual effects of miR156-targeted SPL genes and CYP78A5/KLUH on plastochron length and organ size in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell. 2008;20:1231–1243. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.058180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Wu G, Poethig RS. Temporal regulation of shoot development in Arabidopsis thaliana by miR156 and its target SPL3. Development. 2006;133:3539–3547. doi: 10.1242/dev.02521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Schwab R, Palatnik JF, Riester M, Schommer C, Schmid M, Weigel D. Specific effects of microRNAs on the plant transcriptome. Dev. Cell. 2005;8:517–527. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.01.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Palatnik JF, Allen E, Wu X, Schommer C, Schwab R, Carrington JC, Weigel D. Control of leaf morphogenesis by microRNAs. Nature. 2003;425:257–263. doi: 10.1038/nature01958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Millar AA, Gubler F. The Arabidopsis GAMYB-Like Genes, MYB33 and MYB65, are MicroRNA-Regulated Genes that Redundantly Facilitate Anther Development. Plant Cell. 2005;17:705–721. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.027920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Guo H-S, Xie Q, Fei J-F, Chua N-H. MicroRNA Directs mRNA Cleavage of the Transcription Factor NAC1 to Downregulate Auxin Signals for Arabidopsis Lateral Root Development. Plant Cell. 2005;17:1376–1386. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.030841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Emery JF, Floyd SK, Alvarez J, Eshed Y, Hawker NP, Izhaki A, Baum SF, Bowman JL. Radial patterning of Arabidopsis shoots by class III HD-ZIP and KANADI genes. Curr. Biol. 2003;13:1768–1774. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2003.09.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Laufs P, Peaucelle A, Morin H, Traas J. MicroRNA regulation of the CUC genes is required for boundary size control in Arabidopsis meristems. Development. 2004;131:4311–4322. doi: 10.1242/dev.01320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Mallory AC, Dugas DV, Bartel DP, Bartel B. MicroRNA regulation of NAC-domain targets is required for proper formation and separation of adjacent embryonic, vegetative, and floral organs. Curr. Biol. 2004;14:1035–1046. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.06.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Aukerman MJ, Sakai H. Regulation of flowering time and floral organ identity by a MicroRNA and its APETALA2-like target genes. Plant Cell. 2003;15:2730–2741. doi: 10.1105/tpc.016238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Chen X. A microRNA as a translational repressor of APETALA2 in Arabidopsis flower development. Science. 2004;303:2022–2025. doi: 10.1126/science.1088060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Zhao B, Ge L, Liang R, Li W, Ruan K, Lin H, Jin Y. Members of miR-169 family are induced by high salinity and transiently inhibit the NF-YA transcription factor. BMC Mol. Biol. 2009;10:29. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-10-29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Xie Z, Kasschau KD, Carrington JC. Negative feedback regulation of Dicer-Like1 in Arabidopsis by microRNA-guided mRNA degradation. Curr. Biol. 2003;13:784–789. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Yu B, Bi L, Zheng B, Ji L, Chevalier D, Agarwal M, Ramachandran V, Li W, Lagrange T, Walker JC, Chen X. The FHA domain proteins DAWDLE in Arabidopsis and SNIP1 in humans act in small RNA biogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2008;105:10073–10078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804218105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Laubinger S, Sachsenberg T, Zeller G, Busch W, Lohmann JU, Rätsch G, Weigel D. Dual roles of the nuclear cap-binding complex and SERRATE in pre-mRNA splicing and microRNA processing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2008;105:8795–8800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0802493105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Kim S, Yang J-Y, Xu J, Jang I-C, Prigge MJ, Chua N-H. Two Cap-Binding Proteins CBP20 and CBP80 are involved in Processing Primary MicroRNAs. Plant Cell Physiol. 2008;49:1634–1644. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcn146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Smith MR, Willmann MR, Wu G, Berardini TZ, Möller B, Weijers D, Poethig RS. Cyclophilin 40 is required for microRNA activity in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2009 doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812729106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]