Abstract
Salmonella enterica is divided into four subspecies containing a large number of different serovars, several of which are important zoonotic pathogens and some show a high degree of host specificity or host preference. We compare 45 sequenced S. enterica genomes that are publicly available (22 complete and 23 draft genome sequences). Of these, 35 were found to be of sufficiently good quality to allow a detailed analysis, along with two Escherichia coli strains (K-12 substr. DH10B and the avian pathogenic E. coli (APEC O1) strain). All genomes were subjected to standardized gene finding, and the core and pan-genome of Salmonella were estimated to be around 2,800 and 10,000 gene families, respectively. The constructed pan-genomic dendrograms suggest that gene content is often, but not uniformly correlated to serotype. Any given Salmonella strain has a large stable core, whilst there is an abundance of accessory genes, including the Salmonella pathogenicity islands (SPIs), transposable elements, phages, and plasmid DNA. We visualize conservation in the genomes in relation to chromosomal location and DNA structural features and find that variation in gene content is localized in a selection of variable genomic regions or islands. These include the SPIs but also encompass phage insertion sites and transposable elements. The islands were typically well conserved in several, but not all, isolates—a difference which may have implications in, e.g., host specificity.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1007/s00248-011-9880-1) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Introduction
Salmonella are intracellular pathogens in cold-blooded as well as warm-blooded animals and important zoonotic agents. The genus Salmonella is currently divided into two species: Salmonella enterica and Salmonella bongori. S. enterica is further divided into six subspecies: S. enterica subsp. enterica, S. enterica subsp. salamae, S. enterica subsp. arizonae, S. enterica subsp. diarizonae, S. enterica subsp. houtenae, and S. enterica subsp. indica. To date, more than 2,500 different serovars have been characterized, with most (1,531) classified as part of the Salmonella subsp. enterica [1], which is the cause of more than 99% of the diseases in humans [1, 2]. The characterization is based on their surface antigens, where the O (somatic) antigens are part of the variable long chain lipopolysaccharide located on the outer membrane and the two H (flagellar) antigens are presented, when the two flagellar structures are expressed [1, 3].
S. enterica serovar Typhimurium and serovar Enteritidis are amongst the most common generalist pathovars, causing disease in a variety of animals [4, 5]. A smaller proportion of the serovars is host-specific and cause severe diseases. S. Typhi and Salmonella Paratyphi are human-restricted, causing typhoid and paratyphoid fever respectively [6]. The bovine-adapted Salmonella Dublin and the porcine-adapted Salmonella Choleraesuis are occasionally seen in humans, causing severe disease [7–9]. Traditionally, animal models have successfully been employed to elucidate the pathogenicity of intestinal Salmonella [10, 11], but these methods have inherent limits. Many disease mechanisms in Salmonella are host-specific, most famously the enteroinvasive behavior of S. Typhi in human infections [12], or more recently the human-adapted behavior of strain Salmonella Typhimurium D23580 [13]. In these cases, comparative genomics represent an alternative approach [14]
Salmonella is closely related to Escherichia coli, but have an additional large number of virulence genes [15, 16]. Some of these virulence genes are located in genomic islands (GIs), which are large segments of DNA acquired by horizontal gene transfer. These GIs often display a different AT content than from the rest of the genome of S. enterica (which is ~48% AT) [15]. These are usually located near tRNA genes, which are believed to facilitate the integration of the GIs into the chromosome due to their high degree of conservation. Many Salmonella-specific GIs, Salmonella pathogenicity islands (SPIs) play a role in virulence and have been linked to influencing host specificity as well as the degree of invasiveness of the bacteria [17].
Much research has been invested in order to identify Salmonella-specific genes and to determine genes specific to the different serovars. The S. Typhi and S. Paratyphi A serovars are both adapted to the same host and cause enteric fever in humans. This study shows that they are highly homologous at the protein level. A comparison of their evolutionary relatedness has suggested that they have evolved the ability to cause human-specific systemic disease by different paths. S. Paratyphi A is less diverse in terms of the proteins encoded in the genome, and contains fewer pseudogenes, which indicates that it has evolved more recently than S. Typhi [18]. When the complete genome sequence of S. Typhi CT18 was published, 204 pseudogenes were annotated, out of a genome of 4,599 genes [19]. This total was increased later, when the second Paratyphi A genome (strain AKU_12601) was sequenced and through comparative genomics revealed several additional pseudogenes in S. Typhi. Further, the two strains shared 66 pseudogenes, revealing that many of these have appeared from adaption to the same niche [6]. Some of these genes have been shown to relate to virulence and gastroenteritis, leading to the hypothesis that the original function of many of these pseudogenes was to cause gastroenteritis or infection in other hosts [18].
This work represents a data-driven approach towards elucidating the differences as well as similarities between fully sequenced Salmonella genomes. As the number of fully sequenced genomes available for analysis increases, so will the possibility to differentiate at greater detail between phenotypic characteristic such as host-specificity and the degree of invasiveness. At the time of writing (late 2010) we found 45 fully sequenced Salmonella genomes publicly available covering 21 serotypes within Salmonella subsp. enterica and representing, to our knowledge, the total sum of public genomes. Of these, 22 were complete, and 23 were draft sequences (consisting of many pieces or “contigs” and often with incomplete gene annotation). This study compares the sequences having the highest quality, which corresponds to 35 Salmonella genomes. We estimated both the sizes of the pan- and core genomes, as well as illustrated the spatial distribution of core and non-core genes across the chromosome. From these data, we describe several variable gene islands in specific locations on the chromosome including, but not limited to, the SPIs [20]. It follows that some of these unnamed gene islands are likely to play a role in Salmonella virulence and/or host specificity, even if others may be a little more than inactive remnants of phage inserts.
Materials and Methods
Genomes and Gene Annotations
All available genome sequences of S. enterica from NCBI as of 1 July, 2010, were downloaded and used in this work [21], and are shown in Table 1, which also contains accession numbers and references to the sequencing centers. This list includes 18 fully sequenced and 23 almost completed genomes of S. enterica which we supplemented with another four genomes from the Sanger Center [22]. In addition, two E. coli genomes were also downloaded and used for comparison. All genomes were subjected to de novo gene finding using two previously published gene finders: EasyGene [23, 24] and Prodigal [25] with the Prodigal annotation software providing the optimal foundation for comparisons (see Supplemental Data). Both gene finders were run using default settings.
Table 1.
General properties of the S. enterica and E. coli genomes used in this study
| Organisma (publication reference) | Genome Size | Contigs | Quality Score | Accession | PID | Genes | Specificity | Serogroup (O antigen) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. Paratyphi A str. AKU_12601 [6] | 4.58 MB | 1 | 1 | FM200053 | 30943 | 4,351 | Human-restricted | O:2 | Blue |
| S. Paratyphi A str. ATCC 9150 [18] | 4.59 MB | 1 | 1 | CP000026 | 13086 | 4,348 | Human-restricted | O:2 | Blue |
| S. 4,[5],12:i:- str. CVM23701 [45] | 4.90 MBb | 113 | 3 | ABAO00000000 | 19465 | 4,694 | Ubiquitous | O:4 | Green |
| S. Agona str. SL483 | 4.84 MB | 2 | 1 | CP001138 | 20063 | 4,508 | Ubiquitous | O:4 | Green |
| S. Heidelberg str. SL476 | 4.89 MB | 3 | 1 | CP001120 | 20045 | 4,680 | Ubiquitous | O:4 | Green |
| S. Heidelberg str. SL486 | 4.73 MBb | 48 | 3 | ABEL00000000 | 20065 | 4,432 | Ubiquitous | O:4 | Green |
| S. Paratyphi B str. SPB7 | 4.86 MB | 1 | 1 | CP000886 | 27803 | 4,555 | Ubiquitous | O:4 | Green |
| S. Saintpaul str. SARA23 | 4.72 MBb | 2 | 1 | ABAM00000000 | 19461 | 4,350 | Ubiquitous | O:4 | Green |
| S. Saintpaul str. SARA29 | 4.93 MBb | 182 | 5 | ABAN00000000 | 19463 | 4,757 | Ubiquitous | O:4 | Green |
| S. Schwarzengrund str. CVM19633 | 4.71 MB | 3 | 1 | CP001127 | 19459 | 4,551 | Ubiquitous | O:4 | Green |
| S. Schwarzengrund str. SL480 | 4.76 MBb | 67 | 3 | ABEJ00000000 | 20071 | 4,547 | Ubiquitous | O:4 | Green |
| S. Typhimurium str. 14028S [72] | 4.76 MB | 2 | 1 | CP001363 | 33067 | 4,653 | Ubiquitous | O:4 | Green |
| S. Typhimurium str. D23580 [13] | 4.88 MB | 1 | 1 | FN424405 | 40625 | 4,804 | Ubiquitous | O:4 | Green |
| S. Typhimurium str. DT104 | 4.93 MB | 2 | 1 | – | – | 4,752 | Ubiquitous | O:4 | Green |
| S. Typhimurium str. LT2 [4] | 4.86 MB | 2 | 1 | AE006468 | 241 | 4,635 | Ubiquitous | O:4 | Green |
| S. Typhimurium str. SL1344 | 4.88 MB | 4 | 1 | – | – | 4,774 | Ubiquitous | O:4 | Green |
| S. Choleraesuis str. SC-B67 [69] | 4.76 MB | 3 | 1 | AE017220 | 9618 | 4,792 | Porcine-adapted | O:7 | Orange |
| S. Paratyphi C str. RKS4594 [52] | 4.83 MB | 2 | 1 | CP000857 | 20993 | 4,690 | Ubiquitous | O:7 | Orange |
| S. Tennessee str. CDC07-0191 | 4.79 MBb | 94 | 3 | ACBF00000000 | 30831 | 4,546 | Ubiquitous | O:7 | Orange |
| S. Virchow str. SL491 | 4.88 MBb | 5 | 2 | ABFH00000000 | 20595 | 4,596 | Ubiquitous | O:7 | Orange |
| S. Hadar str. RI_05P066 | 4.79 MBb | 50 | 3 | ABFG00000000 | 20593 | 4,487 | Ubiquitous | O:8 | Yellow |
| S. Hadar str. 18 Bela Nagy | 4.79 MB | 3 | 1 | – | – | 4,448 | Ubiquitous | O:8 | Yellow |
| S. Kentucky str. CDC 191 | 4.70 MBb | 53 | 3 | ABEI00000000 | 20069 | 4,383 | Ubiquitous | O:8 | Yellow |
| S. Kentucky str. CVM29188 [70] | 4.79 MBb | 4 | 2 | ABAK00000000 | 19457 | 4,745 | Ubiquitous | O:8 | Yellow |
| S. Newport str. SL317 | 4.95 MBb | 63 | 3 | ABEW00000000 | 20047 | 4,720 | Ubiquitous | O:8 | Yellow |
| S. Newport str. SL254 | 4.83 MB | 3 | 1 | CP001113 | 18747 | 4,710 | Ubiquitous | O:8 | Yellow |
| S. Dublin str. CT_02021853 | 4.84 MB | 2 | 1 | CP001144 | 19467 | 4,682 | Bovine adapted | O:9 | Red |
| S. Enteritidis str. P125109 [5] | 4.69 MB | 1 | 1 | AM933172 | 30687 | 4,363 | Ubiquitous | O:9 | Red |
| S. Gallinarum str. 287/91 | 4.66 MB | 1 | 1 | AM933173 | 30689 | 4,466 | Avian restricted | O:9 | Red |
| S. Javiana str. GA_MM04041433 | 4.55 MBb | 19 | 4 | ABEH00000000 | 20049 | 4,221 | Ubiquitous | O:9 | Red |
| S. Typhi str. CT18 [19] | 4.81 MB | 3 | 1 | AL513382 | 236 | 5,065 | Human-restricted | O:9 | Red |
| S. Typhi str. Ty2 [58] | 4.79 MB | 1 | 1 | AE014613 | 371 | 4,632 | Human-restricted | O:9 | Red |
| S. Typhi str. J185c | 4.74 MBb | 1065 | 6 | CAAW00000000 | 28303 | 5,626d | Human-restricted | O:9 | Red |
| S. Typhi str. M223c | 5.02 MBb | 3024 | 6 | CAAX00000000 | 28305 | 7,442d | Human-restricted | O:9 | Red |
| S. Typhi str. E98-0664c | 4.71 MBb | 3939 | 6 | CAAU00000000 | 28299 | 7,759d | Human-restricted | O:9 | Red |
| S. Typhi str. E98-2068c | 4.76 MBb | 3682 | 6 | CAAV00000000 | 28301 | 7,637d | Human-restricted | O:9 | Red |
| S. Typhi str. E98-3139c | 4.60 MBb | 415 | 5 | CAAZ00000000 | 28309 | 5,051 | Human-restricted | O:9 | Red |
| S. Typhi str. 404tyc | 4.68 MBb | 6441 | 6 | CAAQ00000000 | 28289 | 10,055d | Human-restricted | O:9 | Red |
| S. Typhi str. AG3c | 4.75 MBb | 7336 | 6 | CAAY00000000 | 28307 | 10,675d | Human-restricted | O:9 | Red |
| S. Typhi str. E00-7866c | 4.76 MBb | 1445 | 6 | CAAR00000000 | 28291 | 5,749d | Human-restricted | O:9 | Red |
| S. Typhi str. E01-6750c | 4.58 MBb | 4564 | 6 | CAAS00000000 | 28293 | 8,315d | Human-restricted | O:9 | Red |
| S. Typhi str. E02-1180c | 4.71 MBb | 422 | 5 | CAAT00000000 | 28295 | 5,097 | Human-restricted | O:9 | Red |
| S. Weltevreden str. HI_N05-537 | 5.05 MBb | 81 | 3 | ABFF00000000 | 20591 | 4,784 | Ubiquitous | O:9 | Cyan |
| S. arizonae 62:z4,z23:- str. RSK2980 | 4.60 MB | 1 | 1 | CP000880 | 13030 | 4,278 | Ubiquitous | O:3,10 | |
| S. bongori str. NCTC_12419 | 4.79 MB | 1 | 1 | – | – | 4,049 | Ubiquitous | ||
| E. coli str. K-12 substr. DH10B [71] | 4.69 MB | 1 | 1 | CP000948 | 20079 | 4,398 | Ubiquitous | ||
| E. coli APEC O1 [73] | 5.08 MB | 3 | 1 | CP000468 | 16718 | 5,259 | Ubiquitous |
PID project ID
aData for organisms is collected from NCBI.
bNote that draft genomes may contain plasmid DNA
cStrains not used in this study because of bad quality score and high number of contigs.
dGene counts are included here for completeness sake even though poor genome quality leads to spurious gene prediction
16S rRNA Phylogeny
Two phylogenetic trees were constructed based on 16S rRNA: one tree included 21 enteric strains and the other tree included only Salmonella strains. In both cases, the sequences were identified using RNAmmer [26] with a length between 1,400 and 1,700 nt and an RNAmmer score above 1,700. When several 16S rRNAs from the same strain met the criteria, the closest match to the first 16S rRNA in S. Typhimurium LT2, rssH, was selected. While 16S rRNA was already annotated in many of the genomes analyzed, then because each genome contains several 16S rRNA, using this approach eliminates any arbitrary bias from having to select one by hand. The ClustalX [27] program was used to align the 16S rRNA sequences and subsequently in constructing a tree using the bootstrap neighborhood-joining method with 1,000 trials. The tree was visualized by using NJplot [28]. It was not possible to find 16S rRNA sequences obeying the aforementioned quality criteria for all 45 sequenced Salmonella genomes.
Definition of Gene Families
To identify and process homology within and across genomes, all genes were assigned into unique gene families based on sequence similarity. The genes were translated into amino acid sequences and aligned all-against-all using BLASTP [29], and any two genes were considered a gene pair if the alignment could meet “the 50/50 rule”; at least 50% of the length of the longest sequence was continuously aligned under default gap penalties, and more than 50% of the aligned sequences must be reported identical. Since each member of a pair can be a member of other pairs as well, all gene pairs sharing members were subsequently combined into one gene family. Each gene will then exclusively belong to one gene family [30]. This is the same method used previously to describe the core and pan-genome of Vibrio, E. coli, and Bacteroides [31–33].
BLAST Matrix
All proteomes were compared with BLASTP using “the 50/50 rule” to categorize genes into gene families. The BLAST matrix shows the comparison of each proteome to another. The percentages show the amount of proteins shared between two proteomes along with the corresponding fraction showing the number of gene families present in both genomes over the total amount of gene families in the two strains [34].
Pan- and Core genome Plot
The pan- and core genome plot is a simple illustration of the distribution of gene families defined above, as more and more genomes are considered. It is the result of applying a basic set theory, each genome being a set of gene family, some of which are also found in other genomes. In this context, the pan-genome becomes the union of the genomes under consideration, while the core genome is the intersection of those genomes. Thus, the total number of gene families is shown for the leftmost genome. Then, moving to the right, more genomes are considered, and any gene families not previously encountered are added to the pan-genome (the union), while the core genome is reduced to only those gene families shared by every genome analyzed at this point (the intersection). The last point defines the total pan- and core genome, corresponding to the union and intersection of all genomes, respectively.
This approach differs from that of Tettelin et al. [30] in that we chose to rely on prodigal gene predictions as a method of coping with annotation biases. We also chose not to do permutations of the genomes as that would prevent us from visualizing the progression across serogroups. Even if the shape of the pan and core genome curves would be different for a different ordering of the genomes, the endpoints would remain the same, and thus the estimates of the size of the core and pan-genomes are unaffected by the order of the genomes.
Pan-genome Trees
The pan-genome tree is based on the absence or presence of each gene family in the serovars. The tree is constructed based on the Manhattan distance calculated from the BLAST matrix. Three different trees were constructed to show different groups of genes in the pan-genome. The “zero” tree counts all gene present only once as zero and the rest as one. The “shell” tree weighs genes that present in more number higher than genes in lower number. The “cloud” tree gives more weight to genes that present in lower number higher than genes in more number [35, 36].
BLAST Atlas
Comparisons from the BLAST were displayed using a reference genome in a BLAST atlas. All genes from the reference genome were aligned at the protein level by BLASTP with default settings against all other genomes. The presence and absence of genes are visualized in a circle, with increasing intensity of color representing greater similarity. The BLAST atlas also indicates properties of the DNA structure in the five innermost circles and the coding sequences (CDS), including rRNA and tRNA, in the following two circles [37].
The four innermost circles show structural parameters of the DNA. The position preference is used to measure the DNA flexibility, where dark purple means rigid DNA and dark green represents regions of anisotropic flexibility, that is, these regions with low-position preference (dark green on this scale) are likely not to be compacted by chromatin and could contain highly expressed genes [38, 39]. The stacking energy is used to measure how readily the DNA will melt, where dark green means more stable and dark red that it will melt more easily. The intrinsic curvature describes how likely the DNA is to be curved. The dark orange indicates straight regions, whereas dark blue suggests strongly curved regions. Percent AT reveals regions having substantially different AT content compared to the rest of the genomes. Turquoise means low AT content and red means high AT content [40].
Identification of Gene Islands Across Genomes
GenBank entries for all SPIs listed for S. enterica in the Pathogenicity Island Database (PAI DB) were downloaded [41] and subjected to re-annotation using Prodigal with a training template constructed from the complete genomes [25]. The sequences of all proteins identified by Prodigal were subsequently aligned against all the Prodigal proteomes of all Salmonella in Table 1 to determine the absence or presence for each SPI in each genome. The identity score from the best match reported by BLASTP for each SPI protein was multiplied by the ratio of the alignment length to the total sequence length and averaged for all proteins in each SPI to arrive at an overall identity for each island. The island scores were clustered in both dimensions using the complete linkage method for hierarchical clustering available in the R software package [42].
Results and Discussion
The genomes of all fully sequenced Salmonella strains were compared and analyzed (Table 1). Observations on the amount of annotated genes in Salmonella revealed striking differences, particularly for S. Typhi, where the total number of reported genes for some genomes was as much as twice that of the average of all genomes with a corresponding decrease in the average gene length. Such biases, arising from differences in the methods by which the genomes were annotated and/or the data quality, lead to the accumulation of errors as more and more genomes are compared. To investigate this, all 45 initial genomes were subjected to de novo gene finding using two previously published gene finders: EasyGene [23, 24] and Prodigal [25]. The results were compared to the original annotations and while EasyGene generally displayed good performance, then for certain genomes the number of genes estimated was unrealistically low. A probable cause being that the pre-trained model upon which Easygene relies was insufficient to describe these. Prodigal has no such reliance and gave more consistent and believable genome sizes [data shown in Suppl. Section]. All genomes were then subjected to standardized gene finding using Prodigal.
Since more than half the genome sequences were not completely assembled, some of them being in thousands of contigs or more, a quality score described in Chain et al. 2009 [43] was calculated for all the genome sequences and is given in Table 1. The quality score ranges from 1 to 6, where 1 is described as finished and 6 as a standard draft. Based on this quality score and on the number of contigs, ten of the S. Typhi strains were excluded from most of this analysis (strains 404ty, AG3, E00-7866, E01-6750, E02-1180, E98-0664, E98-2068, E98-3139, J185, and M223). This left 35 genomes for the rest of the analysis
Pairwise Comparisons
The relation between the different genomes showed a conservation of the gene families between any two Salmonella isolates to be above 65% while the homology of the gene families within each genome was generally less than 5% (Fig. 1). Similar comparisons within E. coli genomes show considerably more variation, with less than half the genes conserved between some E. coli strains [34]. We use the term “gene family” to describe a collection of copies of the same gene identified from different genomes or occasionally from duplication within the same genome. It is a process associated with a small, but unavoidable, degree of error. The construction of gene families is described in the “Materials and methods” section.
Figure 1.
BLAST Matrix of 35 S. enterica genomes. The figure shows the number of gene families found in common between the Salmonella strains and the degree of gene duplication within each by pairwise all-against-all BLAST comparisons at the amino acid level. A higher resolution version is available in the Supplemental Section with additional data viewable under zoom
For most strains, a greater degree of homology was observed within the serovars. This is particularly visible in the S. Typhimurium strains and the monophasic strain 4,[5],12:i- (darkly shaded region at the bottom of Fig. 1); the only documented difference between these strains is that the latter either lacks the entire phase 2 antigen gene fljB or contains partial deletions in fljB and an adjacent gene hin [44–46]. It is noteworthy that S. Dublin str. CT_02021853, Salmonella Enteritidis str. P125109, and Salmonella Gallinarum str. 287/91 (upper right in Fig. 1) display a higher degree of gene family homology than the norm for cross-serovar comparisons. Furthermore, Salmonella Saintpaul str. SARA23 stands out by displaying a relatively high degree of similarity to most other strains in cross-serovar comparisons. A similar behavior was not observed for S. Saintpaul str. SARA 29; however, results observed for that genome are marred and brought into doubt by a poor quality score of 5 for the sequence.
Evolutionary Relationships
16S rRNAs are functionally conserved and relatively long, making them ideal for phylogenetic studies. Two phylogenetic trees were constructed based on 16S rRNA and are shown in Fig. 2. The sequences were identified using RNAmmer [26] which was not able to find sufficiently high-quality sequences for all draft sequences (due to the difficulty in assembling large repeated regions like the rRNA operons from short read lengths). This makes the 16S rRNA comparison between all the strains in this study impossible, but it was possible to find reliable, full-length 16S rRNA genes in 27 of the Salmonella strains.
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of 16S rRNA. (Left) 16S rRNA tree of different genus in the enterobacteria family, Salmonella is marked with color. (Right) 16S rRNA tree of 27 Salmonella genomes, colors indicate serogroups (see Table 1 for key). The Salmonella genomes of Table 1 which are not presented here are absent because full length 16S rRNA could not be identified in most draft genomes (see “Materials and methods”). The bootstrap values, based on 1,000 iterations, are shown in red numbers, next to the branches
Studies of the evolutionary relationship of Salmonellae within Enterobacteriaceae have defined the Salmonella genus and the division into the two species [47, 48]. The relationship between the Salmonellae, on subspecies and species level, has been extensively studied based on MLEE [49], microarray [50], and four housekeeping genes [51]. Figure 2 shows a 16S rRNA phylogenetic tree of 20 enterobacteria giving a good description of the relationship of the different genera, as well as a tree based on the 16S rRNA of the sequenced genomes within the Salmonella genus. Although there is some overlap between the 16S rRNA similarity and serotype within the genus, the correlation is far from complete. Another interesting observation is that strains known for being host specific—S. Dublin, S. Gallinarum, and S. Choleraesuis—are grouped together with strains known for having a broader range of hosts, e.g., S. Typhimurium and S. Enteritidis, again showing that host specificity and the degree of invasiveness is not necessarily linked to evolutionary relationship.
The human-restricted serovars S. Typhi and S. Paratyphi A show high proteome similarity in Fig. 1, but in the 16S rRNA relationship, the S. Paratyphi A are grouped distant from the rest of the Salmonella subsp. enterica including the S. Typhi genomes, which are found with the generalist pathovar Salmonella Javiana. The two non-specific paratyphoid pathovars S. Paratyphi B and S. Paratyphi C neither show gene homology nor much evolutionary relatedness in 16S similarity to the S. Paratyphi A. Interestingly, S. Paratyphi C consistently cluster with S. Choleraesuis, both in protein similarity and 16S rRNA similarity. Indeed, a recent study has shown that S. Paratyphi C is likely to have diverged from S. Choleraesuis even though the serovars differ in the host they infect [52].
During adaption to a new niche, changes in the Salmonella genome can occur, for example by horizontal gene transfer, rearrangement, and duplication, but also by gene excision and pseudogene formation [53]. Due to this, an analysis of their gene similarity at different levels which includes differences and similarities in the SPIs, is better at describing the relationship between the strains with different host specificities.
The Salmonella core genome
The core genome consists of all the gene families present in all the Salmonella strains, whereas the pan-genome consists of all gene families found in any of the Salmonella strains. A plot of the evolution of the pan- and core genome as more and more genomes are considered is seen in Fig. 3. The core genome of 35 sequenced Salmonella is 2,811 gene families, and the pan-genome is 10,015; the corresponding numbers within the Salmonella subsp. enterica are 3,224 and 9,161. The first genome under consideration was S. Typhimurium str. LT2, and when the second genome, S. Typhimurium str. D23580 is added, the size of the pan-genome grows slightly while the core genome decreases. This trend continues as more and more strains are added reaching a milestone first with the addition of a second serovar and again when Salmonella subsp. arizonae is added.
Figure 3.
Pan- and core genome plot of 35 Salmonella strains. The red and blue lines show the progression in the core and pan genomes as more and more genomes are considered, while the columns indicate the amount of novel gene families encountered. The color of the columns represents the serogroup as defined in Table 1 (see Table 1 for key)
While the exact size of the pan- and core genome is dependent on the amount of genomes under analysis as well as the chosen methodology, it is clear that Salmonella exhibits what has tentatively been called a “closed” pan-genome structure [54]. This is in contrast to the close relative E. coli which clearly displays an open pan-genome structure [55], but congruent with other pathogens such as Yersinia pestis, Listeria, or Campylobacter jejuni [35, 56, 57]
In most cases, the addition of a second or third isolate of a given serotype has much less impact than the addition of the first, although exceptions exist. Most notably, the addition of a genome which is fragmented and incomplete affects the size of the core and pan-genome proportionally more than the addition of a completed genome. For example, consider the fragmented S. Saintpaul str. SARA29 and the proportional increase in novel gene families observed for it relative to S. Saintpaul str. SARA23.This can be accurate—while the sharing of serotype suggests a similarity for the entire proteome, it need not be the case—two strains of the same serotype can, potentially, be very different. Another explanation exists, however, since incomplete genomes may not always contain the full sequence for genes otherwise present, and such truncated genes might erroneously be identified as novel gene families.
We identified the average number of gene families unique to each serotype, encountered in each genome and visualized the result in Fig. 4. The analysis shows that the average number of distinct gene families varies considerably from serotype to serotype, but is at least weakly correlated to genome size (Table 1). Amongst the S. enterica, serovar S. Typhi clearly stands out having the highest number of unique gene families; this is likely due to the presence of several large pathogenicity islands characteristic to the serovar [19, 58]. The smallest number of unique gene families was found in serovar S. Enteritidis which is among the smaller Salmonella genomes, although S. Javiana is the smallest. Interestingly, the Salmonella subsp. arizonae genome has almost twice the number of unique genes compared to S. bongori, although it remains a subspecies of S. enterica while the latter is recognized as a separate species.
Figure 4.
Flowerplot of unique gene families in each Salmonella serovar. The figure presents the average number of gene families found in each genome as being unique to the serovar. Also given is the size of the core genome. The color of the petals represents the S. enterica serogroups (see Table 1 for key)
BLAST Atlas of S. Typhimurium D23580 and S. Typhi Ty2
The BLAST atlas is a visualization of gene conservation in a number of species against a single reference genome (Fig. 5). The BLAST atlas thus shows which genes from the reference genome are present in the other genomes. As references, we selected the genome of the pathogens S. Typhimurium str. D23580 and S. Typhi str. Ty2 because they are human-adapted and human specific, respectively. Also, a recent study did a thorough analysis of SPIs in S. Typhi CT18 with the generalist S. Typhimurium LT2 [14]. The proteomes of the Salmonella and E. coli strains were aligned against the reference genomes illustrating similarity by color intensity. The general picture is that the Salmonella strains are highly conserved, with most genetic variation being concentrated in specific variable regions, as can be seen in Fig. 5.
Figure 5.
BLAST atlases of the 35 S. enterica and two E. coli. a BLAST atlas with S. Typhimurium str. D23580 as reference, representing the generalist strains. Six SPIs are marked on the atlas. b BLAST atlas with S. Typhi str. Ty2 as reference, representing a host-specific serovar. Four SPIs that were published along with the genome sequence are marked on the atlas. Generally, the Salmonellas show high homology with a few variable regions as SPIs. Also marked are several poorly characterized gene islands, I-a to VI-a and I-b to III-b (additional information in the Supplementary Section)
The E. coli genomes show the lowest number of BLAST hits to the reference Salmonellas, in particular little homology exists in the regions containing the different SPIs which are important for virulence in Salmonella. Between the Salmonella genomes, the conservation of the SPIs was generally high but with notable differences, particularly for S. Typhi str. Ty2 where SPI-7, the characteristic S. Typhi pathogenicity island, is clearly unique to that serovar. SPI-7 has previously been reported in both serovars S. Paratyphi C and S. Dublin [59–61], but our analysis finds only fragments of SPI-7 in these serovars, not the complete island. In the S. Typhi str. Ty2 genome, a part of SPI-7 was found duplicated, marked in Fig. 5 by the red SPI-7 label. This duplicated part is the principle fragment of SPI-7 conserved in S. Dublin but not in S. Paratyphi C suggesting that the island may consist of several independently mobile parts.
Most of the SPIs have been under intense study. SPI-1 and SPI-2 encode type III secretion systems [17]. T3SS of SPI-1 is important for the penetration of intestinal epithelium, whereas the T3SS of SPI-2 is also considered important after access to macrophages [62, 63], although not all studies on its role in macrophage survival are congruent [64]. SPI-3 contains ten ORFs in six transcriptional units and encodes proteins with little known functional relation to each other. The most important is the Mg2+ transporter, a putative ToxR regulatory protein and a putative AIDA-I adhesion [65]. The function of SPI-4 is mostly unknown, but has been shown in a mouse model to contribute to intestinal inflammation [66]. The SPI-4 encodes a type I secretion system, T1SS, and a substrate protein of the T1SS, SiiE [67]. SPI-5 was first located in S. Dublin and is mainly composed of effector proteins [68].
In addition to the established SPIs that are present in most members of the Salmonella subsp. enterica, the atlases also reveal several genomic regions which are absent from most or all Salmonella genomes. These regions are gene islands likely of viral origin. For example, the region marked “I-a” is flanked by several genes encoding integrase/recombinase-like proteins and contains several phage-related proteins. Similar images can be seen for the regions marked II-a to VI-a. In all cases, though, the majority of the proteins in the inserts are without any well-described functions, which makes the impact on the host difficult to gauge. This may be “junk DNA,” and their conservation in certain isolates of Salmonella can be attributed to the proliferation of the responsible phages. Alternatively, some of these proteins may confer selective advantages for the host, thus providing an evolutionary incitement for their retention.
Distribution of SPIs across genomes
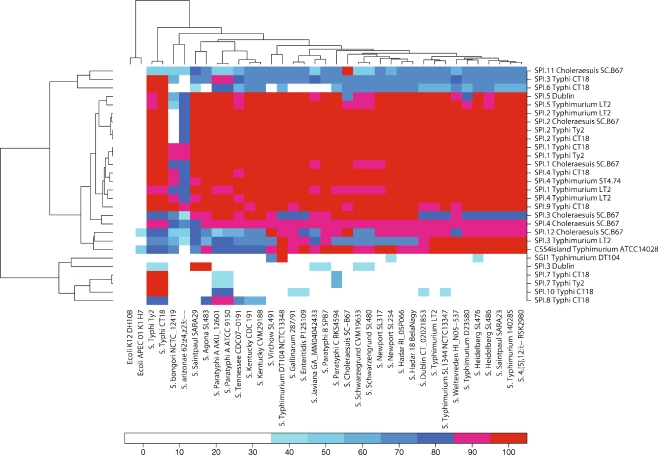
We extracted all S. enterica genomic islands from the Pathogenicity Island Database (PAI DB) (Table 2) [41]. The proteomes of each island were aligned against the proteomes of the species in Table 1, and the average identity for each island was clustered in a heat map (Fig. 6).
Table 2.
Salmonella pathogenicity islands used in this study, obtained from the pathogenicity island database
| PAIa | Host strain | Insertion site | Accession | Size (kb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPI-1_CholeraesuisSC-B67 | S. Choleraesuis SC-B67 | fhlA/mutS | NC_006905_P5 | 43.5 |
| SPI-1_TyphiCT18 | S. Typhi CT18 | fhlA/mutS | NC_003198_P5 | 41.9 |
| SPI-1_TyphiTy2 | S. Typhi Ty2 | fhlA/mutS | NC_004631_P2 | 41.9 |
| SPI-1_TyphimuriumLT2 | S. Typhimurium LT2 | fhlA/mutS | NC_003197_P3 | 44.3 |
| SPI-2_CholeraesuisSC-B67 | S. Choleraesuis SC-B67 | tRNA-val | NC_006905_P3 | 41.8 |
| SPI-2_TyphiCT18 | S. Typhi CT18 | tRNA-val | NC_003198_P3 | 41.6 |
| SPI-2_TyphiTy2 | S. Typhi Ty2 | tRNA-val | NC_004631_P1 | 41.6 |
| SPI-2_TyphimuriumLT2 | S. Typhimurium LT2 | tRNA-valV | NC_003197_P2 | 40.1 |
| SPI-3_Dublin | S. Dublin | tRNA-selC | AY144490 | 10.1 |
| SPI-3_CholeraesuisSC-B67 | S. Choleraesuis SC-B67 | tRNA-selC | NC_006905_P6 | 12.8 |
| SPI-3_TyphiCT18 | S. Typhi CT18 | tRNA-pro | NC_003198_P7 | 16.9 |
| SPI-3_TyphimuriumLT2 | S. Typhimurium LT2 | tRNA-selC | NC_003197_P4 | 16.6 |
| SPI-4_CholeraesuisSC-B67 | S. Choleraesuis str. SC-B67 | ssb/soxSR | NC_006905_P7 | 26.7 |
| SPI-4_TyphiCT18 | S. Typhi CT18 | ssb | NC_003198_P8 | 23.4 |
| SPI-4_TyphimuriumLT2 | S. Typhimurium LT2 | ssb/soxSR | NC_003197_P5 | 23.4 |
| SPI-4_TyphimuriumLT2_2 | S. Typhimurium LT2 | ssb/soxSR | AF060869 | 27.3 |
| SPI-4_TyphimuriumST4-74 | S. Typhimurium ST4/74 | Not published | AJ576316 | 24.7 |
| SPI-5_Dublin | S. Dublin | tRNA-serT | AF060858 | 9.7 |
| SPI-5_TyphimuriumLT2 | S. Typhimurium LT2 | tRNA-serT | NC_003197_P1 | 9.1 |
| SPI-6_TyphiCT18 | S. Typhi CT18 | tRNA-asp | NC_003198_P1 | 58.7 |
| SPI-7_TyphiCT18 | S. Typhi CT18 | tRNA-phe | NC_003198_P9 | 133.6 |
| SPI-7_TyphiTy2 | S. Typhi Ty2 | tRNA-phe | NC_004631_P3 | 131.7 |
| SPI-8_TyphiCT18 | S. Typhi CT18 | tRNA-phe | NC_003198_P6 | 6.9 |
| SPI-9_TyphiCT18 | S. Typhi CT18 | Not published | NC_003198_P4 | 15.7 |
| SPI-10_TyphiCT18 | S. Typhi CT18 | tRNA-leu | NC_003198_P10 | 32.9 |
| SPI-11_CholeraesuisSC-B67 | S. Choleraesuis SC-B67 | Gifsy-1 prophage | NC_006905_P2 | 15.7 |
| SPI-12_CholeraesuisSC-B67 | S. Choleraesuis SC-B67 | tRNA-pro | NC_006905_P4 | 11.1 |
| CS54island_TyphimuriumATCC14028 | S. Typhimurium ATCC14028 | xseA/yfgK | AF140550 | 25.3 |
| SGI1_TyphimuriumDT104 | S. Typhimurium DT104 | thdF | AF261825 | 47.7 |
aDownloaded from http://www.gem.re.kr/paidb/browse_pais.php?m=p#Salmonella%20enterica
Figure 6.
Heatmap of SPI conservation. SPIs from the Pathogenicity Island Database were aligned against genomes, and the average identity of all proteins in each SPI was hierarchically clustered in two dimensions. The vertical axis lists the SPIs while the genomes are located horizontally
Since many SPIs were historically first identified as being present in Salmonella but absent in E. coli (strain K-12) [17], it is not surprising that no SPI proteins were found in E. coli K-12. Because of the diversity within the E. coli species, other non-K12 strains might potentially contain SPI proteins, but for the APEC strain at least, no significant similarity was found. Even within Salmonella many SPI proteins are found exclusively within Salmonella subsp. enterica and not in S. bongori or Salmonella subsp. arizonae which supports the hypothesis that these islands are an integral part of what gives Salmonella subsp. enterica its genetic identity. The same can be said for serovar S. Typhi where the exclusivity of the characteristic typhoid SPIs is clearly seen.
The SPIs appear very well conserved despite being isolated from different serovars. The different versions of SPI-1 in particular, cluster perfectly together, but also SPI-2 and SPI-4 follow identical distributions. Only SPI-3 is in discord; the four different versions of SPI-3 are clearly not identical copies of the same island, as illustrated by the leftmost dendrogram which divides the islands into at least three distinct versions. Most apparent is the SPI-3 isolated from S. Dublin, which clusters together with otherwise Typhi-specific islands. It is clearly separate from the other versions of SPI-3 and shares no homology with them. The island is also present in only very few genomes. The S. Typhi CT18 SPI-3 is also a distinct version of SPI-3 found within the two genomes of the serovar, with partial alignments to non-Typhi genomes only. Unlike the S. Dublin SPI-3 which is an almost unique SPI-3; it consists of a core shared with the remaining two copies of SPI-3 and a part which is unique. It is the shared core which aligns with the non-Typhi genomes, while the unique part is found in S. Typhi alone. The remaining two copies of SPI-3 are much closer to each other. The SPI-3 S. Typhimurium str. LT2 is found with a perfect alignment in the other S. Typhimuriums and in S. Heidelberg, but only to a lesser degree in most other genomes, many of which instead show perfect conservation to the SPI-3 from S. Choleraesuis.
In all cases, the variance between the islands arises from certain specific proteins being either present or absent and not from general mutational drift. It is, however, unclear what the consequences for a given cell of having one version of SPI-3 as opposed to another, but could potentially impact the organism’s pathogenicity quite profoundly.
There is a good correlation between the clustering of the topmost dendrogram and the serotype, but it is not perfect. For example, the antibiotic resistance island SGI1 from S. Typhimurium str. DT104 appears to be more or less unique to that particular strain and causes it to cluster away from the other S. Typhimuriums. Another example is the SPI-3 S. Dublin originally identified in serotype S. Dublin, but here it was found only in S. Agona and S. Saintpaul str. SARA29 and appears completely absent in the sequenced S. Dublin str. CT_02021853. This is not an error; the SPI was identified from a different isolate of S. Dublin than the one which lies sequenced in GenBank. Rather, this emphasizes that the distribution of SPIs is not always linked to serotype.
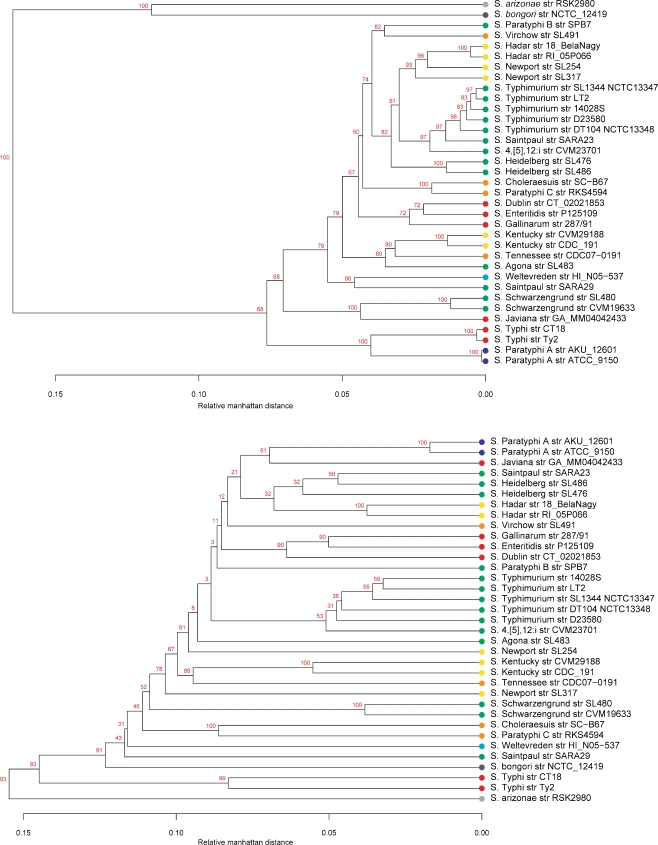
Pan-genome Tree
Two dendrograms constructed from the overall genomic content in Salmonella are illustrated in Fig. 7 by weighing the presence of non-core gene families according to two different schemes. The upper panel in Fig. 7 shows a dendrogram where gene families are weighted higher the more strains they are present in, while the lower panel displays a tree made from weighing gene families higher the fewer genomes they are present in [36]. In general, the two representations illustrate the impact of the choice of method on what relations are observed.
Figure 7.
Pan genome family trees based on the absence and presence of gene families. In the upper panel, the tree is constructed by weighting gene families higher the more genomes they are present in. The lower panel shows the opposite scheme where genes present in smaller numbers are weighted higher. The serogroup colors are defined in Table 1
The human-restricted serovars, S. Paratyphi A and S. Typhi, show close relation in the first dendrogram emphasizing genes present in most serovars, but when we give more weight to genes present in few strains, this image reverses and the two organisms become far apart. This is likely the result of SPI-7 being present only in S. Typhi which will be much more significant when rare genes are weighted the highest. In the two representations, the S. Typhi genomes have also changed orientation in relation to S. bongori and Salmonella subsp. arizonae, being more distantly related to the rest of Salmonella subsp. enterica than S. bongori when rare gene families are weighted the highest. The two different S. Newport serovars show more or less the same relative distance in both dendrograms, but cluster with S. Kentucky instead of S. Hadar when gene families present in few strains are weighed higher. The S. Typhimurium strains cluster together in both plots. The same can be seen for S. Paratyphi C and S. Choleraesuis, and for S. Gallinarum, S. Enteritidis, and S. Dublin.
Conclusion
A comparative genomic analysis of 35 Salmonella genomes with standardized gene findings provides insight into the relationship between the different serovars as well as offering a glimpse into the relationship of Salmonella subsp. enterica to subsp. arizonae and S. bongori. Generally, the Salmonellas show fairly high similarity in protein sequences when visualized by the BLAST atlas or BLAST Matrix, where the identity between the genomes within Salmonella subsp. enterica ranges from 65% to 99%. Although exceptions exist, the pan-genome study shows that the addition of each new isolate of S. enterica reveals relatively few novel genes, and even fewer genes if an isolate of the same serotype has already been considered.
In general, the number of Salmonella “core genes” (2,800) seems relatively large, compared to other bacterial genera. For example, there are roughly a thousand core genes found in E. coli, in Bacteroides, and also in Vibrio genomes [31–33]. Similarly, the pan-genome size of Salmonella is smaller than that found for other genera, reflecting a less open pan-genome for Salmonella.
Many of the previously characterized pathogenicity islands in Salmonella were found throughout all genomes within Salmonella subsp. enterica, with notable exceptions such as SPI-6 and SPI-7 found only in serovar S. Typhi; SPI-3 seems to exist in several similar but distinct versions. The presence of these rare SPIs undoubtedly plays a substantial role in giving the host genomes their characteristic phenotypes. Further studies into the importance of these SPIs for host-specificity/preference of different serovars are needed.
In addition to the Salmonella-specific genomic islands (SPIs), there are other genome islands in Salmonella genomes, which are also found in other organisms. Many of these appear to be of viral origin, and are strain specific. Compared to E. coli, the pan-genome of Salmonella genome seems fairly static, and genomic islands, in particular SPIs could represent an important avenue for the evolution of the Salmonella genus.
Electronic Supplementary Material
While the differences between the three plots generally are minor, it should be evident that EasyGene has problems with sttsp. arthome and species bongori, probably the result of the methods reliance on a pre-calculated model. Comparing the Prodigal predictions to the pre-calculated annotation, there is the obvious difference that not all genomes have pre-calculated annotation, but the Prodigal predictions also correlate slightly better with serotype.
Pan- and core genome plot using pre-annotated features (Plot only displays those genomes which had pre-calculated annotations). (PDF 11.8 kb)
Pan-and core genome plot using EasyGene predictions. (PDF 11.8 kb)
Pan- and core genome plot using Prodigal predictions (Essentially the same as Figure 3 in main publication). (PDF 11.8 kb)
All genes from all genomes. (FSA 65.5 mb)
Genes unique to given serotypes (Data taken from Figure 4). (FSA 3.47 mb)
Complete nucleotide sequence of each island. (FSA 278 kb)
Prodigal predicted features within islands. (FSA 465 kb)
Corrplete nucleotide sequence of each island. (FSA 62 kb)
Prodiqal predicted features within islands. (FSA 72 kb)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the sequencing centers mentioned in Table 1 for kindly providing their data and making it available for use in comparative genomic studies. This work was supported by grants from the Danish Center for Scientific Computing, as well as grant 09-067103/DSF from the Danish Council for Strategic Research, and by grant 3304-FVFP-08- from the Danish Food Industry Agency.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
References
- 1.Grimont PAD, Weill F-X. Antigenic formulae of the Salmonella serovars. 9. Paris, France: WHO Collaborating Center for Reference and Research on Salmonella. Institut Pasteur; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 2.CDC . Salmonella surveillance: annual summary, 2006. Atlanta: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Guibourdenche M, Roggentin P, Mikoleit M, Fields PI, Bockemuhl J, Grimont PA, Weill FX. Supplement 2003–2007 (No. 47) to the White-Kauffmann-Le Minor scheme. Res Microbiol. 2010;161:26–29. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2009.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.McClelland M, Sanderson KE, Spieth J, Clifton SW, Latreille P, Courtney L, Porwollik S, Ali J, Dante M, Du F, Hou S, Layman D, Leonard S, Nguyen C, Scott K, Holmes A, Grewal N, Mulvaney E, Ryan E, Sun H, Florea L, Miller W, Stoneking T, Nhan M, Waterston R, Wilson RK. Complete genome sequence of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium LT2. Nature. 2001;413:852–856. doi: 10.1038/35101614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Thomson NR, Clayton DJ, Windhorst D, Vernikos G, Davidson S, Churcher C, Quail MA, Stevens M, Jones MA, Watson M, Barron A, Layton A, Pickard D, Kingsley RA, Bignell A, Clark L, Harris B, Ormond D, Abdellah Z, Brooks K, Cherevach I, Chillingworth T, Woodward J, Norberczak H, Lord A, Arrowsmith C, Jagels K, Moule S, Mungall K, Sanders M, Whitehead S, Chabalgoity JA, Maskell D, Humphrey T, Roberts M, Barrow PA, Dougan G, Parkhill J. Comparative genome analysis of Salmonella Enteritidis PT4 and Salmonella Gallinarum 287/91 provides insights into evolutionary and host adaptation pathways. Genome Res. 2008;18:1624–1637. doi: 10.1101/gr.077404.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Holt KE, Thomson NR, Wain J, Langridge GC, Hasan R, Bhutta ZA, Quail MA, Norbertczak H, Walker D, Simmonds M, White B, Bason N, Mungall K, Dougan G, Parkhill J. Pseudogene accumulation in the evolutionary histories of Salmonella enterica serovars Paratyphi A and Typhi. BMC Genomics. 2009;10:36. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ikumapayi UN, Antonio M, Sonne-Hansen J, Biney E, Enwere G, Okoko B, Oluwalana C, Vaughan A, Zaman SM, Greenwood BM, Cutts FT, Adegbola RA. Molecular epidemiology of community-acquired invasive non-typhoidal Salmonella among children aged 2–29 months in rural Gambia and discovery of a new serovar, Salmonella enterica Dingiri. J Med Microbiol. 2007;56:1479–1484. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.47416-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cohen JI, Bartlett JA, Corey GR. Extra-intestinal manifestations of salmonella infections. Medicine (Baltimore) 1987;66:349–388. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198709000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sirichote P, Hasman H, Pulsrikarn C, Schonheyder HC, Samulioniene J, Pornruangmong S, Bangtrakulnonth A, Aarestrup FM, Hendriksen RS. Molecular characterization of extended-spectrum cephalosporinase-producing Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis isolates from patients in Thailand and Denmark. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48:883–888. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01792-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Grassl GA, Finlay BB. Pathogenesis of enteric Salmonella infections. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2008;24:22–26. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0b013e3282f21388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Haraga A, Ohlson MB, Miller SI. Salmonellae interplay with host cells. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008;6:53–66. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Tsolis RM, Young GM, Solnick JV, Baumler AJ. From bench to bedside: stealth of enteroinvasive pathogens. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008;6:883–892. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kingsley RA, Msefula CL, Thomson NR, Kariuki S, Holt KE, Gordon MA, Harris D, Clarke L, Whitehead S, Sangal V, Marsh K, Achtman M, Molyneux ME, Cormican M, Parkhill J, MacLennan CA, Heyderman RS, Dougan G. Epidemic multiple drug resistant Salmonella Typhimurium causing invasive disease in sub-Saharan Africa have a distinct genotype. Genome Res. 2009;19:2279–2287. doi: 10.1101/gr.091017.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sabbagh SC, Forest CG, Lepage C, Leclerc JM, Daigle F. So similar, yet so different: uncovering distinctive features in the genomes of Salmonella enterica serovars Typhimurium and Typhi. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2010;305:1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2010.01904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Haneda T, Ishii Y, Danbara H, Okada N. Genome-wide identification of novel genomic islands that contribute to Salmonella virulence in mouse systemic infection. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009;297:241–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01686.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ochman H, Lawrence JG, Groisman EA. Lateral gene transfer and the nature of bacterial innovation. Nature. 2000;405:299–304. doi: 10.1038/35012500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hensel M. Evolution of pathogenicity islands of Salmonella enterica. Int J Med Microbiol. 2004;294:95–102. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2004.06.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.McClelland M, Sanderson KE, Clifton SW, Latreille P, Porwollik S, Sabo A, Meyer R, Bieri T, Ozersky P, McLellan M, Harkins CR, Wang C, Nguyen C, Berghoff A, Elliott G, Kohlberg S, Strong C, Du F, Carter J, Kremizki C, Layman D, Leonard S, Sun H, Fulton L, Nash W, Miner T, Minx P, Delehaunty K, Fronick C, Magrini V, Nhan M, Warren W, Florea L, Spieth J, Wilson RK. Comparison of genome degradation in Paratyphi A and Typhi, human-restricted serovars of Salmonella enterica that cause typhoid. Nat Genet. 2004;36:1268–1274. doi: 10.1038/ng1470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Parkhill J, Dougan G, James KD, Thomson NR, Pickard D, Wain J, Churcher C, Mungall KL, Bentley SD, Holden MT, Sebaihia M, Baker S, Basham D, Brooks K, Chillingworth T, Connerton P, Cronin A, Davis P, Davies RM, Dowd L, White N, Farrar J, Feltwell T, Hamlin N, Haque A, Hien TT, Holroyd S, Jagels K, Krogh A, Larsen TS, Leather S, Moule S, O'Gaora P, Parry C, Quail M, Rutherford K, Simmonds M, Skelton J, Stevens K, Whitehead S, Barrell BG. Complete genome sequence of a multiple drug resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi CT18. Nature. 2001;413:848–852. doi: 10.1038/35101607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Marcus SL, Brumell JH, Pfeifer CG, Finlay BB. Salmonella pathogenicity islands: big virulence in small packages. Microbes Infect. 2000;2:145–156. doi: 10.1016/S1286-4579(00)00273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Benson DA, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Lipman DJ, Ostell J, Sayers EW. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:D46–D51. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sanger Center (2010) Salmonella. http://www.sanger.ac.uk/resources/downloads/bacteria/salmonella. html. Accessed 5 August 2010
- 23.Larsen TS, Krogh A. EasyGene—a prokaryotic gene finder that ranks ORFs by statistical significance. BMC Bioinform. 2003;4:21. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-4-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nielsen P, Krogh A. Large-scale prokaryotic gene prediction and comparison to genome annotation. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:4322–4329. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hyatt D, Chen GL, Locascio PF, Land ML, Larimer FW, Hauser LJ. Prodigal: prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 2010;11:119. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rodland EA, Staerfeldt HH, Rognes T, Ussery DW. RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:3100–3108. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:2947–2948. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Perriere G, Gouy M. WWW-query: an on-line retrieval system for biological sequence banks. Biochimie. 1996;78:364–369. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(96)84768-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tettelin H, Masignani V, Cieslewicz MJ, Donati C, Medini D, Ward NL, Angiuoli SV, Crabtree J, Jones AL, Durkin AS, Deboy RT, Davidsen TM, Mora M, Scarselli M, Ros I, Peterson JD, Hauser CR, Sundaram JP, Nelson WC, Madupu R, Brinkac LM, Dodson RJ, Rosovitz MJ, Sullivan SA, Daugherty SC, Haft DH, Selengut J, Gwinn ML, Zhou L, Zafar N, Khouri H, Radune D, Dimitrov G, Watkins K, O'Connor KJ, Smith S, Utterback TR, White O, Rubens CE, Grandi G, Madoff LC, Kasper DL, Telford JL, Wessels MR, Rappuoli R, Fraser CM. Genome analysis of multiple pathogenic isolates of Streptococcus agalactiae: implications for the microbial "pan-genome". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:13950–13955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506758102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lukjancenko O, Wassenaar TM, Ussery DW. Comparison of 61 sequenced Escherichia coli genomes. Microb Ecol. 2010;60:708–720. doi: 10.1007/s00248-010-9717-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Vesth T, Wassenaar TM, Hallin PF, Snipen L, Lagesen K, Ussery DW. On the origins of a Vibrio species. Microb Ecol. 2010;59:1–13. doi: 10.1007/s00248-009-9596-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Karlsson FH, Ussery DW, Nielsen J, Nookaew I. A closer look at Bacteroides: phylogenetic relationship and genomic implications of a life in the human gut. Microb Ecol. 2011;61:473–485. doi: 10.1007/s00248-010-9796-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Binnewies TT, Hallin PF, Staerfeldt HH, Ussery DW. Genome update: proteome comparisons. Microbiology. 2005;151:1–4. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27760-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Snipen L, Almoy T, Ussery DW. Microbial comparative pan-genomics using binomial mixture models. BMC Genomics. 2009;10:385. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Snipen L, Ussery DW. Standard operating procedure for computing pangenome trees. Standards in Genomic Science. 2010;2:135–141. doi: 10.4056/sigs.38923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hallin PF, Binnewies TT, Ussery DW. The genome BLASTatlas—a GeneWiz extension for visualization of whole-genome homology. Mol Biosyst. 2008;4:363–371. doi: 10.1039/b717118h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Jensen LJ, Friis C, Ussery DW. Three views of microbial genomes. Res Microbiol. 1999;150:773–777. doi: 10.1016/S0923-2508(99)00116-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Pedersen AG, Jensen LJ, Brunak S, Staerfeldt HH, Ussery DW. A DNA structural atlas for Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 2000;299:907–930. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ussery DW, Wassenaar T, Borini S. Computing for comparative microbial genomics. London: Springer; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Yoon SH, Park YK, Lee S, Choi D, Oh TK, Hur CG, Kim JF. Towards pathogenomics: a web-based resource for pathogenicity islands. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:D395–D400. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.R Development Core Team . R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Chain PS, Grafham DV, Fulton RS, Fitzgerald MG, Hostetler J, Muzny D, Ali J, Birren B, Bruce DC, Buhay C, Cole JR, Ding Y, Dugan S, Field D, Garrity GM, Gibbs R, Graves T, Han CS, Harrison SH, Highlander S, Hugenholtz P, Khouri HM, Kodira CD, Kolker E, Kyrpides NC, Lang D, Lapidus A, Malfatti SA, Markowitz V, Metha T, Nelson KE, Parkhill J, Pitluck S, Qin X, Read TD, Schmutz J, Sozhamannan S, Sterk P, Strausberg RL, Sutton G, Thomson NR, Tiedje JM, Weinstock G, Wollam A, Detter JC. Genomics. Genome project standards in a new era of sequencing. Science. 2009;326:236–237. doi: 10.1126/science.1180614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zamperini K, Soni V, Waltman D, Sanchez S, Theriault EC, Bray J, Maurer JJ. Molecular characterization reveals Salmonella enterica serovar 4,[5],12:i:- from poultry is a variant Typhimurium serovar. Avian Dis. 2007;51:958–964. doi: 10.1637/7944-021507-REGR.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hopkins KL, Kirchner M, Guerra B, Granier SA, Lucarelli C, Porrero MC, Jakubczak A, Threlfall EJ, Mevius DJ. Multiresistant Salmonella enterica serovar 4,[5],12:i:- in Europe: a new pandemic strain? Euro Surveill. 2010;15:19580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Echeita MA, Herrera S, Usera MA. Atypical, fljB-negative Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica strain of serovar 4,5,12:i:- appears to be a monophasic variant of serovar Typhimurium. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39:2981–2983. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.8.2981-2983.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Fukushima M, Kakinuma K, Kawaguchi R. Phylogenetic analysis of Salmonella, Shigella, and Escherichia coli strains on the basis of the gyrB gene sequence. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40:2779–2785. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.8.2779-2785.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Reeves MW, Evins GM, Heiba AA, Plikaytis BD, Farmer JJ., III Clonal nature of Salmonella typhi and its genetic relatedness to other salmonellae as shown by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis, and proposal of Salmonella bongori comb. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 1989;27:313–320. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.313-320.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Boyd EF, Wang FS, Whittam TS, Selander RK. Molecular genetic relationships of the salmonellae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1996;62:804–808. doi: 10.1128/aem.62.3.804-808.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Porwollik S, Wong RM, McClelland M. Evolutionary genomics of Salmonella: gene acquisitions revealed by microarray analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:8956–8961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.122153699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.McQuiston JR, Herrera-Leon S, Wertheim BC, Doyle J, Fields PI, Tauxe RV, Logsdon JM., Jr Molecular phylogeny of the salmonellae: relationships among Salmonella species and subspecies determined from four housekeeping genes and evidence of lateral gene transfer events. J Bacteriol. 2008;190:7060–7067. doi: 10.1128/JB.01552-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Liu WQ, Feng Y, Wang Y, Zou QH, Chen F, Guo JT, Peng YH, Jin Y, Li YG, Hu SN, Johnston RN, Liu GR, Liu SL. Salmonella paratyphi C: genetic divergence from Salmonella choleraesuis and pathogenic convergence with Salmonella typhi. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e4510. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Abby S, Daubin V. Comparative genomics and the evolution of prokaryotes. Trends Microbiol. 2007;15:135–141. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2007.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Tettelin H, Riley D, Cattuto C, Medini D. Comparative genomics: the bacterial pan-genome. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2008;11:472–477. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2008.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Touchon M, Hoede C, Tenaillon O, Barbe V, Baeriswyl S, Bidet P, Bingen E, Bonacorsi S, Bouchier C, Bouvet O, Calteau A, Chiapello H, Clermont O, Cruveiller S, Danchin A, Diard M, Dossat C, Karoui ME, Frapy E, Garry L, Ghigo JM, Gilles AM, Johnson J, Le BC, Lescat M, Mangenot S, Martinez-Jehanne V, Matic I, Nassif X, Oztas S, Petit MA, Pichon C, Rouy Z, Ruf CS, Schneider D, Tourret J, Vacherie B, Vallenet D, Medigue C, Rocha EP, Denamur E. Organised genome dynamics in the Escherichia coli species results in highly diverse adaptive paths. PLoS Genet. 2009;5:e1000344. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Friis C, Wassenaar TM, Javed MA, Snipen L, Lagesen K, Hallin PF, Newell DG, Toszeghy M, Ridley A, Manning G, Ussery DW. Genomic characterization of Campylobacter jejuni strain M1. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e12253. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.den Bakker HC, Cummings CA, Ferreira V, Vatta P, Orsi RH, Degoricija L, Barker M, Petrauskene O, Furtado MR, Wiedmann M. Comparative genomics of the bacterial genus Listeria: Genome evolution is characterized by limited gene acquisition and limited gene loss. BMC Genomics. 2010;11:688. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Deng W, Liou SR, Plunkett G, III, Mayhew GF, Rose DJ, Burland V, Kodoyianni V, Schwartz DC, Blattner FR. Comparative genomics of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi strains Ty2 and CT18. J Bacteriol. 2003;185:2330–2337. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.7.2330-2337.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Liu WQ, Liu GR, Li JQ, Xu GM, Qi D, He XY, Deng J, Zhang FM, Johnston RN, Liu SL. Diverse genome structures of Salmonella paratyphi C. BMC Genomics. 2007;8:290. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Morris C, Tam CK, Wallis TS, Jones PW, Hackett J. Salmonella enterica serovar Dublin strains which are Vi antigen-positive use type IVB pili for bacterial self-association and human intestinal cell entry. Microb Pathog. 2003;35:279–284. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2003.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Pickard D, Wain J, Baker S, Line A, Chohan S, Fookes M, Barron A, Gaora PO, Chabalgoity JA, Thanky N, Scholes C, Thomson N, Quail M, Parkhill J, Dougan G. Composition, acquisition, and distribution of the Vi exopolysaccharide-encoding Salmonella enterica pathogenicity island SPI-7. J Bacteriol. 2003;185:5055–5065. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.17.5055-5065.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Brumell JH, Rosenberger CM, Gotto GT, Marcus SL, Finlay BB. SifA permits survival and replication of Salmonella typhimurium in murine macrophages. Cell Microbiol. 2001;3:75–84. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.2001.00087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Ochman H, Soncini FC, Solomon F, Groisman EA. Identification of a pathogenicity island required for Salmonella survival in host cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:7800–7804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.15.7800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Forest CG, Ferraro E, Sabbagh SC, Daigle F. Intracellular survival of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi in human macrophages is independent of Salmonella pathogenicity island (SPI)-2. Microbiology. 2010;156:3689–3698. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.041624-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Blanc-Potard AB, Solomon F, Kayser J, Groisman EA. The SPI-3 pathogenicity island of Salmonella enterica. J Bacteriol. 1999;181:998–1004. doi: 10.1128/jb.181.3.998-1004.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Morgan E, Bowen AJ, Carnell SC, Wallis TS, Stevens MP. SiiE is secreted by the Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium pathogenicity island 4-encoded secretion system and contributes to intestinal colonization in cattle. Infect Immun. 2007;75:1524–1533. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01438-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Gerlach RG, Jackel D, Stecher B, Wagner C, Lupas A, Hardt WD, Hensel M. Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 4 encodes a giant non-fimbrial adhesin and the cognate type 1 secretion system. Cell Microbiol. 2007;9:1834–1850. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.00919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Galyov EE, Wood MW, Rosqvist R, Mullan PB, Watson PR, Hedges S, Wallis TS. A secreted effector protein of Salmonella dublin is translocated into eukaryotic cells and mediates inflammation and fluid secretion in infected ileal mucosa. Mol Microbiol. 1997;25:903–912. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1997.mmi525.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Chiu CH, Tang P, Chu C, Hu S, Bao Q, Yu J, Chou YY, Wang HS, Lee YS. The genome sequence of Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis, a highly invasive and resistant zoonotic pathogen. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:1690–1698. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Fricke WF, McDermott PF, Mammel MK, Zhao S, Johnson TJ, Rasko DA, Fedorka-Cray PJ, Pedroso A, Whichard JM, Leclerc JE, White DG, Cebula TA, Ravel J. Antimicrobial resistance-conferring plasmids with similarity to virulence plasmids from avian pathogenic Escherichia coli strains in Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky isolates from poultry. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009;75:5963–5971. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00786-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Durfee T, Nelson R, Baldwin S, Plunkett G, III, Burland V, Mau B, Petrosino JF, Qin X, Muzny DM, Ayele M, Gibbs RA, Csorgo B, Posfai G, Weinstock GM, Blattner FR. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli DH10B: insights into the biology of a laboratory workhorse. J Bacteriol. 2008;190:2597–2606. doi: 10.1128/JB.01695-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Johnson TJ, Kariyawasam S, Wannemuehler Y, Mangiamele P, Johnson SJ, Doetkott C, Skyberg JA, Lynne AM, Johnson JR, Nolan LK. The genome sequence of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli strain O1:K1:H7 shares strong similarities with human extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli genomes. J Bacteriol. 2007;189:3228–3236. doi: 10.1128/JB.01726-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Jarvik T, Smillie C, Groisman EA, Ochman H. Short-term signatures of evolutionary change in the Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium 14028 genome. J Bacteriol. 2010;192:560–567. doi: 10.1128/JB.01233-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Pan- and core genome plot using pre-annotated features (Plot only displays those genomes which had pre-calculated annotations). (PDF 11.8 kb)
Pan-and core genome plot using EasyGene predictions. (PDF 11.8 kb)
Pan- and core genome plot using Prodigal predictions (Essentially the same as Figure 3 in main publication). (PDF 11.8 kb)
All genes from all genomes. (FSA 65.5 mb)
Genes unique to given serotypes (Data taken from Figure 4). (FSA 3.47 mb)
Complete nucleotide sequence of each island. (FSA 278 kb)
Prodigal predicted features within islands. (FSA 465 kb)
Corrplete nucleotide sequence of each island. (FSA 62 kb)
Prodiqal predicted features within islands. (FSA 72 kb)