Abstract
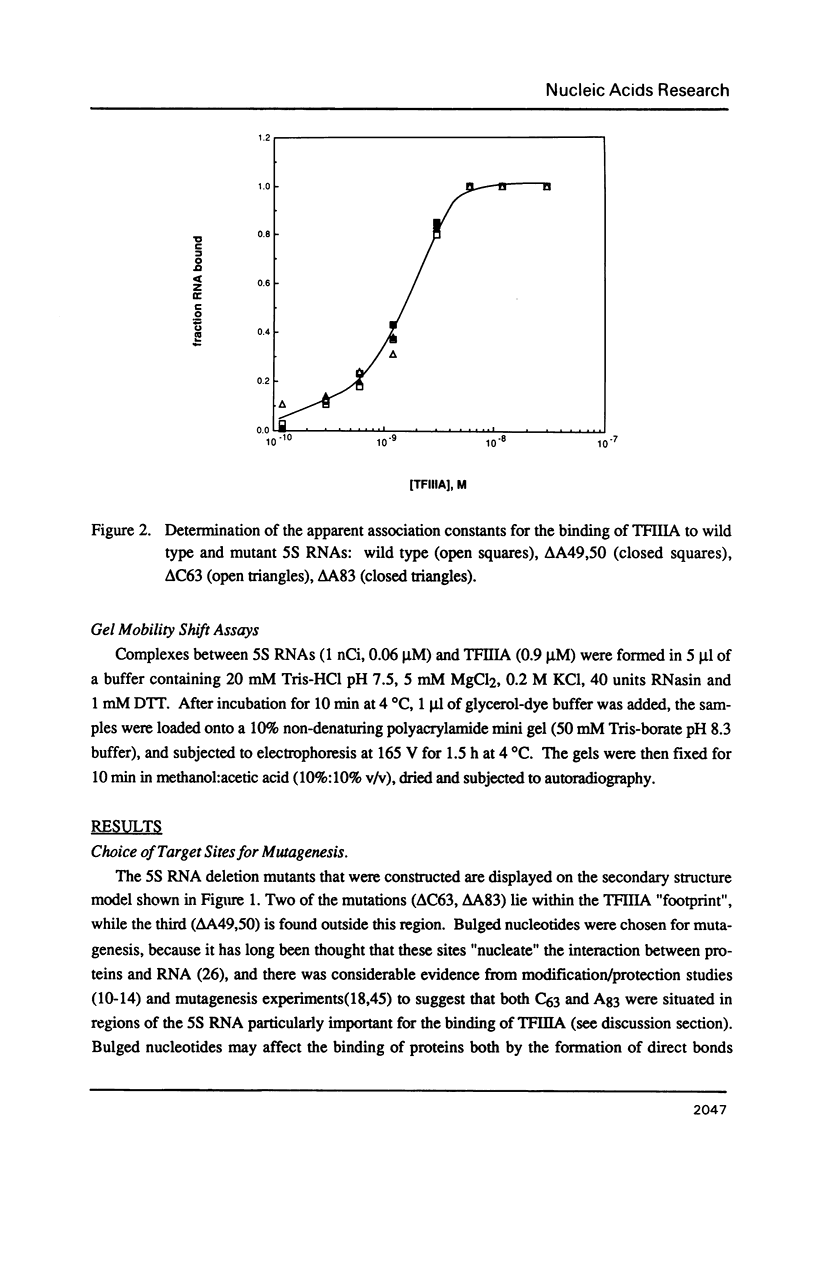
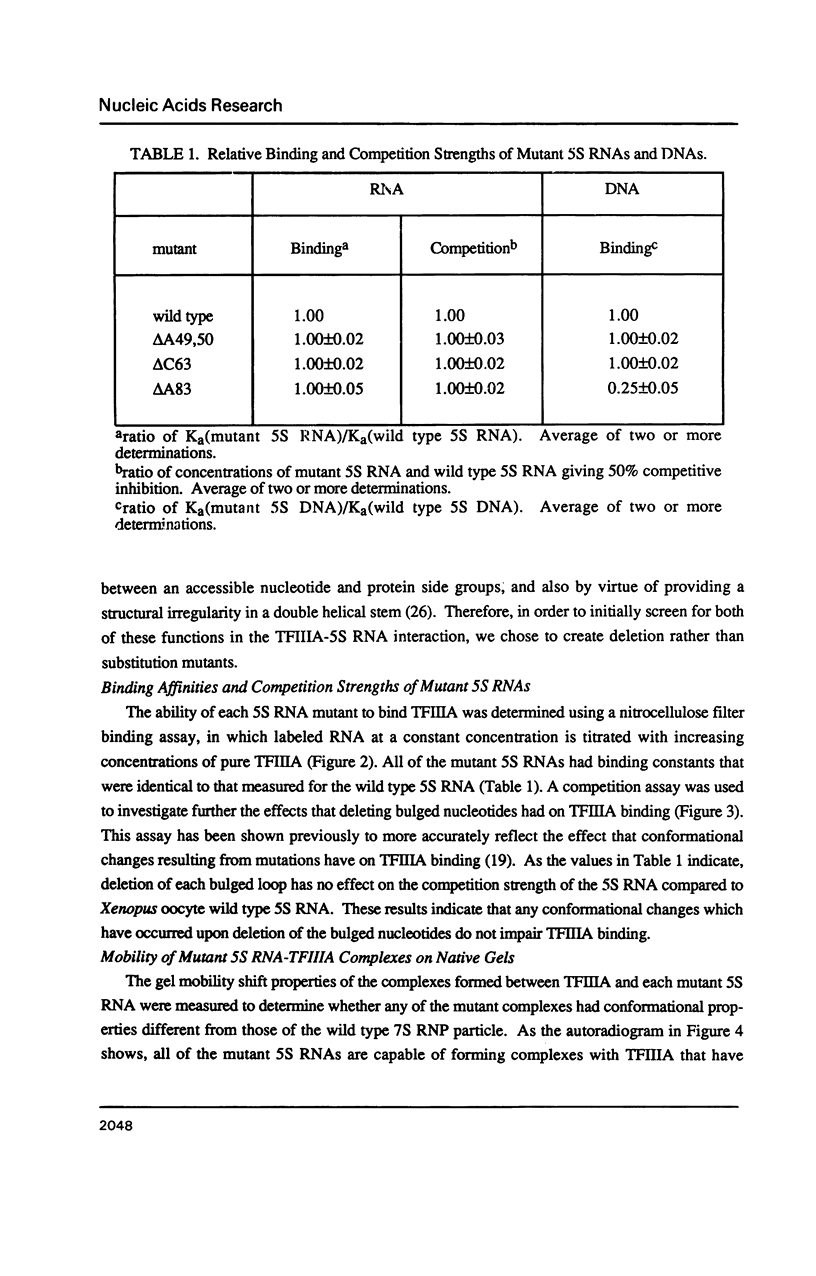
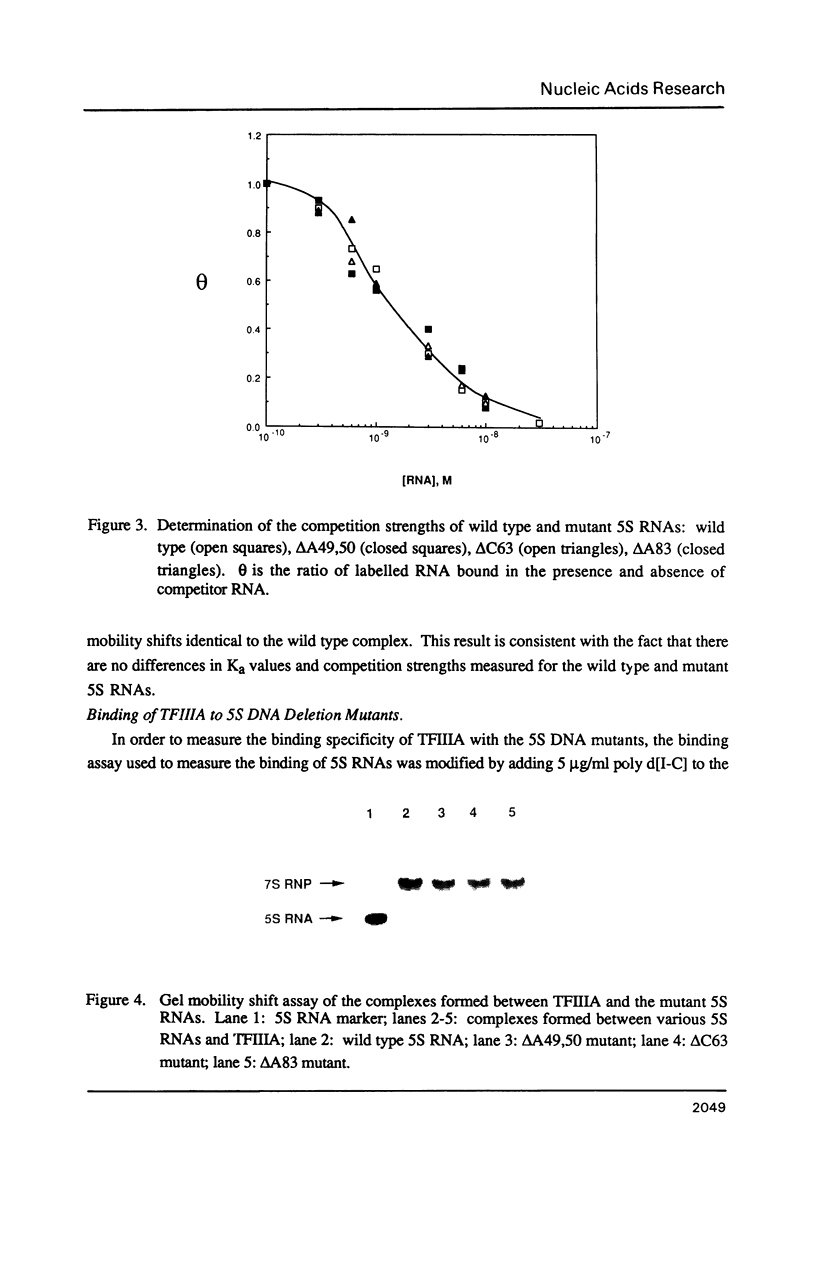
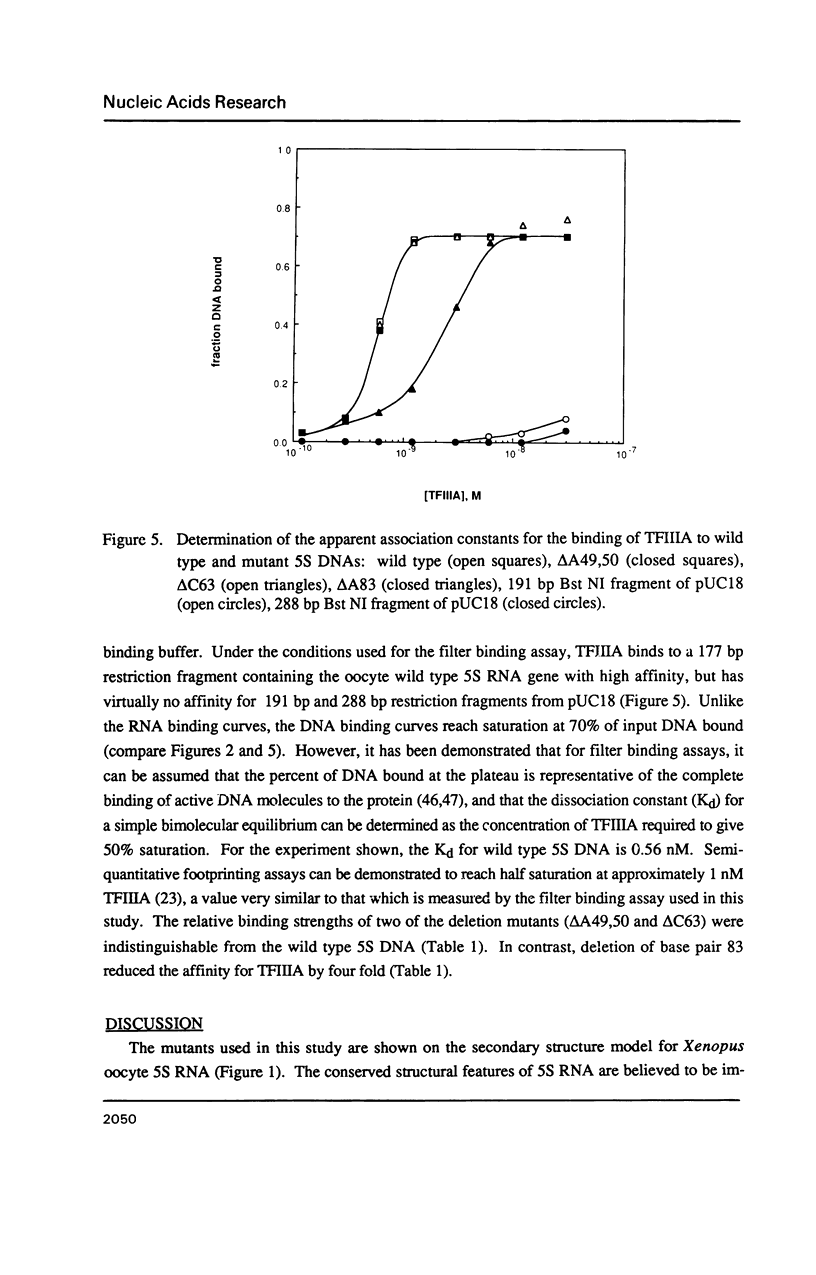
Individual bulge loops present in Xenopus 5S RNA (positions 49A-A50 in helix III, C63 in helix II and A83 in helix IV), were deleted by site directed mutagenesis. The interaction of these mutant 5S RNA molecules with TFIIIA was measured by a direct binding assay and a competition assay. The results of these experiments show that none of the bulged nucleotides in Xenopus 5S RNA are required for the binding of TFIIIA. The affinity of the mutant 5S RNA genes for TFIIIA was also studied by a filter binding assay. In contrast to the effect that deleting bulged nucleotides had on the TFIIIA-RNA binding affinity, deletion of the corresponding A-T base pair at position +83 in 5S DNA was found to reduce the apparent association constant of TFIIIA by a factor of four-fold.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen J., Delihas N. Characterization of RNA-protein interactions in 7 S ribonucleoprotein particles from Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2912–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen J., Delihas N., Hanas J. S., Wu C. W. 5S RNA structure and interaction with transcription factor A. 1. Ribonuclease probe of the structure of 5S RNA from Xenopus laevis oocytes. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5752–5759. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen J., Delihas N., Hanas J. S., Wu C. W. 5S RNA structure and interaction with transcription factor A. 2. Ribonuclease probe of the 7S particle from Xenopus laevis immature oocytes and RNA exchange properties of the 7S particle. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5759–5766. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. E., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. A phage repressor-operator complex at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):596–601. doi: 10.1038/316596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F. The intragenic control region of the Xenopus 5 S RNA gene contains two factor A binding domains that must be aligned properly for efficient transcription initiation. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6466–6471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Sander C., Argos P. The primary structure of transcription factor TFIIIA has 12 consecutive repeats. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 8;186(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80723-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen J., Brown R. S., Sproat B. S., Garrett R. A. Xenopus transcription factor IIIA binds primarily at junctions between double helical stems and internal loops in oocyte 5S RNA. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):453–460. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04775.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen J., Douthwaite S. R., Christensen A., Garrett R. A. Does unpaired adenosine-66 from helix II of Escherichia coli 5S RNA bind to protein L18? EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1019–1024. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03733.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davanloo P., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Cloning and expression of the gene for bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2035–2039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delihas N., Andersen J. Generalized structures of the 5S ribosomal RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7323–7344. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. J., Duncan A. M., Simpson N. E., White B. N. Three RFLPs recognized by an anonymous sequence localized to 21q11.2 [HGM8 D21S72]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 27;14(10):4375–4375. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.10.4375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu C. W. Binding of Xenopus transcription factor A to 5S RNA and to single stranded DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2745–2758. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu C. W. Cooperative model for the binding of Xenopus transcription factor A to the 5S RNA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2142–2145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber P. W., Wool I. G. Identification of the binding site on 5S rRNA for the transcription factor IIIA: proposed structure of a common binding site on 5S rRNA and on the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1593–1597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majowski K., Mentzel H., Pieler T. A split binding site for TFIIIC on the Xenopus 5S gene. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3057–3063. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier N., Göringer H. U., Kleuvers B., Scheibe U., Eberle J., Szymkowiak C., Zacharias M., Wagner R. The importance of individual nucleotides for the structure and function of rRNA molecules in E. coli. A mutagenesis study. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 11;204(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81392-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mougel M., Eyermann F., Westhof E., Romby P., Expert-Bezançon A., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Binding of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S8 to 16 S rRNA. A model for the interaction and the tertiary structure of the RNA binding site. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 5;198(1):91–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90460-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamaye K. L., Eckstein F. Inhibition of restriction endonuclease Nci I cleavage by phosphorothioate groups and its application to oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9679–9698. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A., Douthwaite S., Garrett R. A., Noller H. F. A "bulged" double helix in a RNA-protein contact site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7331–7335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., Wegnez M. Isolation of a 7S particle from Xenopus laevis oocytes: a 5S RNA-protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):241–245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Erdmann V. A., Appel B. Structural requirements for the interaction of 5S rRNA with the eukaryotic transcription factor IIIA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8393–8406. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Erdmann V. A. Isolation and characterization of a 7 S RNP particle from mature Xenopus laevis oocytes. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 4;157(2):283–287. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80562-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Hamm J., Roeder R. G. The 5S gene internal control region is composed of three distinct sequence elements, organized as two functional domains with variable spacing. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Oei S. L., Hamm J., Engelke U., Erdmann V. A. Functional domains of the Xenopus laevis 5S gene promoter. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3751–3756. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04144.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J. Characterization of the RNA binding properties of transcription factor IIIA of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5369–5387. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J., Lowary P., Wu H. N., Stormo G., Uhlenbeck O. C. RNA binding site of R17 coat protein. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 24;26(6):1563–1568. doi: 10.1021/bi00380a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J., de Stevenson I. L., Ehresmann C., Romby P., Ehresmann B. A comparison of the solution structures and conformational properties of the somatic and oocyte 5S rRNAs of Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2295–2312. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J., de Stevenson I. L., Wong H. H. Defining the binding site of Xenopus transcription factor IIIA on 5S RNA using truncated and chimeric 5S RNA molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2737–2755. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D. Contact points between a positive transcription factor and the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):395–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D., Engelke D., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. The binding of a transcription factor to deletion mutants of a 5S ribosomal RNA gene. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):665–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shang Z. G., Windsor W. T., Liao Y. D., Wu C. W. Purification of Xenopus transcription factor IIIA and 5 S RNA from 7 S ribonucleoprotein particle by ammonium sulfate precipitation. Anal Biochem. 1988 Jan;168(1):156–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Schmidt W., Cosstick R., Okruszek A., Eckstein F. The use of phosphorothioate-modified DNA in restriction enzyme reactions to prepare nicked DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8749–8764. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormington W. M., Bogenhagen D. F., Jordan E., Brown D. D. A quantitative assay for Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription in vitro. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):809–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. N., Uhlenbeck O. C. Role of a bulged A residue in a specific RNA-protein interaction. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8221–8227. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]