Abstract
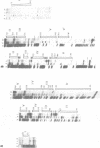
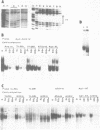
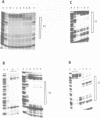
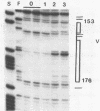
The identification of the binding sites for liver nuclear proteins present in the enhancer that control the cell specific transcription of the human apolipoprotein AII gene is reported. Five adjacent binding sites (motifs I to V) were identified. The motifs III, IV and V can be occupied differently by liver or HeLa nuclear proteins. Two hypersensitive zones (between motifs II-III and IV-V) are present only when liver nuclear extracts were tested. A first characterization of the factors reveal that motif IV interacts with the hepatic transcription factors Tf-LF1 (29) and LF-A1 (28, 30). A CCAAT binding protein, different from CTF/NF1, appears to bind to the motif II. The different binding sites share specific DNA sequences principally with 5' regulatory regions of other apolipoprotein genes.
Full text
PDF

















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. W., Schaefer E. J., Bronzert T. J., Lindgren F. T., Forte T., Starzl T. E., Niblack G. D., Zech L. A., Brewer H. B., Jr Transport of apolipoproteins A-I and A-II by human thoracic duct lymph. J Clin Invest. 1981 Mar;67(3):857–866. doi: 10.1172/JCI110103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisgaier C. L., Glickman R. M. Intestinal synthesis, secretion, and transport of lipoproteins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:625–636. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunel F., Ochoa A., Schaeffer E., Boissier F., Guillou Y., Cereghini S., Cohen G. N., Zakin M. M. Interactions of DNA-binding proteins with the 5' region of the human transferrin gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10180–10185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung M. C., Albers J. J. Distribution of high density lipoprotein particles with different apoprotein composition: particles with A-I and A-II and particles with A-I but no A-II. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jul;23(5):747–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das H. K., Leff T., Breslow J. L. Cell type-specific expression of the human apoB gene is controlled by two cis-acting regulatory regions. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11452–11458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein C., Halari M., Scanu A. M. On the mechanism of the displacement of apolipoprotein A-I by apolipoprotein A-II from the high density lipoprotein surface. Effect of concentration and molecular forms of apolipoprotein A-II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7189–7195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Walker D. W., Paik Y. K., Boguski M. S., Freeman M., Gordon J. I., Taylor J. M. Structure and expression of the human apolipoprotein A-IV gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):7973–7981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fager G., Wiklund O., Olofsson S. O., Wilhelmsen L., Bondjers G. Multivariate analyses of serum apolipoproteins and risk factors in relation to acute myocardial infarction. Arteriosclerosis. 1981 Jul-Aug;1(4):273–279. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.1.4.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A. The plasma lecithins:cholesterol acyltransferase reaction. J Lipid Res. 1968 Mar;9(2):155–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Budelier K. A., Sims H. F., Edelstein C., Scanu A. M., Strauss A. W. Biosynthesis of human preproapolipoprotein A-II. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):14054–14059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardon E. M., Frain M., Paonessa G., Cortese R. Two distinct factors interact with the promoter regions of several liver-specific genes. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1711–1719. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooft van Huijsduijnen R. A., Bollekens J., Dorn A., Benoist C., Mathis D. Properties of a CCAAT box-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7265–7282. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins B., Sharpe C. R., Baralle F. E., Graham C. F. Organ distribution of apolipoprotein gene transcripts in 6-12 week postfertilization human embryos. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1986 Sep;97:177–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn C. E., Osborne J. C., Jr, Schaefer E. J., Brewer H. B., Jr In vitro activation of the enzymic activity of hepatic lipase by apoA-II. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 31;131(2):366–368. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80405-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo M., Matsuzawa Y., Yokoyama S., Tajima S., Ishikawa K., Yamamoto A., Tarui S. Mechanism of inhibition of hepatic triglyceride lipase from human postheparin plasma by apolipoproteins A-I and A-II. J Biochem. 1982 Sep;92(3):865–870. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaci P., Nicosia A., Cortese R. Two different liver-specific factors stimulate in vitro transcription from the human alpha 1-antitrypsin promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2075–2087. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03047.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa A., Brunel F., Mendelzon D., Cohen G. N., Zakin M. M. Different liver nuclear proteins binds to similar DNA sequences in the 5' flanking regions of three hepatic genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):119–133. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with the insulin gene enhancer. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. F., Albers J. J., Cheung M. C., Bierman E. L. The effects of subfractions of high density lipoprotein on cholesterol efflux from cultured fibroblasts. Regulation of low density lipoprotein receptor activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8348–8356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paik Y. K., Chang D. J., Reardon C. A., Walker M. D., Taxman E., Taylor J. M. Identification and characterization of transcriptional regulatory regions associated with expression of the human apolipoprotein E gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13340–13349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilger E., Pristautz H., Pfeiffer K. P., Kostner G. Risk factors for peripheral atherosclerosis. Retrospective evaluation by stepwise discriminant analysis. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(1):57–63. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachmilewitz D., Albers J. J., Saunders D. R., Fainaru M. Apoprotein synthesis by human duodenojejunal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1978 Oct;75(4):677–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajavashisth T. B., Kaptein J. S., Reue K. L., Lusis A. J. Evolution of apolipoprotein E: mouse sequence and evidence for an 11-nucleotide ancestral unit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8085–8089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymondjean M., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. Several distinct "CCAAT" box binding proteins coexist in eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):757–761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reue K., Leff T., Breslow J. L. Human apolipoprotein CIII gene expression is regulated by positive and negative cis-acting elements and tissue-specific protein factors. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6857–6864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry K. N., Seedorf U., Karathanasis S. K. Different cis-acting DNA elements control expression of the human apolipoprotein AI gene in different cell types. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):605–614. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M., Lagocki P., Chung J. Effect of apolipoprotein A-II on the structure of high-density lipoproteins: relationship to the activity of lecithin:cholesterol acyl transferase in vitro. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;348:160–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb21298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Gruss P. Cell type-specific transcriptional enhancement in vitro requires the presence of trans-acting factors. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):3005–3013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelley C. S., Baralle F. E. Dual tissue-specific expression of apo-AII is directed by an upstream enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 11;15(9):3801–3821. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.9.3801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomiya M., Sasaki N., Barnhart R. L., Shirai K., Jackson R. L. Effect of apolipoproteins on the hepatic lipase-catalyzed hydrolysis of human plasma high density lipoprotein2-triacylglycerols. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 12;713(2):292–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. D., Melián A., Leff T., Breslow J. L. Expression of the human apolipoprotein E gene is regulated by multiple positive and negative elements. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8300–8308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei C. F., Tsao Y. K., Robberson D. L., Gotto A. M., Jr, Brown K., Chan L. The structure of the human apolipoprotein C-II gene. Electron microscopic analysis of RNA:DNA hybrids, complete nucleotide sequence, and identification of 5' homologous sequences among apolipoprotein genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15211–15221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]