This study provides the first evidence that monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1)–activated monocytes induce intracellular Ca2+ signaling and subsequent reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation that promotes RPE apoptosis and that cluster of differentiation 14 (CD14) and cyclic adenosine diphosphate ribose (cADPR) may contribute to these changes. Understanding the complex interactions among CD14, cADPR, Ca2+, and ROS may provide new insights and treatments of retinal diseases, including age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Abstract
Purpose.
The inflammatory response in age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is characterized by mononuclear leukocyte infiltration of the outer blood–retina barrier formed by the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). A key mechanistic element in AMD progression is RPE dysfunction and apoptotic cell loss. The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1–activated monocytes induce human RPE apoptosis and whether Ca2+ and reactive oxygen species (ROS) are involved in this process.
Methods.
A cell-based fluorometric assay was used to measure intracellular Ca2+ concentrations ([Ca2+]i) in RPE cells loaded with fluorescent Ca2+ indicator. Intracellular RPE ROS levels were measured by using the 5- and 6-chloromethyl-2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescence diacetate acetyl ester (CM-H2DCFDA) assay. RPE apoptosis was evaluated by activated caspase-3, Hoechst staining, and apoptosis ELISA.
Results.
MCP-1–activated human monocytes increased [Ca2+]i, ROS levels, and apoptosis in RPE cells, all of which were inhibited by 8-bromo-cyclic adenosine diphosphoribosyl ribose (8-Br-cADPR), an antagonist of cADPR. Although the ROS scavengers pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate (PDTC) and N-acetylcysteine (NAC) significantly inhibited ROS production and apoptosis induced by activated monocytes, they did not affect induced Ca2+ levels. The induced Ca2+ levels and apoptosis in RPE cells were inhibited by an antibody against cluster of differentiation antigen 14 (CD14), an adhesion molecule expressed by these cells.
Conclusions.
These results indicate that CD14, Ca2+, and ROS are involved in activated monocyte-induced RPE apoptosis and that cADPR contributes to these changes. Understanding the complex interactions among CD14, cADPR, Ca2+, and ROS may provide new insights and treatments of retinal diseases, including AMD.
The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), the key supportive retinal epithelium, is interposed between the outer retina and its choroidal blood supply as part of the blood–retina barrier. The RPE is believed to be a key participant in the development of age-related macular degeneration (AMD).1–5 RPE atrophy characterizes atrophic or dry AMD that may evolve to exudative or wet AMD. Mononuclear phagocyte infiltration of the outer blood–retina barrier has been linked to retinal diseases that are leading causes of blindness in the United States. These diseases include AMD, uveitis, endophthalmitis, proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR), and proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR).4,6–11 Previous studies have described RPE-to-mononuclear phagocyte contact and RPE apoptosis within AMD lesions4,12–16 and suggest an association between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and AMD.17–19 However, the mechanisms that underlie the development of AMD are poorly understood. As Ca2+ and ROS have been implicated in apoptosis in other systems,20–24 monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1)—the most potent monocyte chemoattractant and stimulator—is produced by RPE as well as retinal and choroidal microvascular endothelial cells, and activated mononuclear phagocytes induce RPE apoptosis,25,26 we hypothesized that MCP-1–activated monocytes induce RPE apoptosis and that Ca2+ and ROS are involved in apoptosis. In the present study, we provide evidence that MCP-1–activated monocytes induce intracellular Ca2+ signaling and subsequent ROS accumulation that promotes RPE apoptosis. We also show that this pathway may be mediated by activation of cyclic adenosine diphosphate ribose (cADPR), which is known to induce intracellular Ca2+ signaling, ROS accumulation, and apoptosis.27–33
Methods
Materials
Flasks (Falcon and Primaria) were purchased from Becton-Dickinson Inc. (Lincoln Park, NJ) and 35-mm glass-bottom culture dishes were purchased from MatTek Corporation (Ashland, MA). Separation media (Ficoll-Paque Plus and Fico/Lite-Monocytes) were purchased from Amersham Biotechnologies (Arlington Heights, IL) and Atlanta Biologics (Atlanta, GA), respectively. MCP-1 was purchased from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN). Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM)/F12, phenol red-free DMEM/F12, papain, Hoechst 33342, 8-bromo-cyclic adenosine diphosphoribosyl ribose (8-Br-cADPR), 1,2-bis(2-aminophenoxy) ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid tetrakis(acetoxymethyl ester) (BAPTA-AM), pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate (PDTC), N-acetylcysteine (NAC), and poly-d-lysine–coated 96-well plates were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). PBS, Hanks' balanced salt solutions (HBSS), Trizol reagent, and Taq DNA polymerase were obtained from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA). An assay kit (NucView 488 caspase-3 assay kit) was purchased from Biotium, Inc., Hayward, CA. A fluorescent Ca2+ indicator dye (Fura red-AM; acetoxymethyl ester) and 5- and 6-chloromethyl-2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescence diacetate, acetyl ester (CM-H2DCFDA) were purchased from Molecular Probes (Eugene, OR). A DNA removal kit (DNAfree) and a first-strand cDNA synthesis kit (RETROscript) were purchased from Ambion (Austin, TX). Oligonucleotides were synthesized by Integrated DNA Technologies, Inc. (Coralville, IA).
Human RPE Cell Culture
Human eyes from 17 donors 50–86 years of age were obtained from enucleation at the University of Michigan. Human RPE cells were isolated from donor eyes within 4 hours after enucleation by enzymatic digestion as previously described.34,35 The protocol adhered to the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki for the use of human tissue in research. In all experiments, simultaneous, parallel assays were performed on cultured human RPE cells between passages 2 and 6. At least three RPE cell lines from different donors were used for each set of experiments. For imaging experiments, RPE cells were seeded on 22 × 22 mm coverslips in 35-mm culture dishes or on 35-mm glass-bottom culture dishes and grown in phenol red-free complete medium for at least 4 days.
Monocytes and Treatment
Human peripheral monocytes were isolated as previously described.36 Human monocytic U937 cells were purchased from American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, MD) and cultured at 37°C with 5% CO2 in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated FBS, l-glutamine (2 mM), streptomycin (100 μg mL−1), and penicillin G (100 U mL−1). Freshly isolated human peripheral monocytes or cultured human monocytic U937 cells were preincubated with RPMI culture medium containing MCP-1 (40 ng/mL) for 24 hours before co-culturing with RPE monolayers. Functional blocking antibody against cluster of differentiation antigen 14 (CD14), which was characterized by our previous studies,25,37,38 was included in selected assays to antagonize the effects of MCP-1–activated monocytes.
Cell-Based Fluorometric Assay
Intracellular Ca2+ levels were quantitatively determined by a cell-based fluorometric assay using a fluorescent Ca2+ indicator (Fura red-AM). RPE cells grown on 96-well culture plates were incubated with the Ca2+ indicator (Fura red-AM; 10 μM) for 1.5 hours at 37°C in the dark, after which RPE cells were washed, and control medium, MCP-1, monocytes, or MCP-1–activated monocytes were added to RPE cells. The dye was excited at 420 nm and 480 nm, and the fluorescence emission was measured at 660 nm using a fluorometer (FlexStation Scanning Fluorometer; Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA). The fluorescence ratio (F420/F480) was used as a direct index of intracellular Ca2+ concentrations ([Ca 2+]i).
Measurement of Intracellular ROS Production
Intracellular ROS production by human RPE cells in response to monocytes was measured based on deacetylation and oxidation of nonfluorescent reduced CM-H2DCFDA into fluorescent CM-DCF as described previously.26,35
Detection of Activated Caspase-3
Activated caspase-3 was measured by a commercially available caspase-3 substrate assay kit (NucView 488; Biotium, Inc.) as previously described.26 In brief, after treatment, RPE-monocytes co-cultures were incubated with 5 μM caspase-3 substrate (NucView 488) in the dark for 30 minutes and washed once with HBSS/HEPES. The coverslips were mounted onto slides and the cell staining was observed under a fluorescence microscope using a FITC filter. The numbers of stained RPE (green) were scored as activated caspase-3–positive cells.
Hoechst 33342 Staining of Nuclei
After challenge, RPE cells were washed with HBSS/HEPES and then stained with the membrane-permeable and nuclear-specific fluorescent dye Hoechst 33342 (5 μg/mL in HBSS/HEPES) for 10 minutes in the dark at room temperature as described previously.26 After two HBSS/HEPES washes, the coverslips were mounted on microscope slides with HBSS/HEPES and immediately viewed in a microscope using a UV filter. The numbers of stained RPE that exhibited apoptotic nuclear condensation and fragmentation were scored as apoptotic.
Cell Death Detection ELISA
RPE apoptosis was also evaluated by DNA fragmentation as measured using a kit (Cell Death Detection ELISAPLUS kit; Roche Applied Science, Indianapolis, IN) following procedures outlined by the manufacturer.
Total RNA Isolation
Total RNA was isolated from cultured human RPE cells using reagent (Trizol; Invitrogen) following the manufacturer's instructions. The concentration of total RNA was measured by ultraviolet spectrophotometry.
RT-PCR Analysis
Total RNA was treated with DNase I (DNAfree) and reverse transcribed with random decamers using reverse transcriptase (RETROscript) as previously described.39 PCR was performed with cluster of differentiation 38 (CD38)-specific primers, with the forward primer sequence: 5′-TTG GGA ACT CAG ACC GTA CCT TG-3′ and the reverse primer sequence: 5′-CCA CAC CAT GTG AGG TCA TC-3′. The housekeeping gene hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase 1 (HPRT1) served as a control. The forward primer for HPRT1 was 5′ACCGTGTGTTAGAAAAGTAAGAAG-3′ and the reverse primer was: 5′-AGGGAACTGCTGACAAAGATTC-3′.40 The PCR products were generated by adding Taq DNA polymerase and cycled 40 times for CD38 or HPRT1 (1 minute at 94°C, 0.5 minute at 64°C, 0.5 minute at 72°C), followed by a 7-minute extension at 72°C. The RT-PCR products were separated by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis.
Statistical Analysis
Data are expressed as mean ± SE (SEM) and evaluated by unpaired Student's t-test or ANOVA followed by Newman-Keul's post test. P < 0.05 is considered statistically significant.
Results
MCP-1–Activated Monocytes Increase Ca2+ Levels in RPE Cells
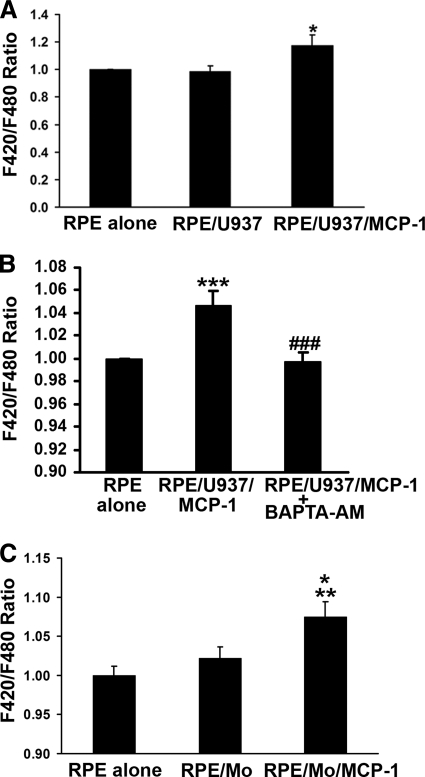
To examine the effects of MCP-1–activated monocytes on [Ca2+]i in RPE cells, confluent monolayers of RPE cells loaded with fluorescent Ca2+ indicator dye (Fura red-AM) were exposed to MCP-1–activated human monocytic U937 cells, and fluorescence ratio (F420/F480) of emissions was measured after excitation at 420 nm and 480 nm, as a direct index of [Ca2+]i of RPE cells. As shown at the right-hand side of Figure 1A, the MCP-1–activated U937 cells (40 ng/mL for 24 hours) mediated an increase in F420/F480 ratio compared to control (RPE alone) or RPE stimulated with unactivated U937 cells (RPE/U937) (n = 9; P < 0.05). To determine whether this increase in F420/F480 ratios was Ca2+ specific, RPE cells were pretreated with an intracellular Ca2+ chelator, BAPTA-AM, then exposed to MCP-1–activated U937 cells in the presence or absence of BAPTA-AM. As shown in Figure 1B, the heightened F420/F480 ratios were blocked by BAPTA-AM treatment. To determine whether this response was also observed using human monocytes, human peripheral blood monocytes were freshly isolated and activated with MCP-1 (40 ng/mL for 24 hours). Figure 1C shows that MCP-1–activated freshly isolated human monocytes also induced an increase in F420/F480 ratios in RPE cells. Unstimulated monocytes had no significant effect on the F420/F480 ratio in RPE cells (Fig. 1C).
Figure 1.
Activated monocytes stimulate Ca2+ signals in RPE cells. (A) RPE cells were preloaded with 10 μM fluorescent Ca2+ indicator dye (Fura red-AM; Molecular Probes), and fluorescence intensities were measured from RPE cells exposed to control medium (RPE alone), U937 cells (RPE/U937), or MCP-1–activated U937 cells (RPE/U937/MCP-1). (B) Fluorescent Ca2+ indicator dye–preloaded RPE cells were preincubated with or without 10 μM BAPTA-AM for 30 minutes, and then exposed to control medium (RPE alone) or MCP-1–activated U937 cells in the presence (RPE/U937/MCP-1+BAPTA-AM) or absence (RPE/U937/MCP-1) of BAPTA-AM. Fluorescence intensities were measured. (C) Fluorescent Ca2+ indicator dye–preloaded RPE cells were exposed to control medium (RPE alone), monocytes freshly isolated from human peripheral blood (RPE/Mo), or MCP-1–activated monocytes (RPE/Mo/MCP-1). Data represent the mean ± SEM (n = 3–20). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, compared to control or RPE/Mo; ###P < 0.001, compared to RPE/U937/MCP-1.
Activated Monocytes Induce ROS Accumulation in RPE Cells
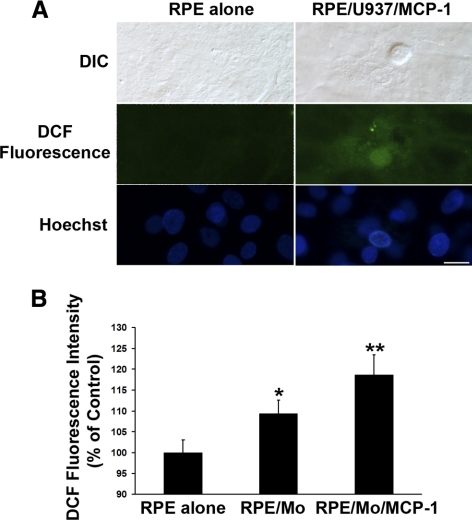
Previous studies have shown that Ca2+ signaling is required for ROS production.41–43 As ROS are involved in apoptosis21–24 and retinal degeneration,17–19 ROS production due to RPE exposure to activated monocytes was studied using the ROS-sensitive fluorescent dye CM-H2DCFDA. RPE cells were loaded with nonfluorescent CM-H2DCFDA that becomes fluorescent in the presence of ROS. As shown in Figure 2A, MCP-1–activated U937 cells promoted intracellular ROS accumulation in RPE cells. This result was confirmed using MCP-1–activated freshly isolated human monocytes in a second assay in which intracellular ROS levels were determined by monitoring DCF fluorescence with a fluorometer (FlexStation Scanning Fluorometer; Molecular Devices) (Fig. 2B). ROS-induced fluorescence levels in RPE cells exposed to monocytes (P < 0.05) or MCP-1–activated monocytes (P < 0.01) were significantly higher than those of control RPE cells (Fig. 2B).
Figure 2.
Activated monocytes induce ROS production in RPE cells. (A) RPE cells were preloaded with 5 μM CM-H2DCFDA, and then exposed to control medium (RPE alone), or MCP-1–activated U937 cells (RPE/U937/MCP-1) for 1 hour. Differential interference contrast (DIC) and fluorescence images of intracellular ROS deposition were displayed. Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) RPE cells were preloaded with 5 μM CM-H2DCFDA, and then exposed to control medium (RPE alone), monocytes (RPE/Mo), or MCP-1–activated monocytes (RPE/Mo/MCP-1) for 1 hour. Intracellular ROS production was measured with a fluorometer (FlexStation Scanning Fluorometer; Molecular Devices). Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared with RPE alone (control).
Activated Monocytes Provoke Apoptosis in RPE Cells
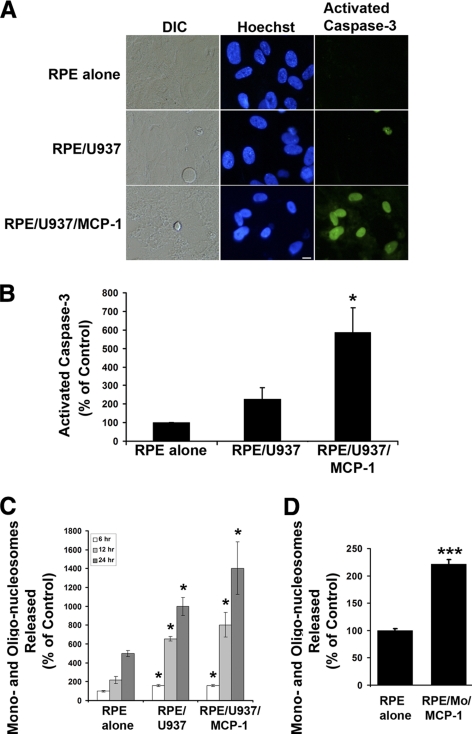
One potential important consequence of Ca2+ and ROS signaling is the induction of apoptosis, a key mechanism of RPE loss during AMD. Thus, we examined whether MCP-1–activated monocytes could induce RPE apoptosis. Figure 3A shows fluorescence images of cells stained with Hoechst 33342 and caspase-3 substrate (NucView 488; Biotium, Inc.). The Hoechst 33342 dye is a fluorescent indicator that binds specifically to the nuclear chromatin, which is traditionally used to monitor the apoptotic status of cells. As shown in the middle panel of Figure 3A, the RPE cells co-cultured with MCP-1–activated U937 cells had condensed nuclei, which is the hallmark of cells undergoing apoptosis. We stained RPE cells with propidium iodide and did not find propidium iodide–positive RPE cells under the same condition (data not shown), indicating that MCP-1–activated U937 cells induced RPE apoptosis rather than necrosis. In contrast, RPE cells exposed to control medium remained healthy with normal nuclear structure with no apparent chromatin condensation. We also confirmed our observations using a more specific activated caspase-3 assay (Fig. 3A, right panel). In this assay, caspase-3 substrate is cleaved by activated caspase-3 to release a high-affinity DNA dye that accumulates as a green nuclear stain. Thus, this assay is used to detect apoptotic cells containing activated caspase-3. Figure 3B quantifies the detection of apoptotic cells with activated caspase-3 and summarizes the results from four independent experiments. A significant increase in RPE apoptosis was observed when RPE monolayers were co-cultured with MCP-1–activated U937 cells. Treatment of RPE cells with activated U937 cells led to a sixfold increase in the number of activated caspase-3–positive RPE cells (Fig. 3B; P < 0.05). The RPE apoptosis, as measured by a third assay, cell death detection ELISA, was also significantly increased by U937 cells and MCP-1–activated U937 cells (Fig. 3C), or by MCP-1–activated freshly isolated human monocytes (Fig. 3D).
Figure 3.
Activated monocytes induce apoptosis in RPE cells. (A) Differential interference contrast (DIC) and fluorescence images of cells stained with Hoechst 33342 and caspase-3 substrate (NucView 488; Biotium, Inc.) in RPE cells exposed control medium (RPE alone), unstimulated U937 cells (RPE/U937), or MCP-1–activated U937 cells (RPE/U937/MCP-1). Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) A quantitative analysis of activated caspase-3–positive RPE cells. Activated caspase-3–positive RPE cells were determined after staining with caspase-3 substrate. (C) RPE cells were treated as described in (A) for 6, 12, and 24 hours. DNA fragmentation or released mono- and oligonucleosomes were measured by a cell death detection ELISA. (D) RPE cells were treated with MCP-1–activated freshly isolated human monocytes (RPE/Mo/MCP-1) for 24 hours. DNA fragmentation or released mono- and oligonucleosomes were measured by a cell death detection ELISA. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3–6). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, compared with RPE alone (control).
Effects of cADPR Antagonist on Activated Monocyte-Induced Ca2+ Levels, ROS Accumulation, and Apoptosis in RPE Cells
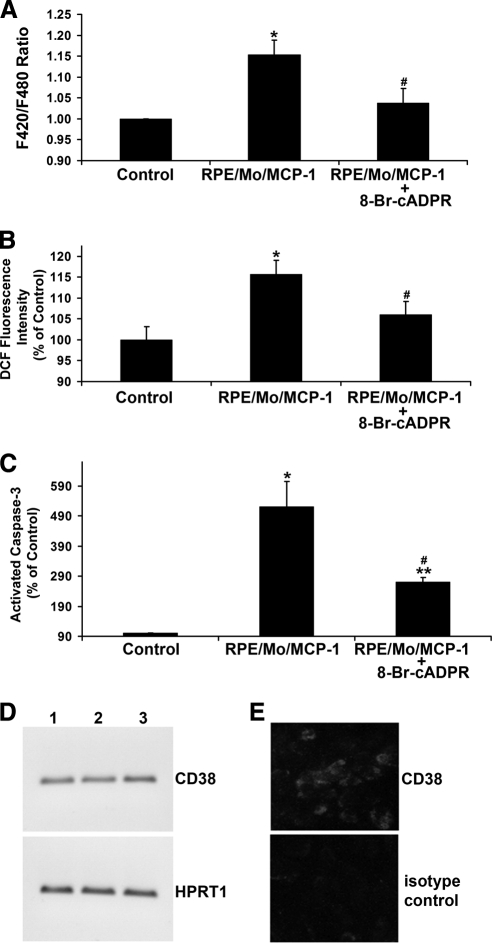
The results show that activated monocytes trigger RPE Ca2+ signaling, ROS generation and apoptosis (Figs. 1–3). There is increasing evidence that cADPR participates in Ca2+ signaling, ROS production, and apoptosis.27–33 To assess the potential role of cADPR in the activated monocyte-induced increase in RPE Ca2+, ROS, and apoptosis, first the effect of the cAPDR antagonist 8-Br-cAPDR on the activated monocyte-induced Ca2+ levels was tested. As shown in Figure 4A, exposure of RPE to activated monocytes increased F420/F480 ratios, indicating an increase in intracellular Ca2+ in RPE cells. Pretreatment of RPE with 8-Br-cAPDR inhibited this increase. Next the effect of 8-Br-cAPDR on activated monocyte-induced ROS production was examined. RPE pretreatment with 8-Br-cAPDR, which was effective in reducing activated monocyte-induced F420/F480 ratios (Fig. 4A), also inhibited ROS accumulation (Fig. 4B). The effect of 8-Br-cAPDR on the activated monocyte-induced RPE apoptosis was also examined. RPE pretreatment with 8-Br-cAPDR also inhibited activated monocyte-induced RPE apoptosis (Fig. 4C). CD38 cyclizes nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) to produce cADPR, and human monocytes express CD38.44 To examine whether human RPE could express CD38, RT-PCR analysis and immunofluorescence microscopy were performed. Both CD38 transcript (Fig. 4D) and protein (Fig. 4E) were expressed by human RPE cells. These parallel sets of observations in Figure 4 suggest that cADPR signaling may contribute to RPE apoptosis.
Figure 4.
Effects of cADPR antagonist on activated monocyte-induced RPE Ca2+ levels, ROS production, and apoptosis. (A) Fluorescent Ca2+ indicator–preloaded RPE cells were preincubated with or without cADPR antagonist 8-Br-cADPR for 30 minutes, and then exposed to control medium (Control) or MCP-1–activated monocytes (RPE/Mo/MCP-1) in the presence or absence of 8-Br-cADPR. (B) CM-H2DCFDA–prelabeled RPE cells were preincubated with or without 8-Br-cADPR for 30 minutes, and then exposed to control medium or MCP-1–activated monocytes in the presence or absence of 8-Br-cADPR. Fluorescence intensities were measured. (C) RPE cells were preincubated with or without cADPR inhibitor, 8-Br-cADPR, for 30 minutes, and then exposed to MCP-1–activated monocytes. After 6 hours, the number of cells with activated caspase-3 was determined after staining with caspase-3 substrate. (D) RT-PCR analysis of CD38 expression in human RPE cells. Total RNA isolated from human RPE cells was treated with DNase I and reverse transcribed (RT). PCR was performed using a primer set specific for CD38 or hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase 1 (HPRT1), which serves as an endogenous control or reference. Lanes 1 to 3 indicate RPE cells derived from three different donors. (E) Immunofluorescence labeling of CD38 in human RPE cells. Isotype-matched IgG2a serves as a control. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3–12). *P < 0.01, **P < 0.001, compared to control; #P < 0.05, compared to RPE/Mo/MCP-1 without 8-Br-cADPR.
Effects of ROS Inhibitors on Activated Monocyte-Induced Ca2+ Levels, ROS Accumulation, and Apoptosis in RPE Cells
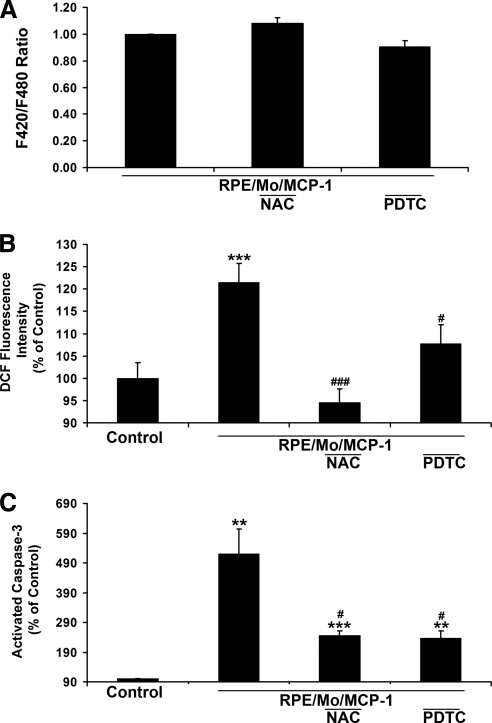
The effects of the ROS inhibitors PDTC and NAC on induced Ca2+ levels, ROS generation, and apoptosis in RPE cells were tested. PDTC and NAC did not significantly affect activated monocyte-induced Ca2+ levels (Fig. 5A), although RPE pretreatment with NAC and PDTC abolished and inhibited ROS generation, respectively (Fig. 5B). Pretreatment with PDTC and NAC, which were effective in the suppression of activated monocyte-increased ROS levels (Fig. 5B), inhibited activated monocyte-induced RPE apoptosis (Fig. 5C).
Figure 5.
Effects of ROS scavengers on activated monocyte-induced RPE Ca2+ levels, ROS production, and apoptosis. (A) Fluorescent Ca2+ indicator–preloaded RPE cells were preincubated with or without ROS scavenger, NAC, or PDTC for 30 minutes, and then exposed to MCP-1–activated monocytes in the presence or absence of NAC or PDTC. (B) CM-H2DCFDA-prelabeled RPE cells were preincubated with or without NAC or PDTC for 30 minutes, and then exposed to unstimulated monocytes (Control), MCP-1–activated monocytes in the presence or absence of NAC or PDTC. Fluorescence intensities were measured. (C) RPE cells were preincubated with or without ROS scavenger (PDTC or NAC) for 30 minutes, and then exposed to MCP-1–activated monocytes. The number of cells with activated caspase-3 was determined after staining with caspase-3 substrate (NucView 488; Biotium, Inc.). Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3–12). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, compared with control. #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.0001, compared with RPE/Mo/MCP-1.
Taken together, the findings suggest that Ca2+ signaling may be required for activated monocyte-induced ROS generation in RPE cells and that activated monocytes induce RPE apoptosis via both intracellular Ca2+ signaling and ROS production.
Effects of Anti-CD14 Antibody on Activated Monocyte-Induced Ca2+ Levels, ROS Accumulation, and Apoptosis in RPE Cells
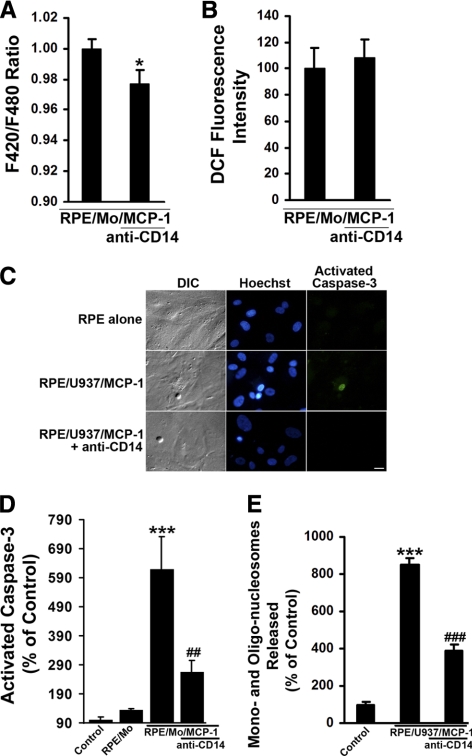
To identify functionally whether adhesion molecule CD14 was involved in activated monocyte-induced intracellular Ca2+ in RPE cells, the activated monocyte-induced Ca2+ rise in the presence or absence of anti-CD14 antibody was tested. As shown in Figure 6A, the activated monocyte-induced F420/F480 ratio was significantly inhibited by anti-CD14 antibody, indicating that CD14 may be involved in activated monocyte-induced increase in intracellular Ca2+ in RPE cells.
Figure 6.
Effects of anti-CD14 on activated monocyte-induced RPE Ca2+ levels, ROS production, and apoptosis. (A) Activated monocytes-induced RPE Ca2+ levels were measured using a fluorometer (FlexStation Scanning Fluorometer; Molecular Devices) in the presence or absence of antibody directed against CD14. RPE cells were loaded with a Ca2+ indicator dye (Fura red-AM; 10 μM), for 1.5 hours at 37°C. After incubation with anti-CD14 antibody for 1 hour, RPE cells were challenged with MCP-1–activated monocytes (RPE/Mo/MCP-1). (B) CM-H2DCFDA–prelabeled RPE cells were preincubated with or without anti-CD14 antibody for 1 hour, and then exposed to MCP-1–activated monocytes in the presence or absence of anti-CD14 antibody. Fluorescence intensities were measured. (C) Differential interference contrast (DIC) and fluorescence images of cells stained with Hoechst 33342 and caspase-3 substrate (NucView 488; Biotium, Inc.) in RPE cells exposed control medium (RPE alone), or MCP-1–activated U937 cells (RPE/U937/MCP-1) in the presence or absence of anti-CD14 antibody for 6 hours. Scale bar, 20 μm. (D) RPE cells were preincubated with or without anti-CD14 antibody for 1 hour, and then exposed to control medium (RPE alone), monocytes (RPE/Mo), or MCP-1–activated monocytes in the presence or absence of anti-CD14 antibody. After 6 hours, the number of cells with activated caspase-3 was determined after staining with caspase-3 substrate. (E) RPE cells were treated as described in (C) for 24 hours. DNA fragmentation or released mono- and oligonucleosomes were measured by a cell death detection ELISA. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3–12). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, compared with control or RPE/Mo/MCP-1 (without antibody); ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, compared with RPE/Mo/MCP-1 or RPE/U937/MCP-1 (without antibody).
As the activated monocyte-induced Ca2+ levels were significantly inhibited by anti-CD14 antibody (Fig. 6A), it was tested whether activated monocytes induced RPE ROS production and apoptosis via CD14. Functional blocking antibody against CD14 significantly reduced activated monocyte–induced apoptosis by different assays: Hoechst 33342 staining for condensed nuclei (Fig. 6C) and caspase-3 substrate staining (Fig. 6C) and quantitative measurement (Fig. 6D) for activated caspase-3, and apoptosis ELISA for DNA fragmentation (Fig. 6E). However, anti-CD14 antibody had no effect on the activated monocyte-induced ROS generation (Fig. 6B). Thus, CD14 appears to be responsible for activated monocyte–induced Ca2+ increase and apoptosis in RPE cells.
Discussion
As monocytic infiltration is a key component of retinal diseases such as PVR, AMD, and uveitis, as evidenced by their presence in histopathologic lesions,4,6,7,10,11,45–50 and MCP-1 plays an important role in regulation of the monocytic infiltration, and is associated with AMD and retinal detachment,51–53 it is important to examine how monocytes induce RPE apoptosis. Both RPE cells and monocytes have critical regulatory functions in the development of these diseases, and monocytes and monocyte-derived cytokines influence RPE functions and integrity.34,54–60 It is well established that activated monocytes and macrophages are capable of directing apoptosis in various types of cells, including RPE cells.25,26,51,61–68 The present authors previously reported that, using a human RPE culture model, RPE apoptosis was induced by activated monocytes.25 The association of superoxide anions with mononuclear phagocyte-induced apoptosis in mouse RPE cells from wild-type and heterozygous superoxide dismutase 2-knockout (Sod2±) mice was also examined.26 Mononuclear phagocyte–induced mouse RPE apoptosis involved enhanced intracellular O2·− generation, loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, and caspase activation, especially when mononuclear phagocytes were immunologically activated and RPE Sod2 gene was partially knocked out.26 This suggested that elevated O2·− levels due to genetic abnormalities of Sod2 or immunologic activation of mononuclear phagocytes lead to greater levels of RPE apoptosis.26 Our present study adds new facets to the mechanisms of activated monocyte-induced RPE apoptosis in that CD14, Ca2+, and ROS are involved in the induced RPE apoptosis and that the induced Ca2+ and ROS may be mediated by cADPR.
This study demonstrates increases in intracellular Ca2+, ROS, and apoptosis when RPE cells are exposed to activated monocytes (Figs. 1–3). Our data are consistent with previous studies in other cell systems showing that several apoptotic stimuli cause Ca2+ increase, ROS induction, and apoptosis.21,22,69–71
We also evaluated the potential pathways involved in activated monocyte-induced Ca2+ signaling, ROS accumulation, and apoptosis in RPE cells. Previous evidence implicates CD38 and cADPR in Ca2+ signaling, ROS production, and apoptosis induced by various stimuli in other cell types.27–33 Although a possible link among cADPR, Ca2+, and ROS production has not been studied in RPE cells, CD38 is expressed in rat RPE cells.72 The present study shows that human RPE cells also express CD38 (Figs. 4D, 4E). CD38 binds to its substrate, NAD+, and catalyzes the cleavage of NAD+ into cADPR with its ADP-ribosyl cyclase activity.73 We show that pretreatment of RPE with 8-Br-cAPDR, a selective and potent antagonist of cADPR-mediated Ca2+ signaling,74 inhibited the induced Ca2+ increase, ROS production, and subsequent apoptosis in RPE cells (Fig. 4). Therefore, we speculate that cAPDR may mediate activated monocyte-induced Ca2+ signaling, ROS production, and apoptosis.
It has been reported that antioxidants inhibited apoptosis induced by various apoptotic stimuli.69,75–80 In the present study, two antioxidants, NAC and PDTC, were used to test their effects on activated monocyte-induced Ca2+, ROS, and apoptosis in RPE cells. Pretreatment RPE with NAC completely blocked ROS production and partially inhibited apoptosis induced by activated monocytes, but this pretreatment did not inhibit activated monocyte-induced Ca2+ increase, indicating Ca2+ signaling may precede ROS production in RPE cells. Similarly, pretreatment of RPE with PDTC inhibited the induced ROS production and apoptosis, but did not significantly inhibit the induced Ca2+ increase. Although NAC completely blocked the induced ROS production, it did not completely inhibit the induced apoptosis of RPE, suggesting that other signaling molecule(s) may play a role in RPE apoptosis.
Previous studies demonstrated that CD14 is involved in the regulation of apoptosis and apoptotic cell clearance.81–84 In addition, lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated activation of microglial and peripheral blood mononuclear (PBM) cells increases cADPR, intracellular calcium levels, and ROS accumulation.85,86 Anti-CD14 antibody was shown to block the increase in cADPR in LPS-activated PBM cells, but its effects on intracellular calcium levels and ROS accumulation were not studied.86 Removal of monocytes from the activated-PBM cells also inhibited the cADPR increase.86 This indicates that activated monocytes and CD14 may both be involved in the activation of cADPR. The present study shows that anti-CD14 antibody significantly inhibited MCP-1–activated monocyte-induced Ca2+ and apoptosis in RPE cells. As the activated monocyte-induced RPE Ca2+ rise (Fig. 1) precedes the induced RPE apoptosis (Figs. 3 and 6), these findings support the role of CD14 in activated monocyte-induced RPE apoptosis through Ca2+ signaling.
Monocyte and macrophage infiltration are observed in murine AMD models.87,88 Both RPE and microvascular endothelial cells produce MCP-1. The finding in the current study that MCP-1–activated monocytes induce RPE apoptosis implicates that in addition to RPE, microvascular endothelial cells might also be involved in atrophic or dry AMD via MCP-1 secretion. Thus it is possible that both MCP-1 and CD14 could be used as therapeutic targets for AMD.
In summary, activated monocytes increased intracellular Ca2+ levels, ROS generation, and apoptosis in RPE cells. In addition, inhibition of cADPR with 8-Br-cADPR reduced the induced increase in Ca2+, ROS production, and apoptosis. The generation of ROS and apoptosis, but not the Ca2+ increase, was inhibited by NAC or PDTC. The induction of Ca2+ and apoptosis, but not ROS generation, was incompletely blocked by anti-CD14 antibody. Activated monocytes may induce cADPR formation through CD38 activation, and the generated cADPR could increase RPE Ca2+ levels, ROS production, and apoptosis. Understanding how CD38 is activated, how cADPR is regulated, and further elucidating the role of CD14 in RPE cells might therefore provide new insights into retinal diseases, including AMD, and potential therapeutic targets.
Footnotes
Supported by the National Institutes of Health Grants R01EY009441 (VME), EY019986 (HRP) and P30EY07003 (core), and by a pilot grant from the University of Michigan Claude Pepper Older Americans Independence Center (DY). VME is a recipient of the Senior Scientific Investigator Award from Research to Prevent Blindness.
Disclosure: D. Yang, None; S.G. Elner, None; X. Chen, None; M.G. Field, None; H.R. Petty, None; V.M. Elner, None
References
- 1. Zarbin MA. Current concepts in the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004;122:598–614 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Green WR, McDonnell PJ, Yeo JH. Pathologic features of senile macular degeneration. 1985. Retina. 2005;25:615–627 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Young RW. Pathophysiology of age-related macular degeneration. Surv Ophthalmol. 1987;31:291–306 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Penfold PL, Madigan MC, Gillies MC, Provis JM. Immunological and aetiological aspects of macular degeneration. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2001;20:385–414 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Gehrs KM, Anderson DH, Johnson LV, Hageman GS. Age-related macular degeneration—emerging pathogenetic and therapeutic concepts. Ann Med. 2006;38:450–471 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Weller M, Heimann K, Wiedemann P. Immunochemical studies of epiretinal membranes using APAAP complexes: evidence for macrophage involvement in traumatic proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Int Ophthalmol. 1988;11:181–186 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Scheiffarth OF, Tang S, Kampik A. Macrophages and HLA-DR expression in proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Fortschr Ophthalmol. 1990;87:340–343 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Charteris DG, Hiscott P, Grierson I, Lightman SL. Proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Lymphocytes in epiretinal membranes. Ophthalmology. 1992;99:1364–1367 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Proenca R, Carvalho M, Proenca D, Verissimo J, Regadas I, Travassos A. HLA antigens and lymphocytes in proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1994;232:25–32 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Seregard S, Algvere PV, Berglin L. Immunohistochemical characterization of surgically removed subfoveal fibrovascular membranes. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1994;232:325–329 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Reddy VM, Zamora RL, Kaplan HJ. Distribution of growth factors in subfoveal neovascular membranes in age-related macular degeneration and presumed ocular histoplasmosis syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995;120:291–301 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Killingsworth MC, Sarks JP, Sarks SH. Macrophages related to Bruch's membrane in age-related macular degeneration. Eye. 1990;4(Pt 4):613–621 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. van der Schaft TL, Mooy CM, de Bruijn WC, de Jong PT. Early stages of age-related macular degeneration: an immunofluorescence and electron microscopy study. Br J Ophthalmol. 1993;77:657–661 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Xu GZ, Li WW, Tso MO. Apoptosis in human retinal degenerations. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1996;94:411–431 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Hinton DR, He S, Lopez PF. Apoptosis in surgically excised choroidal neovascular membranes in age-related macular degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998;116:203–209 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Bok D. Contributions of genetics to our understanding of inherited monogenic retinal diseases and age-related macular degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol. 2007;125:160–164 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Ames BN, Shigenaga MK, Hagen TM. Oxidants, antioxidants, and the degenerative diseases of aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:7915–7922 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Cai J, Nelson KC, Wu M, Sternberg P, Jr, Jones DP. Oxidative damage and protection of the RPE. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2000;19:205–221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Liang FQ, Godley BF. Oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial DNA damage in human retinal pigment epithelial cells: a possible mechanism for RPE aging and age-related macular degeneration. Exp Eye Res. 2003;76:397–403 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Dypbukt JM, Ankarcrona M, Burkitt M, et al. Different prooxidant levels stimulate growth, trigger apoptosis, or produce necrosis of insulin-secreting RINm5F cells. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:30533–30560 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Sakaguchi N, Inoue M, Ogihara Y. Reactive oxygen species and intracellular Ca2+, common signals for apoptosis induced by gallic acid. Biochem Pharmacol. 1998;55:1973–1981 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Asada S, Fukuda K, Nishisaka F, Matsukawa M, Hamanisi C. Hydrogen peroxide induces apoptosis of chondrocytes; involvement of calcium ion and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase. Inflamm Res. 2001;50:19–23 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Kanno T, Sato EE, Muranaka S, et al. Oxidative stress underlies the mechanism for Ca2+-induced permeability transition of mitochondria. Free Radic Res. 2004;38:27–35 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Flora SJ, Saxena G, Mehta A. Reversal of lead-induced neuronal apoptosis by chelation treatment in rats: role of reactive oxygen species and intracellular Ca2+. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007;322:108–116 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Yoshida A, Elner SG, Bian ZM, Kindezelskii AL, Petty HR, Elner VM. Activated monocytes induce human retinal pigment epithelial cell apoptosis through caspase-3 activation. Lab Invest. 2003;83:1117–1129 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Yang D, Elner SG, Lin LR, Reddy VN, Petty HR, Elner VM. Association of superoxide anions with retinal pigment epithelial cell apoptosis induced by mononuclear phagocytes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009;50:4998–5005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Bai N, Lee HC, Laher I. Emerging role of cyclic ADP-ribose (cADPR) in smooth muscle. Pharmacol Ther. 2005;105:189–207 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Bréchard S, Brunello A, Bueb JL, Tschirhart EJ. Modulation by cADPr of Ca2+ mobilization and oxidative response in dimethylsulfoxide- or retinoic acid-differentiated HL-60 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1763:129–136 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Gao Y, Camacho LH, Mehta K. Retinoic acid-induced CD38 antigen promotes leukemia cells attachment and interferon-gamma/interleukin-1beta-dependent apoptosis of endothelial cells: implications in the etiology of retinoic acid syndrome. Leuk Res. 2007;31:455–463 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Criddle DN, Gerasimenko JV, Baumgartner HK, et al. Calcium signalling and pancreatic cell death: apoptosis or necrosis? Cell Death Differ. 2007;14:1285–1294 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Guse AH, Berg I, da Silva CP, Potter BV, Mayr GW. Ca2+ entry induced by cyclic ADP-ribose in intact T-lymphocytes, J Biol Chem. 1997;272:8546–8550 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Schöttelndreier H, Potter BV, Mayr GW, Guse AH. Mechanisms involved in alpha6beta1–integrin-mediated Ca2+ signalling. Cell Signal. 2001;13:895–899 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Song EK, Lee YR, Yu HN, et al. Extracellular NAD is a regulator for FcgammaR-mediated phagocytosis in murine macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;367:156–161 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Elner SG, Strieter RM, Elner VM, Rollins BJ, Del Monte MA, Kunkel SL. Monocyte chemotactic protein gene expression by cytokine-treated human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Lab Invest. 1991;64:819–825 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Yang D, Elner SG, Bian ZM, Till GO, Petty HR, Elner VM. Pro-inflammatory cytokines increase reactive oxygen species through mitochondria and NADPH oxidase in cultured RPE cells. Exp Eye Res. 2007;85:462–472 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Yoshida A, Elner SG, Bian ZM, Kunkel SL, Lukacs NW, Elner VM. Thrombin regulates chemokine induction during human retinal pigment epithelial cell/monocyte interaction. Am J Pathol. 2001;159:1171–1180 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Elner VM, Elner SG, Bian ZM, Kindezelskii AL, Yoshida A, Petty HR. RPE CD14 immunohistochemical, genetic, and functional expression. Exp Eye Res. 2003;76:321–331 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Elner SG, Petty HR, Elner VM, et al. TLR4 mediates human retinal pigment epithelial endotoxin binding and cytokine expression. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005;46:4627–4633 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Yang D, Swaminathan A, Zhang X, Hughes BA. Expression of Kir7.1 and a novel Kir7.1 splice variant in native human retinal pigment epithelium. Exp Eye Res. 2008;86:81–91 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Yang D, Elner SG, Clark AJ, Hughes BA, Petty H, Elner VM. Activation of P2X receptors induces apoptosis in human retinal pigment epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52:1522–1530 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Irita K, Fujita I, Takeshige K, Minakami S, Yoshitake J. Calcium channel antagonist induced inhibition of superoxide production in human neutrophils. Mechanisms independent of antagonizing calcium influx. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986;35:3465–3471 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Hotchkiss RS, Bowling WM, Karl IE, Osborne DF, Flye MW. Calcium antagonists inhibit oxidative burst and nitrite formation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated rat peritoneal macrophages. Shock. 1997;8:170–178 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Duan Y, Gross RA, Sheu SS. Ca2+-dependent generation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species serves as a signal for poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 activation during glutamate excitotoxicity. J Physiol. 2007;585(Pt 3):741–758 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Musso T, Deaglio S, Franco L, et al. CD38 expression and functional activities are up-regulated by IFN-gamma on human monocytes and monocytic cell lines. J Leukoc Biol. 2001;69:605–612 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Baudouin C, Peyman GA, Fredj-Reygrobellet D, et al. Immunohistological study of subretinal membranes in age-related macular degeneration. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 1992;36:443–451 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Grossniklaus HE, Ling JX, Wallace TM, et al. Macrophage and retinal pigment epithelium expression of angiogenic cytokines in choroidal neovascularization. Mol Vis. 2002;8:119–8126 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Harper FH, Liversidge J, Thomson AW, Forrester JV. Interphotoreceptor retinoid binding protein induced experimental autoimmune uveitis: an immunophenotypic analysis using alkaline phosphatase anti-alkaline phosphatase staining, dual immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy. Curr Eye Res. 1992;11(suppl):129–134 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Jerdan JA, Pepose JS, Michels RG, et al. Proliferative vitreoretinopathy membranes: an immunohistochemical study. Ophthalmology. 1989;96:801–810 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Kampik A, Kenyon KR, Michels RG, Green WR, de la Cruz ZC. Epiretinal and vitreous membranes. Comparative study of 56 cases. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981;99:1445–1454 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Vinores SA, Campochiaro PA, Conway BP. Ultrastructural and electron-immunocytochemical characterization of cells in epiretinal membranes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1990;31:14–28 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Nakazawa T, Hisatomi T, Nakazawa C, et al. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 mediates retinal detachment-induced photoreceptor apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:2425–2430 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Deshmane SL, Kremlev S, Amini S, Sawaya BE. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): an overview. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009;29:313–326 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Jonas JB, Tao Y, Neumaier M, Findeisen P. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1, and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 in exudative age-related macular degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010;128:1281–1286 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Elner VM, Strieter RM, Elner SG, Baggiolini M, Lindley I, Kunkel SL. Neutrophil chemotactic factor (IL-8) gene expression by cytokine-treated retinal pigment epithelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1990;136:745–750 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Elner SG, Elner VM, Pavilack MA, et al. Modulation and function of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (CD54) on human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Lab Invest. 1992;66:200–211 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Elner VM, Elner SG, Standiford TJ, Lukacs NW, Strieter RM, Kunkel SL. Interleukin-7 (IL-7) induces retinal pigment epithelial cell MCP-1 and IL-8. Exp Eye Res. 1996;63:297–303 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Elner VM, Burnstine MA, Strieter RM, Kunkel SL, Elner SG. Cell-associated human retinal pigment epithelium interleukin-8 and monocyte chemotactic protein-1: immunochemical and in-situ hybridization analyses. Exp Eye Res. 1997;65:781–789 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Hollborn M, Kohen L, Wiedemann P, Enzmann V. The influence of pro- inflammatory cytokines on human retinal pigment epithelium cell receptors. Graefes Arch. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2001;239:294–301 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Jaffe GJ, Van Le L, Valea F, et al. Expression of interleukin-1 alpha, interleukin-1 beta, and an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res. 1992;55:325–335 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Jaffe GJ, Roberts WL, Wong HL, Yurochko AD, Cianciolo GJ. Monocyte-induced cytokine expression in cultured human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res. 1995;60:5335–5343 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Arantes RM, Lourenssen S, Machado CR, Blennerhassett MG. Early damage of sympathetic neurons after co-culture with macrophages: a model of neuronal injury in vitro. NeuroReport. 2000;11:177–181 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Diez-Roux G, Lang RA. Macrophages induce apoptosis in normal cells in vivo. Development. 1997;124:3633–3638 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Duffield JS, Erwig LP, Wei X, Liew FY, Rees AJ, Savill JS. Activated macrophages direct apoptosis and suppress mitosis of mesangial cells. J Immunol. 2000;164:2110–2119 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Griffith TS, Wiley SR, Kubin MZ, Sedger LM, Maliszewski CR, Fanger NA. Monocyte-mediated tumoricidal activity via the tumor necrosis factor-related cytokine, TRAIL. J Exp Med. 1999;189:1343–1354 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Hirano S. Nitric oxide-mediated cytotoxic effects of alveolar macrophages on transformed lung epithelial cells are independent of the beta 2 integrin-mediated intercellular adhesion. Immunology. 1998;93:102–108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Lang RA, Bishop JM. Macrophages are required for cell death and tissue remodeling in the developing mouse eye. Cell. 1993;74:453–462 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Meszaros AJ, Reichner JS, Albina JE. Macrophage-induced neutrophil apoptosis. J Immunol. 2000;165:435–441 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Nakayama M, Kayagaki N, Yamaguchi N, Okumura K, Yagita H. Involvement of TWEAK in interferon gamma-stimulated monocyte cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 2000;192:1373–1380 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Honda H, Kondo T, Zhao QL, Feril LB, Jr, Kitagawa H. Role of intracellular calcium ions and reactive oxygen species in apoptosis induced by ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2004;30:683–692 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Liu GY, Chen KJ, Lin-Shiau SY, Lin JK. Peroxyacetyl nitrate-induced apoptosis through generation of reactive oxygen species in HL-60 cells. Mol Carcinog. 1999;25:196–206 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Mortimer AJ, Dyson M. The effect of therapeutic ultrasound on calcium uptake in fibroblasts. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1988;14:499–506 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Khoo KM, Chang CF. Characterization and localization of CD38 in the vertebrate eye. Brain Res. 1999;821:17–25 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Lee HC. ADP-ribosyl cyclases-a family of cADPR and NAADP metabolizing enzymes. Cyclic ADP-Ribose and NAADP. Structure, Metabolism and Functions. Norwell, MA: Kluwer; 2002:23–43 [Google Scholar]
- 74. Walseth TF, Lee HC. Synthesis and characterization of antagonists of cyclic-ADP-ribose-induced Ca2+ release. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993;1178:235–242 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Choi YJ, Park JW, Suh SI, et al. Arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis in U937 cells involve generation of reactive oxygen species and inhibition of Akt. Int J Oncol. 2002;21:603–610 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Custodio JB, Cardoso CM, Almeida LM. Thiol protecting agents and antioxidants inhibit the mitochondrial permeability transition promoted by etoposide: implications in the prevention of etoposide-induced apoptosis. Chem Biol Interact. 2002;140:169–184 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Recchioni R, Marcheselli F, Moroni F, Pieri C. Apoptosis in human aortic endothelial cells induced by hyperglycemic condition involves mitochondrial depolarization and is prevented by N-acetyl-l-cysteine. Metabolism. 2002;51:1384–1388 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Samuel W, Kutty RK, Nagineni S, Vijayasarathy C, Chandraratna RA, Wiggert B. N-(4–hydroxyphenyl)retinamide induces apoptosis in human retinal pigment epithelial cells: retinoic acid receptors regulate apoptosis, reactive oxygen species generation, and the expression of heme oxygenase-1 and Gadd153. J Cell Physiol. 2006;209:854–865 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Szotowski B, Antoniak S, Goldin-Lang P, et al. Antioxidative treatment inhibits the release of thrombogenic tissue factor from irradiation- and cytokine-induced endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Res. 2007;73:806–812 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Zafarullah M, Li WQ, Sylvester J, Ahmad M. Molecular mechanisms of N-acetylcysteine actions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003;60:6–20 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Frey EA, Finlay BB. Lipopolysaccharide induces apoptosis in a bovine endothelial cell line via a soluble CD14 dependent pathway. Microb Pathog. 1998;24:101–109 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Gregory CD, Devitt A. CD14 and apoptosis. Apoptosis. 1999;4:11–20 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Kol A, Lichtman AH, Finberg RW, Libby P, Kurt-Jones EA. Cutting edge: heat shock protein (HSP) 60 activates the innate immune response: CD14 is an essential receptor for HSP60 activation of mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 2000;164:13–17 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Schlegel RA, Krahling S, Callahan MK, Williamson P. CD14 is a component of multiple recognition systems used by macrophages to phagocytose apoptotic lymphocytes. Cell Death Differ. 1999;6:583–592 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Franco L, Bodrato N, Moreschi I, et al. Cyclic ADP-ribose is a second messenger in the lipopolysaccharide-stimulated activation of murine M9 microglial cell line. J Neurochem. 2006;99:165–176 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. Bruzzone S, De Flora A, Usai C, Graeff R, Lee HC. Cyclic ADP-ribose is a second messenger in the lipopolysaccharide-stimulated proliferation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Biochem J. 2003;375:395–403 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Espinosa-Heidmann DG, Suner IJ, Hernandez EP, Monroy D, Csaky KG, Cousins SW. Macrophage depletion diminishes lesion size and severity in experimental choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003;44:3586–3592 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Sakurai E, Anand A, Ambati BK, van Rooijen N, Ambati J. Macrophage depletion inhibits experimental choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003;44:3578–3585 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]