Abstract
Two velogenic Newcastle disease viruses (NDV) obtained from outbreaks in domestic ducks in China were characterized in this study. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that both strains clustered with the class II viruses, with one phylogenetically close to the genotype VII NDVs and the other closer to genotype IX. The deduced amino acid sequence of the cleavage site of the fusion (F) protein confirmed that both isolates contained the virulent motif 112RRQK/RRF117 at the cleavage site. The two NDVs had severe pathogenicity in fully susceptible chickens, resulting in 100% mortality. One of the isolates also demonstrated some pathogenicity in domestic ducks. The present study suggests that more than one genotype of NDV circulates in domestic ducks in China and viral transmission may occur among chickens and domestic ducks.
Introduction
Newcastle disease virus (NDV) belongs to genus Avulavirus in the family Paramyxoviridae and has also been designated as avian paramyxovirus 1 [1]. Its genome is a non-segmented, single-stranded, negative-sense RNA molecule of approximately 15,186 nucleotides (nt) that contains six genes encoding the six structural proteins (from the 3′ to 5′ terminus): nucleoprotein (NP), phosphoprotein (P), matrix (M), fusion (F), hemagglutinin-neuraminidase (HN) and the large protein (L) [2]. Additionally, two nonstructural proteins (V and W) may be generated due to an mRNA-editing event in which one (V) or two (W) G residues are inserted at a specific position within the P gene mRNA [3], [4].
NDV strains are classified as high virulence (velogenic), intermediate (mesogenic) or low virulence (lentogenic) based on some biological parameters, such as the mean death time (MDT) of chicken embryos infected with the minimum lethal dose of virus, the intracerebral pathogenicity index (ICPI) in 1-day-old chicks and the intravenous pathogenicity index (IVPI) in 6-week-old chickens. The velogenic strains are involved in fatal infections of chickens. The mesogenic strains cause moderate respiratory signs with occasional nervous signs while the lentogenic strains typically cause subclinical infections or mild respiratory disease [5], [6], [7]. The molecular basis for NDV pathogenicity is dependent on the cleavability of precursor F (F0) to active F1 and F2 polypeptides by cellular proteases [2], [8].
Phylogenetic analysis revealed that NDV strains consist of two distinct classes (class I and class II) within a single serotype. Class I viruses comprise at least nine (1–9) genotypes and have been recovered primarily from wild waterfowl and live bird markets. Class II viruses comprise the vast majority of the sequenced NDVs and include isolates recovered from poultry, pet birds and wild birds, and are further categorized into genotypes I–XI [9], [10], [11], [12], [13], [14], [15].
NDV has a wide host range with most orders of birds reported to have been infected by the virus, the more commonly affected species include chickens, turkeys, pigeons and ducks. Other species can be infected, and this occasionally includes mammals [5], [16]. Chicken infection with virulent NDVs can be devastating due to the resulting high mortality or significant egg drop, and is characterized by very rapid spread. The disease remains one of the major problems affecting existing or developing poultry industries in many countries. In general, ducks are considered natural reservoirs of NDV and show few or no clinical signs after infection even for NDV strains lethal to chickens [13], [17], [18], [19]. Many NDVs have been isolated from domestic ducks in recent years [12], [13], [20]. Most of these are low-virulence strains, occasionally a high-virulence strain is isolated but little is known about their potential to cause disease in domestic ducks.
In the present study, two velogenic NDVs obtained from outbreaks in domestic ducks in China were pathotypically and genotypically characterized. We also discuss the evolutionary relationship of NDVs from different origins.
Results
Biological characteristic assessment of the two isolates
As determined by the MDT and IVPI, both NDV isolates were velogenic strains. The MDT/IVPI values and other details are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Details of the two NDV isolates investigated in this study.
| Isolate name | Species | Province | Country | MDTa | ICPIb | EID50/0.1 ml |
| SD09 | Duck | Shandong | China | 55 | 1.675 | 104.32 |
| GD09-2 | Duck | Guangdong | China | 38 | 1.725 | 107.25 |
Mean death time in embryonating eggs (hours) (<60: velogen; 60–90: mesogen; >90: lentogen).
Intracerebral pathogenicity index in day-old chicks (1.5–2.0: velogen; 1.0–1.5: mesogen; <0.5: lentogen).
RT-PCR and sequence analysis
The RT-PCRs performed with all primers (Table 2) resulted in amplification of the expected products. The amplified products were sequenced, annotated and assembled to obtain the entire nucleotide sequences of two isolates. The nucleotide sequence data were deposited into the Genbank database and the accession numbers were HQ317394 (GD09-2) and HQ317395 (SD09). The coding regions of both strains were 14,879 nt in length. Compared with NDV Lasota, the two isolates bear a 6 nt insertion (CCCCCC or TCCCAC) in positions 1647–1648 nt of the NP gene.
Table 2. Primers used in the study.
| Primers | Sequences(5′-3′) | Position | Expected size (bp) |
| 1-F | TACGATAAAAGGCGAAGGAG | 23–42 | 1122 |
| 1-R | CAGGACTGATGCCATACCC | 1126–1144 | |
| 2-F | CGGAGAAGCAATCGAGATCGTAC | 77–99 | 1501 |
| 2-R | CACTGGGTAGAAGGGAGAACAGA | 1555–1577 | |
| 3-F | ACCAAGACTTCAGCCCTCG | 950–968 | 1173 |
| 3-R | GACGGTTGTTTGTCTGGTCTGT | 2101–2122 | |
| 4-F | GGAGACTTGGAGTAGAGTATGCT | 1200–1222 | 1464 |
| 4-R | CATAGGAATGGAGGATGTCTG | 2143–2663 | |
| 5-F | CTTCTACCCAGCAGACCAG | 1867–1885 | 1157 |
| 5-R | ATCCAGCTTACTCAGGAGTTTA | 3002–3023 | |
| 6-F | CAAGCAACTCCCTTCTGTCC | 2230–2249 | 1173 |
| 6-R | TGTTTCTTCCCGTCTCCTG | 3384–3402 | |
| 7-F | TAAACCTGCCACGGTAAGC | 2906–2924 | 1785 |
| 7-R | GTCTCCCGTTACTACAATCC | 4671–4690 | |
| 8-F | CCACGCTTCAACACCCAAAAC | 3157–3177 | 1478 |
| 8-F | TCGGACGGATACAGCCCAAT | 4615–4634 | |
| 9-F | TTACTTGCTCCTTTCTTCTC | 4160–4179 | 2188 |
| 9-R | TACTCTGACCGTTCTACCC | 6329–6347 | |
| 10-F | AGTCTGGGTTTAGCGTGTTA | 6101–6120 | 2111 |
| 10-R | AGCATTATGGGAGATGATTGG | 8191–8211 | |
| 11-F | GGGAAGACGACACCGCACCAATC | 8174–8196 | 1868 |
| 11-R | CGCCCATTCACTTTCACCTCTTT | 10019–10041 | |
| 12-F | TGGAATACCTGACAACCCTC | 9951–9970 | 1882 |
| 12-R | TCTCCCTCCACAAGTTCTATG | 11812–11832 | |
| 13-F | GGCAGGAAGATACTGGGTGT | 11177–11196 | 2319 |
| 13-R | CGCAGGTTGTCGGGTAAATG | 13476–13495 | |
| 14-F | CTGTGGGTAGGAGAAAGC | 11523–11540 | 1802 |
| 14-R | CGTGATTATGTTGGGAGAC | 13306–13324 | |
| 15-F | GCTGTGAGACCATTACTTAG | 13262–13281 | 1908 |
| 15-R | ACAGAACTACACTCAAGAGC | 15150–15169 | |
| 16-F | ACCTGAATGAGAAGATGCT | 13116–13134 | 1623 |
| 16-R | TGAGACCCAGTATTGTGAC | 14720–14738 | |
| 17-F | TGTGCGGAAAGTTTGGTGAC | 14510–14529 | 539 |
| 17-R | GAGGGAGTCATCAGTTAGGAAG | 15027–15048 |
Proteolytic cleavage site motifs (residues 112–117) for the F0 protein in the two isolates were analyzed. Strain SD09 was shown to have a virulent motif (112RRQKRF117) composed of multibasic amino acids at the F0 cleavage site. This motif is commonly found in strains that are highly virulent in chickens, especially in genotype VII viruses [2], [21]. Strain GD09-2 exhibited the sequence motif 112RRQRRF117, which is another common motif in other virulent NDVs including strain F48E9 (a genotype IX virus that was isolated only in China).
Phylogenetic analysis
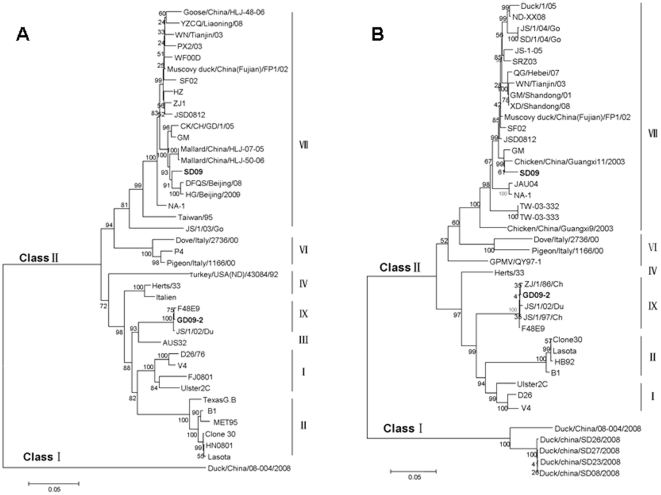
The predicted amino acid sequences of the two isolate were compared. Nucleotide and amino acid sequence data of 63 NDV reference strains obtained from the GenBank database (Table 3) were used for comparison. The GD09-2 isolate showed greatest nucleotide and amino acid identities (99.75%) with the velogenic strain F48 (Accession number FJ436302). Strain SD09 was highly similar to GM (97.78%; Accession number DQ486859), a classic genotype VII virus. The two isolates (GD09-2 and SD09) had sequence homologies of 87.70% and 82.64% respectively at the nucleotide level with strain LaSota, the common vaccine strain used in China.
Table 3. NDV strains and their accession numbers used for phylogenetic analysis.
| Virus strains | Year | Country | Genotype | Accession number |
| GM | 2007 | China | VII | DQ486859 |
| Muscovy duck/China(Fujian)/FP1/02 | 2009 | China | VII | FJ872531 |
| Chicken/China/Guangxi9/2003 | 2008 | China | VII | DQ485230 |
| Chicken/China/Guangxi11/2003 | 2008 | China | VII | DQ485231 |
| SF02 | 2005 | China | VII | AF473851 |
| JSD0812 | 2009 | China | VII | GQ849007 |
| NA-1 | 2006 | China | VII | DQ659677 |
| ZJ1 | 2007 | China | VII | AF431744 |
| Mallard/China/HLJ-07-05 | 2007 | China | VII | EF592500 |
| Mallard/China/HLJ-50-06 | 2007 | China | VII | EF592505 |
| DFQS/Beijing/08 | 2010 | China | VII | FJ608350 |
| WF00D | 2009 | China | VII | FJ754272 |
| WN/Tianjin/03 | 2010 | China | VII | FJ608334/FJ608352 |
| Goose/China/HLJ-48-06 | 2007 | China | VII | EF592504 |
| YZCQ/Liaoning/08 | 2010 | China | VII | FJ608351 |
| GM/Shandong/01 | 2010 | China | VII | FJ608361 |
| XD/Shandong/08 | 2010 | China | VII | FJ608365 |
| JAU04 | 2006 | China | VII | EF141104 |
| TW-03-332 | 2010 | Taiwan,China | VII | EU526308 |
| TW-03-333 | 2010 | Taiwan,China | VII | EU526309 |
| QG/Hebei/07 | 2010 | China | VII | FJ608355 |
| HG/Beijing/2009 | 2010 | China | VII | FJ882015 |
| PX2/03 | 2007 | China | VII | EF175145 |
| HZ | 2005 | China | VII | DQ114478 |
| Taiwan/95 | 1996 | Taiwan,China | VII | U62620 |
| JS/1/03/Go | 2008 | China | VII | DQ682437 |
| Dove/Italy/2736/00 | 2004 | Italy | VI | AY562989 |
| P4 | 2010 | China | VI | HM063425 |
| Pigeon/Italy/1166/00 | 2004 | USA | VI | AY288996 |
| Turkey/USA(ND)/43084/92 | 2004 | USA | IV | AY289001 |
| Herts/33 | 2005 | Netherlands | IV | AY741404 |
| Italien | 2008 | Italy | IV | EU293914 |
| F48E9 | 2005 | China | IX | AY508514/AY997298 |
| CK/CH/GD/1/05 | 2008 | China | VII | FJ480789 |
| JS/1/02/Du | 2009 | China | IX | FJ436306 |
| AUS32 | 2003 | Austria | III | AF542891 |
| D26/76 | 1999 | Austria | I | M24692 |
| V4 | 2003 | Austria | I | AF542946 |
| FJ0801 | 2009 | China | I | FJ600541 |
| ND-XX08 | 2009 | China | VII | GQ853450 |
| JS/1/04/Go | 2008 | China | VII | DQ682448 |
| SD/1/04/Go | 2008 | China | VII | DQ682450 |
| Ulster 2C | 1994 | U.K | I | Z30084 |
| TexasG.B | 1988 | USA | II | M23407 |
| B1 | 2000 | USA | II | AF309418 |
| MET95 | 2003 | Japan | II | AY143159 |
| Clone 30 | 2005 | Germany | II | Y18898 |
| HN0801 | 2009 | China | II | FJ600543 |
| Lasota | 1999 | Netherlands | II | AF077761 |
| GPMV/QY97-1 | 1999 | China | VI | AF192406 |
| ZJ1 | 2007 | China | VII | AF431744 |
| JS/1/97/Ch | 2009 | China | IX | FJ436305 |
| HB92 | 2003 | China | II | AY225110 |
| D26 | 1993 | Japan | I | M19432 |
| JS-1-05 | 2006 | China | VII | DQ469830 |
| SRZ03 | 2005 | China | VII | DQ234584 |
| Duck/1/05 | 2008 | China | VII | EU649675 |
| ZJ/1/86/Ch | 2009 | China | IX | FJ436303 |
| Duck/China/SD27/2008 | 2010 | China | Class I | FJ492893 |
| Duck/China/SD23/2008 | 2010 | China | Class I | FJ492892 |
| Duck/China/SD08/2008 | 2010 | China | Class I | FJ492891 |
| Duck/China/SD26/2008 | 2010 | China | Class I | FJ492894 |
| Duck/China/08-004/2008 | 2008 | China | Class I | EU589149 |
Phylogenetic analysis was conducted based on nucleotide sequences of the two important surface genes of NDV, the F and HN genes. Both isolates clustered within class II NDVs, as shown in Fig. 1. Within class II, strain SD09 was phylogenetically close to genotype VII NDVs, which displayed a high nucleotide sequence homology of 95.59–97.78%. Strain GD09-2 was phylogenetically close to genotype IX NDVs. However, both viruses were genetically distinct and phylogenetically distant from the vaccine strains (Lasota, AF077761; B1, AF309418), and clustered in different groups.
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree based on the nucleotide sequences of the fusion gene (A) (nt 1–1662) and hemagglutinin-neuraminidase gene (B) (nt 1–1713 or 1731) of NDV.
The phylogenetic tree was constructed by the Neighbor-Joining method with 1000 bootstrap replicates (bootstrap values are shown on the tree).
Pathogenicity in chickens
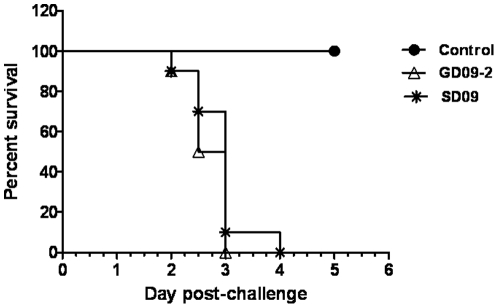
Birds infected with SD09 or GD09-2 exhibited severe clinical disease. Slight depression and head tremor were evident in some birds at 2 dpi. Whereas at 3 dpi all birds were depressed, and some had severe nervous signs such as incoordination accompanied by leg paralysis. All infected birds were dead by 5 dpi (Fig. 2). At necropsy, severe hemorrhage could be seen in the gastrointestinal tract, especially in the proventriculus, duodenum and appendix. Hemorrhaging of liver, spleen, trachea and kidney could also be seen occasionally. Small intestine, proventriculus, spleen and kidney tissues were collected for histological observation.
Figure 2. Percentage survival of chickens after inoculation with SD09 or GD09-2 velogenic NDVs.
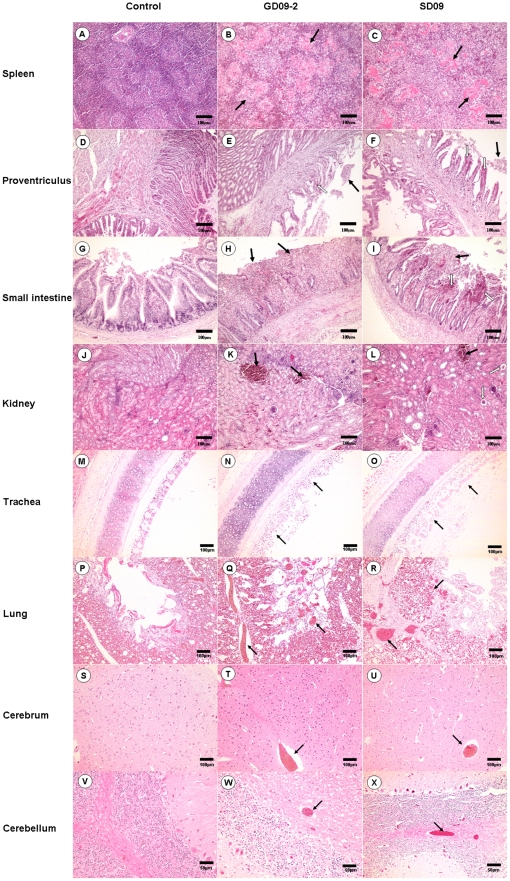
Chickens in the two inoculation groups exhibited histopathological changes, with the GD09-2 group displaying more severe changes than in the SD09 group. The spleen lesions exhibited a “starry sky” change, which was the result of a large number of lymphocytes disrupting and disappearing. The amalgamation of collapsed cell and inflammatory exudates created the homogeneous and pink-staining appearance of white pulps in the spleen (Fig. 3B and C). Pathological changes in the glandular stomach were hemorrhage and atrophy of the proventriculus papillae, with mucus on the surface of papillae. Dropout and necrosis of the mucosal epithelia of the proventriculus was also observed (Fig. 3E and F). The small intestine lesions of chickens infected with GD09-2 or SD-09 virus showed signs of enteritis, characterized by broken villi, dropout of epithelium and numerous inflammatory cell infiltrates (Fig. 3H and I). The lesions in the kidney were relatively slight, with congestion or glomerulus atrophy occasionally seen (Fig. 3K and L). Dropout and necrosis of mucous epithelial cells were seen in the trachea (Fig. 3N and O). In lung, congestion and hemorrhage (erythrocytes infiltrating in the pulmonary alveoli) were observed (Fig. 3Q and R). Venous congestion was present in cerebrum (Fig. 3T and U) and cerebellum (Fig. 3W and X). In comparison, all tissues from the control group had no apparent histological changes (Fig. 3A, D, G, J, M, P, S and V).
Figure 3. Histopathology on tissues from 1-week-old chickens infected with NDV GD09-2 or SD09 (H&E).
B and C: amalgamation of collapsed cell and inflammatory exudates created the homogeneous and pink-staining appearance in the white pulps of spleens (black arrow); E and F: dropout and necrosis of the mucosal epithelia in the proventriculus (black arrow); H and I: dropout of epithelium and numerous inflammatory cell infiltration in the small intestine (black arrow); K and L: congestion (black arrow) or glomerulus atrophy (white arrow) in the kidneys; N and O: dropout and necrosis of mucous epithelial cells in the trachea (black arrow); Q and R: congestion and hemorrhage in the lung (black arrow); T and U: venous congestion in the cerebrum (black arrow); W and X: venous congestion in the cerebellum (black arrow); A, D, G, J, M, P, S and V: Corresponding control tissues. Scale bar = 50 µm in cerebellum or 100 µm in other tissues.
Pathogenicity in ducks
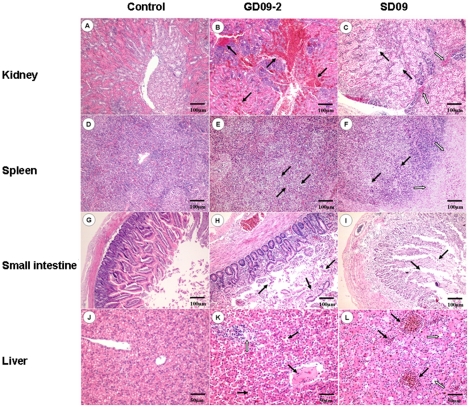
No obvious clinical signs were seen in ducks within the two week observation period in the SD09 inoculation group. However, four ducks exhibited obvious clinical signs in the GD09-2 group, including depression, tears and anorexia. One duck died at 9 dpi (Fig. 4A), and bile reflux and hemorrhaging in the liver were seen at necropsy. Obvious histopathological changes could be seen in two inoculation groups including hemorrhage (Fig. 5B) and degeneration of renal tubules epithelial cells (Fig. 5C) in the kidneys, necrosis of lymphocyte and coagulation necrosis of massive tissue (Fig. 5E, F) in the spleens, villus missing and necrosis of epithelial cell infiltration (Fig. 5H, I) in the small intestines, lymphocyte infiltration, dilatation of hepatic sinus and venous congestion (Fig. 5K, L) in the livers. Using IHC, antigens of NDV were detected extensively in the liver cells in the group infected with the GD09-2 strain (Fig. 6B). Detected by RT-PCR, over 50% of the cloacal samples were positive for viral RNA on day 3, 5 and 7 dpi (Table 4). No viral RNA was detected in any of the cloacal swabs of the control ducks.
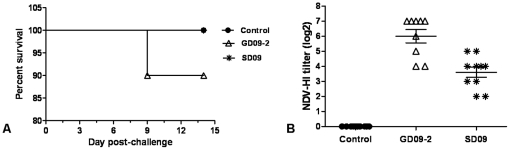
Figure 4. Percentage survival (A) and sero-conversion at 14 dpi (B) of ducks after inoculation with SD09 or GD09-2 velogenic NDVs.
Figure 5. Histopathology on tissues from 1-week-old ducks infected with NDV GD09-2 or SD09 (H&E).
B and C: hemorrhage (group GD09-2, black arrow) or degeneration of renal tubules epithelial cells (group SD09, black arrow) and eosinophil infiltration (group SD09, white arrow) in the kidneys; E and F: necrosis and disappear of lymphocyte (black arrow) or coagulation necrosis of massive tissue (white arrow) in the spleens; H and I: villus missing (white arrow) and necrosis of epithelial cell infiltration (black arrow) in the small intestines; K and L: dilatation of hepatic sinus and thrombus (group GD09-2, black arrow), lymphocyte infiltration (group GD09-2, white arrow), dilatation of hepatic sinus (group SD09, black arrow) and venous congestion (group SD09, white arrow) in the livers. A, D, G and J: Corresponding control tissues. A–I: scale bar = 100 µm, J–L: scale bar = 50 µm.
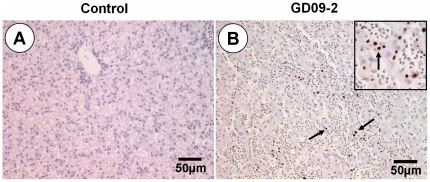
Figure 6. Immunohistochemical detection of NDV antigens in liver after experimental infection with NDV GD09-2.
B: Viral antigen was detected extensively in the liver cells (black arrow). A: Corresponding control tissues. Scale bar = 50 µm.
Table 4. Virus shedding from ducks by the cloacal route following inoculation with GD09-2 virus.
| Group | No. viral RNAa/No. ducks tested | |||
| Days postinoculation | ||||
| Day 1 | Day 3 | Day 5 | Day 7 | |
| GD09-2 | 0/10 | 5/10 | 6/10 | 8/10 |
| Control | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 |
By reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction.
Sera were collected at 14 dpi from surviving ducks and hemagglutination-inhibition (HI) tests were performed to detect specific NDV antibody (Fig. 4B). All sera were positive for NDV HI antibody after SD09 or GD09-2 inoculation, and the average HI titers were 6log2 and 3.6log2 respectively.
Discussion
Outbreaks of Newcastle disease (ND) were first reported in poultry in 1926 [5]. Since then, vaccination has been widely used for prevention and control of the disease in many countries including China, but the disease is still enzootic in some areas and is recognized as major disease of poultry [2]. The prevailing NDV strains have significant differences from the current vaccine strains in their biology, serology and genetics, which might be considered as reasons for the outbreaks [2], [22], [28], [30]. In the past decade, the predominant NDV strain was genotype VII viruses in China, while the most commonly used live vaccine LaSota and Clone-30 belong to genotype II. Up to 8-fold titer differences might be observed between the vaccine and field strains on mean HI titers, which may reflect apparent antigenic differences among them.
Phylogenetic analysis reveals that NDVs are continually evolving due to immune pressure and the broad genetic diversity of NDV. Some reports have revealed that waterfowl and wild birds may play an important role in the evolution of NDV [6], [12], [23], [24], [25], [26], [27]. However, virological and epidemiological information about NDV strains circulating in waterfowl and wild birds is still extremely limited. In ducks, many NDVs have been isolated in recent years [12], [13], [17], [18], [19], [20]. Most of them belong to class I NDVs and are low-virulence strains, occasionally a high-virulence strain is isolated but little is known about their potential to cause disease in domestic ducks.
Two representative NDV isolates obtained from outbreaks in domestic ducks in China were characterized both pathotypically and genotypically in the study. Pathogenicity tests showed that both isolates (SD09 and GD09-2) were velogenic strains. They had severe pathogenicity in fully susceptible chickens, resulting in 100% mortality. The GD09-2 strain also demonstrated some pathogenicity in domestic ducks. The results revealed that ducks may not only be a natural reservoir of NDV but also become susceptible to flocks, similar to the changes that occurred with the highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) over recent decades. Therefore, more attention must be paid to NDV infection of domestic ducks involved in poultry production.
Over the past decade, previous studies have shown that genotype VII viruses, circulating predominantly in many Asian countries including China, were responsible for disease outbreaks in chicken flocks [2], [28], [29]. Phylogenetic analysis in this study revealed that the SD09 strain had highest similarity (97.78%) to the GM isolate (Accession number DQ486859), which is a classic genotype VII virus from chickens in China. The close phylogenetic proximity between SD09 and GM suggests that viral transmission may occur among chickens and domestic ducks, although further investigation is required. In addition, GD09-2 strain was found to be a genotype IX virus, which has been seldom isolated from chicken flocks in recent years. The results further indicate that genotype IX viruses still causes sporadic infections in domestic ducks in China.
In summary, we have demonstrated that there is more than one genotype of NDV circulating in the domestic ducks of China, and some strains have obvious pathogenicity to domestic ducks suggesting that ducks may play an important role in driving the evolution of NDVs. More studies are needed to further clarify the relationship and origin of NDVs in chickens and domestic ducks.
Materials and Methods
Viruses and animals
Two NDV isolates were recovered from diseased duck flocks in China in 2009, in which the infected ducks manifest a clinical symptom with egg drop and sporadic mortality. The strains were designated NDV/Duck/China/GD09-2/2009 (abbreviated as GD09-2) and NDV/Duck/China/SD09/2009 (abbreviated as SD09) respectively. The two viruses were purified three times using a plaque technique before being propagated in the allantoic cavities of 10-day-old specific pathogen free (SPF) embryonated chicken eggs. Virus stocks were stored at −80°C until use. To investigate the pathogenicity of two NDV isolates, SPF chickens and NDV antibody-negative Beijing ducks from Beijing Golden Star Duck Centre were used. All animal research was approved by Beijing Administration Committee of Laboratory Animals under the leadership of the Beijing Association for Science and Technology, the approve ID is SYXK (Beijing) 2007-0023.
Assessment of the biological characteristics of two isolates
The pathogenic potential for the two isolated viruses was evaluated using standard assay methods to determine the MDT in 10-day-old chick embryos and the ICPI in 1-day-old chicks [5]. The 50% embryo infectious doses (EID50) of two isolates was also determined with 10-day-old chick embryos and calculated by the method of Reed and Muench.
Primer design
Based on the available NDV nucleotide sequences (SF02, FP1/02, ZJ1, F48, JS/1/97/Ch and ZJ/1/86/Ch, with GenBank accession numbers AF473851, FJ872531, AF431744, FJ436302, FJ436305 and FJ436303, respectively), 17 pairs of specific primers were designed to amplify the complete genome of SD09 and GD09-2, excluding the 5′ and 3′ terminal segments. All primers used for this study are listed in Table 2.
Total RNA extraction and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
Viral genomic RNA was extracted from allantoic fluid using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, San Diego, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Reverse transcription was performed at 37°C for 1 h using 3 µg total RNA, 1 µL random primers (500 µg/mL random hexadeoxynucleotides) (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) and 0.5 µL M-MLV reverse transcriptase (200 U/µL) (Promega). The PCRs were performed in a thermocycler (Biometra, Germany) with 100 ng cDNA as template in a 20 µL reaction volume containing 10 pmol of each primer and 1 U Taq DNA polymerase (Promega). Reactions were performed according to the following protocol: 95°C for 5 min, followed by 35 cycles of 95°C for 45 s, 53°C or 55°C for 45 s, 72°C for 2 min, and a final elongation step of 10 min at 72°C [30]. PCR products were examined by electrophoresis on a 1.5% (w/v) agarose gel and visualized after Goldview staining.
Cloning and sequencing of PCR products
PCR products of the expected length were purified with a Gel Extraction kit (OMEGA, USA), then cloned into the PMD18-T vector (TaKaRa, Japan) according to the manufacturer's instructions and sequenced at BGI (Beijing, China). At least three clones of each segment were sequenced to control for Taq DNA polymerase misincorporation errors.
Phylogenetic analysis
Complete NDV genomic sequences were obtained from GenBank (Table 3), and these included current vaccine strains, typical prevailing isolates in China and the reference strains for each known NDV genotype. These NDV sequences and the complete coding sequences of the two NDV isolates were aligned and analyzed using the ClustalW multiple alignment algorithm in the MegAlign program of the DNASTAR software suite (version 3.1; DNAstar, Madison, WI, USA).
A phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA4.0 software (Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis, version 4.0) by Neighbor-Joining method (1000 replicates for bootstrap). The evolutionary distances were computed by Pairwise Distance method using the Maximum Composite Likelihood Model [31].
Clinicopathologic assessment in chickens
Three groups, each containing ten 1-week-old SPF White Leghorn chickens were inoculated via the intranasal route with 0.3 mL of one of the viruses (SD09 or GD09-2) or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) as a non-infected control. Each bird received approximately 105.0 (SD09) or 107.0 (GD09-2) EID50 of viral inoculum based on titrations in embryonated eggs to confirm the administered dose.
All birds were monitored clinically every day for signs of disease (disheveled feathers, lethargy, fever or paralysis) and mortality. Tissues (trachea, lung, brain, spleen, small intestine, proventriculus and kidney) were collected and fixed by immersion in 10% neutral buffered formalin for approximately 72 h, then 3 µm sections were prepared for histological observation.
Clinicopathologic assessment in ducks
Thirty 1-week-old Peking NDV antibody-negative ducks were randomly divided into three groups. The challenge procedure was carried out as described in the chicken experiments with slight modifications. All ducks were monitored daily for two weeks. Serum samples were collected from all birds before inoculation and at 14 days post infection (dpi) for NDV-specific antibody detection by a hemagglutination inhibition (HI) test in microtiter plates with 1% chicken red blood cells. Tissues (liver, spleen, small intestine and kidney) were collected for histological observation as described. To confirm the pathology in ducks, antigens of NDV in liver of GD09-2 inoculation group was further examined by immunohistochemistry (IHC) which employed an HN-protein-specific mouse monoclonal antibody. To test for virus shedding, cloacal swab samples were collected from all birds in GD09-2 group on 1, 3, 5 and 7 dpi to detect viral RNA by RT-PCR as previously described [2], [31].
Footnotes
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Funding: This work was supported by the Chinese Universities Scientific Fund (2009-1-11), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31001063), the earmarked fund for Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System (nycytx-45-11), and the Program for Cheung Kong Scholars and Innovative Research Teams in Chinese Universities (No. IRT0866). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Mayo MA. A summary of taxonomic changes recently approved by ICTV. Arch Virol. 2002;147:1655–1663. doi: 10.1007/s007050200039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rui Z, Juan P, Jingliang S, Jixun Z, Xiaoting W, et al. Phylogenetic characterization of Newcastle disease virus isolated in the mainland of China during 2001–2009. Vet Microbiol. 2010;141:246–257. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2009.09.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Peeters P, Verbruggen P, Nelissen F, de Leeuw O. The P gene of Newcastle disease virus does not encode an accessory X protein. J Gen Virol. 2004;85:2375–2378. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.80160-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wakamatsu N, King DJ, Seal BS, Samal SK, Brown CC. The pathogenesis of Newcastle disease: a comparison of selected Newcastle disease virus wild-type strains and their infectious clones. Virology. 2006;353:333–343. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Alexander DJ. Newcastle disease virus and other avian paramyxoviruses. In: Swayne DE, editor. A laboratory manual for the isolation and identification of avian pathogens. The American Association of Avian Pathologists, Kennett Square, PA; 1998. pp. 156–163. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jindal N, Chander Y, Chockalingam AK, de Abin M, Redig PT, et al. Phylogenetic analysis of Newcastle disease viruses isolated from waterfowl in the upper midwest region of the United States. Virol J. 2009;6:191. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-6-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tsunekuni R, Ito H, Otsuki K, Kida H, Ito T. Genetic comparisons between lentogenic Newcastle disease virus isolated from waterfowl and velogenic variants. Virus Genes. 2010;40:252–255. doi: 10.1007/s11262-009-0427-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Seal BS, King DJ, Sellers HS. The avian response to Newcastle disease virus. Dev Comp Immunol. 2000;24:257–268. doi: 10.1016/s0145-305x(99)00077-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Aldous EW, Mynn JK, Banks J, Alexander DJ. A molecular epidemiological study of avian paramyxovirus type 1 (Newcastle disease virus) isolates by phylogenetic analysis of a partial nucleotide sequence of the fusion protein gene. Avian Pathol. 2003;32:239–256. doi: 10.1080/030794503100009783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Liu XF, Wan HQ, Ni XX, Wu YT, Liu WB. Pathotypical and genotypical characterization of strains of Newcastle disease virus isolated from outbreaks in chicken and goose flocks in some regions of China during 1985–2001. Arch Virol. 2003;148:1387–1403. doi: 10.1007/s00705-003-0014-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Seal BS, Wise MG, Pedersen JC, Senne DA, Alvarez R, et al. Genomic sequences of low-virulence avian paramyxovirus-1 (Newcastle disease virus) isolates obtained from live-bird markets in North America not related to commonly utilized commercial vaccine strains. Vet Microbiol. 2005;106:7–16. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2004.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kim LM, King DJ, Curry PE, Suarez DL, Swayne DE, et al. Phylogenetic diversity among low-virulence newcastle disease viruses from waterfowl and shorebirds and comparison of genotype distributions to those of poultry-origin isolates. J Virol. 2007;81:12641–12653. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00843-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lee EK, Jeon WJ, Kwon JH, Yang CB, Choi KS. Molecular epidemiological investigation of Newcastle disease virus from domestic ducks in Korea. Vet Microbiol. 2009;134:241–248. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2008.08.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Miller PJ, Decanini EL, Afonso CL. Newcastle disease: evolution of genotypes and the related diagnostic challenges. Infect Genet Evol. 2010;10:26–35. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2009.09.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Maminiaina OF, Gil P, Briand FX, Albina E, Keita D, et al. Newcastle disease virus in Madagascar: identification of an original genotype possibly deriving from a died out ancestor of genotype IV. PLoS One. 2010;5:e13987. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sinkovics JG, Horvath JC. Newcastle disease virus (NDV): brief history of its oncolytic strains. J Clin Virol. 2000;16:1–15. doi: 10.1016/s1386-6532(99)00072-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Shengqing Y, Kishida N, Ito H, Kida H, Otsuki K, et al. Generation of velogenic Newcastle disease viruses from a nonpathogenic waterfowl isolate by passaging in chickens. Virology. 2002;301:206–211. doi: 10.1006/viro.2002.1539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Stanislawek WL, Wilks VR, Meers J, Horner GW, Alexander DJ, et al. Avian paramyxoviruses and influenza viruses isolated from mallard ducks (Anas platyrhynchos) in New Zealand. Arch Virol. 2002;147:1287–1302. doi: 10.1007/s00705-002-0818-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tsai HJ, Chang KH, Tseng CH, Frost KM, Manvell RJ, et al. Antigenic and genotypical characterization of Newcastle disease viruses isolated in Taiwan between 1969 and 1996. Vet Microbiol. 2004;104:19–30. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2004.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Liu H, Chen F, Zhao Y, Zheng D, Li J, et al. Genomic characterization of the first class I Newcastle disease virus isolated from the mainland of China. Virus Genes. 2010;40:365–371. doi: 10.1007/s11262-010-0452-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Collins MS, Bashiruddin JB, Alexander DJ. Deduced amino acid sequences at the fusion protein cleavage site of Newcastle disease viruses showing variation in antigenicity and pathogenicity. Arch Virol. 1993;128:363–370. doi: 10.1007/BF01309446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Miller PJ, King DJ, Afonso CL, Suarez DL. Antigenic differences among Newcastle disease virus strains of different genotypes used in vaccine formulation affect viral shedding after a virulent challenge. Vaccine. 2007;25:7238–7246. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.07.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Takakuwa H, Ito T, Takada A, Okazaki K, Kida H. Potentially virulent Newcastle disease viruses are maintained in migratory waterfowl populations. Jpn J Vet Res. 1998;45:207–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Roy P, Venugopalan AT, Manvell R. Characterization of Newcastle disease viruses isolated from chickens and ducks in Tamilnadu, India. Vet Res Commun. 2000;24:135–142. doi: 10.1023/a:1006416724050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jorgensen PH, Handberg KJ, Ahrens P, Therkildsen OR, Manvell RJ, et al. Strains of avian paramyxovirus type 1 of low pathogenicity for chickens isolated from poultry and wild birds in Denmark. Vet Rec. 2004;154:497–500. doi: 10.1136/vr.154.16.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Otim OM, Christensen H, Mukiibi GM, Bisgaard M. A preliminary study of the role of ducks in the transmission of Newcastle disease virus to in-contact rural free-range chickens. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2006;38:285–289. doi: 10.1007/s11250-006-4309-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Liu H, Wang Z, Wang Y, Sun C, Zheng D, et al. Characterization of Newcastle disease virus isolated from waterfowl in China. Avian Dis. 2008;52:150–155. doi: 10.1637/8030-061507-Reg. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Qin ZM, Tan LT, Xu HY, Ma BC, Wang YL, et al. Pathotypical characterization and molecular epidemiology of Newcastle disease virus isolates from different hosts in China from 1996 to 2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46:601–611. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01356-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mase M, Inoue T, Imada T. Genotyping of Newcastle disease viruses isolated from 2001 to 2007 in Japan. J Vet Med Sci. 2009;71:1101–1104. doi: 10.1292/jvms.71.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhang R, Wang XT, Su JL, Zhao JX, Zhang GZ. Isolation and analysis of two naturally-occurring multi-recombination Newcastle disease viruses in China. Virus Res. 2010;151:45–53. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24:1596–1599. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msm092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]