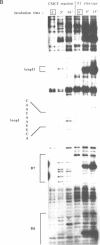
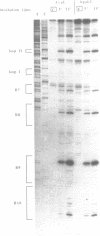
Abstract
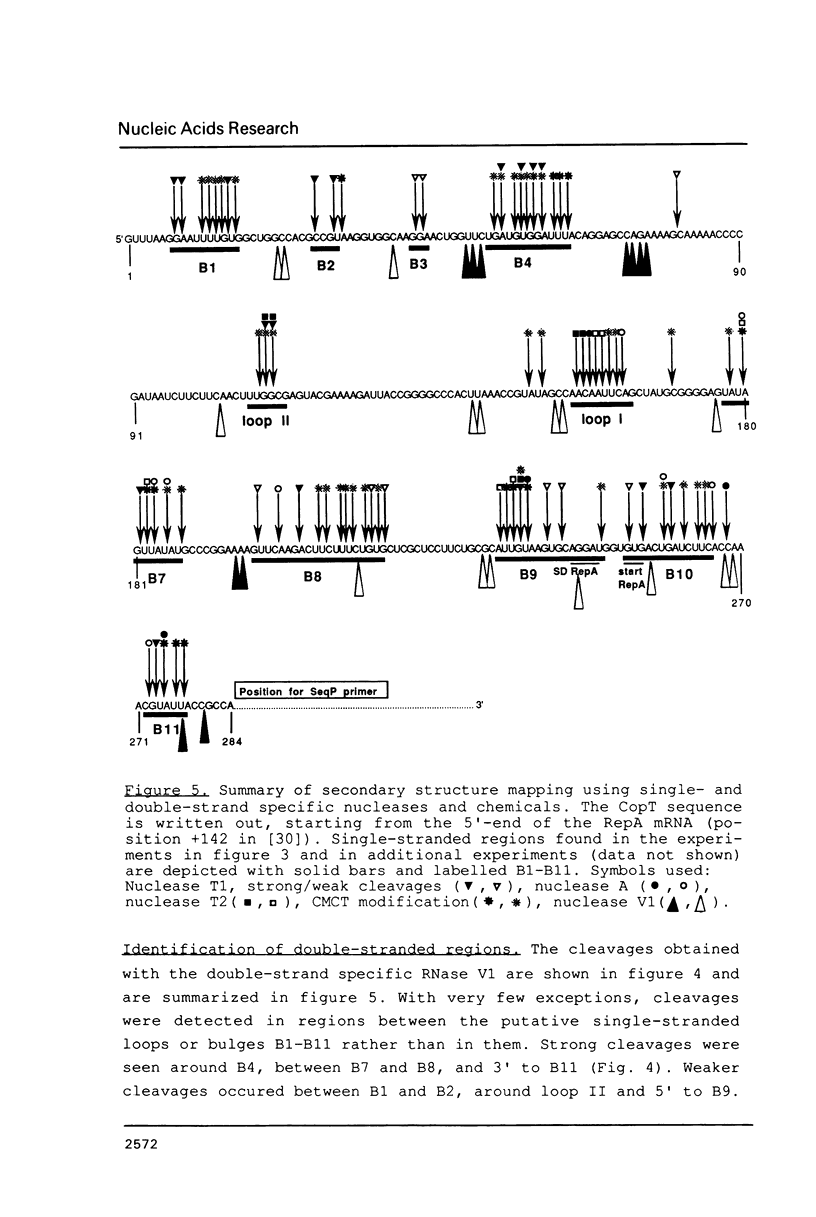
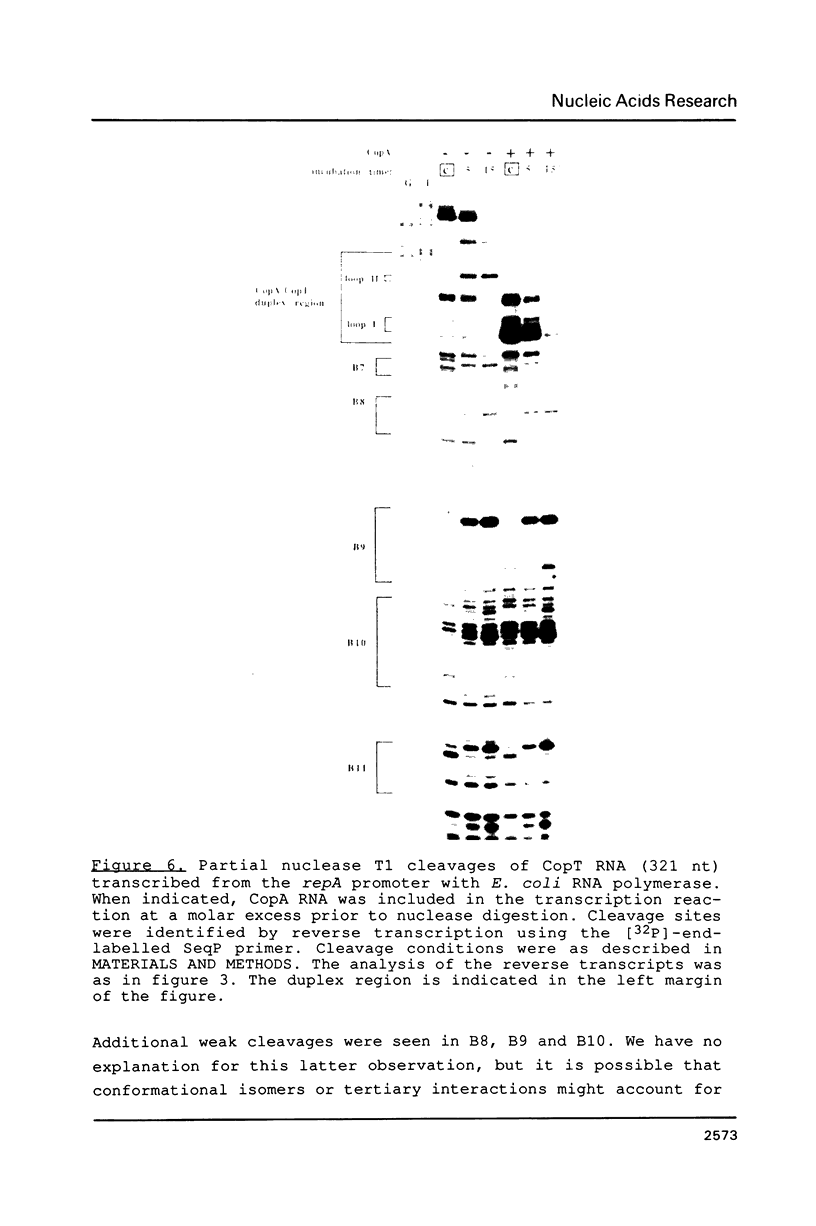
The main replication control function in plasmid R1 is an antisense RNA, CopA RNA. By binding to its target (CopT) in the leader of the RepA mRNA, CopA RNA inhibits the expression of the rate-limiting RepA protein. The formation of the RNA duplex has been proposed to alter the folding around the RepA start region. Knowledge of the secondary structure of both CopA and CopT RNA is crucial for an understanding of the regulation. Previously, we reported the structure of CopA RNA under native conditions. In the present communication we have analyzed the secondary structure of the RepA leader transcript. Our main findings are: The two loops of CopA RNA have their correspondence in CopT RNA. No major structural changes are found downstream of the duplex when CopA was bound to its target RNA during transcription. Furthermore, in agreement with CopA/CopT RNA binding studies reported recently we do not find evidence for the existence of a binding window.
Full text
PDF
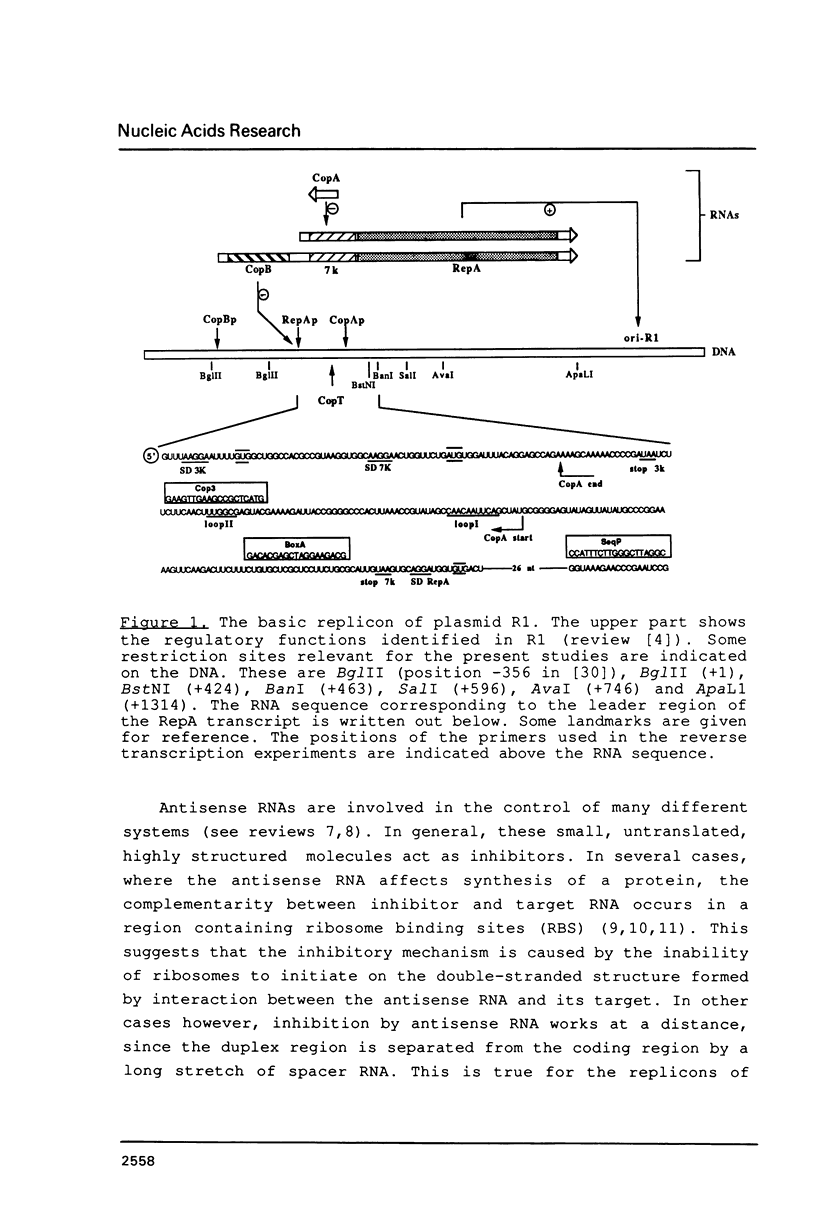










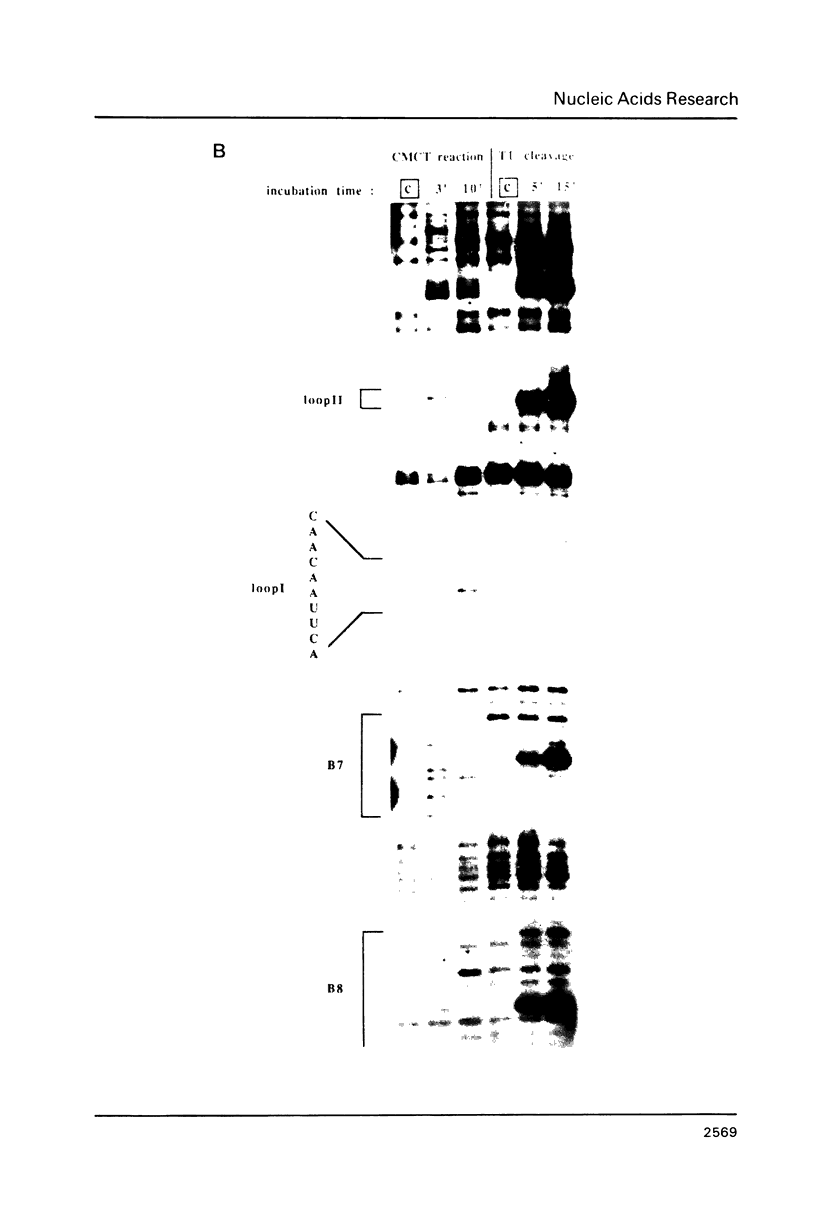








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altuvia S., Locker-Giladi H., Koby S., Ben-Nun O., Oppenheim A. B. RNase III stimulates the translation of the cIII gene of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6511–6515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong X. N., Womble D. D., Rownd R. H. Transcriptional pausing in a region important for plasmid NR1 replication control. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5353–5363. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5353-5363.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H. Site specific enzymatic cleavage of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 11;7(1):179–192. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann C., Baudin F., Mougel M., Romby P., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B. Probing the structure of RNAs in solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9109–9128. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart E., Wagner H., Nordström K. Structural analysis of an RNA molecule involved in replication control of plasmid R1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2523–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. J., Pines O., Inouye M. The role of antisense RNA in gene regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:569–597. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Grandi G., Hahn J., Grandi R., Dubnau D. Conformational alteration of mRNA structure and the posttranscriptional regulation of erythromycin-induced drug resistance. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6081–6097. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Weisblum B. Posttranscriptional modification of mRNA conformation: mechanism that regulates erythromycin-induced resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7079–7083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Meyer R. J. Copy-number of broad host-range plasmid R1162 is regulated by a small RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8027–8046. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolter R., Yanofsky C. Attenuation in amino acid biosynthetic operons. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:113–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao S. M., Wu T. H., Chiang C. H., Susskind M. M., McClure W. R. Control of gene expression in bacteriophage P22 by a small antisense RNA. I. Characterization in vitro of the Psar promoter and the sar RNA transcript. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):197–203. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light J., Molin S. Post-transcriptional control of expression of the repA gene of plasmid R1 mediated by a small RNA molecule. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):93–98. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masukata H., Tomizawa J. Control of primer formation for ColE1 plasmid replication: conformational change of the primer transcript. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90491-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masukata H., Tomizawa J. Effects of point mutations on formation and structure of the RNA primer for ColE1 DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):513–522. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90244-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moine H., Romby P., Springer M., Grunberg-Manago M., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C., Ehresmann B. Messenger RNA structure and gene regulation at the translational level in Escherichia coli: the case of threonine:tRNAThr ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7892–7896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Projan S. J., Kumar C. C., Carleton S., Gruss A., Highlander S. K., Kornblum J. Replication control for pT181, an indirectly regulated plasmid. Basic Life Sci. 1985;30:299–320. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-2447-8_24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson C., Wagner E. G., Nordström K. Control of replication of plasmid R1: kinetics of in vitro interaction between the antisense RNA, CopA, and its target, CopT. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3279–3288. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03195.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder T. B., Davidson D. B., Rosen J. I., Ohtsubo E., Ohtsubo H. Analysis of plasmid genome evolution based on nucleotide-sequence comparison of two related plasmids of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Kleckner N. Translational control of IS10 transposition. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):683–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W. Naturally occurring antisense RNA control--a brief review. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steger G., Hofmann H., Förtsch J., Gross H. J., Randles J. W., Sänger H. L., Riesner D. Conformational transitions in viroids and virusoids: comparison of results from energy minimization algorithm and from experimental data. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1984 Dec;2(3):543–571. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1984.10507591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stougaard P., Molin S., Nordström K. RNAs involved in copy-number control and incompatibility of plasmid R1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6008–6012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J. Control of ColE1 plasmid replication: binding of RNA I to RNA II and inhibition of primer formation. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90369-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J., Itoh T. Plasmid ColE1 incompatibility determined by interaction of RNA I with primer transcript. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6096–6100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. G., von Heijne J., Nordström K. Control of replication of plasmid R1: translation of the 7k reading frame in the RepA mRNA leader region counteracts the interaction between CopA RNA and CopT RNA. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):515–522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04783.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Womble D. D., Dong X., Wu R. P., Luckow V. A., Martinez A. F., Rownd R. H. IncFII plasmid incompatibility product and its target are both RNA transcripts. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):28–35. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.28-35.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]