Abstract
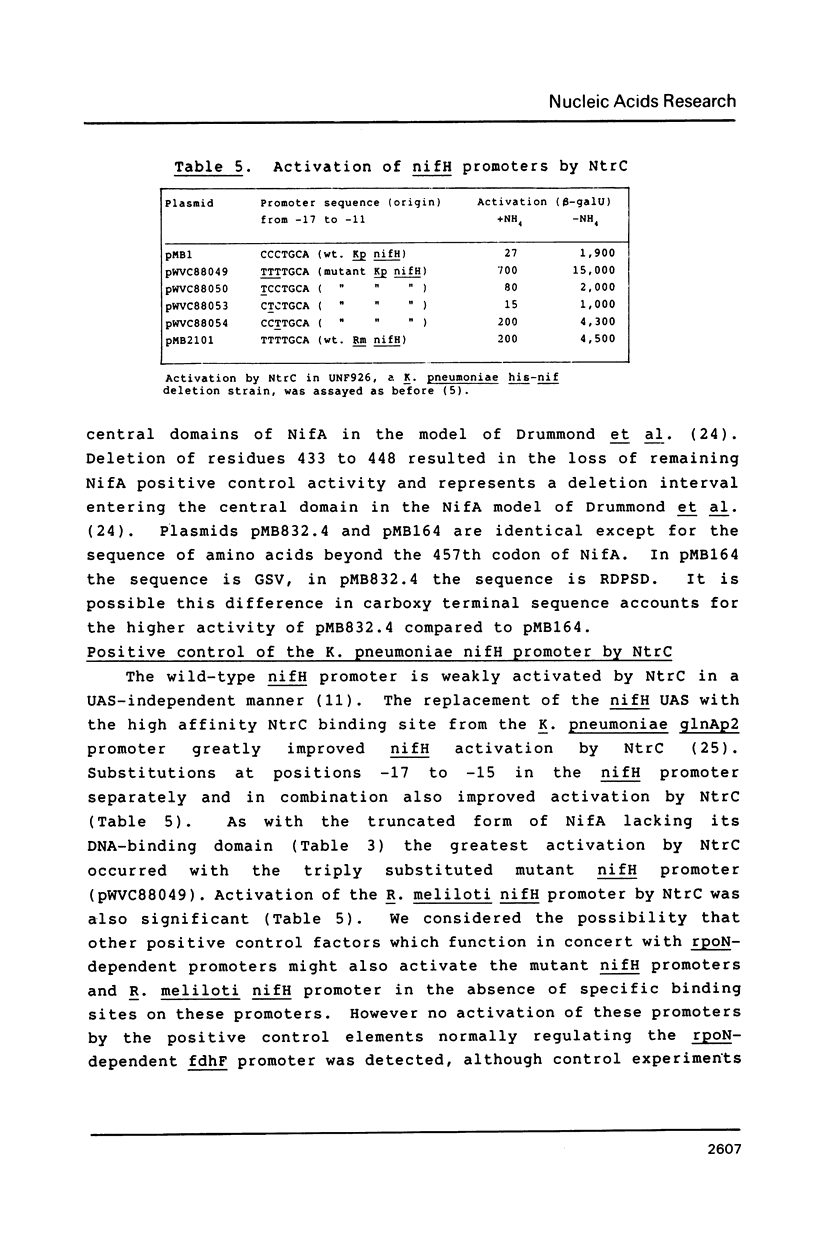
Positive control of the wild-type Klebsiella pneumoniae nifH promoter by the NifA protein requires that NifA is bound at the upstream activator sequence (UAS). By introducing base substitutions at -15 to -17 in the RNA polymerase recognition sequence of the nifH promoter, positive control by a form of NifA unable to bind to the UAS was greatly increased when compared to the wild-type promoter. Transcriptional activation still required the rpoN encoded sigma factor and was initiated at the same nucleotide as in the wild-type promoter. Mutations at -15 to -17 suppressed the requirement that the UAS should be located on the correct face of the DNA helix with respect to the RNA polymerase recognition sequence in order that titration of NifA and efficient activation occur. This result supports the suggestion that upstream bound NifA interacts with the RNA polymerase-RpoN complex. To examine the minimal carboxy terminal sequences required for the positive control function of NifA a series of carboxy terminal deletions were constructed. Efficient positive control at a UAS-independent promoter was only observed in deletions which did not extend beyond the proposed boundary separating the carboxy terminal NifA DNA-binding domain from its central domain.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11905–11910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin S., Henderson N., Dixon R. Requirements for transcriptional activation in vitro of the nitrogen-regulated glnA and nifLA promoters from Klebsiella pneumoniae: dependence on activator concentration. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Jul;1(1):92–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00532.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Better M., Ditta G., Helinski D. R. Deletion analysis of Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic promoters. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2419–2424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkmann A., Sawers R. G., Böck A. Involvement of the ntrA gene product in the anaerobic metabolism of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(3):535–542. doi: 10.1007/BF00327209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan-Wollaston V., Cannon M. C., Beynon J. L., Cannon F. C. Role of the nifA gene product in the regulation of nif expression in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):776–778. doi: 10.1038/294776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M., Cannon W., Woodcock J. Mutational analysis of upstream sequences required for transcriptional activation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifH promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9945–9956. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M., Cannon W., Woodcock J. Transcriptional activation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase promoter may involve DNA loop formation. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Sep;1(2):243–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M., Khan H., Dixon R. Site-directed mutagenesis of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifL and nifH promoters and in vivo analysis of promoter activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7621–7638. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Chou J., Cohen S. N. In vitro gene fusions that join an enzymatically active beta-galactosidase segment to amino-terminal fragments of exogenous proteins: Escherichia coli plasmid vectors for the detection and cloning of translational initiation signals. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):971–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.971-980.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras A., Drummond M. The effect on the function of the transcriptional activator NtrC from Klebsiella pneumoniae of mutations in the DNA-recognition helix. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):4025–4039. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.4025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. The xylABC promoter from the Pseudomonas putida TOL plasmid is activated by nitrogen regulatory genes in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Apr;203(1):129–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00330393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M., Clements J., Merrick M., Dixon R. Positive control and autogenous regulation of the nifLA promoter in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nature. 1983 Jan 27;301(5898):302–307. doi: 10.1038/301302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M., Whitty P., Wootton J. Sequence and domain relationships of ntrC and nifA from Klebsiella pneumoniae: homologies to other regulatory proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):441–447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H. M., Bruderer T., Hennecke H. Essential and non-essential domains in the Bradyrhizobium japonicum NifA protein: identification of indispensable cysteine residues potentially involved in redox reactivity and/or metal binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2207–2224. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gussin G. N., Ronson C. W., Ausubel F. M. Regulation of nitrogen fixation genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:567–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes T., Merrick M., Dixon R. Interaction of purified NtrC protein with nitrogen regulated promoters from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;201(3):492–498. doi: 10.1007/BF00331345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan H., Buck M., Dixon R. Deletion loop mutagenesis of the nifL promoter from Klebsiella pneumoniae: role of the -26 to -12 region in promoter function. Gene. 1986;45(3):281–288. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lers A., Bitoun R., Zamir A. Transcriptional analysis of promoter mutations in the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifHDKY operon. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):175–180. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.175-180.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minchin S. D., Austin S., Dixon R. A. The role of activator binding sites in transcriptional control of the divergently transcribed nifF and nifLA promoters from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jul;2(4):433–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00049.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Buck M. NifA-dependent in vivo protection demonstrates that the upstream activator sequence of nif promoters is a protein binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9401–9405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Cannon W., Buck M. The DNA-binding domain of the transcriptional activator protein NifA resides in its carboxy terminus, recognises the upstream activator sequences of nif promoters and can be separated from the positive control function of NifA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11469–11488. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Magasanik B. Covalent modification of the glnG product, NRI, by the glnL product, NRII, regulates the transcription of the glnALG operon in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5909–5913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Initiation of transcription at the bacterial glnAp2 promoter by purified E. coli components is facilitated by enhancers. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1039–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ow D. W., Xiong Y., Gu Q., Shen S. C. Mutational analysis of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase promoter: sequences essential for positive control by nifA and ntrC (glnG) products. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):868–874. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.868-874.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Transcription of glnA in E. coli is stimulated by activator bound to sites far from the promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):785–792. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90553-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasse-Dwight S., Gralla J. D. Probing the Escherichia coli glnALG upstream activation mechanism in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8934–8938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaresan V., Jones J. D., Ow D. W., Ausubel F. M. Klebsiella pneumoniae nifA product activates the Rhizobium meliloti nitrogenase promoter. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):728–732. doi: 10.1038/301728a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




