Abstract
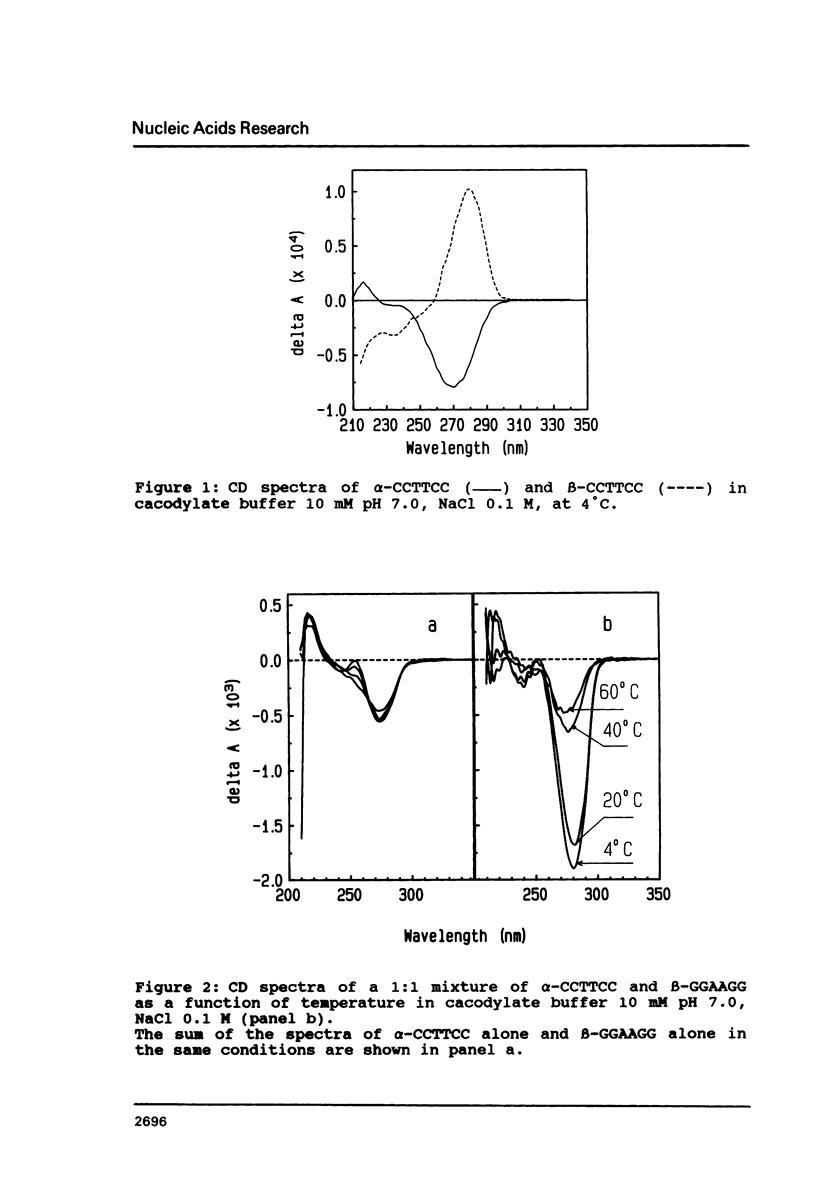
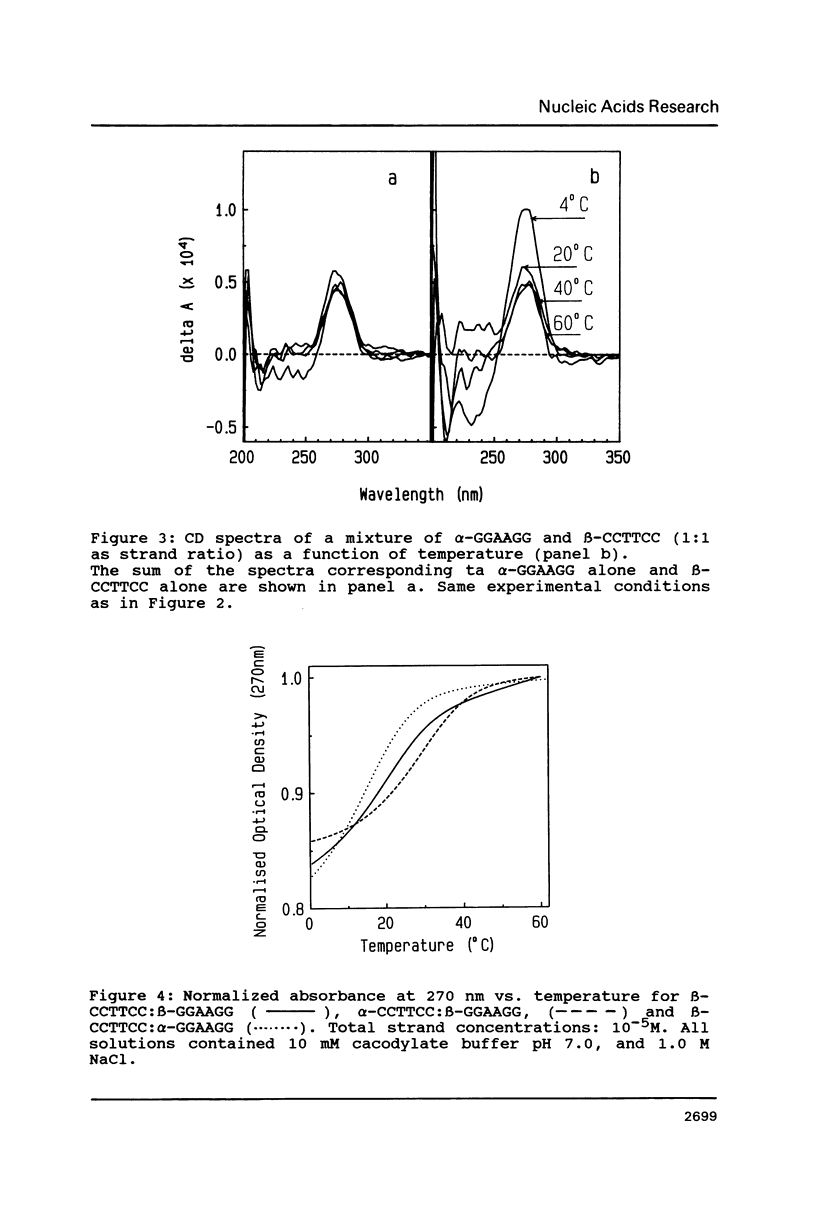
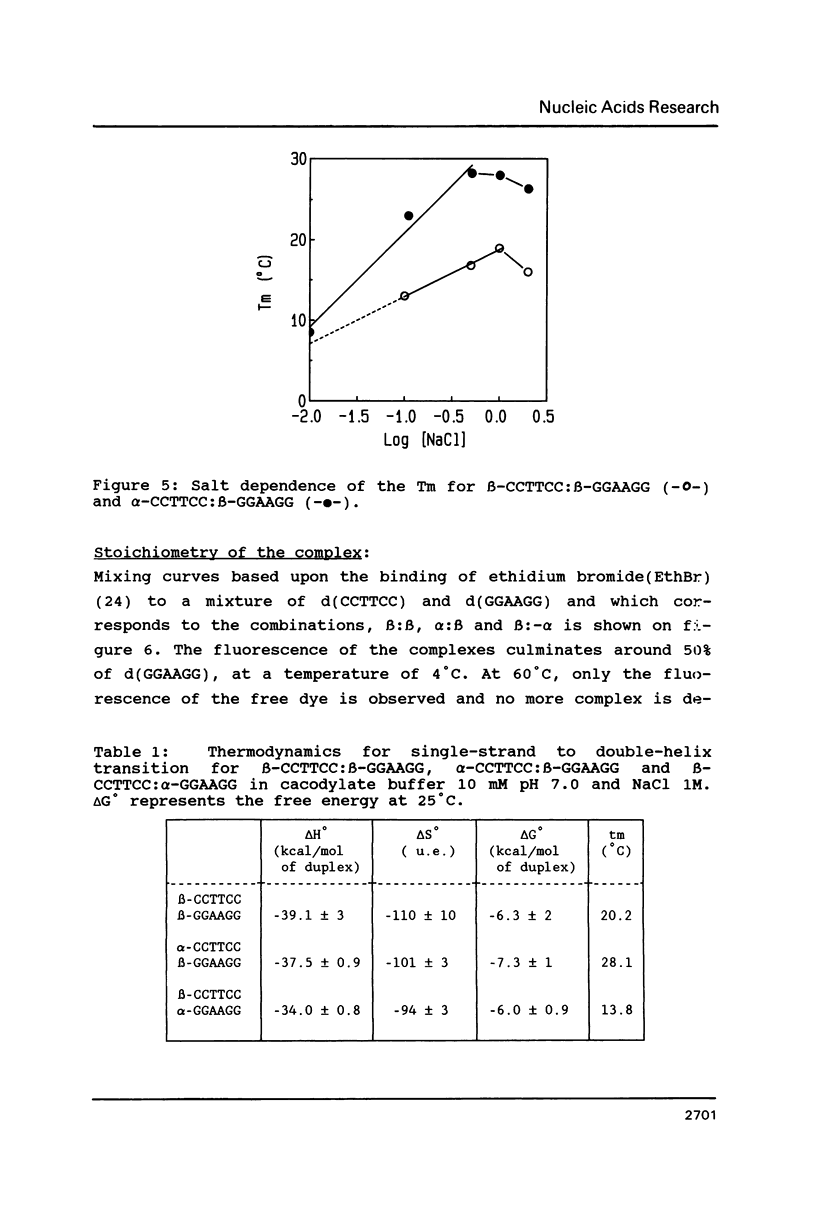
The temperature dependence of the formation of a complex between an alpha-d(CCTTCC) hexanucleotide and its complementary beta-d(GGAAGG) sequence was studied and compared to the formation of the beta-d(CCTTCC):beta-d(GGAAGG) complex. Such alpha-beta complex is more stable than the regular beta:beta complex. The Tm value for the alpha:beta complex is 28 degrees C (delta G degrees = -7.3 kcal/mole) while Tm = 20, 1 degree C (delta G degrees = -6.3 kcal/mole) for the beta:beta complex. The stoechiometry of the alpha:beta complex corresponds to the formation of a 1:1 duplex. However, when the alpha- strand is made of alpha-purines: alpha-d(GGAAGG), the stability of the alpha:beta complex, alpha-d(GGAAGG):beta-d(CCTTCC) is found to be lower (Tm = 13.8 degrees C) than the stability of the regular beta-beta complex, leading to the conclusion that the nature of the alpha-sequence is important in terms of stability when considering the synthesis of such a sequence for using it as antisense oligonucleotide.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albergo D. D., Marky L. A., Breslauer K. J., Turner D. H. Thermodynamics of (dG--dC)3 double-helix formation in water and deuterium oxide. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 17;20(6):1409–1413. doi: 10.1021/bi00509a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleby D. W., Kallenbach N. R. Theory of oligonucleotide stabilization. I. The effect of single-strand stacking. Biopolymers. 1973;12(9):2093–2120. doi: 10.1002/bip.1973.360120915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslauer K. J., Frank R., Blöcker H., Marky L. A. Predicting DNA duplex stability from the base sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3746–3750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslauer K. J., Sturtevant J. M., Tinoco I., Jr Calorimetric and spectroscopic investigation of the helix-to-coil transition of a ribo-oligonucleotide: rA7U7. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 25;99(4):549–565. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80171-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand M., Maurizot J. C., Thuong N. T., Helene C. Circular dichroism studies of an oligo-alpha-thymidylate and of its interactions with complementary sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):5039–5053. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.5039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier C., Bazile D., Paoletti J. Poly(rA) binding of alpha-anomeric and beta-anomeric tetrathymidylates covalently linked to an intercalating oxazolopyridocarbazolium. Determination of the binding parameters. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 15;154(1):252–257. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90677-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier C., Morvan F., Rayner B., Huynh-Dinh T., Igolen J., Imbach J. L., Paoletti C., Paoletti J. Alpha-DNA. IV: Alpha-anomeric and beta-anomeric tetrathymidylates covalently linked to intercalating oxazolopyridocarbazole. Synthesis, physicochemical properties and poly (rA) binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6625–6641. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helene C., Thuong N. T. Oligo-[alpha]-deoxynucleotides covalently linked to intercalating agents. DNA and RNA binding properties. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 May 1;37(9):1797–1798. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90451-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancelot G., Guesnet J. L., Roig V., Thuong N. T. 2D-NMR studies of the unnatural duplex alpha-d(TCTAAAC)-beta-d(AGATTTG). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7531–7547. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morvan F., Rayner B., Imbach J. L., Chang D. K., Lown J. W. alpha-DNA-III. Characterization by high field 1H-NMR, anti-parallel self-recognition and conformation of the unnatural hexadeoxyribonucleotides alpha-[d(CpApTpGpCpG)] and alpha-[d(CpGpCpApTpG)]. Alpha-oligodeoxynucleotides as potential cellular probes for gene control. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4241–4255. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morvan F., Rayner B., Imbach J. L., Chang D. K., Lown J. W. alpha-DNA. I. Synthesis, characterization by high field 1H-NMR, and base-pairing properties of the unnatural hexadeoxyribonucleotide alpha-[d(CpCpTpTpCpC)] with its complement beta-[d(GpGpApApGpG)]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):5019–5035. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.5019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morvan F., Rayner B., Imbach J. L., Lee M., Hartley J. A., Chang D. K., Lown J. W. alpha-DNA-V. Parallel annealing, handedness and conformation of the duplex of the unnatural alpha-hexadeoxyribonucleotide alpha-[d(CpApTpGpCpG)] with its beta-complement beta-[d(GpTpApCpGpC)] deduced from high field 1H-NMR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7027–7044. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morvan F., Rayner B., Imbach J. L., Thenet S., Bertrand J. R., Paoletti J., Malvy C., Paoletti C. alpha-DNA II. Synthesis of unnatural alpha-anomeric oligodeoxyribonucleotides containing the four usual bases and study of their substrate activities for nucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3421–3437. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morvan F., Rayner B., Leonetti J. P., Imbach J. L. alpha-DNA. VII. Solid phase synthesis of alpha-anomeric oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):833–847. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersheim M., Turner D. H. Base-stacking and base-pairing contributions to helix stability: thermodynamics of double-helix formation with CCGG, CCGGp, CCGGAp, ACCGGp, CCGGUp, and ACCGGUp. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):256–263. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praseuth D., Chassignol M., Takasugi M., Le Doan T., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Double helices with parallel strands are formed by nuclease-resistant oligo-[alpha]-deoxynucleotides and oligo-[alpha]-deoxynucleotides covalently linked to an intercalating agent with complementary oligo-[beta]-deoxynucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):939–942. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90416-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuong N. T., Asseline U., Roig V., Takasugi M., Hélène C. Oligo(alpha-deoxynucleotide)s covalently linked to intercalating agents: differential binding to ribo- and deoxyribopolynucleotides and stability towards nuclease digestion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5129–5133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerial A., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Selective inhibition of the cytopathic effect of type A influenza viruses by oligodeoxynucleotides covalently linked to an intercalating agent. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9909–9919. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


