Abstract
We describe a new human subfamily of alpha satellite DNA. The restriction endonuclease XbaI cleaves this subfamily into a collection of fragments which are heterogeneous with respect to size. We compared the sequences of 6 clones from four different XbaI size classes. Clones from a single size class were not necessarily more related than clones from different classes. Clones from different size classes were found to produce almost identical hybridization patterns with XbaI-digested human genomic DNA. All clones were found to share a common dimeric repeat organization, with dimers exhibiting about 84% sequence identities, indicating that the clones evolved from a common progenitor alphoid dimer. We show that this subfamily, and the EcoRI dimer subfamily originally described by Wu and Manuelidis, evolved from different progenitor alphoid dimers, and therefore represent distinct human alphoid subfamilies.
Full text
PDF




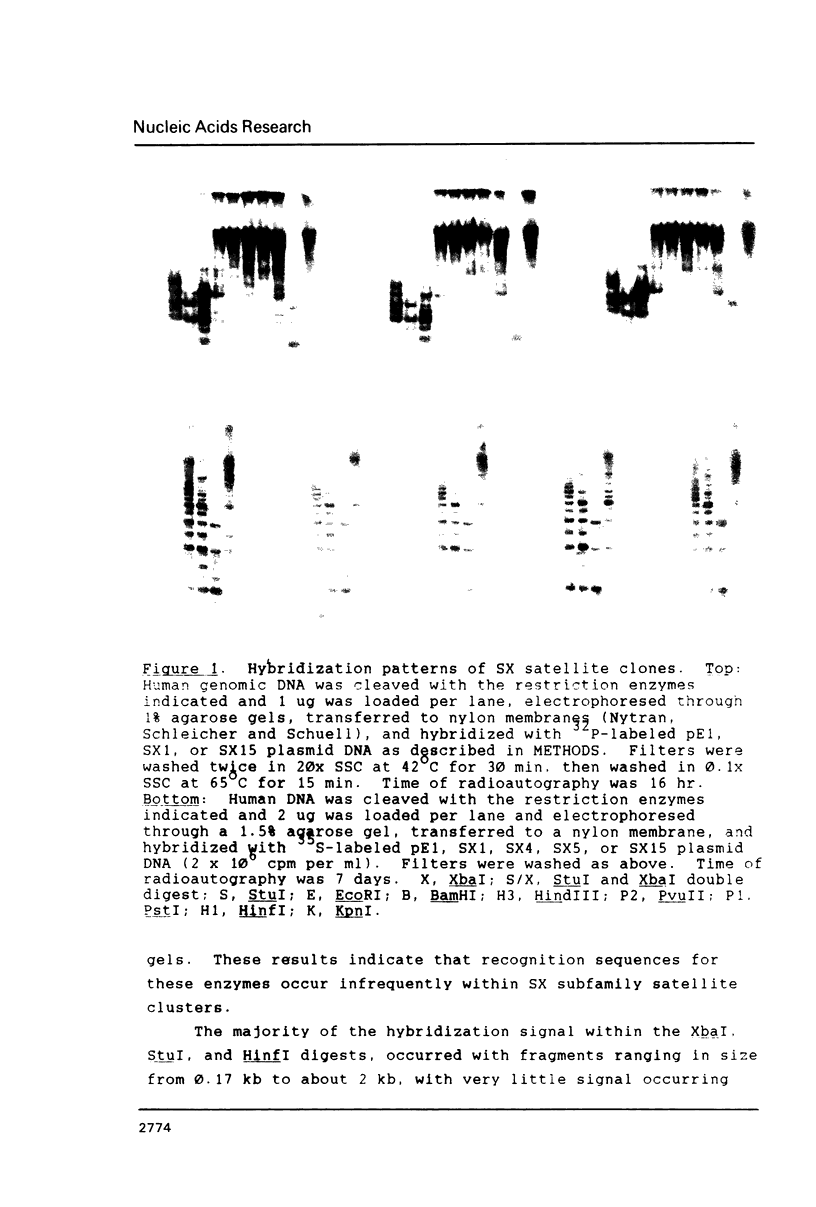

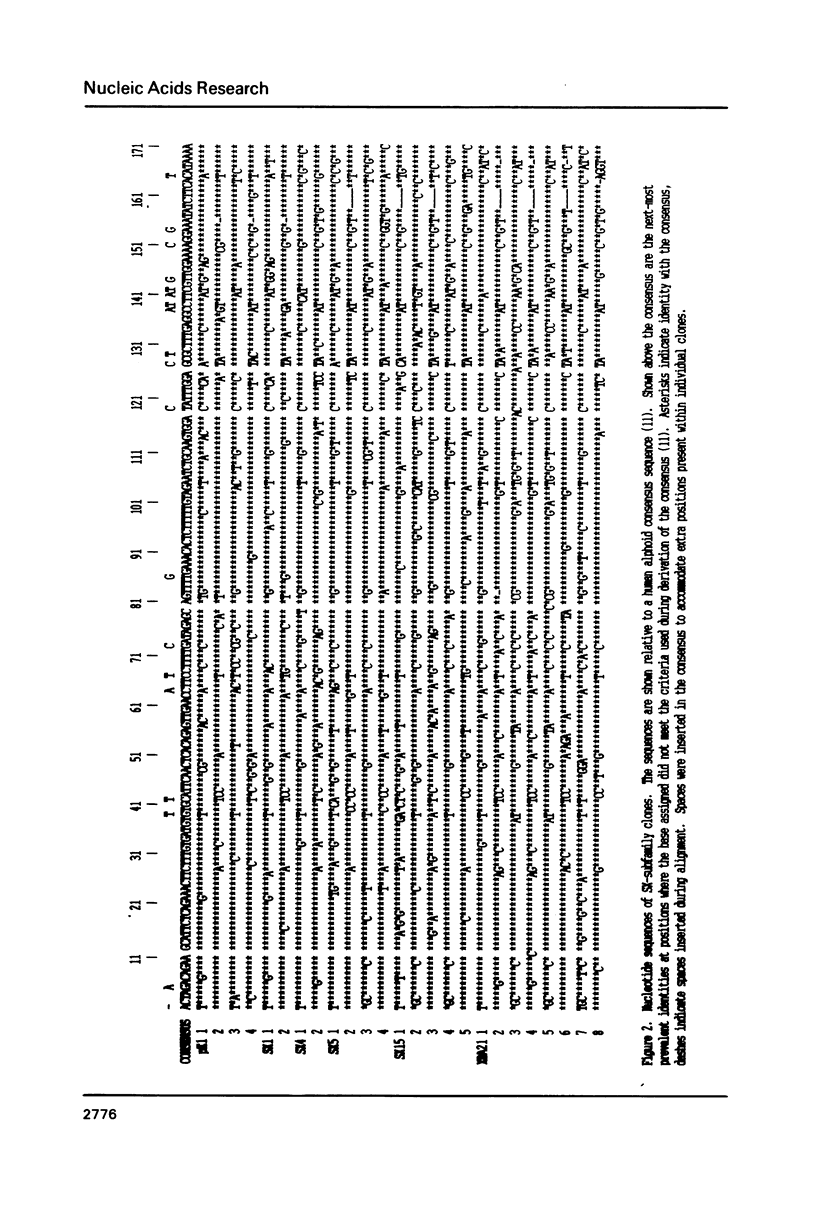
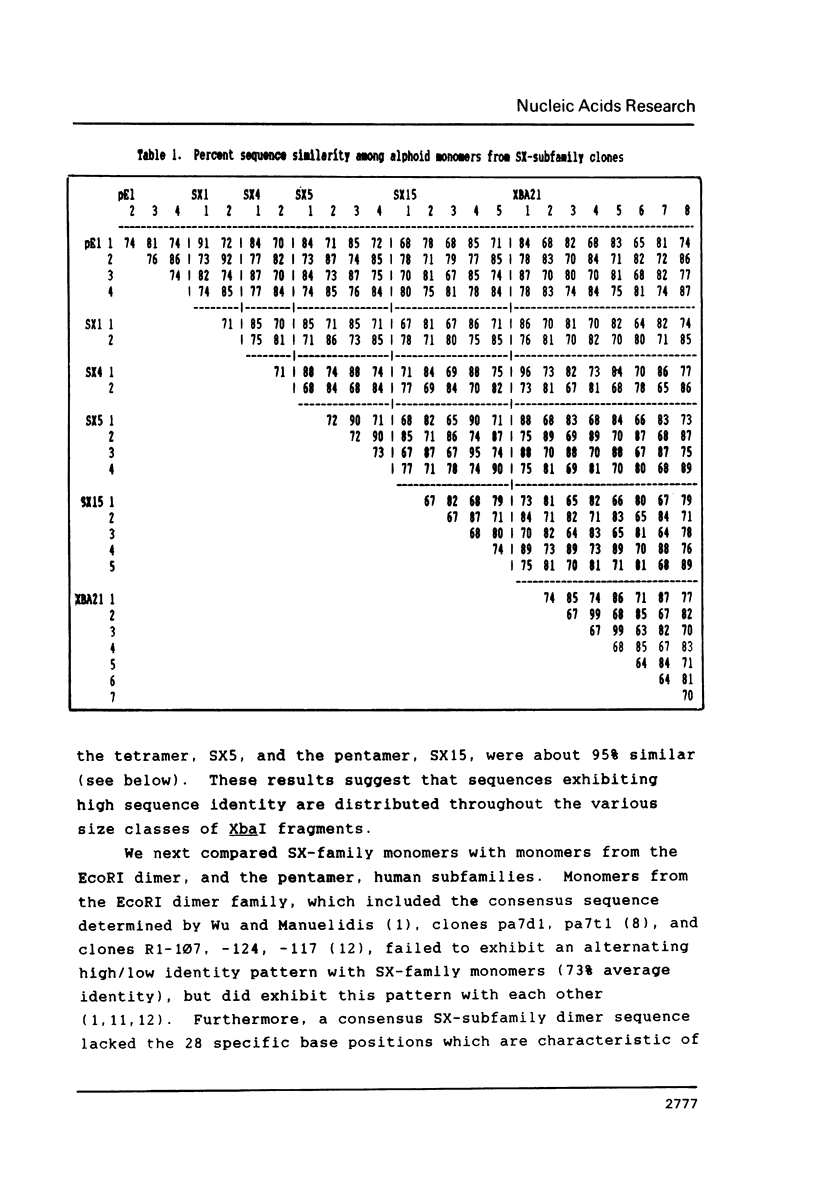





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexandrov I. A., Mitkevich S. P., Yurov Y. B. The phylogeny of human chromosome specific alpha satellites. Chromosoma. 1988;96(6):443–453. doi: 10.1007/BF00303039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D. L. Molecular arrangement and evolution of heterochromatic DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:121–144. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., Vissel B., Brown R., Filby R. G., Earle E. Homologous alpha satellite sequences on human acrocentric chromosomes with selectivity for chromosomes 13, 14 and 21: implications for recombination between nonhomologues and Robertsonian translocations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1273–1284. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling S. M., Crampton J. M., Williamson R. Organization of a family of highly repetitive sequences within the human genome. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 5;154(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90416-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L., Gillespie D. Restriction site periodicities in highly repetitive DNA of primates. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):805–834. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90487-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray K. M., White J. W., Costanzi C., Gillespie D., Schroeder W. T., Calabretta B., Saunders G. F. Recent amplification of an alpha satellite DNA in humans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 25;13(2):521–535. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen A. L., Bostock C. J., Bak A. L. Chromosome-specific subfamilies within human alphoid repetitive DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 20;187(2):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen A. L., Bostock C. J., Bak A. L. Homologous subfamilies of human alphoid repetitive DNA on different nucleolus organizing chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1075–1079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maio J. J. DNA strand reassociation and polyribonucleotide binding in the African green monkey, Cercopithecus aethiops. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 28;56(3):579–595. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90403-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Chromosomal localization of complex and simple repeated human DNAs. Chromosoma. 1978 Mar 22;66(1):23–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00285813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;76:67–112. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61789-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., England S. B., Willard H. F. Genomic organization of alpha satellite DNA on human chromosome 7: evidence for two distinct alphoid domains on a single chromosome. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):349–356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., Willard H. F. Nucleotide sequence heterogeneity of alpha satellite repetitive DNA: a survey of alphoid sequences from different human chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7549–7569. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F. Chromosome-specific organization of human alpha satellite DNA. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):524–532. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F., Smith K. D., Sutherland J. Isolation and characterization of a major tandem repeat family from the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 11;11(7):2017–2033. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.7.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F., Waye J. S. Chromosome-specific subsets of human alpha satellite DNA: analysis of sequence divergence within and between chromosomal subsets and evidence for an ancestral pentameric repeat. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(3):207–214. doi: 10.1007/BF02100014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. C., Manuelidis L. Sequence definition and organization of a human repeated DNA. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):363–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90277-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]