Abstract
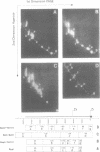
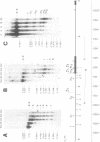
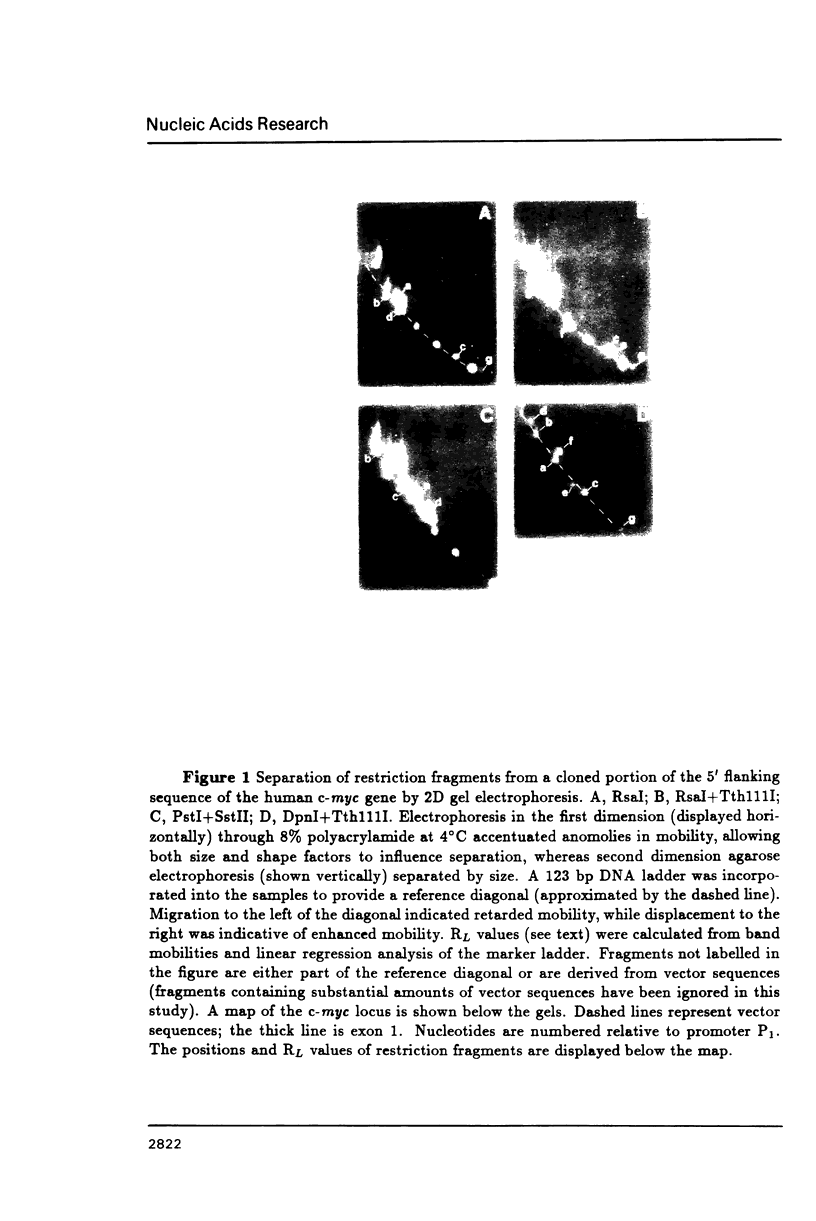
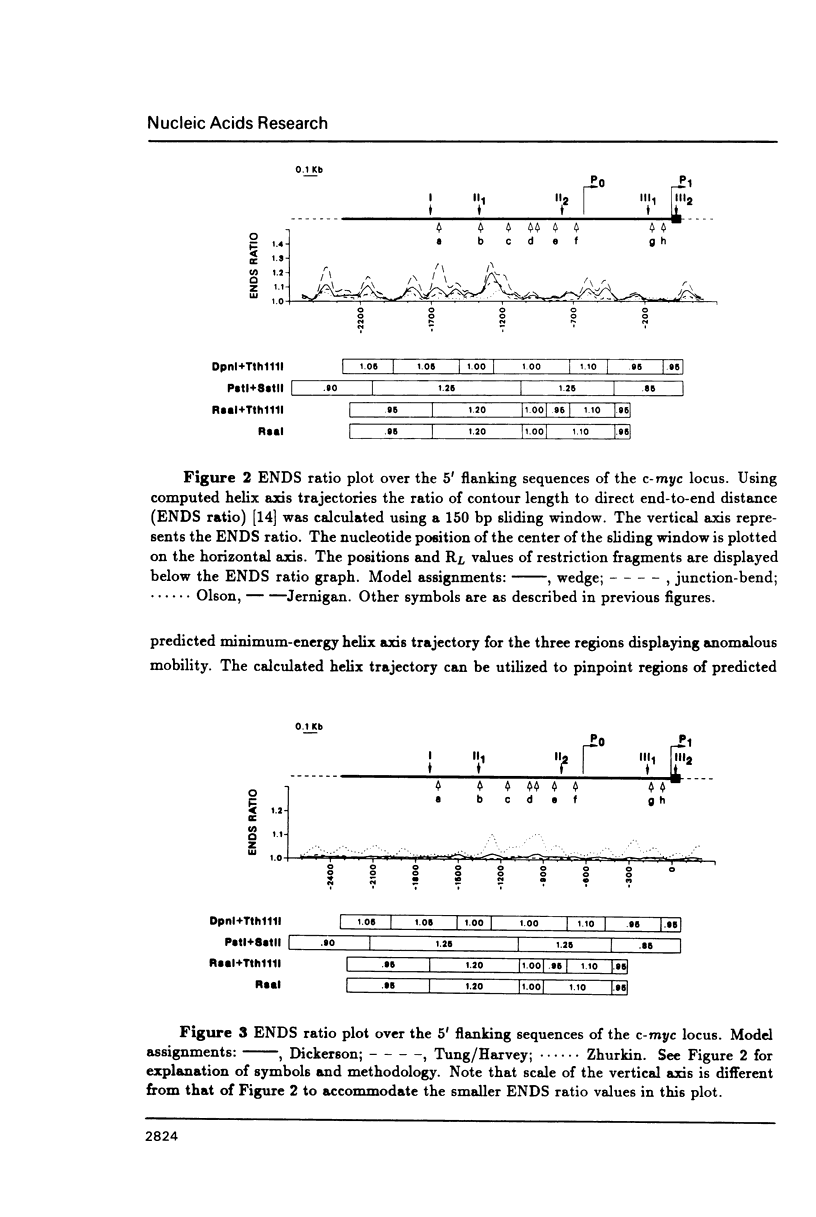
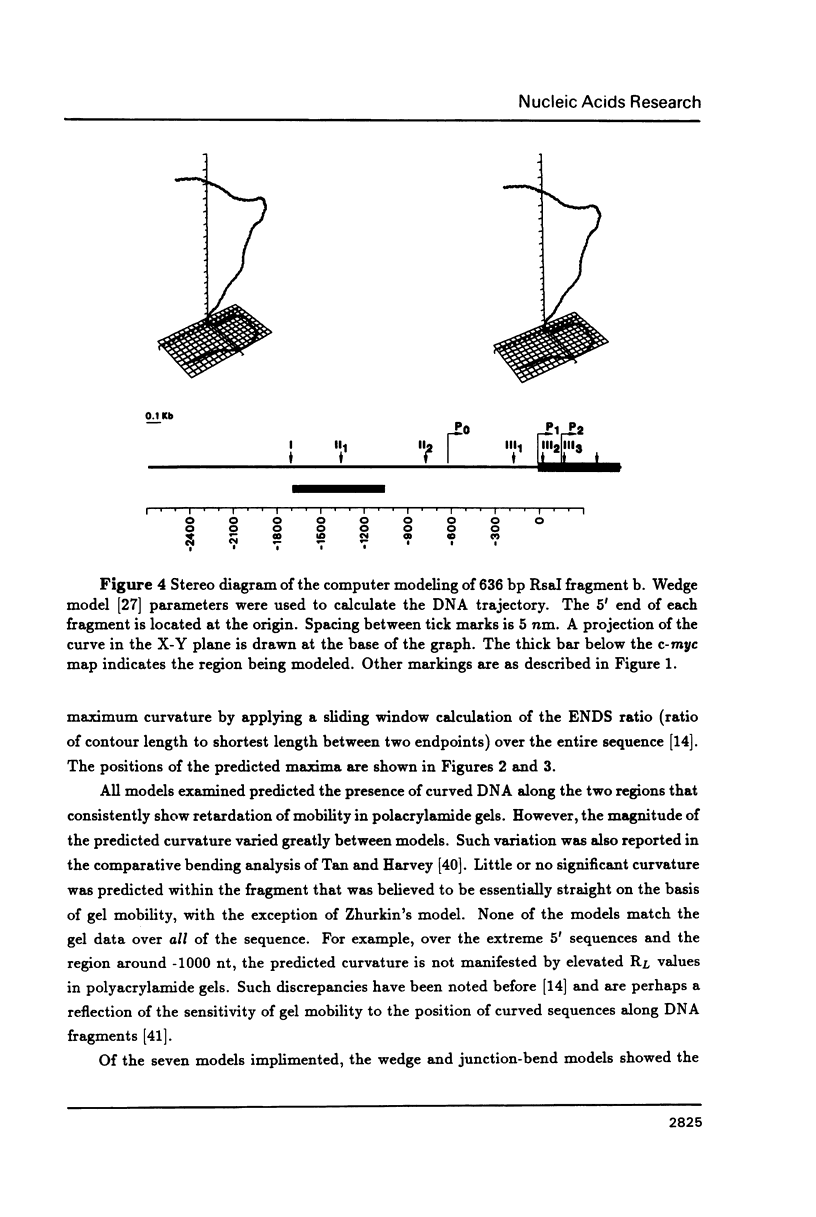
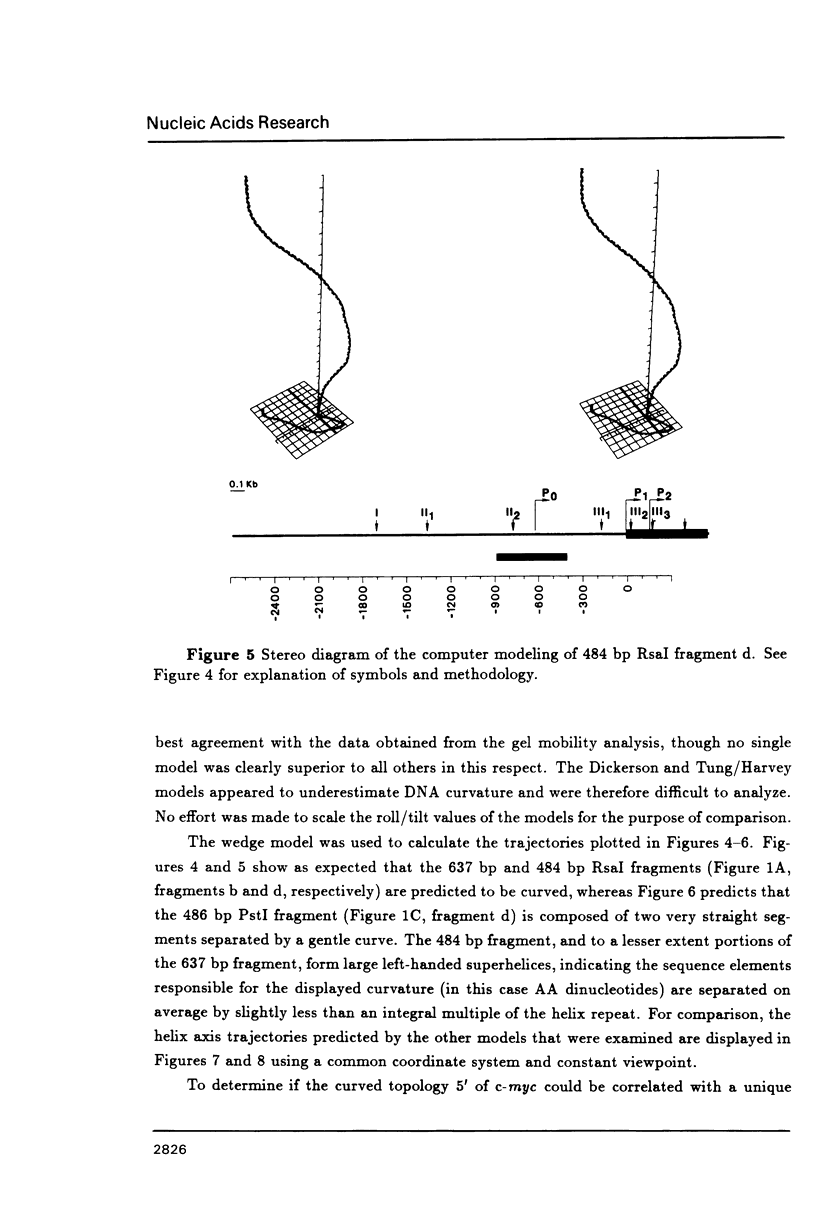
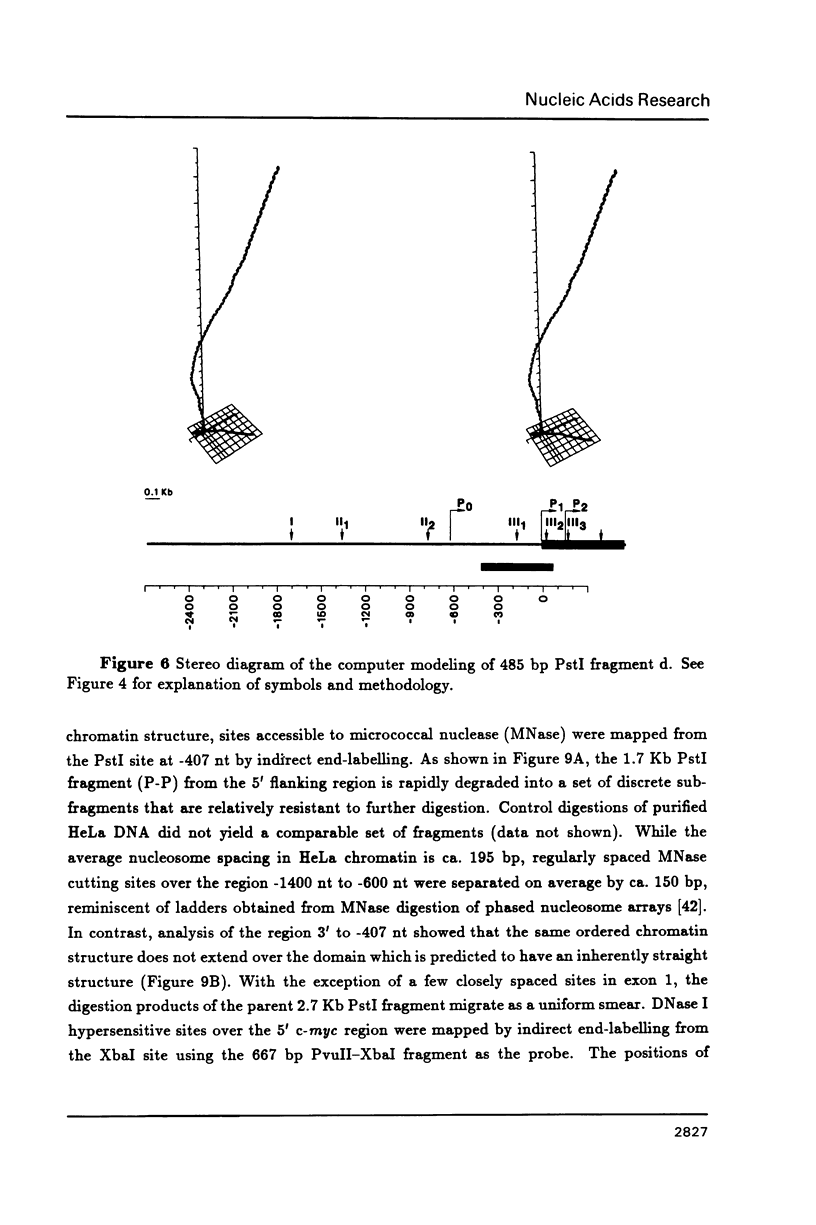
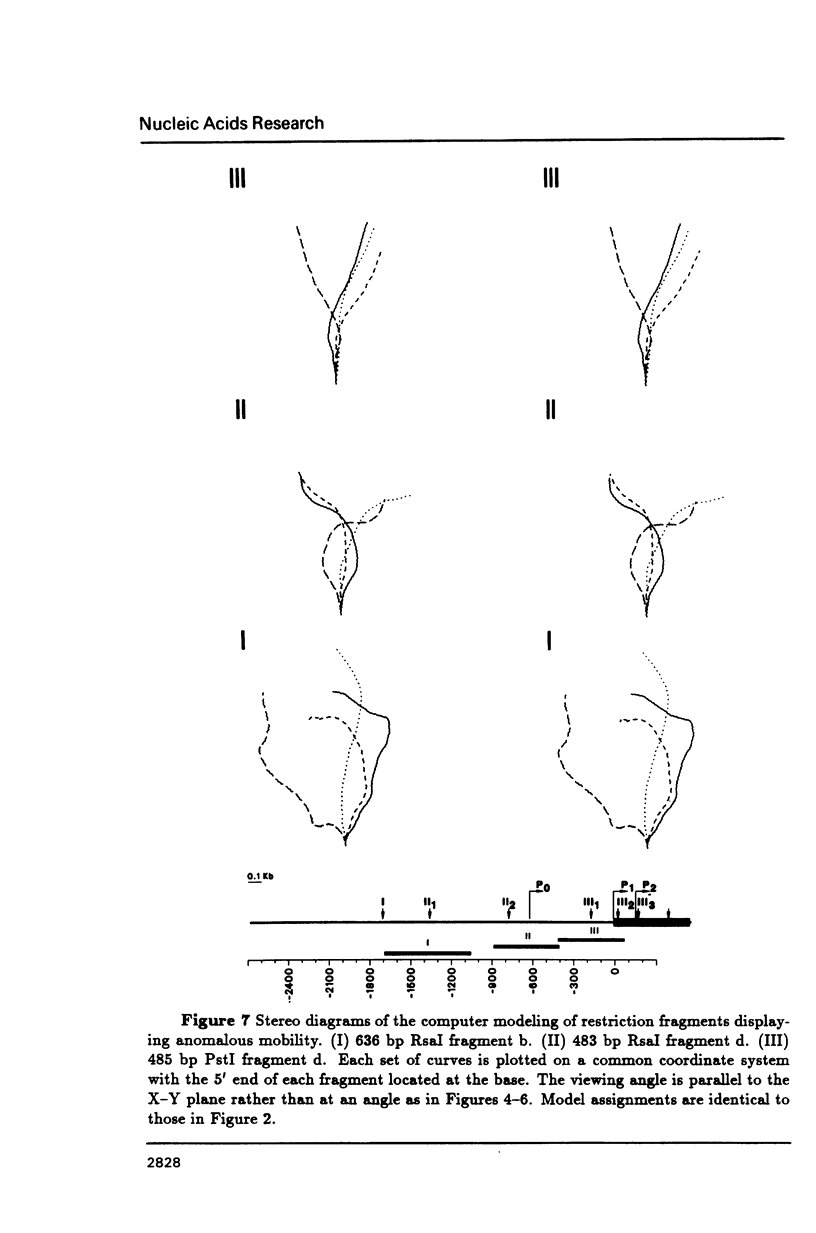
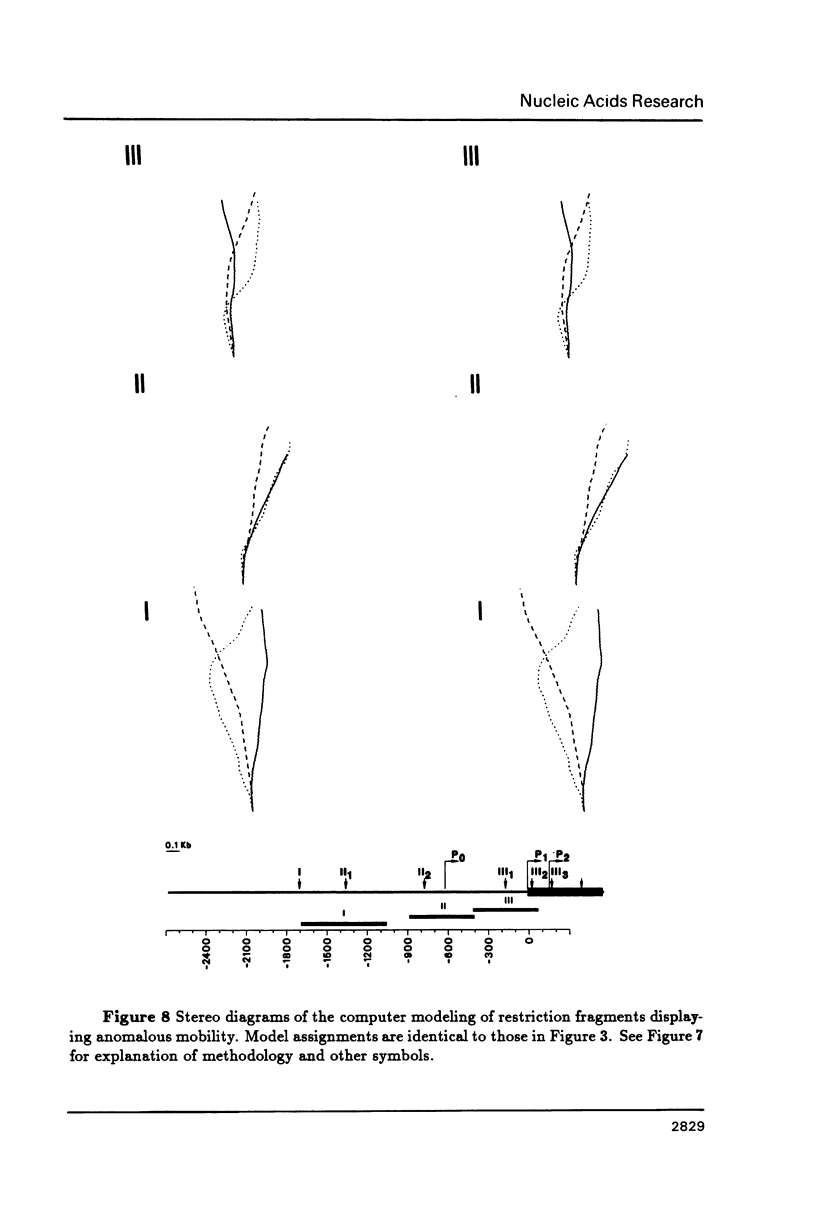
DNA restriction fragments located 5' to the human c-myc gene display anomalous electrophoretic mobility on polyacrylamide gels. Computer modeling of the c-myc flanking DNA suggests that the slow-moving DNA fragments spanning nucleotides -1690 to -1054 (relative to c-myc promoter P1) and -718 to -452 form large left handed superhelices or curved structures while the fast-moving DNA fragment spanning nucleotides -407 to +78 has an unusually straight structure. These analyses also predict a periodic array of localized regions of bending through the superhelical domains. Micrococcal nuclease digestion of isolated nuclei reveals that the slow-moving DNA fragments exist in an ordered chromatin structure stable to nuclease, whereas the digestion pattern of the fast-moving DNA fragment suggests a less ordered array of nucleosomes or a non-nucleosomal chromatin structure.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. N. Detection, sequence patterns and function of unusual DNA structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8513–8533. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. A block to elongation is largely responsible for decreased transcription of c-myc in differentiated HL60 cells. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):702–706. doi: 10.1038/321702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. Novel promoter upstream of the human c-myc gene and regulation of c-myc expression in B-cell lymphomas. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3481–3489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossi L., Smith D. M. Conformational change in the DNA associated with an unusual promoter mutation in a tRNA operon of Salmonella. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):643–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90471-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Sinn E., Reed R. R., Leder P. Trans-acting elements modulate expression of the human c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7918–7922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., DeLucia A. L., Koff A., Tsui S., Tegtmeyer P. The adenine-thymine domain of the simian virus 40 core origin directs DNA bending and coordinately regulates DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4578–4584. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. Base sequence and helix structure variation in B and A DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 25;166(3):419–441. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S. DNA methylation can enhance or induce DNA curvature. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4213–4217. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02769.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA bending and its relation to nucleosome positioning. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):773–790. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90396-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckdahl T. T., Anderson J. N. Computer modelling of DNA structures involved in chromosome maintenance. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8531–8545. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., de Boer H. A., Nomura M. DNA determinants of rRNA synthesis in E. coli: growth rate dependent regulation, feedback inhibition, upstream activation, antitermination. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90498-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J., Bleyman M., Rauch C. A., Kitchin P. A., Englund P. T. Visualization of the bent helix in kinetoplast DNA by electron microscopy. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):717–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90347-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. L., Gregori T. J. Cloning multiple copies of a DNA segment. Gene. 1981 May;13(4):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jernigan R. L., Sarai A., Ting K. L., Nussinov R. Hydrophobic interactions in the major groove can influence DNA local structure. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Aug;4(1):41–48. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10507645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Sander C., Trifonov E. N. The ten helical twist angles of B-DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):1097–1104. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepsel R. R., Khan S. A. Static and initiator protein-enhanced bending of DNA at a replication origin. Science. 1986 Sep 19;233(4770):1316–1318. doi: 10.1126/science.3749879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Crothers D. M. Calibration of DNA curvature and a unified description of sequence-directed bending. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1763–1767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene S. D., Crothers D. M. A computer graphics study of sequence-directed bending in DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(2):429–435. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Shlomai J. Sequence-directed bent DNA helix is the specific binding site for Crithidia fasciculata nicking enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8205–8209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp M., Schilling R., Wiest S., Laux G., Bornkamm G. W. Target sequences for cis-acting regulation within the dual promoter of the human c-myc gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1393–1400. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini J. C., Levene S. D., Crothers D. M., Englund P. T. Bent helical structure in kinetoplast DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7664–7668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Ortín J. E., Estruch F., Matallana E., Franco L. Sliding-end-labelling. A method to avoid artifacts in nucleosome positioning. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):31–33. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81525-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Shulman M., Landy A. Biochemical analysis of att-defective mutants of the phage lambda site-specific recombination system. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):505–522. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90263-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Silver S., DeLucia A. L., Fanning E., Tegtmeyer P. An altered DNA conformation in origin region I is a determinant for the binding of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):719–725. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90838-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarma R. H. New nomenclature for nucleic acid helix parameters Cambridge, UK, September 14, 1988. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1988 Dec;6(3):391–395. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1988.10506496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Bressler P., Kelly K. Two distinct mechanisms of transcriptional control operate on c-myc during differentiation of HL60 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):867–874. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Hennighausen L., Battey J., Leder P. Chromatin structure and protein binding in the putative regulatory region of the c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M., Buchman A. R., Davis R. W. Bent DNA at a yeast autonomously replicating sequence. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):87–89. doi: 10.1038/324087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srienc F., Bailey J. E., Campbell J. L. Effect of ARS1 mutations on chromosome stability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1676–1684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan A. R., Torres R., Clark W., Olson W. K. Base sequence effects in double helical DNA. I. Potential energy estimates of local base morphology. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1987 Dec;5(3):459–496. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1987.10506409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan R. K., Harvey S. C. A comparison of six DNA bending models. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1987 Dec;5(3):497–512. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1987.10506410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Bergman L. W., Simpson R. T. Nuclease digestion of circular TRP1ARS1 chromatin reveals positioned nucleosomes separated by nuclease-sensitive regions. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 25;177(4):715–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F. Protein-DNA interactions and nuclease-sensitive regions determine nucleosome positions on yeast plasmid chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 20;190(2):177–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90291-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Simpson R. T. Local protein-DNA interactions may determine nucleosome positions on yeast plasmids. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):250–252. doi: 10.1038/315250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifonov E. N. Curved DNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;19(2):89–106. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung C. S., Harvey S. C. Base sequence, local helix structure, and macroscopic curvature of A-DNA and B-DNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3700–3709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulanovsky L. E., Trifonov E. N. Estimation of wedge components in curved DNA. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):720–722. doi: 10.1038/326720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. S., Eckdahl T. T., Anderson J. N. Bent DNA functions as a replication enhancer in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2763–2769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahn K., Blattner F. R. Sequence-induced DNA curvature at the bacteriophage lambda origin of replication. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):451–453. doi: 10.1038/317451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhurkin V. B. Sequence-dependent bending of DNA and phasing of nucleosomes. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Feb;2(4):785–804. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10506324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]