Abstract
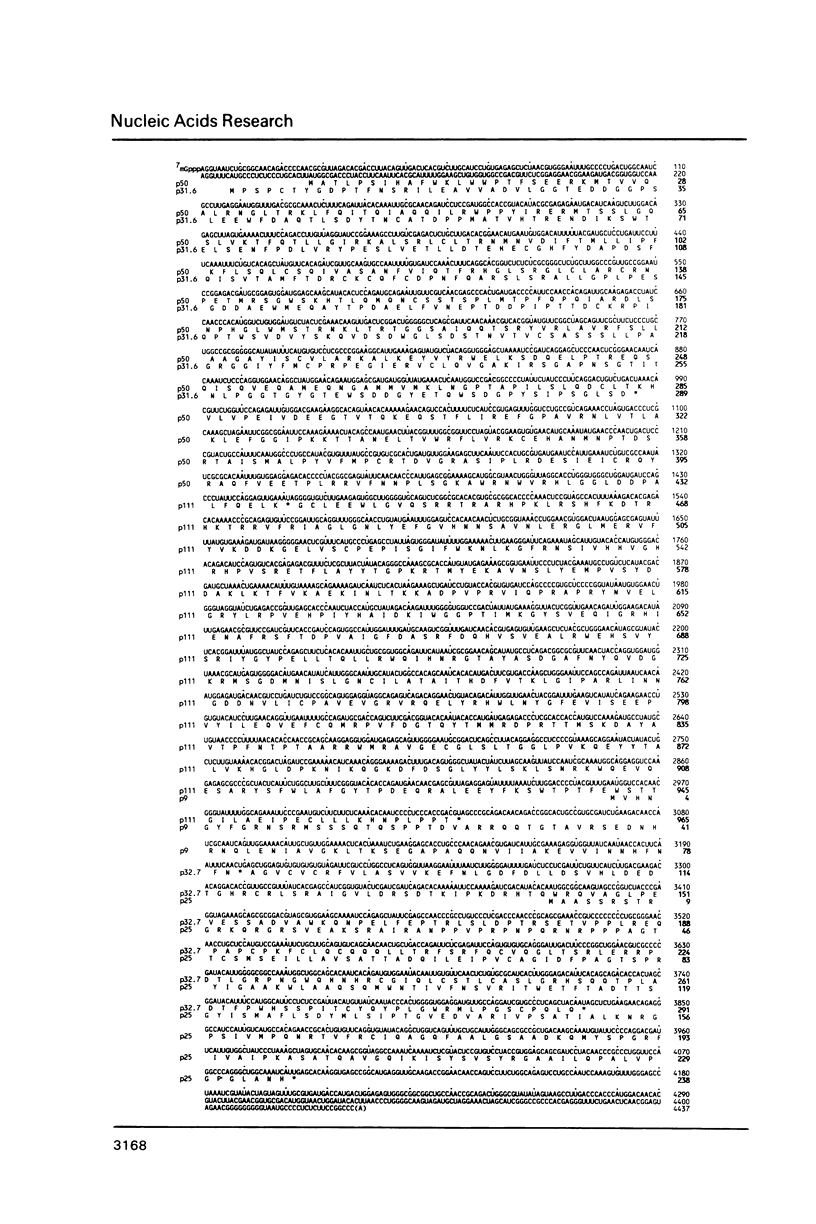
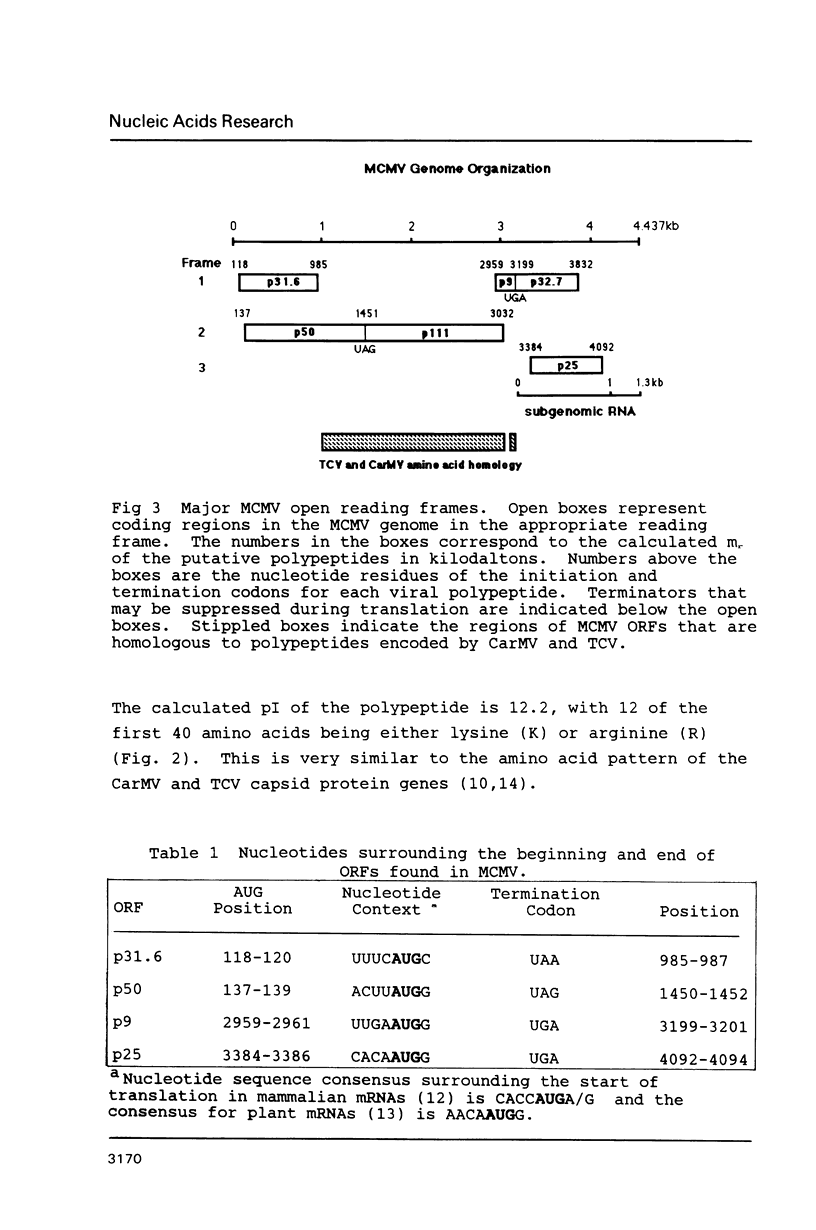
The complete nucleotide sequence of the maize chlorotic mottle virus (MCMV) genome has been determined to be 4437 nucleotides. The viral genome has four long open reading frames (ORFs) which could encode polypeptides of 31.6, 50, 8.9 and 25.1 kd. If the termination codons, for the polypeptides encoded by the 50 and 8.9 kd ORFs are suppressed, readthrough products of 111 and 32.7 kd result. The 31.6 and 50 kd ORFs overlap for nearly the entire length of the 31.6 kd ORF. Striking amino acid homology has been observed between two potential polypeptides encoded by MCMV and polypeptides encoded by carnation mottle virus (CarMV) and turnip crinkle virus (TCV). The 25.1 kd ORF most likely encodes the capsid protein. The similar genome organization and amino acid sequence homology of MCMV with CarMV and TCV suggest an evolutionary relationship with these members of the carmovirus group.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beier H., Barciszewska M., Krupp G., Mitnacht R., Gross H. J. UAG readthrough during TMV RNA translation: isolation and sequence of two tRNAs with suppressor activity from tobacco plants. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):351–356. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01810.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beier H., Barciszewska M., Sickinger H. D. The molecular basis for the differential translation of TMV RNA in tobacco protoplasts and wheat germ extracts. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1091–1096. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Morris T. J., Stockley P. G., Harrison S. C. Structure and assembly of turnip crinkle virus. IV. Analysis of the coat protein gene and implications of the subunit primary structure. J Mol Biol. 1987 Mar 20;194(2):265–276. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90374-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goelet P., Lomonossoff G. P., Butler P. J., Akam M. E., Gait M. J., Karn J. Nucleotide sequence of tobacco mosaic virus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5818–5822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilley H., Carrington J. C., Balàzs E., Jonard G., Richards K., Morris T. J. Nucleotide sequence and genome organization of carnation mottle virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6663–6677. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamer G., Argos P. Primary structural comparison of RNA-dependent polymerases from plant, animal and bacterial viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7269–7282. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütcke H. A., Chow K. C., Mickel F. S., Moss K. A., Kern H. F., Scheele G. A. Selection of AUG initiation codons differs in plants and animals. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):43–48. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. A., Waterhouse P. M., Gerlach W. L. Sequence and organization of barley yellow dwarf virus genomic RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6097–6111. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morch M. D., Benicourt C. Polyamines stimulate suppression of amber termination codons in vitro by normal tRNAs. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Apr;105(3):445–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Weber K. Natural read-through at the UGA termination signal of Q-beta coat protein cistron. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 15;234(50):206–209. doi: 10.1038/newbio234206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. X., Rinehart C. A., Kaesberg P. Sequence and organization of southern bean mosaic virus genomic RNA. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


