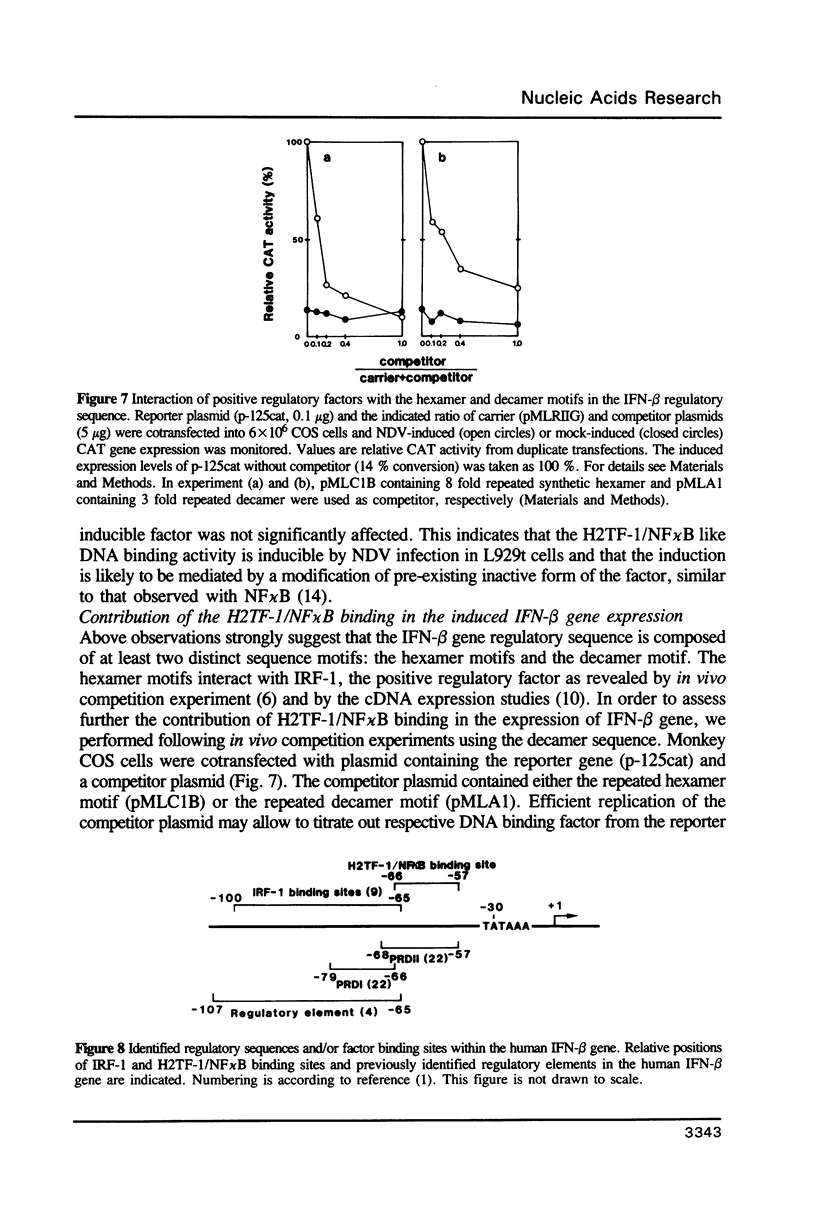
Abstract
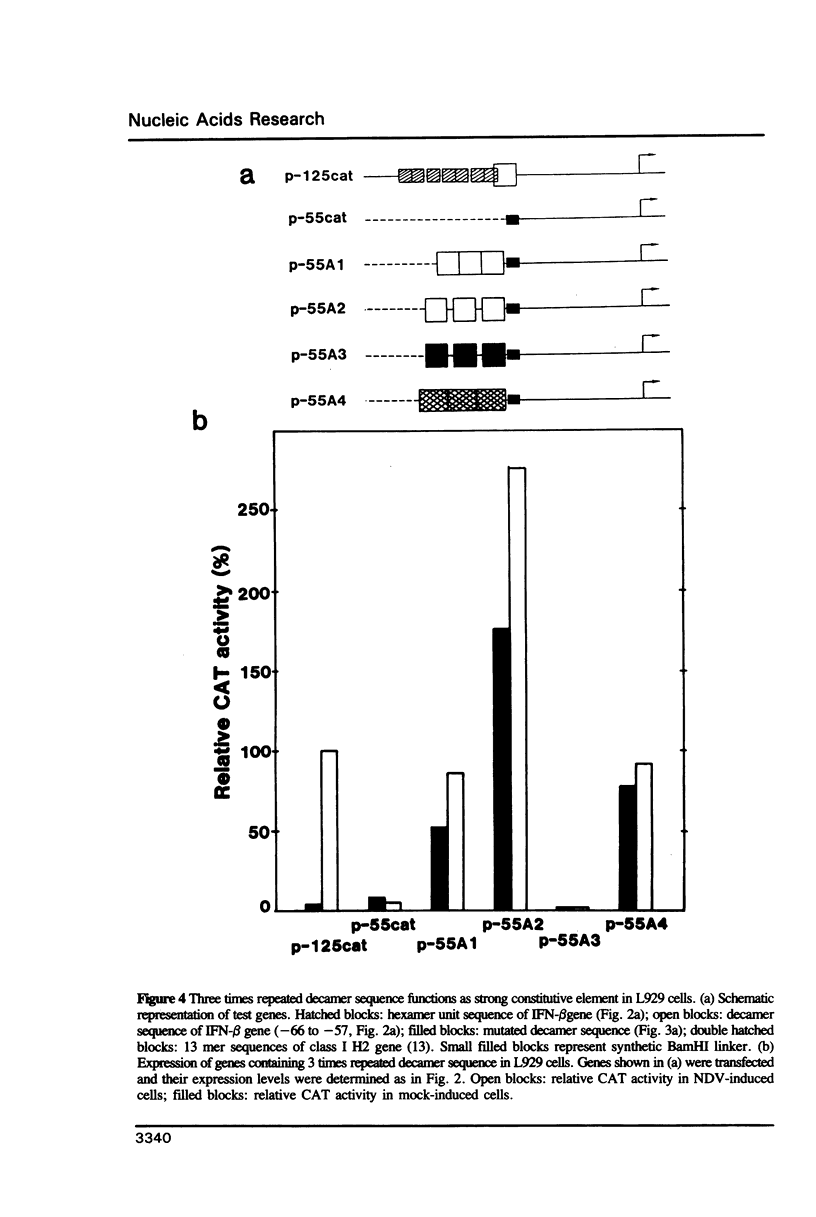
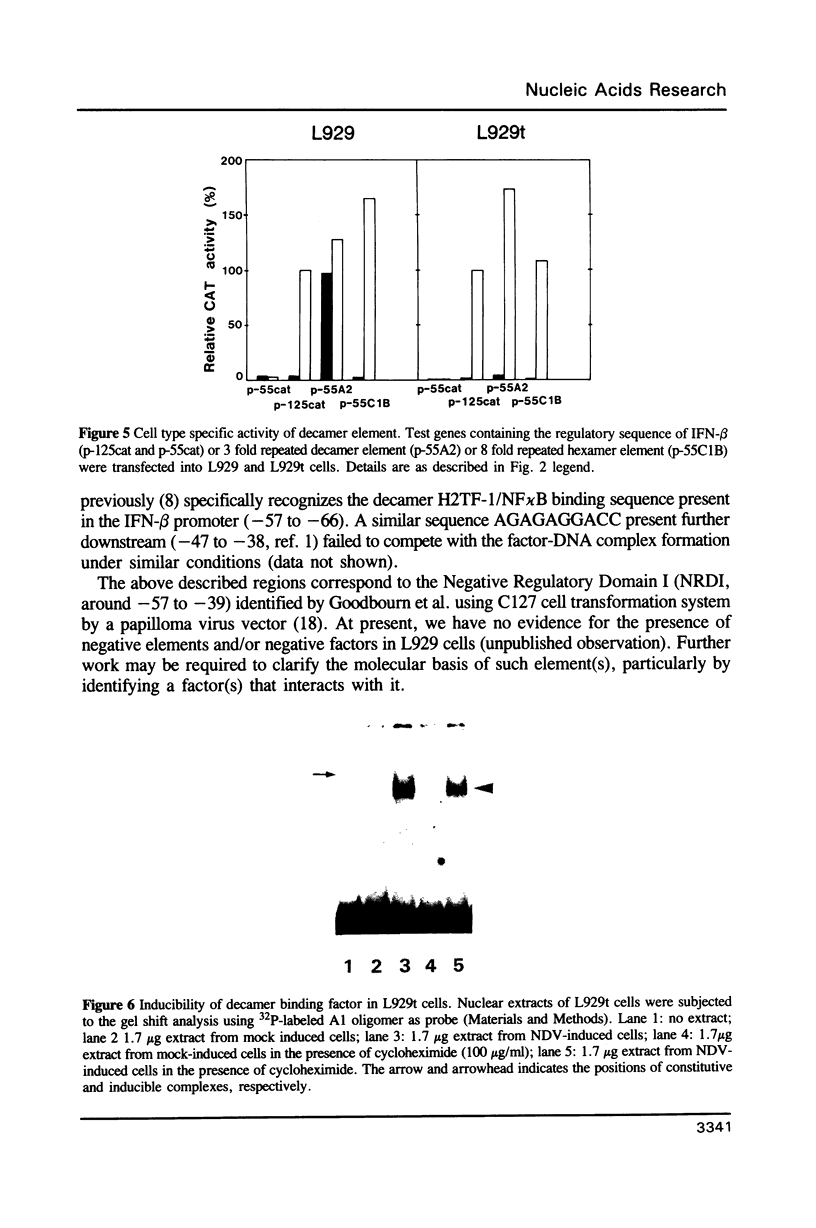
Interferon-beta (IFN-beta) gene is transcriptionally activated following virus infection of various cell types such as fibroblasts. In the previous studies, regulatory DNA sequences that mediate the virus-induced transcriptional activation have been identified within the 5'-flanking region (up to around -117 respect to the CAP site) of the human IFN-beta gene. The sequences contain binding sites (-100 to -61) for a transcriptional activator, IRF-1, the gene of which is also virus-inducible. In the present study, we focused on an additional cis-element, located between the IRF-1 binding sites and TATA box. Interestingly, the element coincides with the previously identified elements for the transcription factors H2TF-1 and NF kappa B. The element, when tandemly repeated, functions in activating the distal gene expression in either constitutive or virus-inducible manner depending on the cell type. The results suggest the importance of cooperation between IRF-1 and H2TF-1/NF kappa B-like factor in the maximal IFN-beta gene induction.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Binding of a nuclear factor to a regulatory sequence in the promoter of the mouse H-2Kb class I major histocompatibility gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):305–313. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Lowenthal J. W., Siekevitz M., Ballard D. W., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. The same inducible nuclear proteins regulates mitogen activation of both the interleukin-2 receptor-alpha gene and type 1 HIV. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):827–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark L., Hay R. T. Sequence requirement for specific interaction of an enhancer binding protein (EBP1) with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):499–516. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Maniatis T. Two different virus-inducible elements are required for human beta-interferon gene regulation. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):101–110. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03353.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Kimura Y., Miyamoto M., Barsoumian E. L., Taniguchi T. Induction of endogenous IFN-alpha and IFN-beta genes by a regulatory transcription factor, IRF-1. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):270–272. doi: 10.1038/337270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Kohno S. Studies on interferon priming: cellular response to viral and nonviral inducers and requirement of protein synthesis. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):62–69. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90612-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Ohno S., Yasumitsu H., Taniguchi T. Delimitation and properties of DNA sequences required for the regulated expression of human interferon-beta gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):489–496. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Sakakibara J., Sudo Y., Miyamoto M., Kimura Y., Taniguchi T. Evidence for a nuclear factor(s), IRF-1, mediating induction and silencing properties to human IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3397–3405. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Shibuya H., Hotta H., Yamanishi K., Taniguchi T. Interferon-beta gene regulation: tandemly repeated sequences of a synthetic 6 bp oligomer function as a virus-inducible enhancer. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):357–367. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90288-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Burstein H., Maniatis T. The human beta-interferon gene enhancer is under negative control. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):601–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Maniatis T. Overlapping positive and negative regulatory domains of the human beta-interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1447–1451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Zinn K., Maniatis T. Human beta-interferon gene expression is regulated by an inducible enhancer element. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):509–520. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Clarke J. The SV40 enhancer is composed of multiple functional elements that can compensate for one another. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):461–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90332-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller A. D., Maniatis T. Identification of an inducible factor that binds to a positive regulatory element of the human beta-interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3309–3313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhl D., de la Fuente J., Chaturvedi M., Parimoo S., Ryals J., Meyer F., Weissmann C. Reversible silencing of enhancers by sequences derived from the human IFN-alpha promoter. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1057–1069. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung K., Nabel G. J. HTLV-1 transactivator induces interleukin-2 receptor expression through an NF-kappa B-like factor. Nature. 1988 Jun 23;333(6175):776–778. doi: 10.1038/333776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroteaux L., Kahana C., Mory Y., Groner Y., Revel M. Sequences involved in the regulated expression of the human interferon-beta1 gene in recombinant SV40 DNA vectors replicating in monkey cells. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):325–332. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M., Fujita T., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Harada H., Sudo Y., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Regulated expression of a gene encoding a nuclear factor, IRF-1, that specifically binds to IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):903–913. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryals J., Dierks P., Ragg H., Weissmann C. A 46-nucleotide promoter segment from an IFN-alpha gene renders an unrelated promoter inducible by virus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):497–507. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya H., Yoneyama M., Taniguchi T. Involvement of a common transcription factor in the regulated expression of IL-2 and IL-2 receptor genes. Int Immunol. 1989;1(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. W., Searle P. F., Palmiter R. D. Identification of multiple metal regulatory elements in mouse metallothionein-I promoter by assaying synthetic sequences. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):828–831. doi: 10.1038/317828a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séguin C., Felber B. K., Carter A. D., Hamer D. H. Competition for cellular factors that activate metallothionein gene transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):781–785. doi: 10.1038/312781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]