Abstract
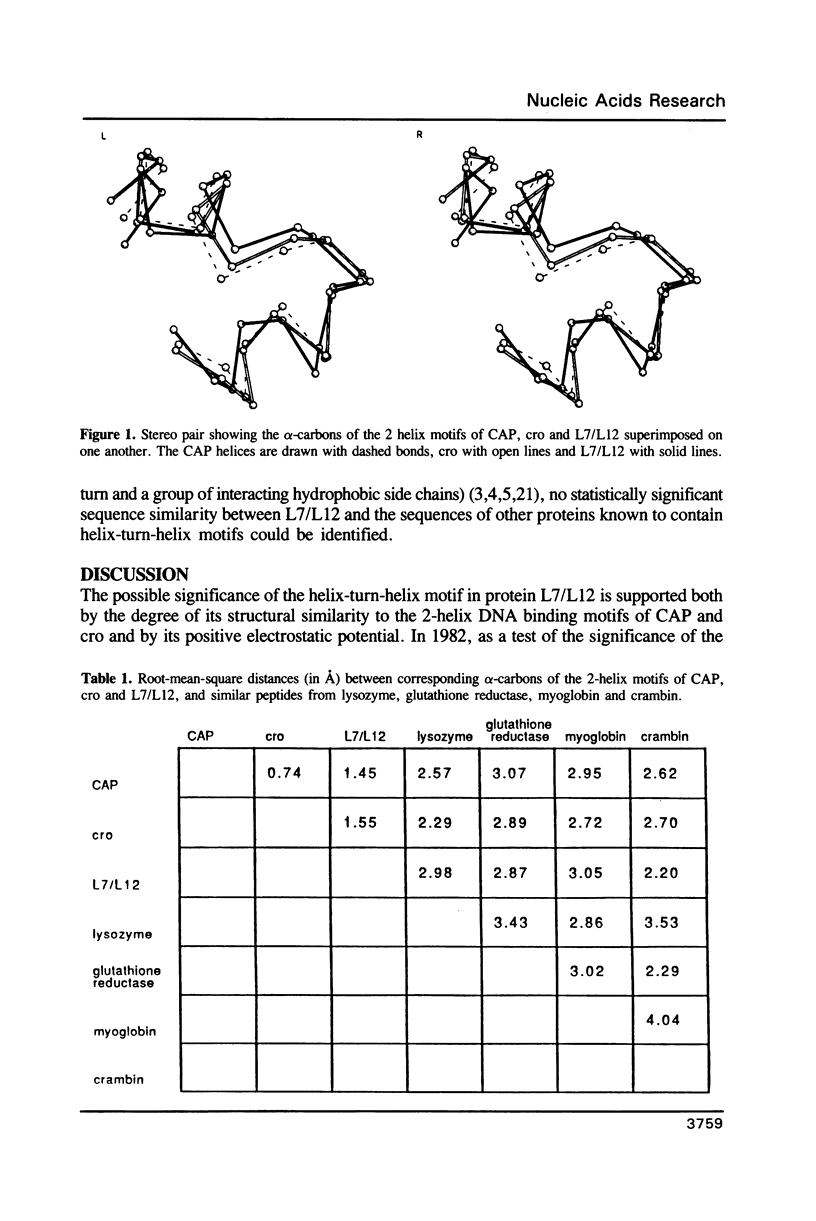
Inspection of the structure of the C-terminal domain of ribosomal protein L7/L12 (1) reveals a helix-turn-helix motif similar to the one found in many DNA-binding regulatory proteins (2-5). The 19 alpha-carbon atoms of the L7/L12 alpha-helices superimpose on the DNA binding helices of CAP and cro with root-mean-square distances between corresponding alpha carbons of 1.45 and 1.55 A, respectively. These helices in L7/L12 are within a patch of highly conserved residues on the surface of L7/L12 whose role is as yet uncertain. We raise the possibility that they may constitute a binding site for nucleic acids, most probably RNA. Consistent with this hypothesis are calculations of the electrostatic charge potential surrounding the protein, which show a region of positive potential centered on the first of these helices.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. E., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. Structure of the repressor-operator complex of bacteriophage 434. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):846–852. doi: 10.1038/326846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson W. F., Ohlendorf D. H., Takeda Y., Matthews B. W. Structure of the cro repressor from bacteriophage lambda and its interaction with DNA. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):754–758. doi: 10.1038/290754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson W. F. Proposed alpha-helical super-secondary structure associated with protein-dna recognition. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 25;159(4):745–751. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowgill C. A., Nichols B. G., Kenny J. W., Butler P., Bradbury E. M., Traut R. R. Mobile domains in ribosomes revealed by proton nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15257–15263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. Real-space refinement of the structure of hen egg-white lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 25;82(3):371–391. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90598-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd I. B., Egan J. B. Systematic method for the detection of potential lambda Cro-like DNA-binding regions in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 5;194(3):557–564. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90681-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efimov A. V. A novel super-secondary structure of proteins and the relation between the structure and the amino acid sequence. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 23;166(1):33–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández F., de Nó C., Palacián E. Functional implication of the sole arginine residue of ribosomal proteins L7/L12. Mol Biol Rep. 1984 Dec;10(2):75–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00776977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsebom L. A., Amons R., Isaksson L. A. Primary structures of mutationally altered ribosomal protein L7/L12 and their effects on cellular growth and translational accuracy. Eur J Biochem. 1986 May 2;156(3):669–675. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsebom L. A., Isaksson L. A. Involvement of ribosomal protein L7/L12 in control of translational accuracy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):717–721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Scott M. P. Sequence of a Drosophila segmentation gene: protein structure homology with DNA-binding proteins. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):25–31. doi: 10.1038/310025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijonmarck M., Liljas A. Structure of the C-terminal domain of the ribosomal protein L7/L12 from Escherichia coli at 1.7 A. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):555–579. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijonmarck M., Liljas A., Subramanian A. R. Computed spatial homology between the L12 protein of chloroplast ribosome and 1.7 A structure of Escherichia coli L12 domain. Biochem Int. 1984 Jan;8(1):69–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. B., Steitz T. A. Structure of catabolite gene activator protein at 2.9 A resolution suggests binding to left-handed B-DNA. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):744–749. doi: 10.1038/290744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlendorf D. H., Anderson W. F., Takeda Y., Matthews B. W. High resolution structural studies of Cro repressor protein and implications for DNA recognition. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(2):553–563. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Lewis M. The operator-binding domain of lambda repressor: structure and DNA recognition. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):443–447. doi: 10.1038/298443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington S. J., Matthews B. W. A systematic approach to the comparison of protein structures. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 15;140(1):77–99. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90357-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer R. T., Yocum R. R., Doolittle R. F., Lewis M., Pabo C. O. Homology among DNA-binding proteins suggests use of a conserved super-secondary structure. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):447–451. doi: 10.1038/298447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schevitz R. W., Otwinowski Z., Joachimiak A., Lawson C. L., Sigler P. B. The three-dimensional structure of trp repressor. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):782–786. doi: 10.1038/317782a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A., Ohlendorf D. H., McKay D. B., Anderson W. F., Matthews B. W. Structural similarity in the DNA-binding domains of catabolite gene activator and cro repressor proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3097–3100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano T. Structure of myoglobin refined at 2-0 A resolution. II. Structure of deoxymyoglobin from sperm whale. J Mol Biol. 1977 Mar 5;110(3):569–584. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teeter M. M. Water structure of a hydrophobic protein at atomic resolution: Pentagon rings of water molecules in crystals of crambin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6014–6018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thieme R., Pai E. F., Schirmer R. H., Schulz G. E. Three-dimensional structure of glutathione reductase at 2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 15;152(4):763–782. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90126-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warwicker J. Continuum dielectric modelling of the protein-solvent system, and calculation of the long-range electrostatic field of the enzyme phosphoglycerate mutase. J Theor Biol. 1986 Jul 21;121(2):199–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(86)80093-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warwicker J., Engelman B. P., Steitz T. A. Electrostatic calculations and model-building suggest that DNA bound to CAP is sharply bent. Proteins. 1987;2(4):283–289. doi: 10.1002/prot.340020404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warwicker J., Watson H. C. Calculation of the electric potential in the active site cleft due to alpha-helix dipoles. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 5;157(4):671–679. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90505-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber I. T., McKay D. B., Steitz T. A. Two helix DNA binding motif of CAP found in lac repressor and gal repressor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):5085–5102. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.5085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. Structure of a complex of catabolite gene activator protein and cyclic AMP refined at 2.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberger C., Dong Y. C., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. Structure of a phage 434 Cro/DNA complex. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):789–795. doi: 10.1038/335789a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang R. G., Joachimiak A., Lawson C. L., Schevitz R. W., Otwinowski Z., Sigler P. B. The crystal structure of trp aporepressor at 1.8 A shows how binding tryptophan enhances DNA affinity. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):591–597. doi: 10.1038/327591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuiderweg E. R., Billeter M., Boelens R., Scheek R. M., Wüthrich K., Kaptein R. Spatial arrangement of the three alpha helices in the solution conformation of E. coli lac repressor DNA-binding domain. FEBS Lett. 1984 Sep 3;174(2):243–247. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81166-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]