Abstract
We describe a simple, compact, inexpensive thermal cycler that can be used for the polymerase chain reaction. Based on heat transfer with air to samples in sealed capillary tubes, the apparatus resembles a recirculating hair dryer. The temperature is regulated via thermocouple input to a programmable set-point process controller that provides proportional output to a solid state relay controlling a heating coil. For efficient cooling after the denaturation step, the controller activates a solenoid that opens a door to vent hot air and allows cool air to enter. Temperature-time profiles and amplification results approximate those obtained using water baths and microfuge tubes.
Full text
PDF
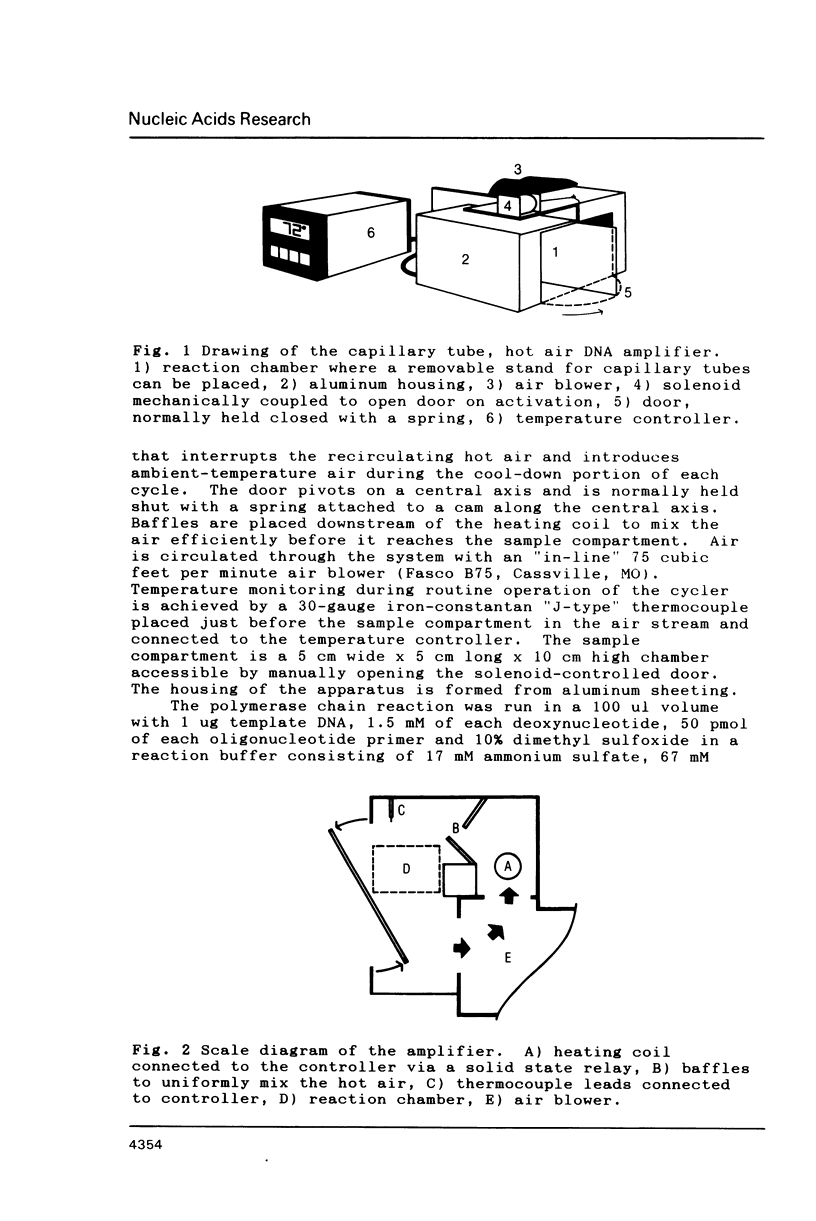
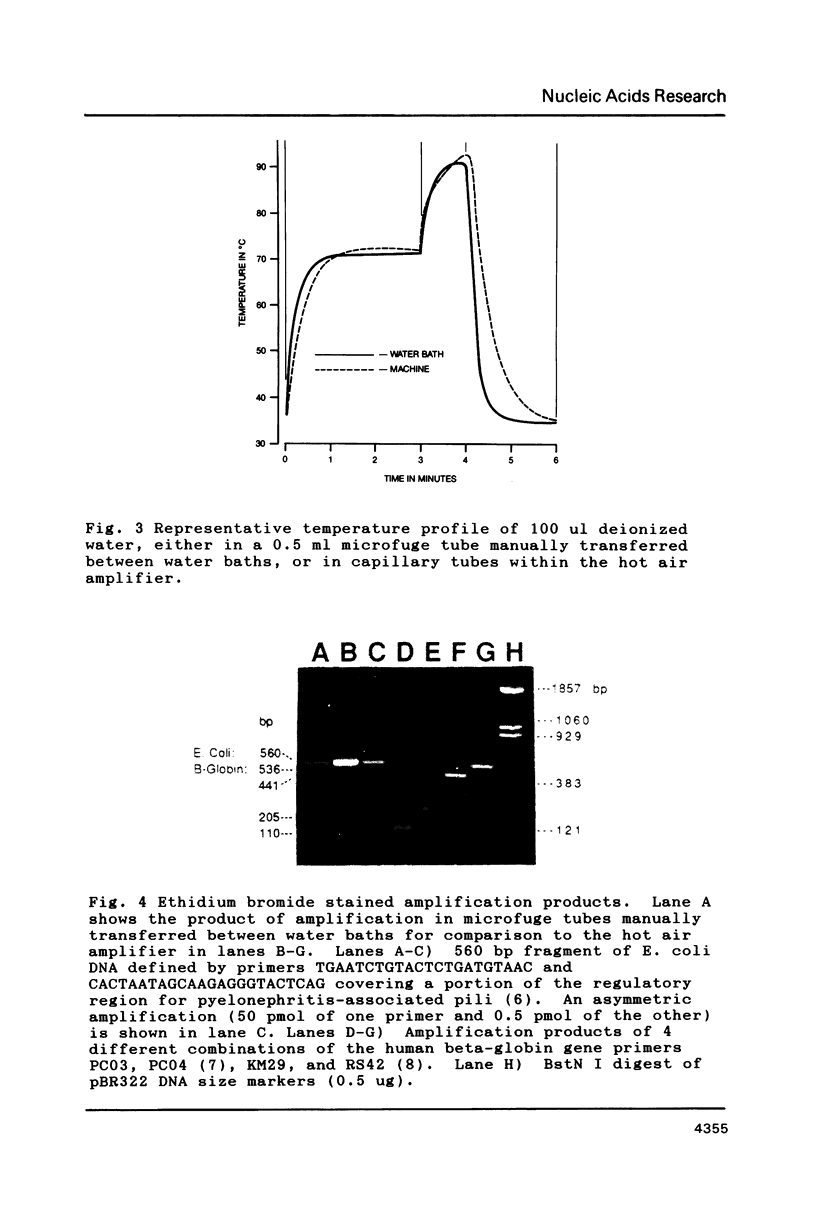


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blyn L. B., Braaten B. A., White-Ziegler C. A., Rolfson D. H., Low D. A. Phase-variation of pyelonephritis-associated pili in Escherichia coli: evidence for transcriptional regulation. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):613–620. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03416.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Pandolfi de Rinaldis P. P., Macdonnell J., Cross N. C., Luzzatto L. Polymerase chain reaction automated at low cost. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5687–5688. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogan S. C., Doherty M., Gitschier J. An improved method for prenatal diagnosis of genetic diseases by analysis of amplified DNA sequences. Application to hemophilia A. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 15;317(16):985–990. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710153171603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollo F., Amici A., Salvi R. A simple and low cost DNA amplifier. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):3105–3106. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Chang C. A., Levenson C. H., Warren T. C., Boehm C. D., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Erlich H. A. Diagnosis of sickle cell anemia and beta-thalassemia with enzymatically amplified DNA and nonradioactive allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 1;319(9):537–541. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



