Abstract
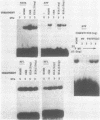
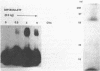
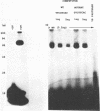
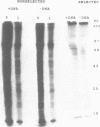
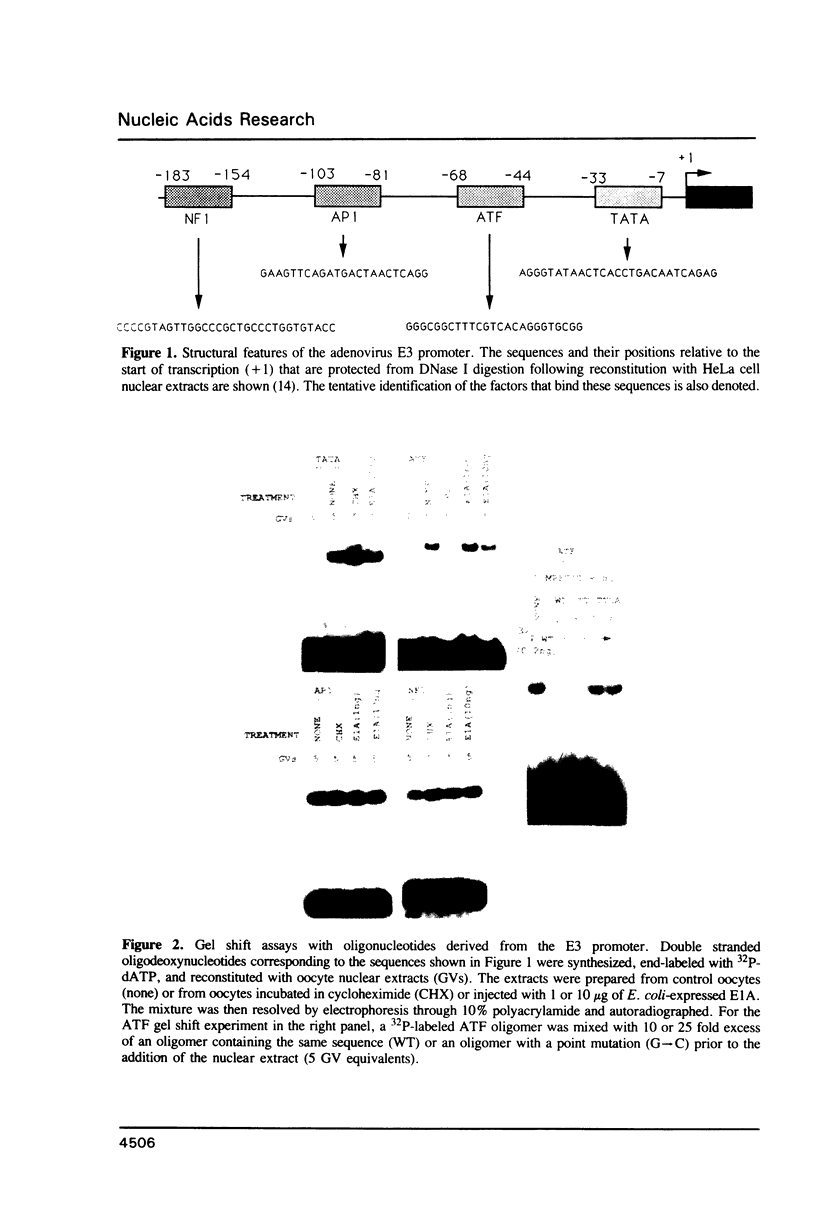
The adenovirus E1A 13S mRNA product transactivates genes injected into Xenopus laevis oocytes that are normally E1A-inducible in mammalian cells. However, E1A-stimulated transcription, but not basal (uninduced) transcription, was inhibited if oocytes were incubated in the presence of protein synthesis inhibitors. This suggests that a cellular protein(s) is required for E1A-induced transactivation, but that it is dispensable for basal transcription. In order to identify such a protein from Xenopus oocytes that interacts with the adenovirus E3 promoter, gel shift assays, a new in vivo photocrosslinking assay, and immunoselection of biotinylated oligonucleotides were employed. A protein of molecular size 75 kd, which bound to the mammalian ATF recognition sequence in vivo, was found to be essential for E1A-induced transactivation. Although cycloheximide treatment of oocytes inhibited factor binding. E1A exerted no effect on factor binding. These data suggest that E1A modulates the activity of an oocyte transcription factor, either directly or indirectly, but not its ability to bind DNA.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J. Adenovirus promoters and E1A transactivation. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:45–79. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Hen R., Chambon P. Adenovirus-2 E1A products repress enhancer-induced stimulation of transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):608–612. doi: 10.1038/312608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. A single polypeptide possesses the binding and transcription activities of the adenovirus major late transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4723–4733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson B., Jones N., Richter J., Rosenberg M. Adenovirus E1a gene product expressed at high levels in Escherichia coli is functional. Science. 1984 Jun 22;224(4655):1343–1346. doi: 10.1126/science.6374895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson B., Krippl B., Andrisani O., Jones N., Westphal H., Rosenberg M. E1A 13S and 12S mRNA products made in Escherichia coli both function as nucleus-localized transcription activators but do not directly bind DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2653–2661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J., Wu F., Gaynor R. Upstream regulatory regions required to stabilize binding to the TATA sequence in an adenovirus early promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8367–8385. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Borrelli E., Chambon P. Repression of the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer by the adenovirus-2 E1A products. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1391–1394. doi: 10.1126/science.2999984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Hai T., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Transcription factor ATF interacts with the TATA factor to facilitate establishment of a preinitiation complex. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst H. C., Jones N. C. Identification of factors that interact with the E1A-inducible adenovirus E3 promoter. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1132–1146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Hart R. P., Nevins J. R. An enhancer-like element in the adenovirus E2 promoter contains sequences essential for uninduced and E1A-induced transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus 5 E2 transcription unit: an E1A-inducible promoter with an essential element that functions independently of position or orientation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):875–882. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Richter J. D., Weeks D. L., Smith L. D. Regulation of adenovirus transcription by an E1a gene in microinjected Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2131–2142. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A. Regulation of transcription of the adenovirus EII promoter by EIa gene products: absence of sequence specificity. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1970–1977. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. E1A transcription induction: enhanced binding of a factor to upstream promoter sequences. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):719–722. doi: 10.1126/science.2935935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Green M. R. A cellular transcription factor E4F1 interacts with an E1a-inducible enhancer and mediates constitutive enhancer function in vitro. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1345–1353. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Hai T. Y., SivaRaman L., Thimmappaya B., Hurst H. C., Jones N. C., Green M. R. A cellular protein, activating transcription factor, activates transcription of multiple E1A-inducible adenovirus early promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8355–8359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff T., Corden J., Elkaim R., Sassone-Corsi P. Transcriptional analysis of the adenovirus-5 EIII promoter: absence of sequence specificity for stimulation by EIa gene products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1209–1221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Identification and purification of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein with the DNA binding specificity of mammalian activating transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):109–113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Bilezikjian L. M. Binding of a nuclear protein to the cyclic-AMP response element of the somatostatin gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):175–178. doi: 10.1038/328175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Induction of the synthesis of a 70,000 dalton mammalian heat shock protein by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. D., Hurst H. C., Jones N. C. Adenovirus E1A requires synthesis of a cellular protein to establish a stable transcription complex in injected Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3049–3056. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. D., Young P., Jones N. C., Krippl B., Rosenberg M., Ferguson B. A first exon-encoded domain of E1A sufficient for posttranslational modification, nuclear-localization, and induction of adenovirus E3 promoter expression in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8434–8438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P. Cyclic AMP induction of early adenovirus promoters involves sequences required for E1A trans-activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7192–7196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SivaRaman L., Subramanian S., Thimmappaya B. Identification of a factor in HeLa cells specific for an upstream transcriptional control sequence of an EIA-inducible adenovirus promoter and its relative abundance in infected and uninfected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5914–5918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SivaRaman L., Thimmappaya B. Two promoter-specific host factors interact with adjacent sequences in an EIA-inducible adenovirus promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6112–6116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R., Ziff E. B. HeLa cell beta-tubulin gene transcription is stimulated by adenovirus 5 in parallel with viral early genes by an E1a-dependent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2792–2801. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress transcription from the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. L., Jones N. C. E1A control of gene expression is mediated by sequences 5' to the transcriptional starts of the early viral genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1222–1234. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B. J., Hurst H. C., Jones N. C., Morimoto R. I. The E1A 13S product of adenovirus 5 activates transcription of the cellular human HSP70 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2994–2999. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]