Abstract
Full-length cDNA of the 6.3 kb turnip yellow mosaic virus (TYMV) genome was placed between a T7 promoter and a unique Hind III site. In vitro transcription of Hind III-linearized DNA of clone pTYMC yielded full-length RNA transcripts. In inoculations of Chinese cabbage protoplasts and plants, capped transcripts and virion RNA had similar specific infectivities and produced similar systemic symptoms. We have used the pTYMC clone in studies of the expression of two overlapping open reading frames (1.9 kb and 5.5 kb ORFs) by making mutants with alterations in the initiation codons. Evidence is presented from in vitro translations of mutant and wild type RNAs that both ORFs are expressed from TYMV RNA. A mutant in the initiation codon of the 5.5 kb ORF did not replicate in protoplasts, while mutants in the initiation codon of the 1.9 kb ORF replicated at low levels. The two groups of mutants were not able to complement each other.
Full text
PDF








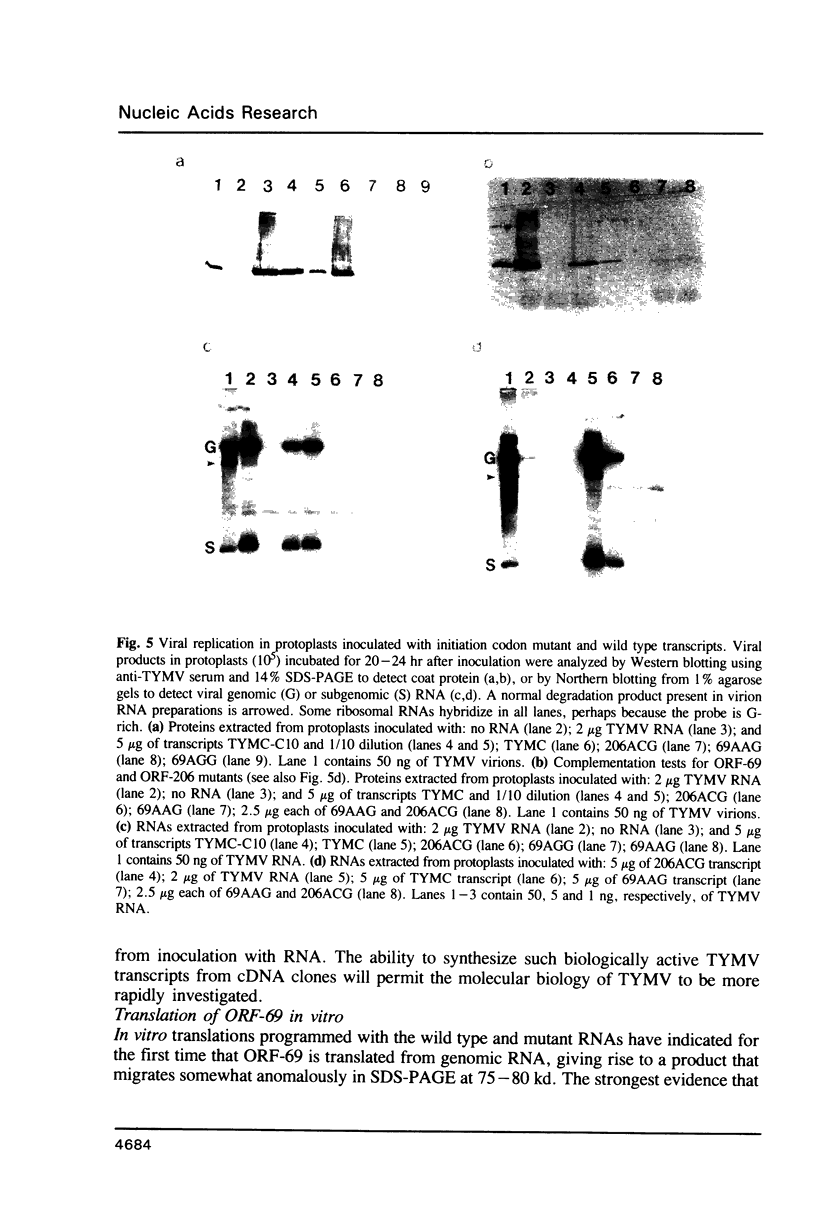



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlquist P., French R., Bujarski J. J. Molecular studies of brome mosaic virus using infectious transcripts from cloned cDNA. Adv Virus Res. 1987;32:215–242. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60478-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahlquist P., French R., Janda M., Loesch-Fries L. S. Multicomponent RNA plant virus infection derived from cloned viral cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7066–7070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briand J. P., Jonard G., Guilley H., Richards K., Hirth L. Nucleotide sequence (n=159) of the amino-acid-accepting 3'-OH extremity of turnip-yellow-mosaic-virus RNA and the last portion of its coat-protein cistron. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb;72(3):453–463. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briand J. P., Keith G., Guilley H. Nucleotide sequence at the 5' extremity of turnip yellow mosaic virus genome RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3168–3172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bénicourt C., Péré J. P., Haenni A. L. Translation of TYMV RNA into high molecular weight proteins. FEBS Lett. 1978 Feb 15;86(2):268–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80577-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras R., Cheroutre H., Degrave W., Fiers W. Simple, efficient in vitro synthesis of capped RNA useful for direct expression of cloned eukaryotic genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6353–6362. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J., Kolakofsky D. Ribosomal initiation from an ACG codon in the Sendai virus P/C mRNA. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):245–251. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02806.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J., Kolakofsky D. Scanning independent ribosomal initiation of the Sendai virus Y proteins in vitro and in vivo. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):521–526. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson W. O., Beck D. L., Knorr D. A., Grantham G. L. cDNA cloning of the complete genome of tobacco mosaic virus and production of infectious transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1832–1836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreher T. W., Florentz C., Giege R. Valylation of tRNA-like transcripts from cloned cDNA of turnip yellow mosaic virus RNA demonstrate that the L-shaped region at the 3' end of the viral RNA is not sufficient for optimal aminoacylation. Biochimie. 1988 Dec;70(12):1719–1727. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreher T. W., Hall T. C. Mutational analysis of the sequence and structural requirements in brome mosaic virus RNA for minus strand promoter activity. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90436-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumas P., Moras D., Florentz C., Giegé R., Verlaan P., Van Belkum A., Pleij C. W. 3-D graphics modelling of the tRNA-like 3'-end of turnip yellow mosaic virus RNA: structural and functional implications. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1987 Apr;4(5):707–728. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1987.10507674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage T7 DNA and the locations of T7 genetic elements. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):477–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florentz C., Giegé R. Contact areas of the turnip yellow mosaic virus tRNA-like structure interacting with yeast valyl-tRNA synthetase. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 5;191(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90427-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilley H., Briand J. P. Nucleotide sequence of turnip yellow mosaic virus coat protein mRNA. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi S., Chapeville F., Haenni A. L. Length requirements for tRNA-specific enzymes and cleavage specificity at the 3' end of turnip yellow mosaic virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):1947–1962. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamer G., Argos P. Primary structural comparison of RNA-dependent polymerases from plant, animal and bacterial viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7269–7282. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Recognition of cap structure in splicing in vitro of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Bifunctional messenger RNAs in eukaryotes. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):481–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90609-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Effects of intercistronic length on the efficiency of reinitiation by eucaryotic ribosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3438–3445. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain W. H., Foss K., Mittelstadt K. L., Schneider J. Variants in clones of gene-machine-synthesized oligodeoxynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6770–6770. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meshi T., Ishikawa M., Motoyoshi F., Semba K., Okada Y. In vitro transcription of infectious RNAs from full-length cDNAs of tobacco mosaic virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5043–5047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morch M. D., Benicourt C. Post-Translational Proteolytic Cleavage of In Vitro-Synthesized Turnip Yellow Mosaic Virus RNA-Coded High-Molecular-Weight Proteins. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):85–94. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.85-94.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morch M. D., Boyer J. C., Haenni A. L. Overlapping open reading frames revealed by complete nucleotide sequencing of turnip yellow mosaic virus genomic RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6157–6173. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morch M. D., Zagórski W., Haenni A. L. Proteolytic maturation of the turnip-yellow-mosaic-virus polyprotein coded in vitro occurs by internal catalysis. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(2):259–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06864.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouches C., Bove C., Bove J. M. Turnip yellow mosaic virus-RNA replicase: partial purification of the enzyme from the solubilized enzyme-template complex. Virology. 1974 Apr;58(2):409–423. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90076-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker B., Li J. K. A method to produce six alkaline northern blots of viral dsRNA within one hour. Biotechniques. 1988 Jan;6(1):22–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleij C. W., Rietveld K., Bosch L. A new principle of RNA folding based on pseudoknotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1717–1731. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Levis R., Strauss J. H., Huang H. V. Production of infectious RNA transcripts from Sindbis virus cDNA clones: mapping of lethal mutations, rescue of a temperature-sensitive marker, and in vitro mutagenesis to generate defined mutants. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3809–3819. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3809-3819.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietveld K., Van Poelgeest R., Pleij C. W., Van Boom J. H., Bosch L. The tRNA-like structure at the 3' terminus of turnip yellow mosaic virus RNA. Differences and similarities with canonical tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):1929–1946. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaklee P. N., Miglietta J. J., Palmenberg A. C., Kaesberg P. Infectious positive- and negative-strand transcript RNAs from bacteriophage Q beta cDNA clones. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):209–213. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90250-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skryabin K. G., Morozov SYu, Kraev A. S., Rozanov M. N., Chernov B. K., Lukasheva L. I., Atabekov J. G. Conserved and variable elements in RNA genomes of potexviruses. FEBS Lett. 1988 Nov 21;240(1-2):33–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80335-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valle R. P., Morch M. D. Stop making sense: or Regulation at the level of termination in eukaryotic protein synthesis. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 1;235(1-2):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81225-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Bradley J., Wimmer E., Studier F. W., Dunn J. J. Synthesis of infectious poliovirus RNA by purified T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






