Abstract
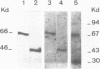
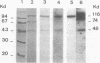
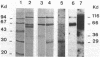
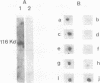
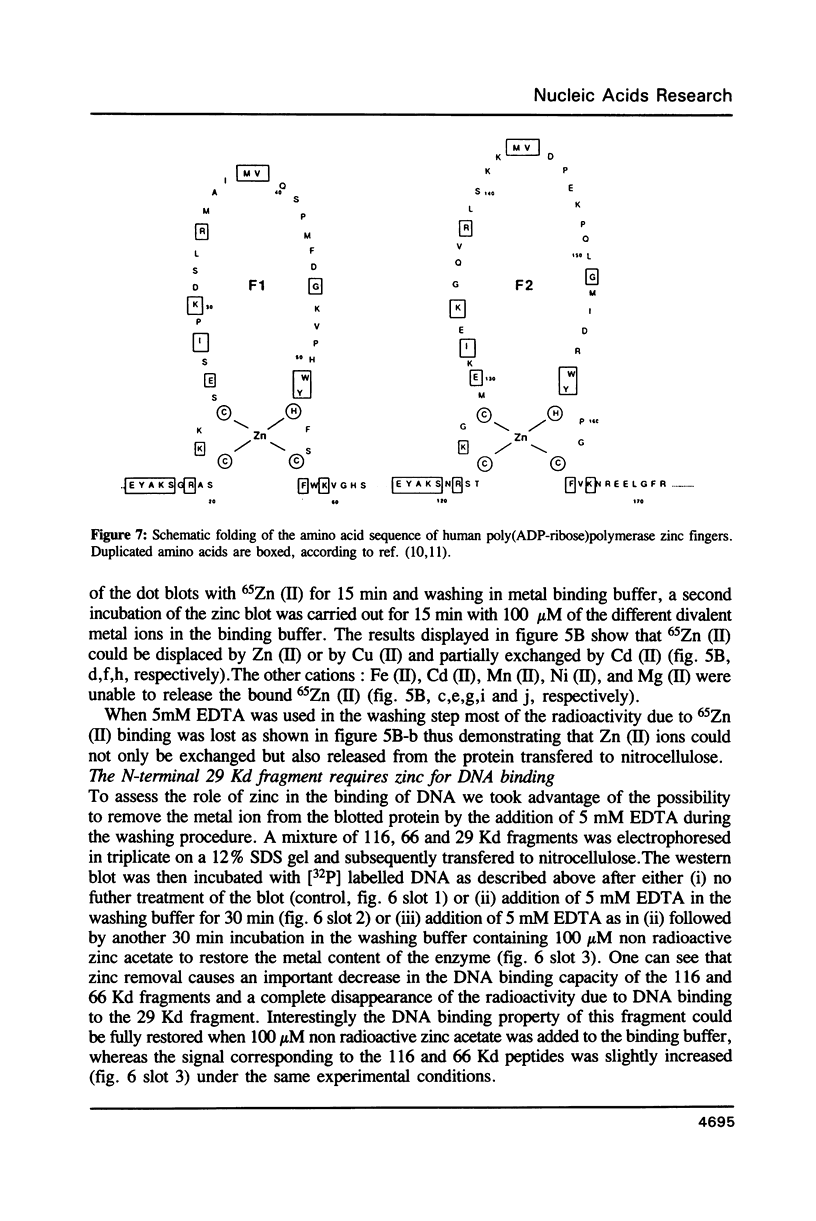
By Energy Dispersive X-ray fluorescence we have determined that calf thymus poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase binds two zinc ions per enzyme molecule. Using 65Zn (II) for detection of zinc binding proteins and polypeptides on western blots, we found that the zinc binding sites are localized in a 29 kd N-terminal fragment which is included in the DNA binding domain. Metal depletion and restoration experiments proved that zinc is essential for the binding of this fragment to DNA as tested by Southwestern assay. These results correlate with the existence of two putative zinc finger motifs present in the N-terminal part of the human enzyme. Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase fingers could be involved in the recognition of DNA strand breaks and therefore in enzyme activation.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benjamin R. C., Gill D. M. Poly(ADP-ribose) synthesis in vitro programmed by damaged DNA. A comparison of DNA molecules containing different types of strand breaks. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10502–10508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buki K. G., Kun E. Polypeptide domains of ADP-ribosyltransferase obtained by digestion with plasmin. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):5990–5995. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diakun G. P., Fairall L., Klug A. EXAFS study of the zinc-binding sites in the protein transcription factor IIIA. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):698–699. doi: 10.1038/324698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Pabo C. O. Fingering too many proteins. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):675–675. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90083-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman L. P., Luisi B. F., Korszun Z. R., Basavappa R., Sigler P. B., Yamamoto K. R. The function and structure of the metal coordination sites within the glucocorticoid receptor DNA binding domain. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):543–546. doi: 10.1038/334543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaal J. C., Pearson C. K. Eukaryotic nuclear ADP-ribosylation reactions. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 15;230(1):1–18. doi: 10.1042/bj2300001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauss P., Krassa K. B., McPheeters D. S., Nelson M. A., Gold L. Zinc (II) and the single-stranded DNA binding protein of bacteriophage T4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8515–8519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Kumar V., Theulaz I., Wahli W., Chambon P. The N-terminal DNA-binding 'zinc finger' of the oestrogen and glucocorticoid receptors determines target gene specificity. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3037–3044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03168.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameshita I., Matsuda M., Nishikimi M., Ushiro H., Shizuta Y. Reconstitution and poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of proteolytically fragmented poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3863–3868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keating K. M., Ghosaini L. R., Giedroc D. P., Williams K. R., Coleman J. E., Sturtevant J. M. Thermal denaturation of T4 gene 32 protein: effects of zinc removal and substitution. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):5240–5245. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosaki T., Ushiro H., Mitsuuchi Y., Suzuki S., Matsuda M., Matsuda Y., Katunuma N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Hirose T. Primary structure of human poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase as deduced from cDNA sequence. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15990–15997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamarre D., Talbot B., Leduc Y., Muller S., Poirier G. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for the functional domains of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;64(4):368–376. doi: 10.1139/o86-051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamarre D., Talbot B., de Murcia G., Laplante C., Leduc Y., Mazen A., Poirier G. G. Structural and functional analysis of poly(ADP ribose) polymerase: an immunological study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jul 13;950(2):147–160. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazen A., Gradwohl G., de Murcia G. Zinc-binding proteins detected by protein blotting. Anal Biochem. 1988 Jul;172(1):39–42. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90408-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson G. Liver alcohol dehydrogenase. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1987;21(4):349–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier G. G., de Murcia G., Jongstra-Bilen J., Niedergang C., Mandel P. Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of polynucleosomes causes relaxation of chromatin structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3423–3427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabbah M., Redeuilh G., Secco C., Baulieu E. E. The binding activity of estrogen receptor to DNA and heat shock protein (Mr 90,000) is dependent on receptor-bound metal. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8631–8635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff L. A., Nibert M. L., Co M. S., Brown E. G., Fields B. N. Distinct binding sites for zinc and double-stranded RNA in the reovirus outer capsid protein sigma 3. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):273–283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff L. A., Nibert M. L., Fields B. N. Characterization of a zinc blotting technique: evidence that a retroviral gag protein binds zinc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4195–4199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Yamauchi K., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K., Harada N., Tanaka H., Takahashi S., Yamamoto H., Fujimoto S. Depression in gene expression for poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase during the interferon-gamma-induced activation process of murine macrophage tumor cells. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Feb 1;171(3):571–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13826.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida K., Morita T., Sato T., Ogura T., Yamashita R., Noguchi S., Suzuki H., Nyunoya H., Miwa M., Sugimura T. Nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA for human fibroblast poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 29;148(2):617–622. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90921-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Hayaishi O. ADP-ribosylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:73–100. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.000445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. T., Johnstone A. P. ADP-ribosyl transferase, rearrangement of DNA, and cell differentiation. Biosci Rep. 1983 Sep;3(9):815–830. doi: 10.1007/BF01133780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahradka P., Ebisuzaki K. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase is a zinc metalloenzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;142(3):503–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Murcia G., Huletsky A., Lamarre D., Gaudreau A., Pouyet J., Daune M., Poirier G. G. Modulation of chromatin superstructure induced by poly(ADP-ribose) synthesis and degradation. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):7011–7017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]