Abstract
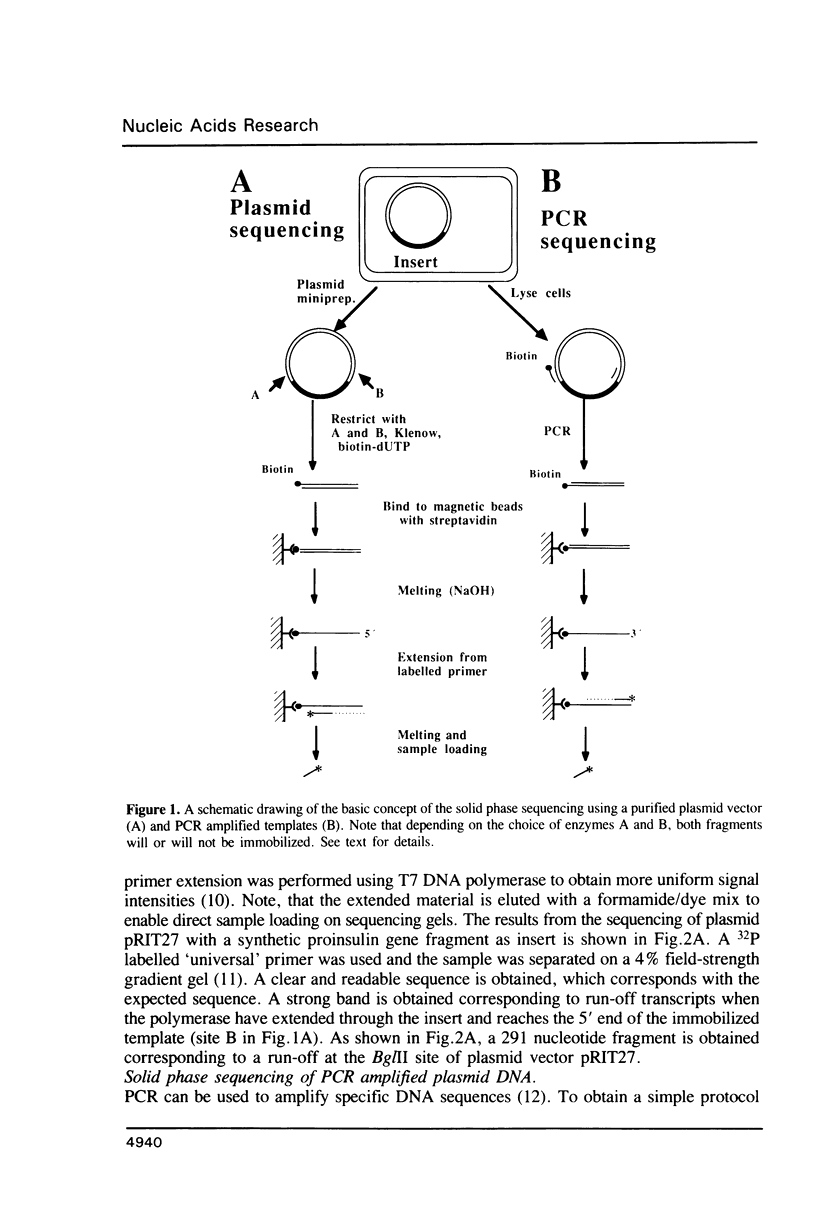
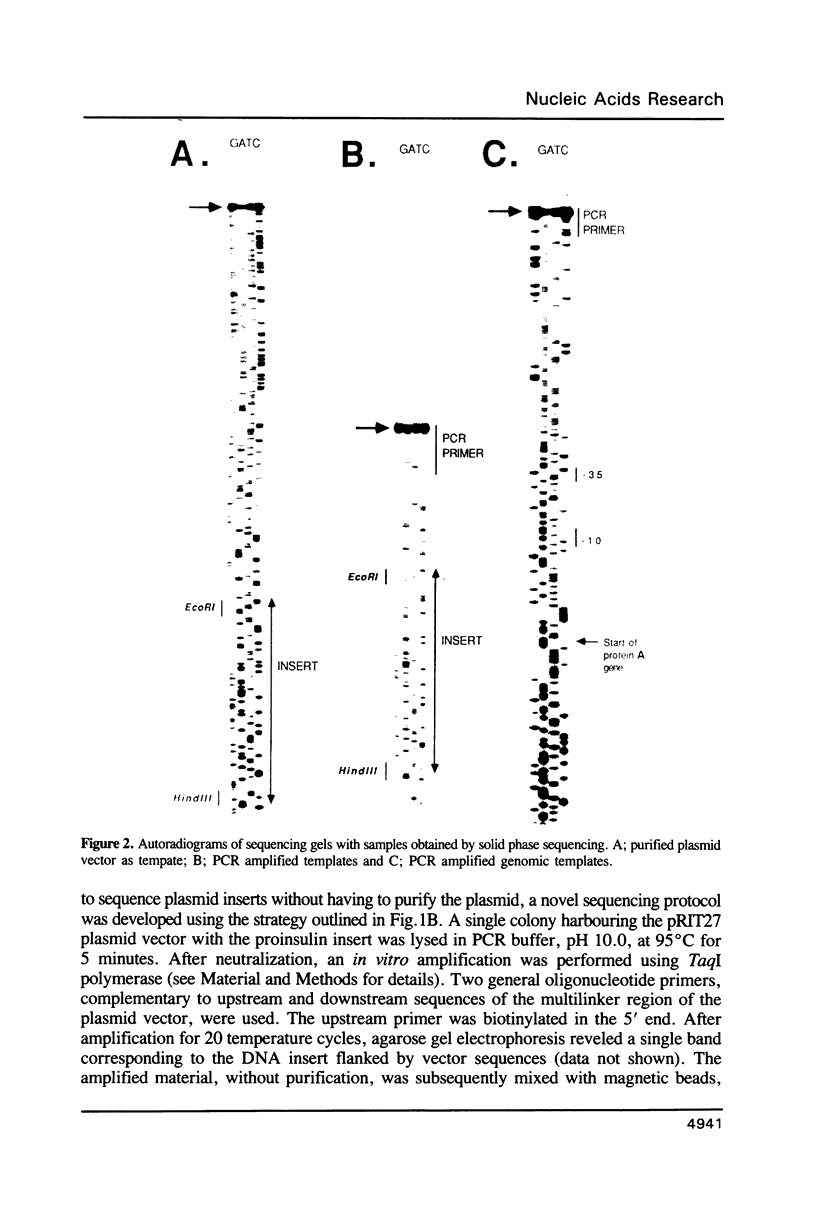
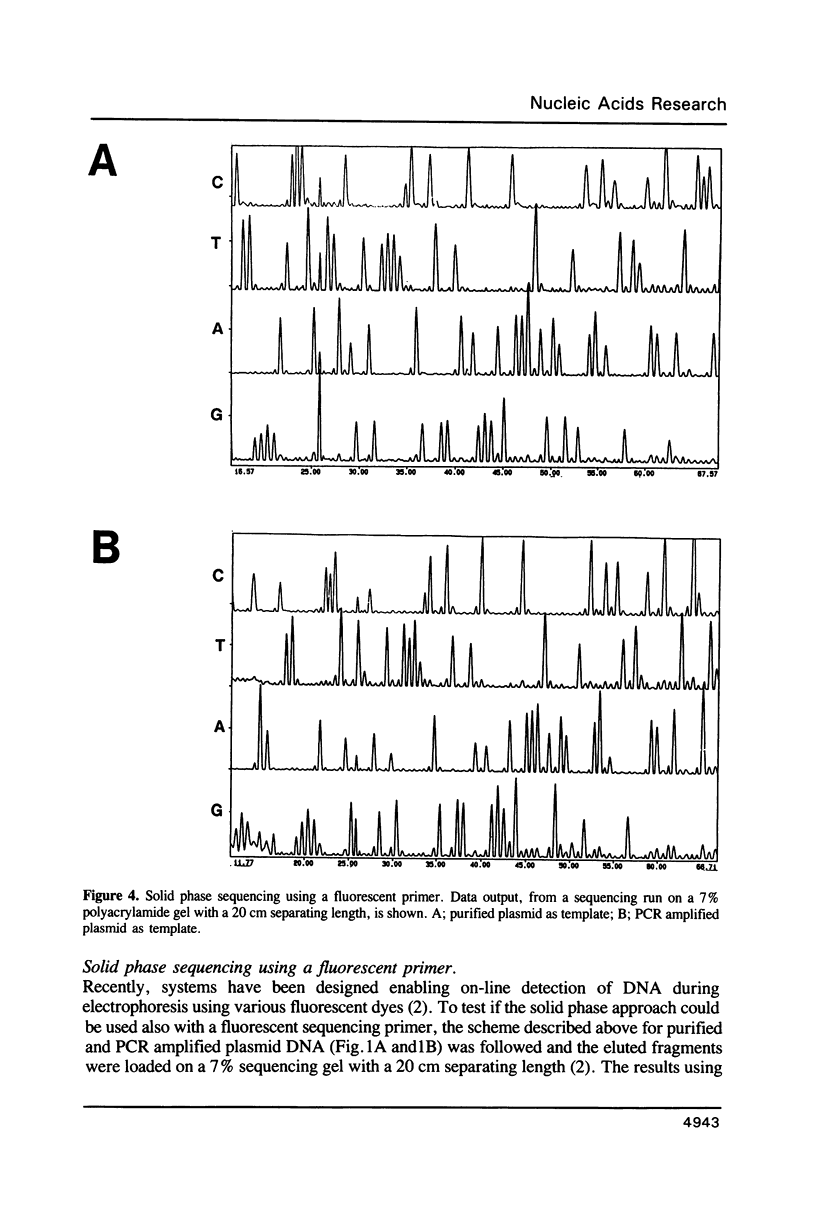
Approaches to direct solid phase sequencing of genomic and plasmid DNA have been developed using magnetic beads, coated with streptavidin, as solid support. The DNA is immobilized through selective incorporation of biotin into one of the strands. A single stranded template, suitable for sequencing, is obtained through strand-specific elution. Using this concept, in vitro amplified plasmid DNA and chromosomal DNA were sequenced directly from single colonies. The solid phase approach ensures that the amplification and the sequencing reactions can be performed under optimal conditions. The system was found to be suitable for sequencing using both isotope- and fluorescent-labelled primers.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansorge W., Sproat B., Stegemann J., Schwager C., Zenke M. Automated DNA sequencing: ultrasensitive detection of fluorescent bands during electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4593–4602. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman E. D. A new method of sequencing DNA. Anal Biochem. 1988 Nov 1;174(2):423–436. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis M. A., Myambo K. B., Gelfand D. H., Brow M. A. DNA sequencing with Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase and direct sequencing of polymerase chain reaction-amplified DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9436–9440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iordănescu S. Host controlled restriction mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. Arch Roum Pathol Exp Microbiol. 1975 Jan-Jun;34(1-2):55–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen T., Voss H., Schwager C., Stegemann J., Sproat B., Ansorge W. T7 DNA polymerase in automated dideoxy sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3487–3496. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson A., Moks T., Uhlén M., Gaal A. B. Uniformly spaced banding pattern in DNA sequencing gels by use of field-strength gradient. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Nov;10(1-2):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prober J. M., Trainor G. L., Dam R. J., Hobbs F. W., Robertson C. W., Zagursky R. J., Cocuzza A. J., Jensen M. A., Baumeister K. A system for rapid DNA sequencing with fluorescent chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides. Science. 1987 Oct 16;238(4825):336–341. doi: 10.1126/science.2443975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf S. J., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A. Direct cloning and sequence analysis of enzymatically amplified genomic sequences. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1076–1078. doi: 10.1126/science.3461561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. M., Sanders J. Z., Kaiser R. J., Hughes P., Dodd C., Connell C. R., Heiner C., Kent S. B., Hood L. E. Fluorescence detection in automated DNA sequence analysis. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):674–679. doi: 10.1038/321674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoflet E. S., Koeberl D. D., Sarkar G., Sommer S. S. Genomic amplification with transcript sequencing. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):491–494. doi: 10.1126/science.3340835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ståhl S., Hultman T., Olsson A., Moks T., Uhlén M. Solid phase DNA sequencing using the biotin-avidin system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):3025–3038. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.3025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén M., Guss B., Nilsson B., Gatenbeck S., Philipson L., Lindberg M. Complete sequence of the staphylococcal gene encoding protein A. A gene evolved through multiple duplications. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1695–1702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. K., Yuen A. S., Clark S. M., Spence C., Arakelian P., Hood L. E. Automation of dideoxynucleotide DNA sequencing reactions using a robotic workstation. Biotechniques. 1988 Sep;6(8):776-7, 781-7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C., Dowling C. E., Saiki R. K., Higuchi R. G., Erlich H. A., Kazazian H. H., Jr Characterization of beta-thalassaemia mutations using direct genomic sequencing of amplified single copy DNA. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):384–386. doi: 10.1038/330384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrischnik L. A., Higuchi R. G., Stoneking M., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N., Wilson A. C. Length mutations in human mitochondrial DNA: direct sequencing of enzymatically amplified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):529–542. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann J., Voss H., Schwager C., Stegemann J., Ansorge W. Automated Sanger dideoxy sequencing reaction protocol. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jun 20;233(2):432–436. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



