Abstract
Genomic biomarkers for the detection of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) from blood are urgently needed for monitoring drug safety. We used a unique data set as part of the Food and Drug Administration led MicroArray Quality Control Phase-II (MAQC-II) project consisting of gene expression data from the two tissues (blood and liver) to test cross-tissue predictability of genomic indicators to a form of chemically-induced liver injury. We then use the genomic indicators from the blood as biomarkers for prediction of acetaminophen-induced liver injury and show that the cross tissue predictability of a response to the pharmaceutical agent (accuracy as high as 92.1%) is better than, or at least comparable to, that of non-therapeutic compounds. We provide a database of gene expression for the highly informative predictors which brings biological context to the possible mechanisms involved in DILI. Pathway-based predictors were associated with inflammation, angiogenesis, Toll-like receptor signaling, apoptosis and mitochondrial damage. The results demonstrate for the first time and support the hypothesis that genomic indicators in the blood can serve as potential diagnostic biomarkers predictive of DILI.
Keywords: prediction, acetaminophen, blood, cross tissue, liver injury, microarray gene expression
INTRODUCTION
Drug-induced hepatotoxicity is the most frequent cause for a drug to be withdrawn from the market, to have its use restricted or to have a warning on the label associated with it. Currently, preclinical models are not always predictive of an adverse response in humans since sensitivity to certain drugs can be influenced by human-specific genetic variability and other variables accounting for idiosyncratic drug reactions. Discovery of diagnostic indicators of liver injury from a minimally invasive bio-available source is of interest to monitor for adverse effects of a drug.
A few recent studies have shown that genomic markers obtained from blood gene expression data are predictive of adverse effects of a drug or chemical compounds. Bushel et al. 1 demonstrated that gene expression profiles from rat blood samples could accurately predict exposure levels of acetaminophen to the rat liver better than traditional clinical panels. Lobenhofer et al. 2 used gene expression data from rats exposed to a compendium of hepatotoxicants to show that blood gene expression patterns could be used to provide an indication of the severity level of liver injury. Wang et al. 3 recently demonstrated the potential of circulating microRNA molecules (small regulatory non-coding RNAs) as biomarkers of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) in an acetaminophen-overdosed mouse model system. Although these efforts are certainly pioneering they do not address the question of whether or not genomic indicators in the blood are truly predictive of DILI.
In this paper we used the Lobenhofer et al. 2 gene expression data set that was contributed to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) led MicroArray Quality Control Phase-II (MAQC-II) effort as a training data set and for internal validation to identify genes and biological processes in the blood that are predictive of liver necrosis (a particular form of DILI). This data set was chosen for analysis for several key reasons: 1) it was the only data set publicly available at the time which contained gene expression measurements from the two tissues of interest, histopathology, clinical chemistry and other ancillary biological data from exposure to a compendium of compounds, 2) the experimental design and data acquisition were performed in a rigorous, standardized fashion (i.e. a common array platform, experimental procedure, data acquisition and analysis methods) in order to reduce the amount of systematic variation in the data, and 3) it permitted a global view of the landscape of the transcriptome of the rat as a model system to explore the possibility of using expression profiles from a non-invasive tissue as potential biomarkers predictive of DILI. We show that the classifiers derived from the gene expression data are highly predictive across tissues (blood and liver) and microarray platforms (Agilent and Affymetrix). We then demonstrate that gene expression profile sets from the blood predict acetaminophen-induced liver injury (samples classified as the subjects having either some or no observable form of liver necrosis as an end-point) in an independent (validation) data set better than (at an accuracy as high as 92.1%), or at least comparable to, that of non-therapeutic compounds used in this study. Cumulatively, these data support the hypothesis that genomic indicators in blood can serve as biomarkers that are highly predictive of a form of DILI and as a model for the acquisition of gene expression signatures that potentially can be used in a clinical setting for monitoring drug treatments and diagnosing adverse drug effects in humans.
MATERIALS and METHODS
Compendium (standardized) gene expression data
The gene expression data set was derived from the studies of the exposure of rats to one of eight compounds (1,2-dichlorobenzene, 1,4-dichlorobenzene, bromobenzene, monocrotaline, N-nitrosomorpholine, thioacetamide, galactosamine and diquat dibromide). The data are publicly available in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database under the MAQC-II reference series accession GSE16716 and in the Chemical Effects in Biological Systems (CEBS) database 4 under accession number 001-00001-0020-000-4. All eight compounds were studied using standardized procedures, i.e. a common array platform, experimental procedures and data retrieving and analysis processes. For details of the experimental design see Lobenhofer et al.2. Briefly, for each compound, four to six male, 12 week old Fischer F344/N rats were exposed to a low dose, mid dose(s) and a high dose of a compound and sacrificed at 6, 24 and 48 hrs later. For each time point, control animal groups were treated with vehicle alone. At necropsy, liver and blood were harvested for RNA extraction, histopathology, clinical chemistry and hematology assessments.
Both Agilent (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA) and Affymetrix (Affymetrix, Inc., Santa Clara, CA) platforms were used for the gene expression profiling. The cross tissue predictions used the Agilent data only whereas the cross platform predictions used both Agilent and Affymetrix data. For the Agilent platform, RNA isolated from the liver from each of the treated rats was labeled and hybridized against the time- and compound-matched control pool to Rat #G4130A oligonucleotide (22,075 probes) arrays. Fluorescent pixel intensities measurements were acquired using an Agilent DNA Microarray Scanner and processed with the Agilent Feature Extraction software. The averaged dye-swap ratio of the pixel intensity values (background subtracted and channel normalized red and green processed signals) were used to represent the gene expression profiles for 318 samples. The same approach was carried out for the rat blood samples. For the Affymetrix platform, the gene expression data were generated only for the rat liver. Specifically, the RNA samples from individual animals were profiled, one hybridization per animal on Rat Genome 230 2.0 (31,099 probe-sets) arrays for a total of 418 liver hybridizations. The data were processed using the MAS5 algorithm 5. The signals were background subtracted, averaged (across probes within a probe-set) using a mean Tukey biweight function and then scaled to account for differences between chips. The intensity data from the compound-treated samples were used to represent the gene expression profiles for 318 samples. The classification of the samples is described in the “Histopathology and sample classification” subsection.
Independent (non-standardized) validation gene expression data
The gene expression data is from the Agilent platform only and is comprised from liver samples of rats exposed to one of three hepatotoxicants (acetaminophen, carbon tetrachloride, and allyl alcohol) with a time-matched vehicle control pool made for each compound and tissue by pooling equal amounts of RNA from the control animals. Acetaminophen: Groups of four male Fischer F344/N rats each received 0 (vehicle), 50, 150, 1,500 or 2,000 mg/kg body weight of acetaminophen at two different times: between 12 (noon)-1PM (“light” subjects) or between 12 (midnight)-1AM (“night” subjects). The animals were sacrificed after 6, 18, 24 or 48 hrs. RNA samples from eight subjects were either not available or did not produce high quality RNA for hybridization leaving a total of 152 samples. Carbon Tetrachloride: Groups of six male Fischer F344/N rats each received 15, 750 or 2,000 mg/kg body weight of carbon tetrachloride. The animals were sacrificed after 3, 6, 24 or 72 hrs. There are a total of 72 samples. Allyl Alcohol: Groups of six male Fischer F344/N rats each received 10, 20, 40 or 50 mg/kg body weight of allyl alcohol. The animals were sacrificed after 6, 24, 48 or 72 hrs. The RNA from one subject was not available or did not produce high quality RNA for hybridization leaving a total of 95 samples.
Each treated animal was hybridized against a time matched control pool to Agilent Rat #G4130A oligonucleotide arrays with a dye-swap technical replicate. The data were acquired and extracted in a similar fashion as the Compendium gene expression data. The averaged dye-swap ratio of the pixel intensity values (background subtracted and channel normalized red and green processed signals) were used to represent the gene expression profiles for the 319 validation samples. For more details see Huang et al. 6 and Bushel et al. 1. The acetaminophen data is publicly available in the CEBS database 4 under accession number 002-00001-0011-000-5. The allyl alcohol and carbon tetrachloride data are stored in the NIEHS MicroArray Project System (MAPS) database 7 under project ID 221 and 236 and is available upon request. The classification of the samples is described in the “Histopathology and sample classification” subsection. ArrayTrack 8 was used to manage the microarray data, histopathology observations and clinical chemistry measurements for this study.
For comparison of the prediction of the blood and liver samples across array platforms, the gene expression data (ratio values for Agilent [blood] and intensity measurements for Affymetrix [liver]) were batch corrected as follows: After log transformation, the mean of the gene expression for each array feature across all the samples within each batch (array platform type or Compendium and validation data sets) is set to zero. This approach is also referred to as Mean Shift, Mean-Centering, or One-Way ANOVA Adjustment.
Histopathology and sample classification
Two sections were taken from the left liver lobes and fixed in 10% formalin. After dehydration with ethanol, the liver sections were embedded in paraffin and H&E stained slides were made. The slides were evaluated by independent pathologists and any disagreements were resolved by a pathology working group review 9. The severity of necrosis was graded into five levels by the pathologists, i.e., 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 representing none, minimal, mild, moderate and marked levels of necrosis respectively. The necrosis severity levels were used as a class label for the samples. Specifically, histopathological severity scores (1–4) of any one of four areas (centrilobular hepatocyte necrosis, centrilobular mid-zonal hepatocyte necrosis, mid-zonal hepatocyte necrosis or focal hepatocyte necrosis) were used to classify samples with at least some observable sign of necrosis (class 1; n = 154 Compendium data set samples and n = 127 validation data set samples). All other liver injuries and no injury observed samples were classified as having no observable sign of necrosis (class 0; n = 164 Compendium data set and n = 192 validation data set samples). See the Supplementary files A and B for the specific classification assignments of the Compendium and validation data sets samples respectively.
Clinical chemistry
At sacrifice, blood was collected into serum separation tubes (BD Microtainer® Tubes, Becton-Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ) and serum was separated. Clinical chemistry analyses were performed on all rats in the Compendium data set at study termination. Serum levels of the established liver injury marker alanine aminotransferase (ALT) are used routinely to assess hepatocyte injury in both animals and humans. Data from the other analytes were not used in this study but are publicly available 2, 4.
Classifier building and prediction
Classifiers were built and used for prediction according to the MAQC-II common practices for developing and validating microarray-based predictive models. For gene-based classifiers a sequential forward array feature selection approach with Welch t-test (fold change [FC] > 1.5 or 2 and P <0.05 criteria) comparisons of two groups (class 1: some observable form of necrosis vs class 0: samples with no observable form of necrosis) was used. The data are considered to be independent and assumed to be normally distributed. The measure of variability is the standard deviation. Optimization of the features selected as predictors was performed by a five-fold internal cross-validation strategy with the Compendium data set samples split into training (n=175) and testing (n=143) subjects. Support vector machines (SVM), k-nearest neighbors (KNN) and nearest centroid (NC) classifiers or a random forest (RF) classifier with 100 trees were used to predict the class of the samples (subjects having either some or no observable form of liver necrosis). The prediction using GeneGo’s canonical pathway maps (CPMs) was performed using the randomForest package in R. GeneGo’s canonical pathway maps were derived from an ontology of experimentally-confirmed signaling and metabolic multi-step pathways in human, mouse and rat 10. The pathways were manually inferred and curated from primary scientific literature. To date there are over 1100 pathway maps in total for normal and disease states. The genes of each of the CPMs were mapped to the array probes and considered as features for prediction using the RF classifier 11. As a result, there are about 350 classifiers built. An internal out-of-bag (OOB) process (a variant of cross validation) was used to estimate prediction performance and to rank the CPMs classifiers by cross validation accuracy. Briefly, 2000 bootstrap (random) samples were taken where at each iteration about one-third of the blood samples from the Compendium data set are left out of the construction of the kth tree [k=100] and then used for prediction. OOB error is estimated as the proportion of times that the predicted class of the samples is not equal to the true class averaged over all predicted cases. The best pathways (those with the highest cross validation prediction accuracy) were chosen for final prediction on the liver test data. On average, the probability of the informative genes in one of the best pathways to be highly predictive of drug-induced liver injury (DILI [characterized as the subjects having either some or no observable form of liver necrosis]) by chance given the blood and liver Compendium data set is 1×10−4. This means that the probability of any random set of genes with the same size as the one of the best pathway to be as predictive, or better than, the informative genes for the considered pathway is substantially small.
Coherent co-expression (cc) - biclustering
In the first step of cc-Biclustering 12 of the Compendium (Agilent) microarray data set, we use a pairwise approach to obtain subsets of the liver gene expression samples and the genes as initial coherent biclusters. Then we apply the Extracting Patterns and Identifying co-expressed Genes (EPIG) method 13 to the initial coherent biclusters in order to further subset the genes into final biclusters that contain coherent and highly co-expressed genes. EPIG uses a filtering process to extract gene expression patterns and then categorizes each gene to one of the patterns for which it has the highest correlation with the gene profile. Briefly, the relationship between two gene expression vectors aik and ajk (ith and jth genes) for the samples within the kth group is assessed with a binary coherent matrix H(h(ij),k) according to an inclusion\exclusion criterion function
| (1) |
where i and j are from 1 to N number of genes and k is from 1 to K number of groups (a given compound used for exposure). The kth group contains the samples exposed to the compound at the treatment doses and time points. CM represents a coherent measure between these two vectors. CM is the p-value of the Pearson correlation (r-value) between aik and ajk. pt is a user-defined threshold for the p-value and is set to 0.001.
Biological processes over-representation and pathway analysis
The Expression Analysis Systematic Explorer (EASE) 14 was used to identify biological processes over-represented by sets of genes identified as predictors or contained within biclusters. The over-represented processes were confirmed by the Gene Ontology (GO) Enrichment Analysis Software Toolkit (GOEAST) 15 using the Adrian Alexa's improved weighted scoring algorithm to account for the hierarchical structure of GO 16 and the Benjamini-Yekutieli procedure to control the false discovery rate under the assumption of gene-to-gene dependency 17.
RESULTS
Hepatocellular injury classified by severity of necrosis
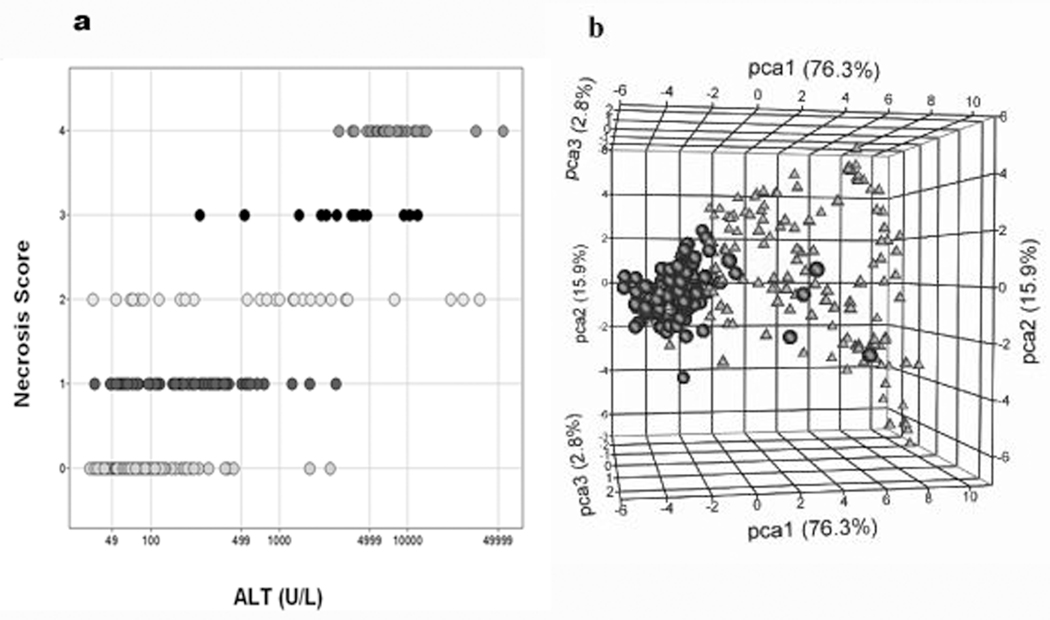
As detailed in Table 1, exposure to any one of the eight compounds in the Compendium data set resulted in necrosis of the liver which was scored using a five-point scale (0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 representing none, minimal, mild, moderate and marked levels of necrosis respectively). The majority of the rats showed no histopathological (observable) evidence of necrosis of the liver. Few samples were found to have a necrosis score that was concordant with levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and the variation of the ALT measure among samples sharing the same necrosis severity score is wide (Figure 1a). When the samples were classified based on the presence or absence of necrosis and a t-test was performed on the blood gene expression data, six genes (Table 2) were found to partition the liver samples fairly well (Figure 1b).
Table 1.
Severity scores and classification of necrosis
| Serverity scores | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | No necrosis |
Some sign of necrosis |
0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Total |
| 1,2-Dichlorobenzene | 17 | 17 | 17 | 8 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 34 |
| 1,4-Dichlorobenzene | 31 | 5 | 31 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 36 |
| Bromobenzene | 16 | 20 | 16 | 7 | 5 | 0 | 8 | 36 |
| Diquat dibromide | 50 | 22 | 50 | 10 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 72 |
| Galactosamine | 18 | 18 | 18 | 7 | 8 | 2 | 1 | 36 |
| Monocrotaline | 16 | 16 | 16 | 11 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 32 |
| N-nitrosomorpholine | 12 | 24 | 12 | 17 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 36 |
| Thioacetamide | 4 | 32 | 4 | 18 | 1 | 5 | 8 | 36 |
| Total | 164 | 154 | 164 | 82 | 29 | 14 | 29 | 318 |
No necrosis means that the liver samples from the rats exposed to a given compound received a histopathology severity score of 0 (no sign of necrosis seen). Any sign of necrosis means a sample received a histopathology score of 1 to 4 (at least some sign of necrosis seen).
Figure 1.
The Compendium data set samples partitioned by necrosis of the liver. a) Distribution of the samples by ALT (x-axis) and necrosis score (y-axis). Necrosis score: 0 (164 samples), 1(82 samples), 2 (29 samples), 3 (14 samples), and 4 (29 samples). The total number of samples is 318. b) Principal component analysis (PCA) of liver samples labeled according to an indication of necrosis. PCA was performed on the liver expression data from the six genes selected from the blood signature using a Welch t-test with P <0.05 and a fold change (FC) >2.0 filtering criteria in ArrayTrack to compare the two classes of samples. Triangles = class 1 (154 samples showing some form of liver necrosis), circles = class 0 (164 samples showing no sign of necrosis)]. The percent of variation captured by the first three principal components (PCs): PC1=76.3% (x-axis), PC2=15.9% (y-axis), and PC3=2.8% (z-axis).
Table 2.
Genes that separated the samples and were found most frequent in the gene-based classifiers that predicted liver necrosis as a form of DILI.
| Separates samples by necrosis* |
Probe ID | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ | A_42_P820657 | Il1r2 | interleukin 1 receeptor, type II |
| ✓ | A_42_P695401 | Ccl2, MCP1 | chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 |
| ✓ | A_42_P597580 | Cxcl10 | chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 10 |
| ✓ | A_43_P12944 | S100a8 | S100 calcium binding protein A8 (calgranulin A) |
| ✓ | A_42_P457572 | Serpinb1a | serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade B, member 1a |
| A_43_P12170 | Mmp8 | matrix metallopeptidase 8 (neutrophil collagenase) | |
| A_42_P733209 | Dgat2 | diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2 | |
| ✓ | A_43_P17175 | Serpinb1a | serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade B, member 1a |
| ✓ | A_42_P620915 | S100a9 | S100 calcium binding protein A9 (calgranulin B) |
| A_43_PP11474 | Hp | haptoglobin |
Check mark denotes the six genes (seven probes) which separated the samples by necrosis in the PCA.
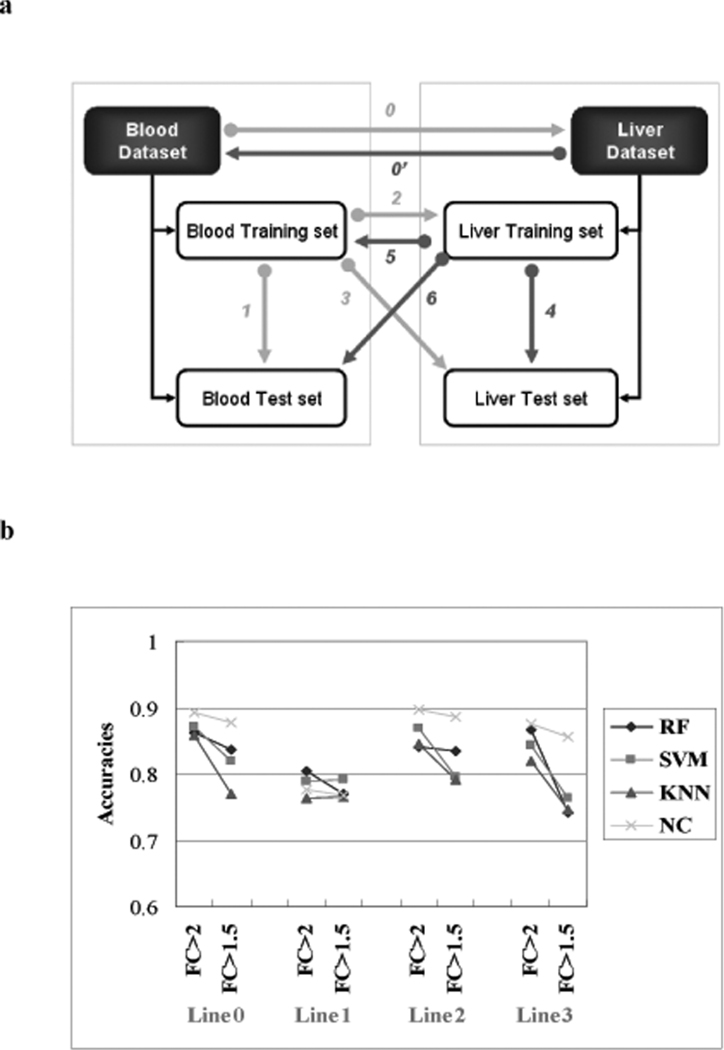
Cross tissue predictability
Several classifier building strategies were used to predict the Compendium data set liver tissue samples (classified as subjects having either some or no observable form of liver necrosis) using gene expression data from the blood and the reciprocal prediction (liver to blood) (Figure 2a). Figure 2b and Table 3 present the accuracies of the predictions using the gene-based models. When considering all cases of the models, the genes selected using the fold change (FC) > 2.0 criteria coupled with a p-value < 0.05 performed better than using a 1.5 cut-off with the same p-value. The nearest centroid (NC) classifier yielded the highest accuracy (~90%) of all predictions except when the blood training set was used for training the model and then for prediction of the blood test set (Line 1, accuracy = 77.7%). Building the classifiers on the samples from the entire blood data set to predict the same samples but profiled in the liver (Line 0, accuracy = 86.2%-88.9%), using the classifiers built on the blood training data set samples to predict the liver training data set samples (Line 2, accuracy = 84.0%-89.7%) and to predict the liver test data set samples (Line 3, accuracy = 82.0%-87.9%) performed better than directly predicting the blood test set samples (Line 1, accuracy = 77.7%-80.4%).
Figure 2.
Prediction across tissues. a) Strategies for building classifiers and making predictions. The line numbers represent the strategy taken. Line 0: Building the classifiers on the entire blood data set to predict the same data set profiled in the liver. Line 1: blood training set was used for training the model and for prediction of the blood test set. Line 2: using the classifiers built on the blood training data to predict the liver training data. Line 3: using the classifiers built on the blood training data to predict the liver test data. Line 0' and 4–6 are the reciprocal predictions from liver to blood. b) Gene-based classifier predictions from the blood to the liver. The x-axis represents the strategies taken to build classifiers and make predictions. The line numbers are as denoted in Figure 2a. FC means the fold change used to select the predictor genes (P <0.05). The y-axis represents the accuracy of prediction (from the average of 100 trials). RF-random forest (# of trees = 100), SVM – support vector machines (RBF kernel), KNN – k-nearest neighbors (k=15), NC-nearest centroids. SVM, KNN and NC were individually combined with a forward array feature selection method (Welch t-tests), evaluated with a five-fold internal cross validation to select best genes in the model construction.
Table 3.
Prediction accuracies of the gene-based classifiers
| 8 hepatotoxicants- blood classifier predict the liver | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classifier | Line 0 | Line 1 | Line 2 | Line 3 |
| RF | 0.862 | 0.804 | 0.840 | 0.867 |
| SVM | 0.874 | 0.785 | 0.867 | 0.844 |
| KNN | 0.859 | 0.763 | 0.845 | 0.820 |
| NC | 0.889 | 0.777 | 0.897 | 0.879 |
| 8 hepatotoxicants- liver classifier predict the blood | ||||
| Classifier | Line 4 | Line 5 | Line 6 | Line 0' |
| RF | 0.895 | 0.589 | 0.503 | 0.556 |
| SVM | 0.867 | 0.629 | 0.517 | 0.560 |
| KNN | 0.884 | 0.587 | 0.491 | 0.520 |
| NC | 0.839 | 0.620 | 0.489 | 0.529 |
Lines numbers denoted as in Figure 2a.
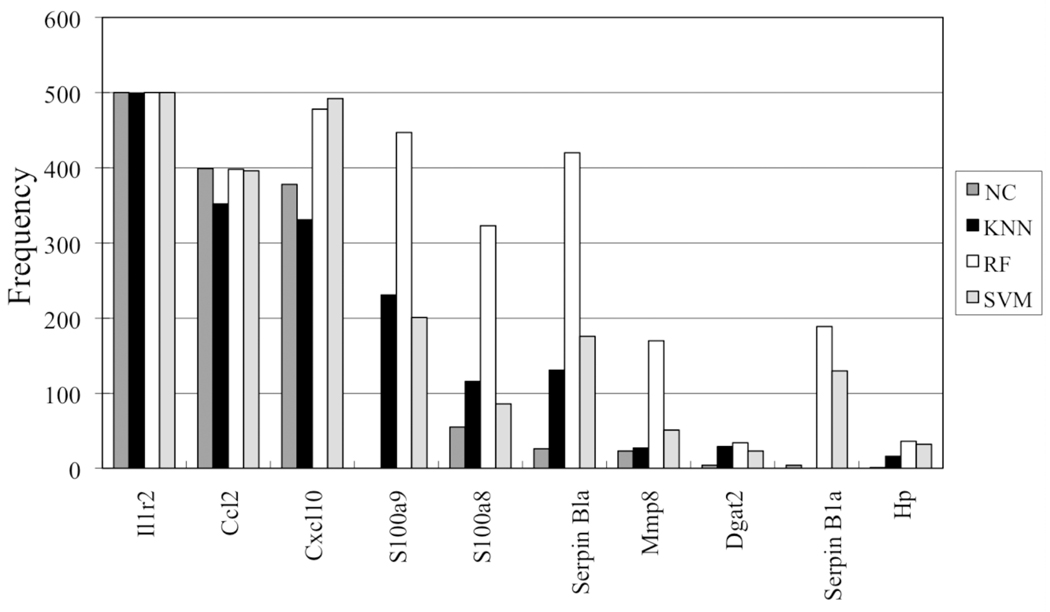
The frequency of the genes selected for prediction revealed that nine genes occurred most often in the classifiers (Figure 3 and Table 2). The genes for interleukin 1 receptor-type II (Il1r2), chemokine (c-c motif) ligand 2 (Ccl2 also known as monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 [MCP-1]) and chemokine (c-x-c motif) ligand 10 (Cxcl10) top the list. Six of these predictor genes were found to have blood gene expression profiles that partitioned the liver samples well based on the presence or absence of necrosis (Figure 1b).
Figure 3.
Frequency of the predictor genes from the overlap between the gene-based classifiers. The x-axis denotes the gene that the Agilent array probe represents and the y-axis denotes the count. See the legend to Figure 2b for identification of the classifier.
As revealed in Table 3, when considering the reciprocal prediction (i.e., from liver to blood) the training of the classifiers on the liver training data set samples and using them to predict the liver test data set samples (Line 4, accuracy = 83.9%-89.5%) performed much better than a) predicting the blood data samples (Lines 5 and 6, accuracy = 58.7%-62.9%) and b) the classifiers that were built on the entire liver data samples directly in order to predict the blood samples (Line 0’, accuracy = 52.0%-56.0%). Moreover, the liver-to-liver prediction (Line 4, accuracy = 83.9%-89.5%) performed better than the blood-to-blood prediction (Line 1, accuracy= 77.7%-80.4%). In all cases, using the classifiers built with the blood data set samples to predict the liver samples performed much better than the converse (Lines 0, 2, 3, versus Lines 0’, 5, 6) (Figure 2b and Table 3).
Cross-tissue predictability was further evaluated at the pathway level based on Line 0 (Figure 2a). In this case, all the genes on the Agilent Array were mapped to the ontology of about 350 canonical pathway maps (CPMs). Classifiers for each pathway were constructed using the genes that were annotated as being present in the pathway. The highest ranked pathways identified in the blood based on the internal cross validation (column 2 of Table 4) are related to PIP3 signaling in B lymphocytes, the Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway leading to a cell proinflammatory response, and regulation of apoptosis by mitochondrial proteins. These and other top predictive pathways are related to an inflammatory response, apoptosis, mitochondrial damage and angiogenesis (see the VEGF-, TPO- and angiotensin- signaling/activation processes). When pathway-based classifiers from the blood were used to predict the liver samples (column 3 of Table 4), two of the top three pathways identified in the blood as highly predictive, ranked high in the cross-tissue prediction along with the anti-apoptotic TNFs, NF-kB, Bcl-2 pathway, which conferred high degrees of predictability of necrosis between the blood and liver tissues (accuracies ranging between 83.6 % and 89.3%). Interestingly, the cumulative impact of the gene expression signal in the regulation of apoptosis by mitochondrial protein pathway was found to be higher in liver than in the blood. This is evident by a larger number of pro-apoptotic genes up-regulated in case of necrosis in liver compare to blood (Supplementary materials Figure 1).
Table 4.
Prediction accuracies of the pathway-based classifiers
| Pathway | blood.acc* | liver.acc** |
|---|---|---|
| PIP3 signaling in B lymphocytes | 81.1 | 78.9 |
|
Toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands and common TLR signalling pathway leading to cell proinflammatory response *** |
78.6 | 83.6 |
| Regulation of Apoptosis by Mitochondrial Proteins *** | 78.3 | 88.1 |
| Cytoplasm/mitochondrial transport of proapoptotic proteins Bid, Bmf and Bim |
78.3 | 72.3 |
| Role of IAP-proteins in apoptosis | 78.3 | 82.4 |
| VEGF-family signaling | 78.0 | 64.2 |
| Leukocyte chemotaxis | 78.0 | 78.6 |
| Angiotensin signaling via STATs | 77.7 | 77.4 |
| Receptor-mediated axon growth repulsion | 77.7 | 79.6 |
| Immune response BCR pathway | 77.7 | 80.8 |
| Membrane trafficking and signal transduction of G-alpha (i) heterotrimeric G-protein |
77.4 | 66.7 |
| Anti-apoptotic TNFs/NF-kB/Bcl-2 pathway *** | 76.7 | 89.3 |
| G-Protein alpha-12 signaling pathway | 76.1 | 70.4 |
| Brca1 as transcription regulator | 76.1 | 73.6 |
| CXCR4 signaling via second messenger | 76.1 | 78.9 |
| G-Protein alpha-i signaling cascades | 76.1 | 70.4 |
| Caspases cascade | 75.8 | 76.4 |
| Apoptotic TNF-family pathways | 75.8 | 80.2 |
| CCR3 signaling in eosinophils | 75.8 | 71.7 |
| FAS signaling cascades | 75.5 | 77.4 |
| Activation of PKC via G-Protein coupled receptor | 75.5 | 74.2 |
| Galactose metabolism | 75.5 | 60.1 |
| Heme metabolism | 75.5 | 81.4 |
| G-Proteins mediated regulation p38 and JNK signaling | 75.2 | 75.5 |
| ChREBP regulation pathway | 75.2 | 69.8 |
| TPO signaling via JAK-STAT pathway | 75.2 | 75.8 |
| Angiotensin signaling via beta-Arrestin | 75.2 | 74.5 |
| PDGF signaling via STATs and NF-kB | 75.2 | 79.6 |
| Angiotensin activation of ERK | 74.8 | 74.8 |
| Angiotensin signaling via PYK2 | 74.8 | 76.7 |
Blood.acc is the internal cross validation accuracy based on the entire blood data set (see Methods);
Liver.acc is the accuracy of the blood classifiers to predict the liver based on Line 0 in Figure 2a;
Top three pathways using the blood to predict the liver are highlighted
Expression signatures transferable across tissues
The investigation of the blood gene signatures transferred to the liver was carried out in order to determine whether or not the high accuracy of predictability across tissues is sustainable. Classifiers for the blood using random forest (RF), support vector machine (SVM), k-nearest neighbor (KNN) and NC were constructed and the resulting expression signatures were used to develop classifiers based on the gene expression data from the liver samples (Supplementary materials Figure 2). The transferability of expression signatures results summarized in Supplementary materials Table 1 (top section) used a gene expression filter selection criteria of FC > 2 or FC >1.5 and P<0.05. Similar to cross tissue predictability, the prediction using the blood training classifiers on the blood test data set samples (Supplementary materials Table 1 top section: 75.9%-78.6%) was slightly worse when compared to the prediction of the liver training classifiers on the liver test data set samples (Supplementary materials Table 1 bottom section: 83.4%-88.8%). However, using the transferred expression signatures from the blood classifiers to the liver test data set samples gave much better prediction results (Supplementary materials Table 1 top section 81.7%- 88.8%). When the transferability was evaluated in the reverse order, the gene expression signatures transferred from the liver (Supplementary materials Table 1 bottom section: 58.6%-72.0%) performed worse than the gene expression signatures transferred from the blood.
Cross tissue predictability extendable across platforms
The two-way cross platform predictability of genomic indicators was also assessed from the blood (Agilent platform) to predict liver samples (Affymetrix platform) and vice versa by correcting the data for batch (array platform differences) and building classifiers using SVM, KNN and a diagonal linear discriminant analysis (DLDA). As shown in Supplementary materials Table 2, the accuracy of prediction from blood to liver was much higher with the batch corrected data (Lines 2 vs 2’ and 3 vs 3’, i.e., before vs after the batch correction) but about the same as the uncorrected data when predicting liver to blood (Line 5 vs 5’ and 6 vs 6’). In addition, the accuracy of the within-tissue prediction (blood to blood and liver to liver) generally produced higher accuracies than predicting cross tissue (Lines 1 vs 2’ and 3’ and Line 4 vs 5’ and 6’), with the only exception of using the DLDA classifier for prediction from blood to liver (Lines 1 vs. 2’ and 3’). In all cases of the classifiers, higher accuracies were observed when the blood from the Agilent platform was used for training to predict the liver on the Affymetrix platform than the converse (Lines 3’ vs 6’). For all three classifiers, the within-tissue (and platform) training and testing using the liver data is higher than that of the blood (Lines 4 vs 1). The highest (cross tissue) prediction accuracy obtained was 81.0% when the DLDA classifier with sequence mapping and the blood Agilent data set samples were used for training and then applied to predict the liver samples profiled by the Affymetrix platform.
External validation of the predictors across tissues
To validate the ability of the gene-based and pathway-based classifiers constructed from the blood to predict DILI, we leveraged an independent gene expression data set derived from rat liver samples exposed to a different set of hepatotoxicants, one of which is a pharmaceutical agent (acetaminophen) and the other two are non-therapeutic compounds (carbon tetrachloride and allyl alcohol). The accuracy of prediction was determined to be the proportion of samples predicted correctly according to their class label (samples classified as subjects displaying either some or no observable form of liver necrosis as an end-point [see the Materials and Methods section for the number of samples binned in each class and the exposure conditions]). As shown in Table 5, the accuracies of the blind predictions using the four gene-based classifiers (RF, KNN, SVM and NC) and three pathway-based classifiers (corresponding to the ones with high accuracy in cross-tissue prediction as shown in Table 4) are typically higher for acetaminophen and carbon tetrachloride than for allyl alcohol. The gene-based classifiers performed slightly better than the pathway-based classifiers. The NC gene-based classifier performed the best across all the independent validation data set samples and achieved a 92.1% accuracy of prediction on the acetaminophen data. The RF pathway-based classifiers consisted of genes in the a) regulation of apoptosis by mitochondrial proteins pathway, b) anti-apoptotic TNFs/NF-kB/Bcl-2 pathway or c) Toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands and common TLR signaling pathway and performed poorly on the allyl alcohol data set (average accuracy = 66.3%). The RF-b pathway-based classifier, which exhibited the best cross-tissue predictability (Table 4), predicted the acetaminophen and carbon tetrachloride samples slightly better than the other two pathway-based classifiers.
Table 5.
Prediction accuracies of gene- and pathway-based classifiers for independent (validation) data set samples.
| Classifier | Independent data sets | Mean Acc | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetaminophen | Carbon Tetrachloride |
Allyl Alcohol |
|||
|
Pathway- based classifiers* |
RF-a | 0.855 | 0.875 | 0.642 | 0.791 |
| RF-b | 0.888 | 0.903 | 0.642 | 0.811 | |
| RF-c | 0.882 | 0.889 | 0.705 | 0.825 | |
|
Gene-based classifiers** |
RF | 0.816 | 0.889 | 0.684 | 0.796 |
| KNN | 0.836 | 0.889 | 0.684 | 0.803 | |
| SVM | 0.888 | 0.931 | 0.747 | 0.855 | |
| NC | 0.921 | 0.917 | 0.747 | 0.862 | |
| Mean Acc | 0.869 | 0.899 | 0.693 | 0.820 | |
Pathway-based random forest (RF) classifiers (Table 2) consist of genes in the a) regulation of apoptosis by mitochondrial proteins pathway, b) Anti-apoptotic TNFs/NF-kB/Bcl-2 pathway, or c) Toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands and common TLR signaling pathway.
Gene-based pathways are developed using the entire blood data set.
DISCUSSION
As part of the Food and Drug Administration led MicroArray Quality Control Phase-II (MAQC-II) effort to develop and validate predictive signatures, we used gene expression data acquired from the blood of rats chemically stressed to identify gene- and pathway-based indicators of liver necrosis. Although others have used blood to either predict the exposure of a single drug 1 or to survey a compendium of hepatotoxicants 2, 6, we took a more formal and comprehensive approach to evaluate the genomic indicators in blood for prediction of liver necrosis across a variety of chemical compounds that target the liver. Our work is the first demonstration of the usefulness of blood as a surrogate tissue to extract genomic indicators for predicting the manifestation of necrosis in the liver based on hepatocellular stress from a drug, therapeutic or across a wide variety of hepatotoxicants. Importantly, the findings are verified by an independent data set comprised of gene expression data from samples stressed by compounds with different characteristics. Acetaminophen is a therapeutic agent while carbon tetrachloride and allyl alcohol are compounds with no pharmacologic benefit. Furthermore, while as hepatotoxicants acetaminophen and carbon tetrachloride require more P450 isoenzyme for bioactivation, allyl alcohol differs in that it requires higher oxygen levels for oxygen-dependent bioactivation 18. Despite these salient differences, from our analysis, the results demonstrate that using the genomic indicators in blood to predict liver necrosis is somewhat of a general phenomenon and is presumably independent of the choice of hepatotoxicant, the extent of chemical stress or the use as a therapeutic.
Our findings are consistent with the role of organ-to-organ communication that has been previously reported for acetaminophen-induced toxicity 19 and the role of transmigration of leukocytes into the liver vasculature by inflammatory mediators at the onset of hepatotoxicity contributing to acute liver injury 20, 21. In contrast to the blood-to-liver prediction, the gene and pathway signatures from the liver to predict the blood were not as highly predictive as those acquired from the blood to predict the liver (Figure 2b and Table 3). A possible reason for this phenomenon may be the fact that the dynamic range and overall changes in gene expression that are statistically significant in the liver are quite different and much greater than what is detected in the blood (Supplementary materials Figure 3). Another possibility could be that many of the animals in this study had lesions other than just necrosis or that the phenotypic response that the classifier captured was for a general necrotic lesion whereas the end-point for the validation data set samples was for a specific form of necrosis. An area for further investigation is the determination of a more complex classification based on the histopathology data to predict a composite representation of liver injury which encompasses many end-points.
The genes and pathways acquired from the blood expression data that comprised the classifiers for prediction of necrosis of the liver represent biological mechanisms related to a severe immune response, induction of apoptosis, targeting of the mitochondria and angiogenesis. These mechanisms agree with the current literature on drug-related hepatotoxicity 22–24 but the latter may be related to the formation of new blood vessels during the regeneration of the liver to compensate for the loss of hepatocytes. Interestingly, one of our top ranking pathway-based classifiers for predicting necrosis in the liver points to the Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway leading to a cell proinflammatory response. TLRs are a class of single membrane-spanning non-catalytic receptors that recognize structurally conserved molecules derived from microbes and activate immune cell responses. Recently, Yohe et al. 25 reported the role of TLR4 in acetaminophen-mediated hepatotoxicity in endotoxin-responsive mice.
We found that the genes for interleukin 1 receptor-type II (Il1r2), chemokine (c-c motif) ligand 2 (Ccl2) and chemokine (c-x-c motif) ligand 10 (Cxcl10) were most frequently selected for prediction among all the classifiers built and six of the nine most frequent genes have blood gene expression profiles that separated the liver samples fairly well based on the presence or absence of necrosis (Figure 1b). Two pathways with high predictability, the regulation of apoptosis by mitochondrial proteins and the anti-apoptotic TNFs, NF-kB, Bcl-2, have three genes that overlap: B-cell CLL/Lymphoma 2 (Bcl2), TNF receptor superfamily member 1a (Tnfrsf1a) and Bcl2-related protein A1 (Bcl2a1). The latter encodes a member of the Bcl2 protein family. The proteins of this family form hetero- or homodimers and act as anti- and pro-apoptotic regulators. Coincidently, the biological processes that these predictor genes represent match several of the enriched Gene Ontology (GO) categories and KEGG pathways from the biclusters of up- and down-regulated (co-expressed) genes from the Compendium data set liver samples (Supplementary materials Figure 4, Supplementary materials Table 3 and Supplementary file C).
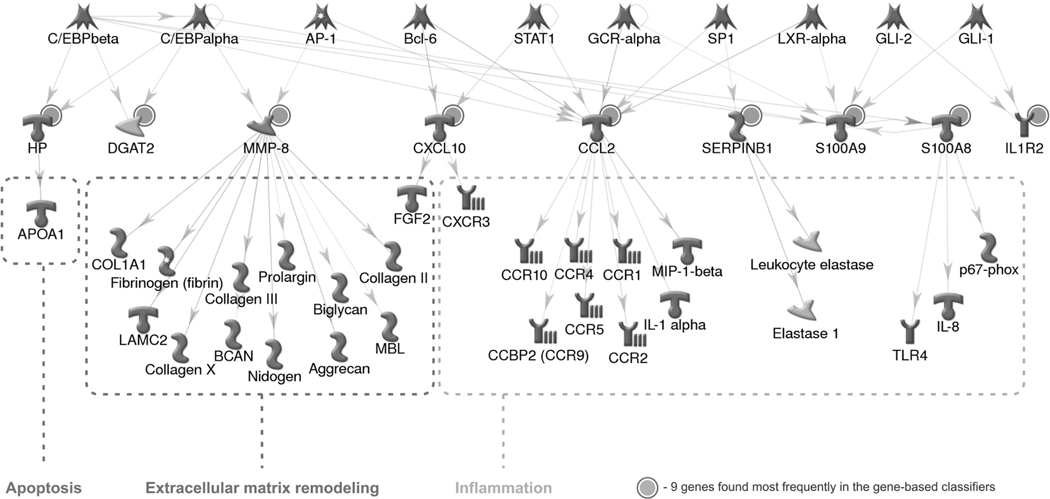
In order to assess the possible mechanisms that the predictor genes contribute to the liver injury phenotype, we built a direct interaction (DI) network using signature genes as seed nodes and the MetaCore collection of over 300,000 curated protein interactions as the source of edges and connected genes (Figure 4). The network revealed that nine signature genes are commonly regulated by 10 transcription factors (TFs) with Ccl2 regulated by seven TFs and S100A9 by six. The downstream targets of the signature genes belong to many of the biological processes ranked highly significant in enrichment and are involved in liver injury: inflammation, extracellular matrix remodeling and apoptosis.
Figure 4.
Network analysis of the upstream and downstream regulation. The nine genes (marked with solid circles) are direct targets of 10 transcription factors. The downstream genes belong to three processes implicated in liver injury.
Although blood serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) have been historically used as a gold standard clinical chemistry marker of liver injury, the enzyme measurements do not always correlate well with histopathologic data 26 (i.e., the true nature and extent of the liver damage is not always proportional to the elevation in the serum enzyme activity 27). Recently, a study was performed that measured the level of gene expression of haptoglobin (Hp) in blood and compared it to serum ALT as a marker of liver damage 28. The group found that Hp gene expression was more sensitive as an indicator of liver damage. Other genes in our predictor list play a role in inflammation. For instance, the chemokine Cxcl10 is a marker of inflammation found in many models of inflammatory liver diseases 29, 30 and is thought to be mainly expressed by hepatocytes but also by macrophages and stellate cells 31. S100A8 and S100A9 make up a complex found in leukocytes that appears to be an anti-inflammatory protein 32. Finally, matrix metallopeptidase 8 (Mmp8), a neutrophil collagenease, is involved in the control of the polymorphonuclear cell feed-forward mechanism in an inflammatory process 33 and others have correlated peripheral blood expression of Mmp8 as a marker of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis 34.
Genome-wide expression profiling using microarray technologies provides a practical way of surveying the global transcriptional response of a stressor on biological systems35. Using this system to assay peripheral blood for the identification of novel biomarkers of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is intriguing and may be a useful diagnostic test in the near future 36. Other assay systems have been proposed or used as a model for identifying serum biomarkers as candidates for liver injury 3, 37–42. Our results strongly support the claim that genomic indicators in the blood can serve as biomarkers of necrosis as a form of a chemically-stressed adverse effect on the rat liver and give credence to the acquisition of gene expression signatures from minimal invasive biomaterial sources potentially for diagnostic testing of DILI in humans.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank the National Center for Toxicogenomics at the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) for the hepatotoxicant Compendium data. In addition, we thank participants of MAQC-II for comments, feedback and discussions on the topic of this paper during teleconferences and face-to-face project meetings. We also thank K. Shockley, A. Merrick, S. Hester, B. Ward and D. Mendrick for their critical review of the manuscript. JH would like to acknowledge the support of the Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education (ORISE) for the Post-graduate Research Program at the National Center for Toxicological Research (NCTR), U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). JH also acknowledges the support of the China State-funded Study Abroad Program that is organized by the China Scholarship Council (CSC). JH and XF both acknowledge the Chinese Key Technologies R&D Program (No.2005CB23402) and the National Science Foundation of China (No. 30801556) for support to participate in the MAQC-II project at the NCTR/FDA. This research was supported, in part by, the Intramural Research Program of the NIH and NIEHS [Z01 ES102345-03]. This document has been reviewed in accordance with U.S. FDA and Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) policies and is approved for publication. Approval does not signify that the contents necessarily reflect the position or opinions of the FDA or EPA nor does mention of trade names or commercial products constitute endorsement or recommendation for use. The findings, views and conclusions in this report are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent or reflect the views of the FDA or EPA.
Footnotes
CONFLICT OF INTERST
The authors declare no competing interests.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
Supplementary information is available at the Pharmacogenomics Journal website. The Supplementary materials file is a pdf file containing additional tables and figures for the manuscript. Supplementary files A, B and C are tab-delimited text files containing the classification assignments of the Compendium data set samples, the classification assignments of the validation data set samples and the co-expressed genes in the biclusters respectively.
REFERENCES
- 1.Bushel PR, Heinloth AN, Li J, Huang L, Chou JW, Boorman GA, et al. Blood gene expression signatures predict exposure levels. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2007;104(46):18211–18216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706987104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lobenhofer EK, Auman JT, Blackshear PE, Boorman GA, Bushel PR, Cunningham ML, et al. Gene expression response in target organ and whole blood varies as a function of target organ injury phenotype. Genome Biol. 2008;9(6):R100. doi: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-6-r100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wang K, Zhang S, Marzolf B, Troisch P, Brightman A, Hu Z, et al. Circulating microRNAs, potential biomarkers for drug-induced liver injury. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2009 doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813371106. Early Edition. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Waters M, Stasiewicz S, Merrick BA, Tomer K, Bushel P, Paules R, et al. CEBS--Chemical Effects in Biological Systems: a public data repository integrating study design and toxicity data with microarray and proteomics data. Nucleic acids research. 2008;36:D892–D900. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm755. (Database issue) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hubbell E, Liu WM, Mei R. Robust estimators for expression analysis. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 2002;18(12):1585–1592. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.12.1585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Huang L, Heinloth AN, Zeng ZB, Paules RS, Bushel PR. Genes related to apoptosis predict necrosis of the liver as a phenotype observed in rats exposed to a compendium of hepatotoxicants. BMC genomics. 2008;9:288. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bushel PR, Hamadeh H, Bennett L, Sieber S, Martin K, Nuwaysir EF, et al. MAPS: a microarray project system for gene expression experiment information and data validation. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 2001;17(6):564–565. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/17.6.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tong W, Harris S, Cao X, Fang H, Shi L, Sun H, et al. Development of public toxicogenomics software for microarray data management and analysis. Mutat Res. 2004;549(1–2):241–253. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2003.12.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Boorman GA, Haseman JK, Waters MD, Hardisty JF, Sills RC. Quality review procedures necessary for rodent pathology databases and toxicogenomic studies: the National Toxicology Program experience. Toxicol Pathol. 2002;30(1):88–92. doi: 10.1080/01926230252824752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nikolsky Y, Kirillov E, Zuev R, Rakhmatulin E, Nikolskaya T. Methods in molecular biology. Vol. 563. Clifton, NJ: 2009. Functional analysis of OMICs data and small molecule compounds in an integrated "knowledge-based" platform; pp. 177–196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Liaw A, Wiener M. Classification and Regression by randomForest. R News. 2002;2(3):18–22. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chou JW, Bushel PR. Discernment of possible mechanisms of hepatotoxicity via biological processes over-represented by co-expressed genes. BMC genomics. 2009;10:272. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chou JW, Zhou T, Kaufmann WK, Paules RS, Bushel PR. Extracting gene expression patterns and identifying co-expressed genes from microarray data reveals biologically responsive processes. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007;8:427. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hosack DA, Dennis G, Jr, Sherman BT, Lane HC, Lempicki RA. Identifying biological themes within lists of genes with EASE. Genome Biol. 2003;4(10):R70. doi: 10.1186/gb-2003-4-10-r70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zheng Q, Wang XJ. GOEAST: a web-based software toolkit for Gene Ontology enrichment analysis. Nucleic acids research. 2008;36:W358–W363. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn276. (Web Server issue) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Alexa A, Rahnenfuhrer J, Lengauer T. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 13. Vol. 22. 2006. Improved scoring of functional groups from gene expression data by decorrelating GO graph structure; pp. 1600–1607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Benjamini Y, Yekutieli D. The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Annals of Statistics. 2001;29(4):1165–1188. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Casarett LJ, Doull J, Klaassen CD. Casarett and Doull's toxicology : the basic science of poisons. 6th edn. xix. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical Pub. Division; 2001. p. 1236. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Neff SB, Neff TA, Kunkel SL, Hogaboam CM. Alterations in cytokine/chemokine expression during organ-to-organ communication established via acetaminophen-induced toxicity. Exp Mol Pathol. 2003;75(3):187–193. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4800(03)00096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jaeschke H, Hasegawa T. Role of neutrophils in acute inflammatory liver injury. Liver Int. 2006;26(8):912–919. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2006.01327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ramaiah SK, Jaeschke H. Role of neutrophils in the pathogenesis of acute inflammatory liver injury. Toxicol Pathol. 2007;35(6):757–766. doi: 10.1080/01926230701584163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jaeschke H, Gores GJ, Cederbaum AI, Hinson JA, Pessayre D, Lemasters JJ. Mechanisms of hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Sci. 2002;65(2):166–176. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/65.2.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kaplowitz N. Biochemical and cellular mechanisms of toxic liver injury. Semin Liver Dis. 2002;22(2):137–144. doi: 10.1055/s-2002-30100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lee WM. Drug-induced hepatotoxicity. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(5):474–485. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra021844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yohe HC, O'Hara KA, Hunt JA, Kitzmiller TJ, Wood SG, Bement JL, et al. Involvement of Toll-like receptor 4 in acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;290(6):G1269–G1279. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00239.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ozer J, Ratner M, Shaw M, Bailey W, Schomaker S. The current state of serum biomarkers of hepatotoxicity. Toxicology. 2008;245(3):194–205. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2007.11.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kaplowitz N, DeLeve LD. Drug-induced liver disease. 2nd edn. xv. New York: Informa Healthcare; 2007. p. 808. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kudo Y, Ochi T, Shimada H, Ogawa S, Shinjo K. Utility of plasma circulating mRNA as a marker to detect hepatic injury. J Vet Med Sci. 2008;70(9):993–995. doi: 10.1292/jvms.70.993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nakken KE, Nygard S, Haaland TK, Berge KE, Odegaard A, Labori KJ, et al. Gene expression profiles reflect sclerosing cholangitis activity in abcb4 (−/ −) mice. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2008:1–8. doi: 10.1080/00365520802400867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhai Y, Shen XD, Gao F, Zhao A, Freitas MC, Lassman C, et al. CXCL10 regulates liver innate immune response against ischemia and reperfusion injury. Hepatology. 2008;47(1):207–214. doi: 10.1002/hep.21986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yoneyama H, Kai Y, Koyama J, Suzuki K, Kawachi H, Narumi S, et al. Neutralization of CXCL10 accelerates liver regeneration in carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury. Med Mol Morphol. 2007;40(4):191–197. doi: 10.1007/s00795-007-0371-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ikemoto M, Murayama H, Itoh H, Totani M, Fujita M. Intrinsic function of S100A8/A9 complex as an anti-inflammatory protein in liver injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats. Clin Chim Acta. 2007;376(1–2):197–204. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2006.08.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tester AM, Cox JH, Connor AR, Starr AE, Dean RA, Puente XS, et al. LPS responsiveness and neutrophil chemotaxis in vivo require PMN MMP-8 activity. PLoS ONE. 2007;2(3):e312. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rosas IO, Richards TJ, Konishi K, Zhang Y, Gibson K, Lokshin AE, et al. MMP1 and MMP7 as potential peripheral blood biomarkers in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS Med. 2008;5(4):e93. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Minami K, Saito T, Narahara M, Tomita H, Kato H, Sugiyama H, et al. Relationship between hepatic gene expression profiles and hepatotoxicity in five typical hepatotoxicant-administered rats. Toxicological Sciences. 2005;87(1):296–305. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfi235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Burczynski ME, Dorner AJ. Transcriptional profiling of peripheral blood cells in clinical pharmacogenomic studies. Pharmacogenomics. 2006;7(2):187–202. doi: 10.2217/14622416.7.2.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gangadharan B, Antrobus R, Dwek RA, Zitzmann N. Novel serum biomarker candidates for liver fibrosis in hepatitis C patients. Clinical chemistry. 2007;53(10):1792–1799. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2007.089144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Miller T, Knapton A, Adeyemo O, Noory L, Weaver J, Hnig J. Cytochrome c: a non-invasive biomarker of drug-induced liver injury. J Appl Toxicol. 2008;28(7):815–828. doi: 10.1002/jat.1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Xu JJ, Henstock PV, Dunn MC, Smith AR, Chabot JR, de Graaf D. Cellular imaging predictions of clinical drug-induced liver injury. Toxicol Sci. 2008;105(1):97–105. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfn109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Merrick BA, Bruno ME, Madenspacher JH, Wetmore BA, Foley J, Pieper R, et al. Alterations in the rat serum proteome during liver injury from acetaminophen exposure. The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics. 2006;318(2):792–802. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.102681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Amacher DE, Adler R, Herath A, Townsend RR. Use of proteomic methods to identify serum biomarkers associated with rat liver toxicity or hypertrophy. Clinical chemistry. 2005;51(10):1796–1803. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2005.049908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Merrick BA. The plasma proteome, adductome and idiosyncratic toxicity in toxicoproteomics research. Briefings in functional genomics & proteomics. 2008;7(1):35–49. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/eln004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.