Abstract
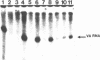
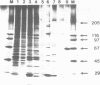
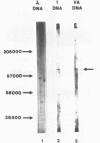
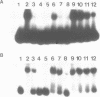
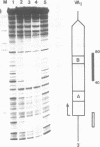
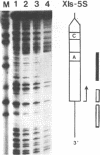
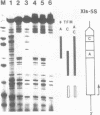
Transcription factor hTFIIIC was purified from cytoplasmic extracts of HeLa cells using four different chromatographic steps. This procedure yields a protein fraction which actively supports transcription in reconstitution assays and contains five major polypeptide chains with a molecular mass ranging from 25 to 250 kDa as estimated by SDS-PAGE and silver staining. In this fraction a polypeptide with a molecular mass of approximately 110 kDa could be identified as a specific DNA-binding component of hTFIIIC. By electrophoretic mobility shift and footprinting analyses it could be demonstrated that purified hTFIIIC binds specifically to the 5S gene. The protected region encompasses the A-Box promoter element and flanking sequences extending toward the 5'-proximal end of the gene. By addition of hTFIIIC to preformed TFIIIA/5S DNA complexes, we observe an additive effect of both factors on the footprint boundaries.
Full text
PDF


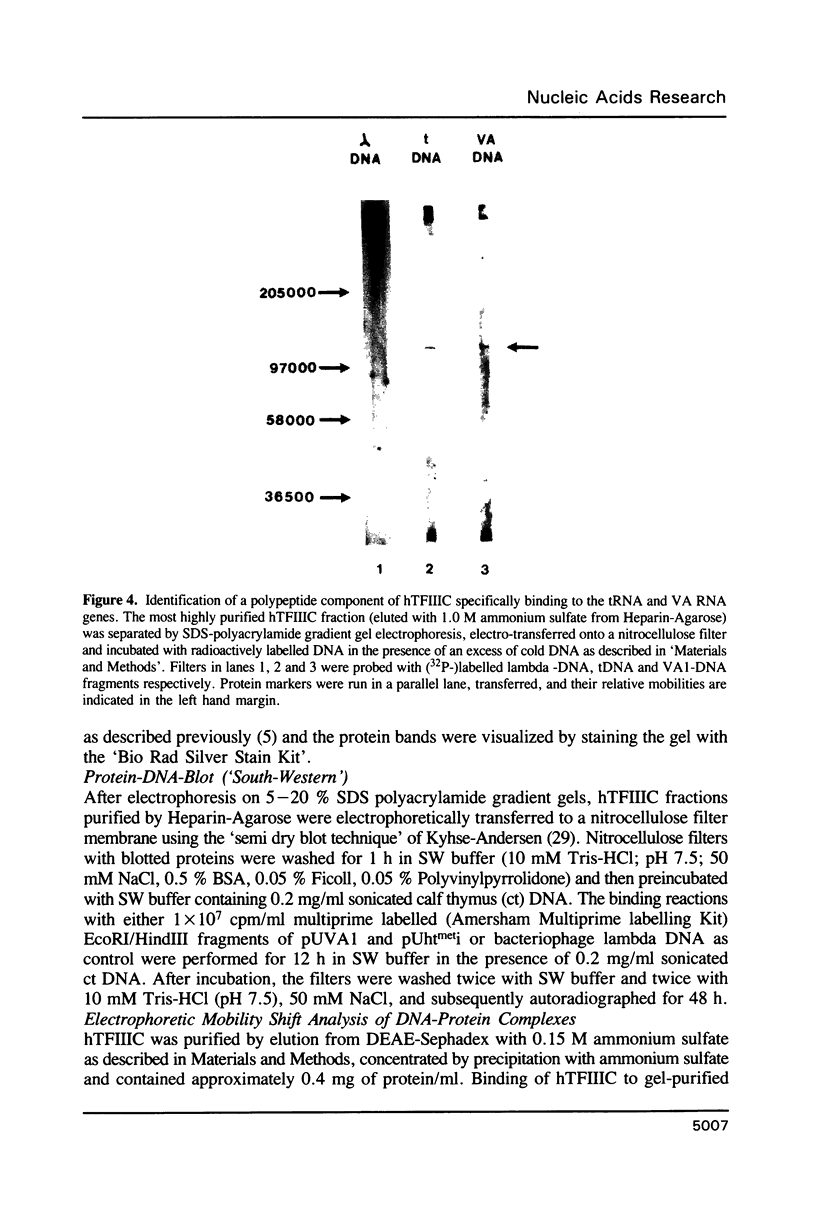


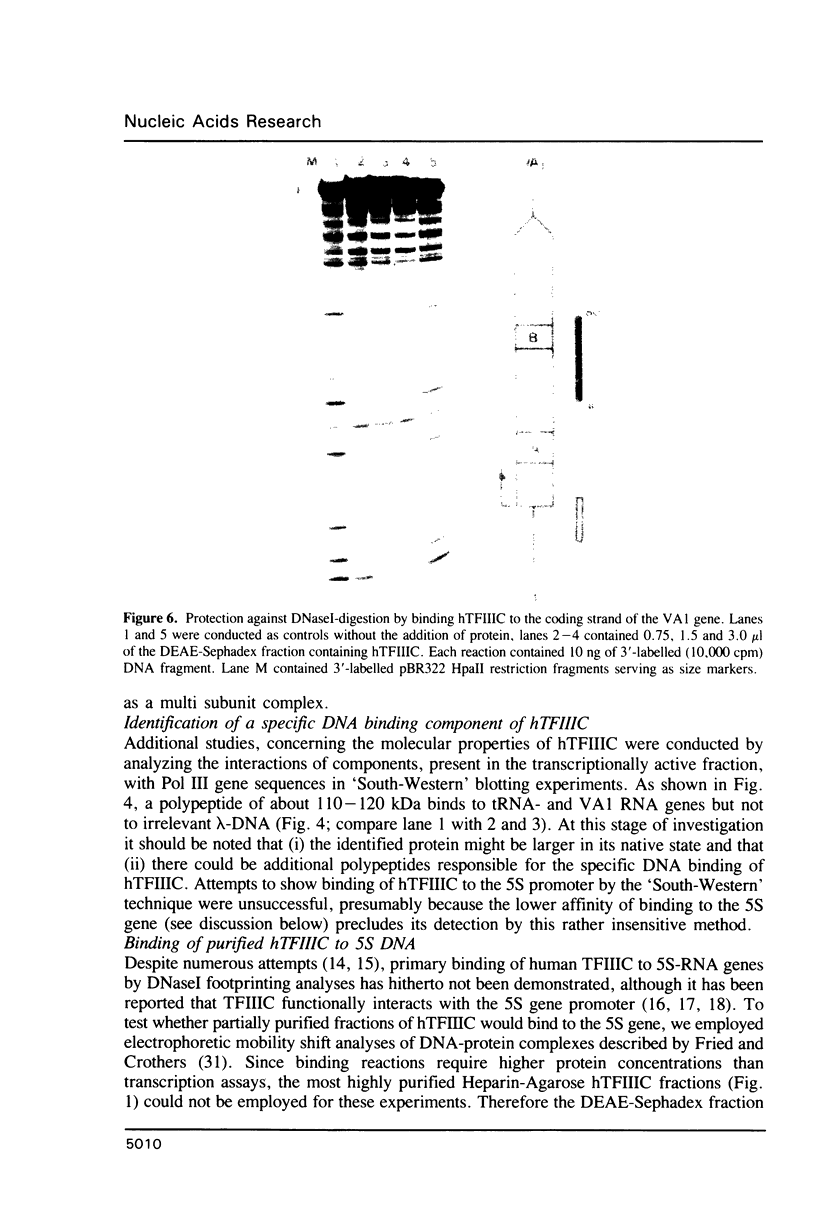

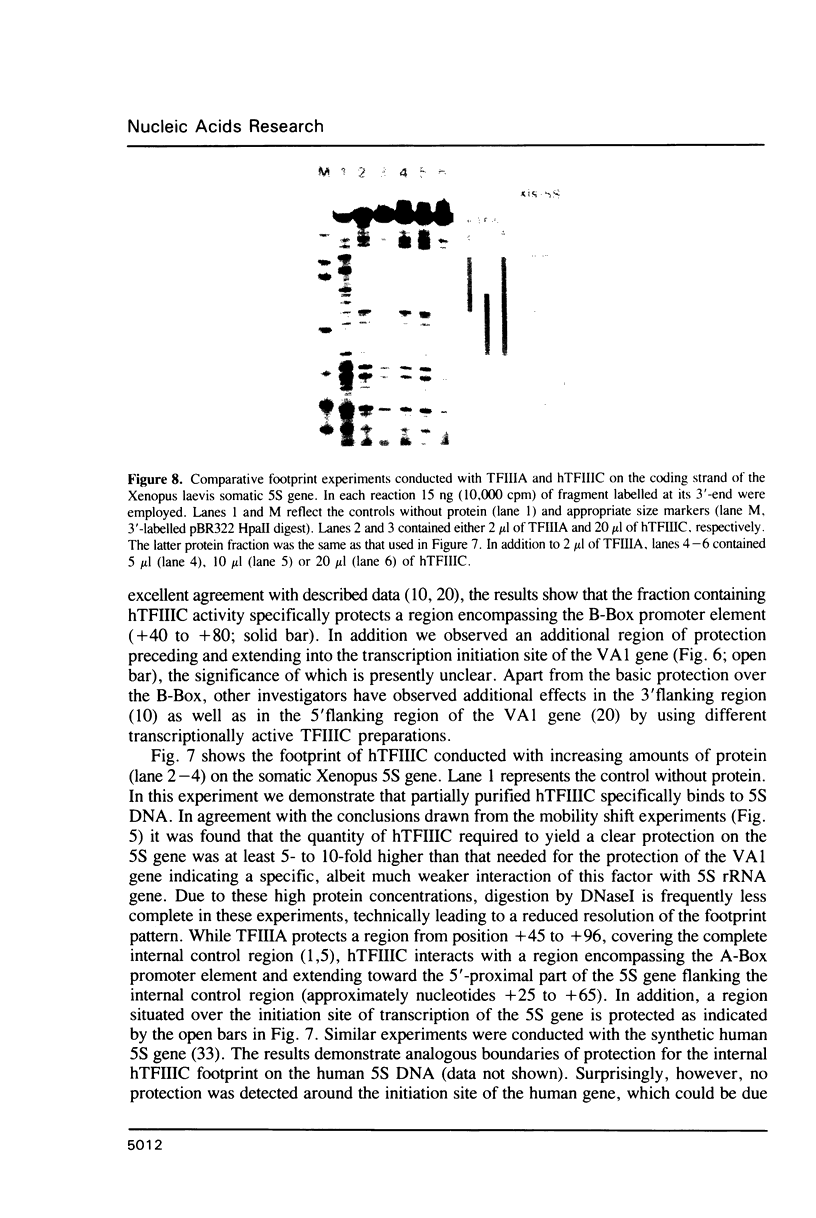




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boulanger P. A., Yoshinaga S. K., Berk A. J. DNA-binding properties and characterization of human transcription factor TFIIIC2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15098–15105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun B. R., Riggs D. L., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Multiple states of protein-DNA interaction in the assembly of transcription complexes on Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5S ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2530–2534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camier S., Gabrielsen O., Baker R., Sentenac A. A split binding site for transcription factor tau on the tRNA3Glu gene. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):491–500. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. F., Gerrard S. P., Cozzarelli N. R. Analysis of RNA polymerase III transcription complexes by gel filtration. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4309–4317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currier T. C., Nester E. W. Isolation of covalently closed circular DNA of high molecular weight from bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1976 Dec;76(2):431–441. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90338-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean N., Berk A. J. Ordering promoter binding of class III transcription factors TFIIIC1 and TFIIIC2. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3017–3025. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean N., Berk A. J. Separation of TFIIIC into two functional components by sequence specific DNA affinity chromatography. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9895–9907. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M. G., Crothers D. M. Equilibrium studies of the cyclic AMP receptor protein-DNA interaction. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jan 25;172(3):241–262. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman S. A., Engelke D. R., Geiduschek E. P. HeLa cell RNA polymerase III transcription factors. Functional characterization of a fraction identified by its activity in a second template rescue assay. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1934–1943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsen O. S., Marzouki N., Ruet A., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Two polypeptide chains in yeast transcription factor tau interact with DNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7505–7511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilfoyle R., Weinmann R. Control region for adenovirus VA RNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3378–3382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn D., Wingender E., Seifart K. H. Transcription complexes for various class III genes differ in parameters of formation and stability towards salt. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 20;193(2):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90221-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. L., Wilson S. L. Identification of a 150-kilodalton polypeptide that copurifies with yeast TFIIIC and binds specifically to tRNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2018–2024. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klekamp M. S., Weil P. A. Partial purification and characterization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae transcription factor TFIIIB. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2819–2827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyhse-Andersen J. Electroblotting of multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Dec;10(3-4):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majowski K., Mentzel H., Pieler T. A split binding site for TFIIIC on the Xenopus 5S gene. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3057–3063. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey G. A., Bogenhagen D. F. Transition mutations within the Xenopus borealis somatic 5S RNA gene can have independent effects on transcription and TFIIIA binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):486–494. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Erdmann V. A. Isolation and characterization of a 7 S RNP particle from mature Xenopus laevis oocytes. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 4;157(2):283–287. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80562-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Hamm J., Roeder R. G. The 5S gene internal control region is composed of three distinct sequence elements, organized as two functional domains with variable spacing. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds W. F., Azer K. Sequence differences upstream of the promoters are involved in the differential expression of the Xenopus somatic and oocyte 5S RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3391–3403. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos T., Zasloff M. Comparative analysis of human chromosomal segments bearing nonallelic dispersed tRNAimet genes. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):699–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90433-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Sklar V. E., Jaehning J. A., Weinmann R., Roeder R. G. Isolation and partial characterization of the multiple forms of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase in the mouse myeloma, MOPC 315. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5889–5897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors are required for the accurate transcription of purified genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11986–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifart K. H., Wang L., Waldschmidt R., Jahn D., Wingender E. Purification of human transcription factor IIIA and its interaction with a chemically synthesized gene encoding human 5 S rRNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1702–1709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastry B. S., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors involved in the transcription of class III genes in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12979–12986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman D. J., Geiduschek E. P. Differential binding of a S. cerevisiae RNA polymerase III transcription factor to two promoter segments of a tRNA gene. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):847–853. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Roeder R. G. Multiple proteins bind to VA RNA genes of adenovirus type 2. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1021–1031. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldschmidt R., Jahn D., Seifart K. H. Purification of transcription factor IIIB from HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13350–13356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. K., Weil P. A. Purification and characterization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae transcription factor IIIA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1092–1099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingender E., Frank R., Blöcker H., Wang L. R., Jahn D., Seifart K. H. Complete synthesis and transcription in vitro of a gene coding for human ribosomal 5S RNA. Gene. 1988 Apr 15;64(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90482-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Transcription fraction TFIIIC can regulate differential Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription in vitro. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1071–1079. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02915.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga S. K., Boulanger P. A., Berk A. J. Resolution of human transcription factor TFIIIC into two functional components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3585–3589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]