Abstract
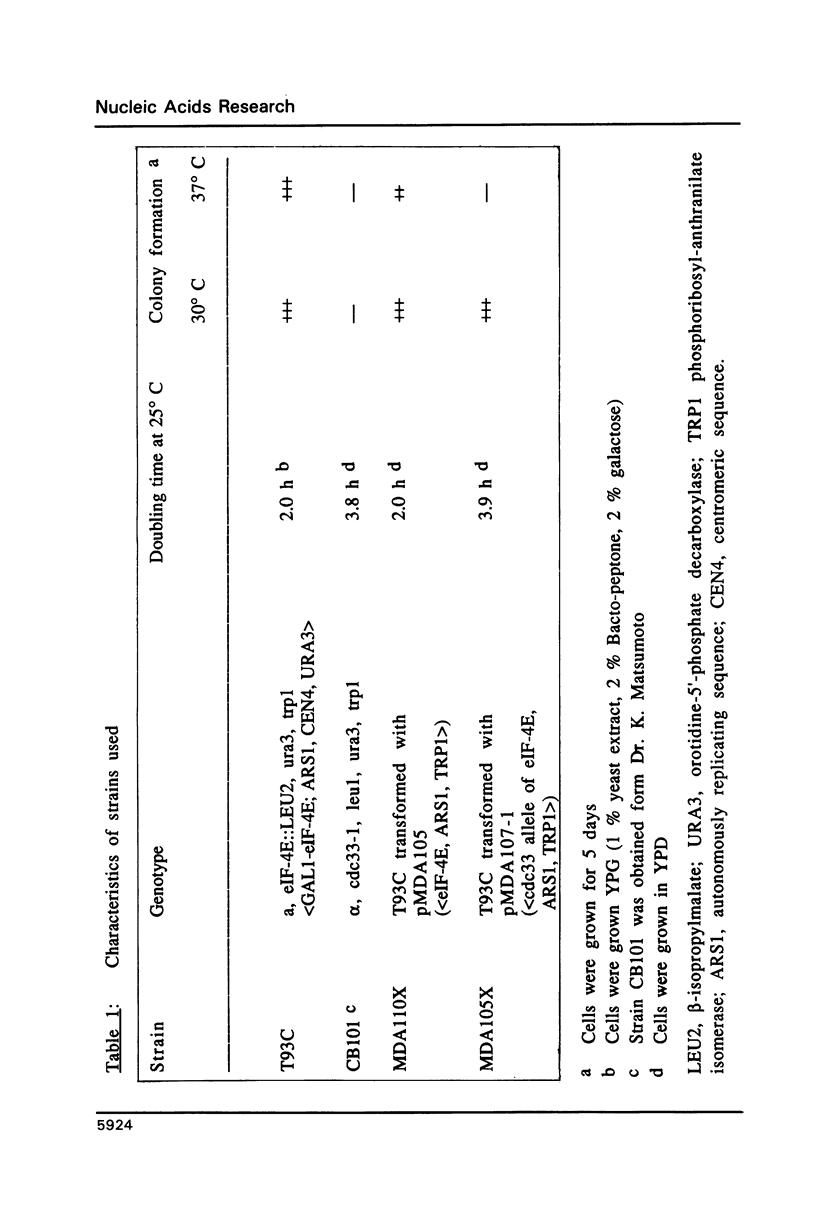
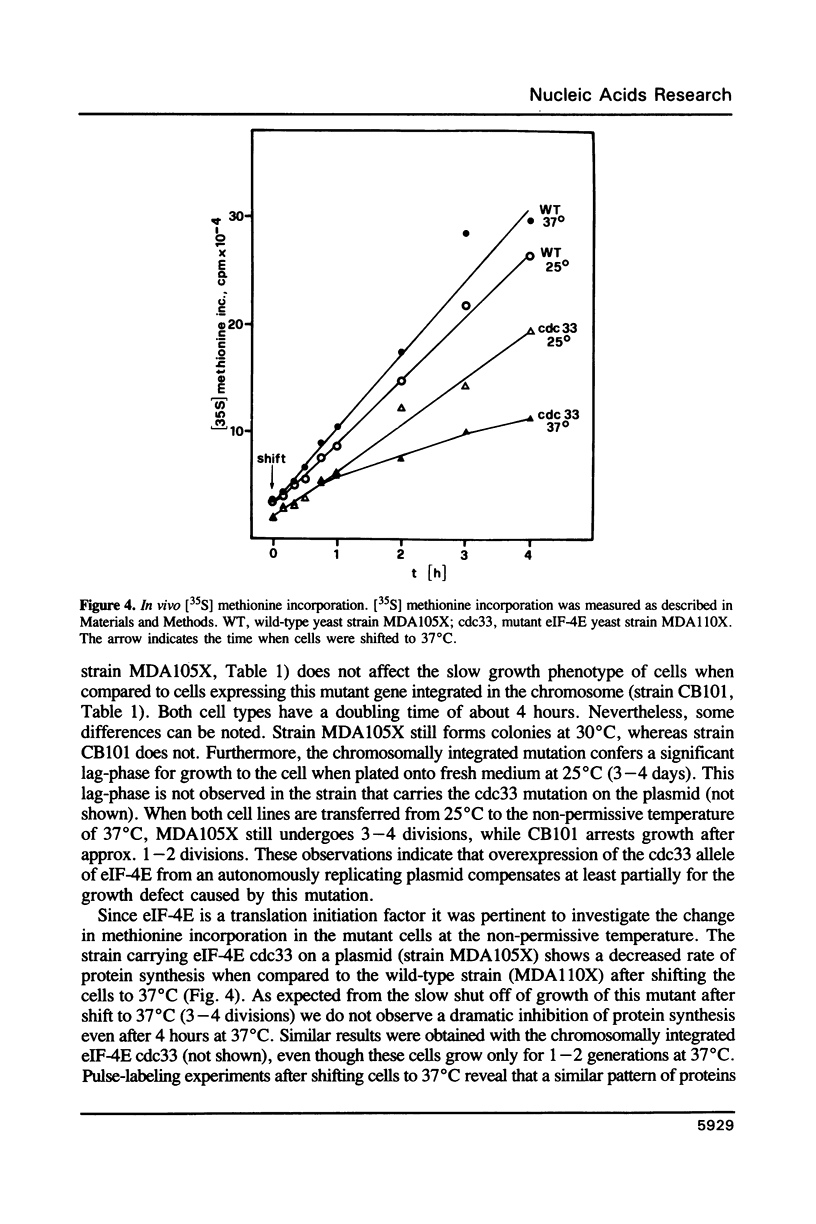
The mutation in the S. cerevisiae cell cycle division mutant cdc33 consists of a single G to A transition in the open reading frame encoding translation initiation factor 4E (eIF-4E). This leads to the substitution of glycine 113 by aspartic acid close to tryptophane 115 in the protein. This mutation reduces cap binding activity of eIF-4E as measured by binding of eIF-4E to m7GDP agarose columns and slows down overall protein synthesis at the non-permissive temperature. Comparison of the cdc33 mutation with other mutations affecting eIF-4E function supports the view that tryptophane residues and their flanking regions are involved in cap binding activity of eIF-4E.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmann M., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Trachsel H. Purification and characterization of protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-4E from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6085–6089. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmann M., Edery I., Trachsel H., Sonenberg N. Site-directed mutagenesis of the tryptophan residues in yeast eukaryotic initiation factor 4E. Effects on cap binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17229–17232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmann M., Handschin C., Trachsel H. mRNA cap-binding protein: cloning of the gene encoding protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-4E from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):998–1003. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. W., Baum P. R., Gesteland R. F. Processing of adenovirus 2-induced proteins. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):241–252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.241-252.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. K. 5'-terminal cap structure in eucaryotic messenger ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):175–205. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.175-205.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner C., Nakayama N., Goebl M., Tanaka K., Toh-e A., Matsumoto K. CDC33 encodes mRNA cap-binding protein eIF-4E of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3556–3559. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery I., Altmann M., Sonenberg N. High-level synthesis in Escherichia coli of functional cap-binding eukaryotic initiation factor eIF-4E and affinity purification using a simplified cap-analog resin. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90184-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipowicz W. Functions of the 5,-terminal m7G cap in eukaryotic mRNA. FEBS Lett. 1978 Dec 1;96(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Uno I., Oshima Y., Ishikawa T. Isolation and characterization of yeast mutants deficient in adenylate cyclase and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2355–2359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Genetic applications of yeast transformation with linear and gapped plasmids. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:228–245. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I. The selection of S. cerevisiae mutants defective in the start event of cell division. Genetics. 1980 Jul;95(3):561–577. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E. Cap recognition and the entry of mRNA into the protein synthesis initiation cycle. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Capping of eucaryotic mRNAs. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. mRNA cap binding proteins: essential factors for initiating translation. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):223–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe M. P., Schatz G. Two nuclear mutations that block mitochondrial protein import in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4819–4823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




