Abstract
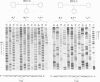
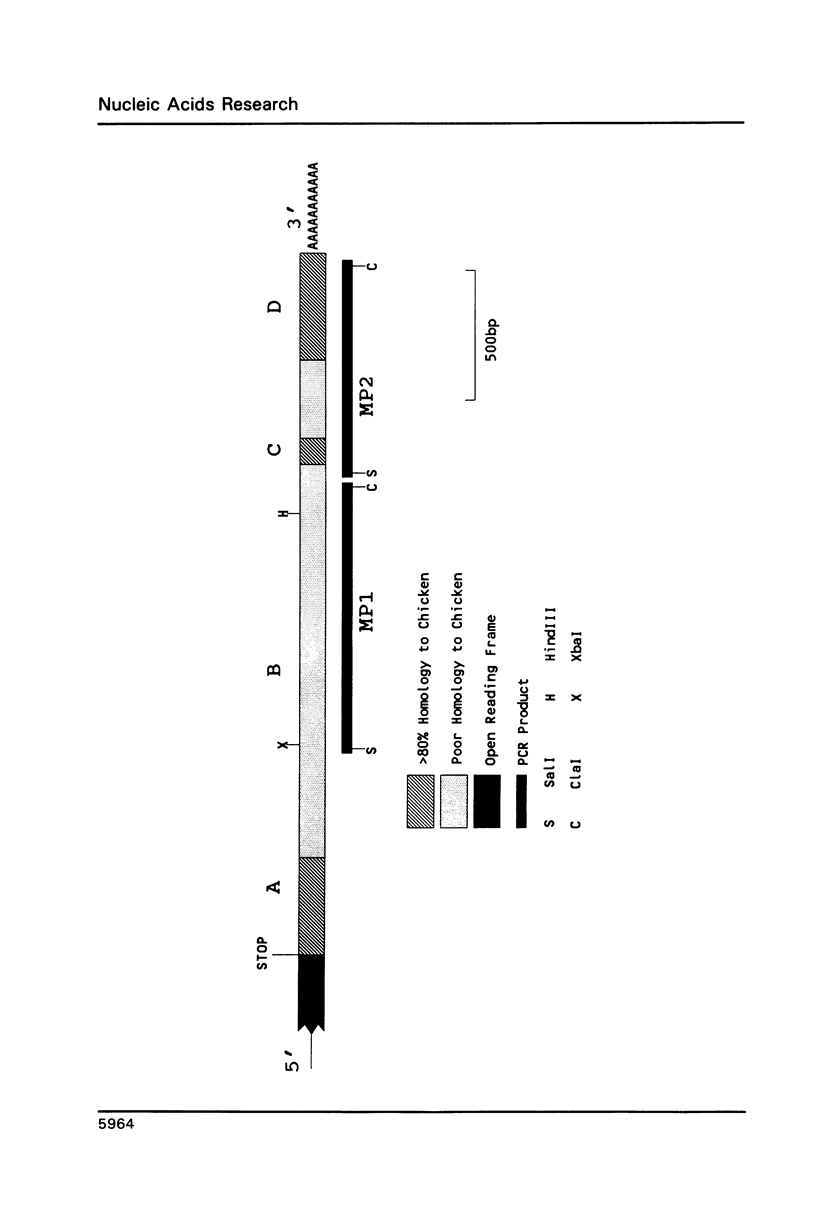
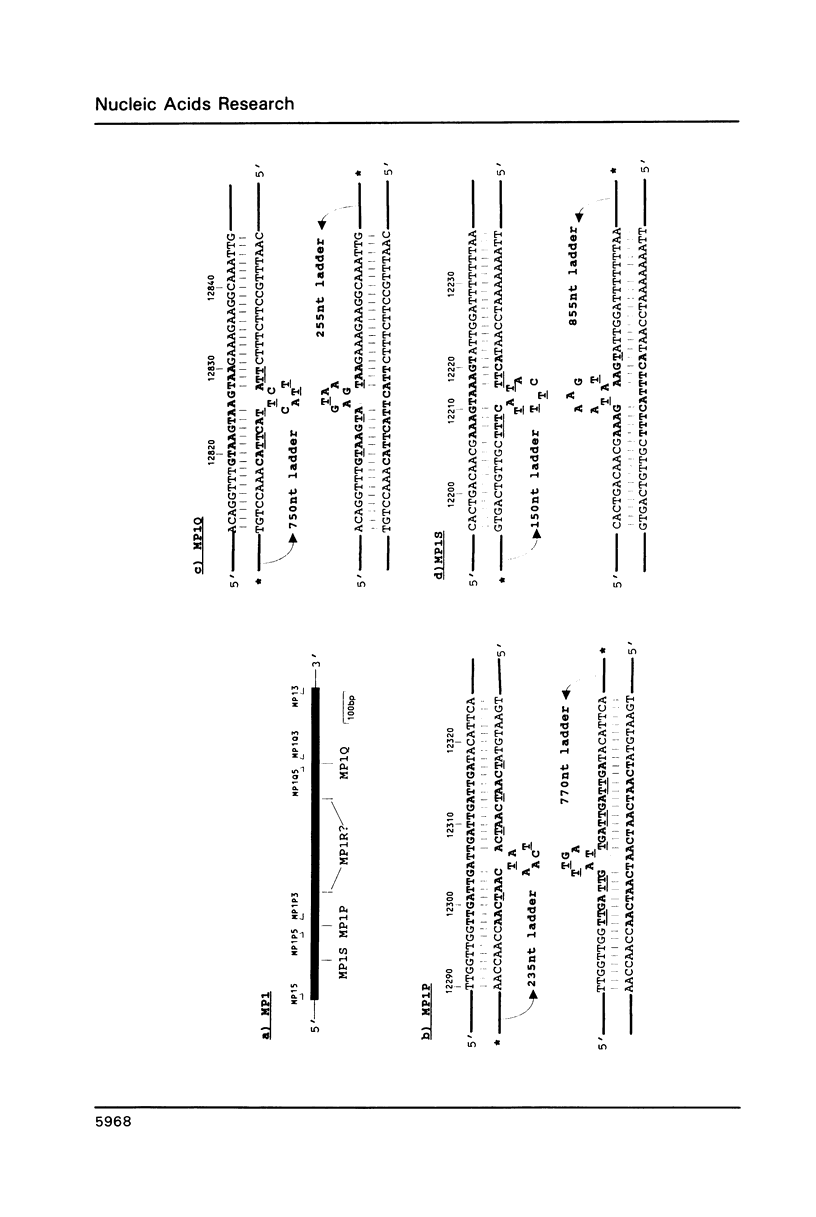
Chemical mismatch detection has been used to identify previously unknown genomic sequence variations that represent a new source of markers for genetic analysis. The approach detects all types of sequence changes, and therefore overcomes the limitation of restriction analysis, which identifies only a small fraction of the available sequence variations. Three new markers identified at the 3' end of the human dystrophin gene result from variable numbers of exact tandem repeats of 4bp (two examples) or 5bp (one example). None of these would have been detected as restriction fragment length polymorphisms by established procedures.
Full text
PDF






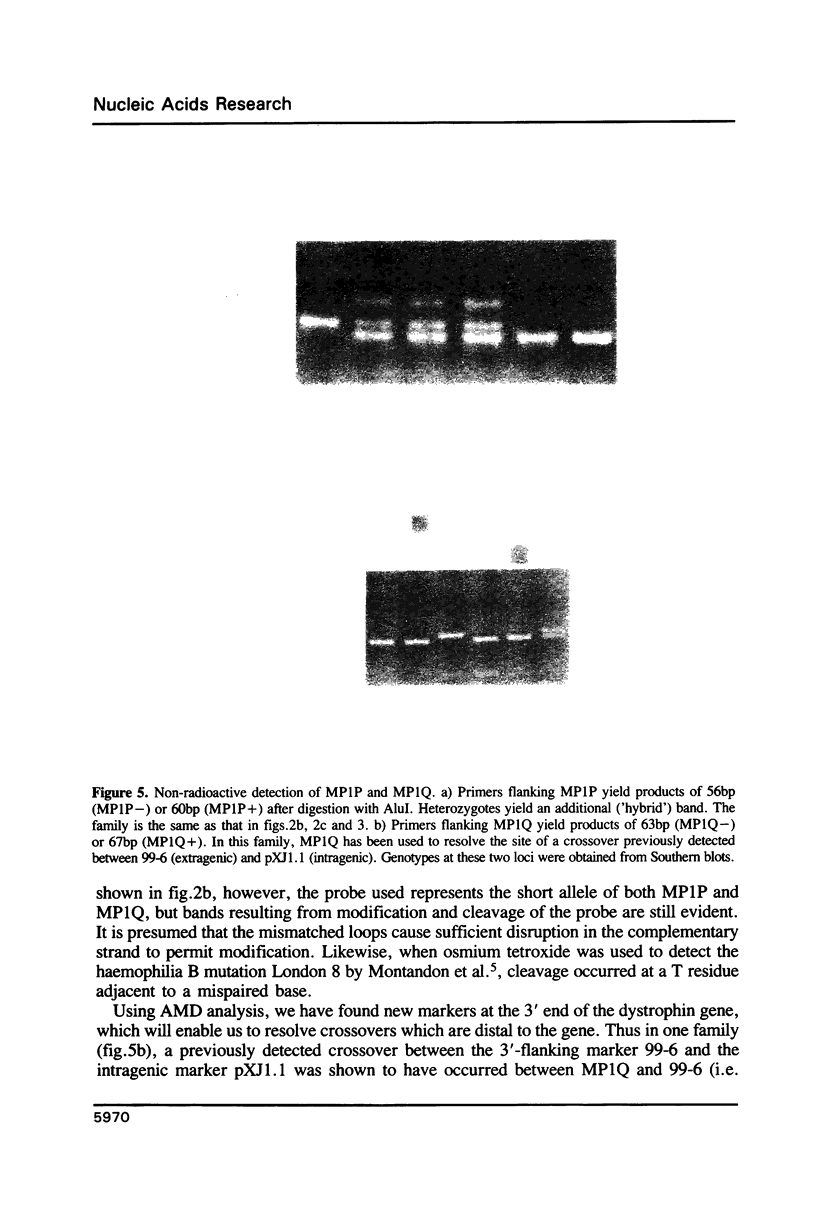

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge J., Kunkel L., Bruns G., Tantravahi U., Lalande M., Brewster T., Moreau E., Wilson M., Bromley W., Roderick T. A strategy to reveal high-frequency RFLPs along the human X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):546–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister M., Monaco A. P., Gillard E. F., van Ommen G. J., Affara N. A., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Kunkel L. M., Lehrach H. A 10-megabase physical map of human Xp21, including the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Genomics. 1988 Apr;2(3):189–202. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. S., Gibbs R. A., Ranier J. E., Nguyen P. N., Caskey C. T. Deletion screening of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus via multiplex DNA amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):11141–11156. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.11141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. G., Walker A., Coyne A., Johnson L., Hart K. A., Hodgson S., Sheridan R., Bobrow M. Prenatal testing for Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy. Lancet. 1988 Feb 6;1(8580):262–266. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90349-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton R. G., Rodrigues N. R., Campbell R. D. Reactivity of cytosine and thymine in single-base-pair mismatches with hydroxylamine and osmium tetroxide and its application to the study of mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4397–4401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Green P., Helms C., Cartinhour S., Weiffenbach B., Stephens K., Keith T. P., Bowden D. W., Smith D. R., Lander E. S. A genetic linkage map of the human genome. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):319–337. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorkins H., Junien C., Mandel J. L., Wrogemann K., Moison J. P., Martinez M., Old J. M., Bundey S., Schwartz M., Carpenter N. Segregation analysis of a marker localised Xp21.2-Xp21.3 in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy families. Hum Genet. 1985;71(2):103–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00283362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbeck K. H., Ritter A. W., Tirschwell D. L., Kunkel L. M., Bertelson C. J., Monaco A. P., Hejtmancik J. F., Boehm C., Ionasescu V., Ionasescu R. Recombination with pERT87 (DXS164) in families with X-linked muscular dystrophy. Lancet. 1986 Jul 12;2(8498):104–104. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91634-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. M., Bentley D. R., Mibashan R. S., Nilsson I. M., Giannelli F. Molecular pathology of haemophilia B. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., Skraastad M. I., Bergen A. A., Wapenaar M. C., Bakker E., Millington-Ward A., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. The X chromosome shows less genetic variation at restriction sites than the autosomes. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;39(4):438–451. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Hoffman E. P., Bertelson C. J., Monaco A. P., Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Complete cloning of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Monaco A. P., Kunkel L. M. The complete sequence of dystrophin predicts a rod-shaped cytoskeletal protein. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogan S. C., Doherty M., Gitschier J. An improved method for prenatal diagnosis of genetic diseases by analysis of amplified DNA sequences. Application to hemophilia A. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 15;317(16):985–990. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710153171603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Hejtmancik J. F., Caskey C. T., Speer A., Monaco A. P., Middlesworth W., Colletti C. A., Bertelson C., Müller U., Bresnan M. Analysis of deletions in DNA from patients with Becker and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):73–77. doi: 10.1038/322073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire C., Heilig R., Mandel J. L. Nucleotide sequence of chicken dystrophin cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11815–11816. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire C., Heilig R., Mandel J. L. The chicken dystrophin cDNA: striking conservation of the C-terminal coding and 3' untranslated regions between man and chicken. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4157–4162. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03311.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon A. J., Green P. M., Giannelli F., Bentley D. R. Direct detection of point mutations by mismatch analysis: application to haemophilia B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3347–3358. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. G., Cole C. G., Hart K. A., Bobrow M., Bentley D. R. Rapid carrier and prenatal diagnosis of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):811–811. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winship P. R. An improved method for directly sequencing PCR amplified material using dimethyl sulphoxide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1266–1266. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]