Abstract
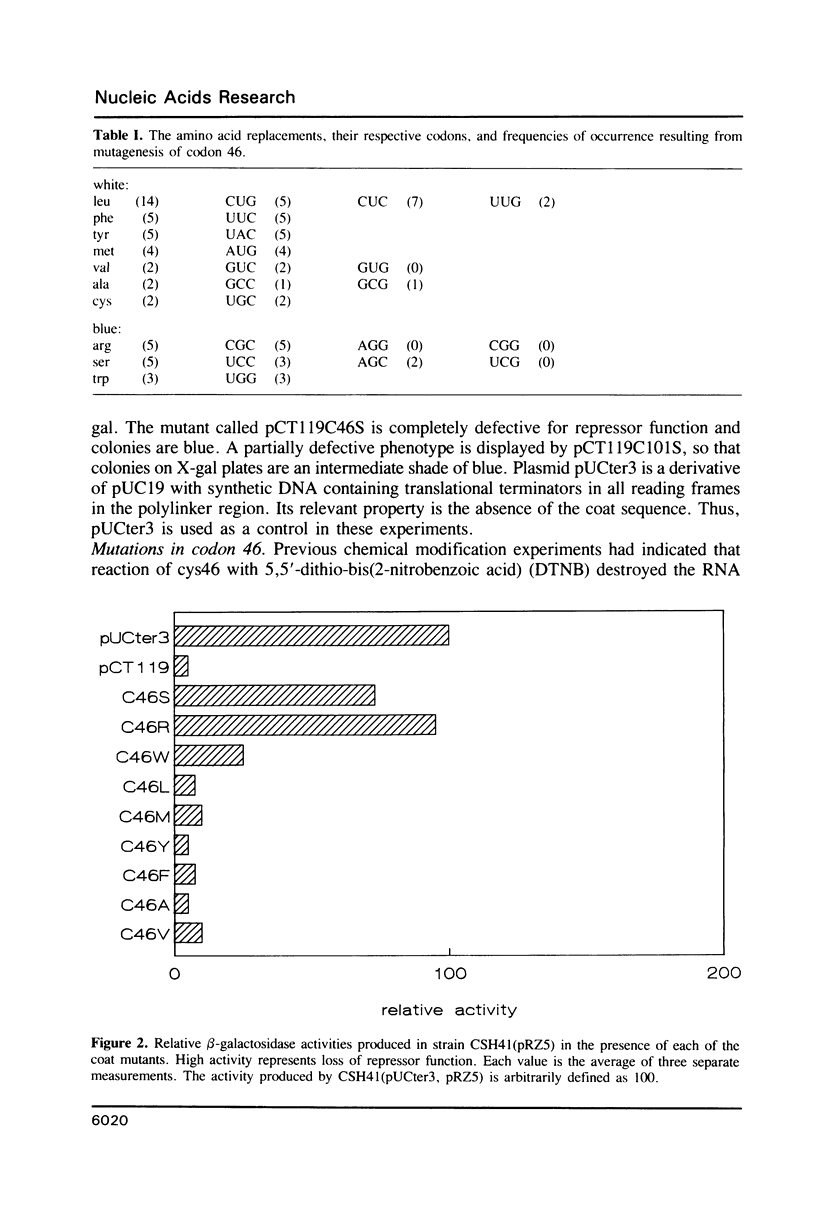
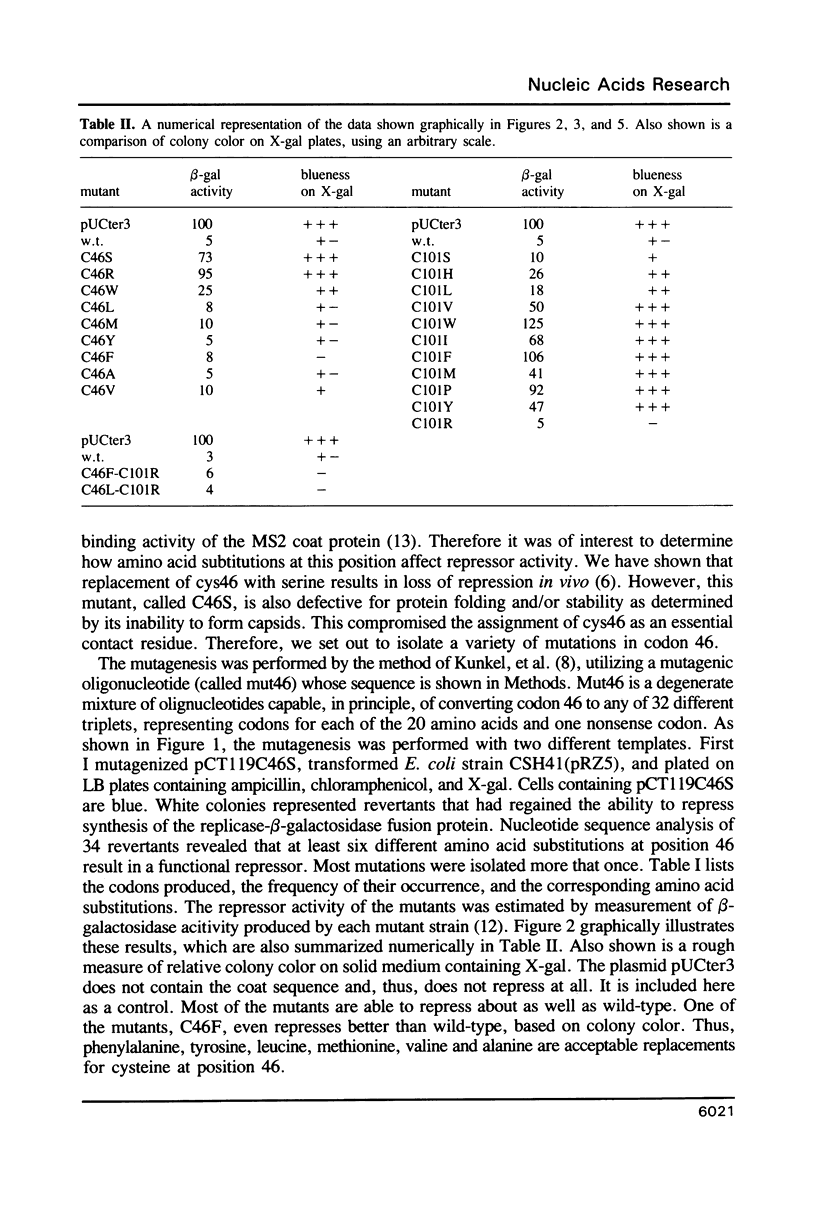
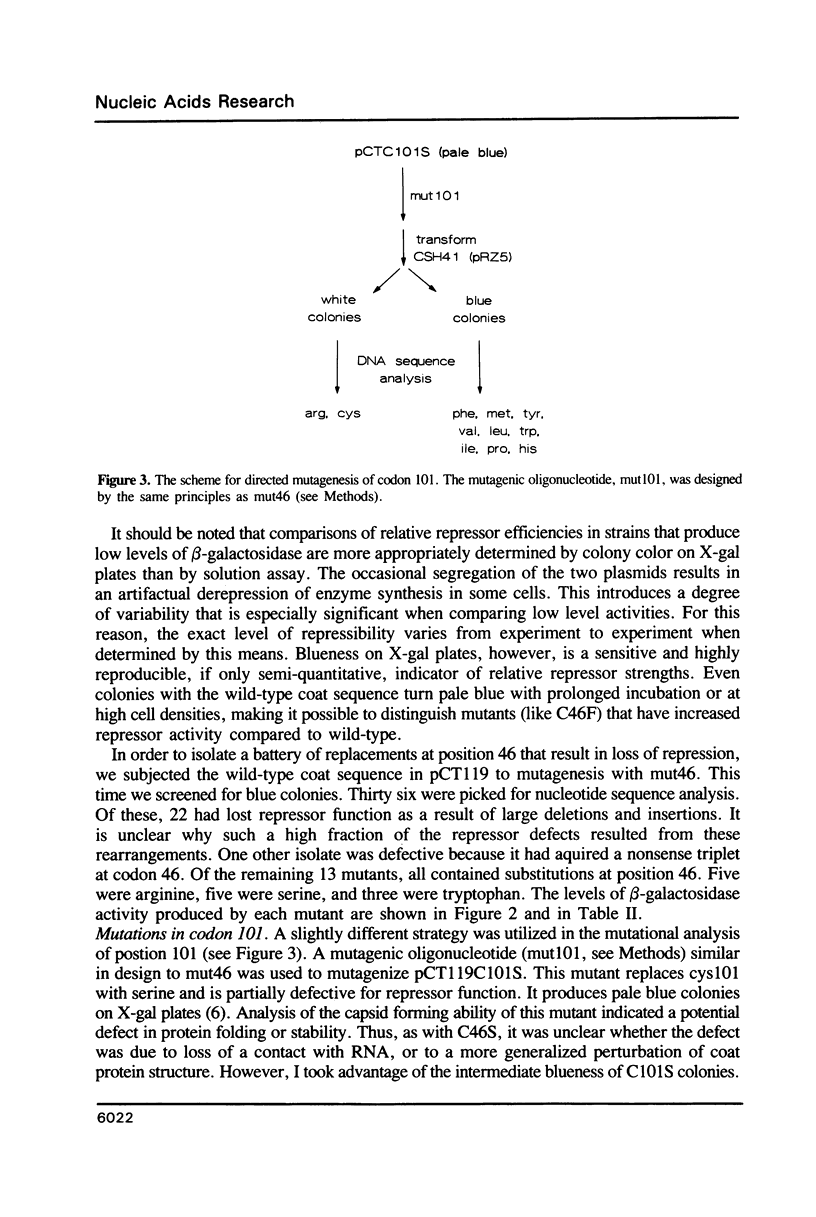
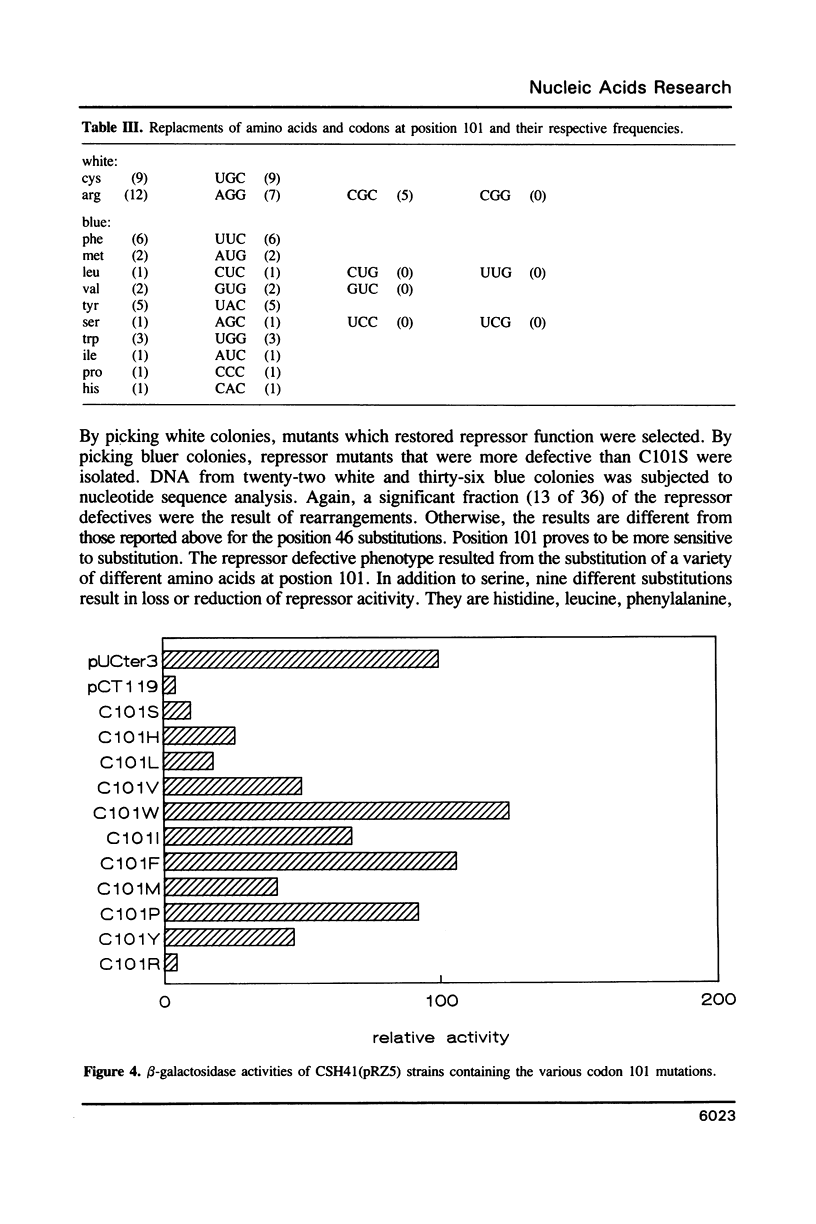
Previous studies implicated cysteine residues in the translational repressor (i.e. RNA binding) activity of the coat protein of bacteriophage MS2. It has been proposed that a protein sulfhydryl forms a transient covalent bond with an essential pyrimidine in the translational operator by a Michael addition reaction. We have utilized codon-directed mutagenesis methods to determine the importance of each of the two coat protein cysteines for repressor function in vivo. The results indicate that cys46 can be replaced by a variety of amino acids without loss of repressor function. Cys101, on the other hand, is more sensitive to substitution. Most position 101 substitutions inactivate the repressor, but one (arginine) results in normal repressor activity. Although the possibility of a transient covalent contact between cys101 and RNA is not categorically ruled out, construction of double mutants demonstrates that cysteines are not absolutely required for translational repression by coat protein.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bass S., Sorrells V., Youderian P. Mutant Trp repressors with new DNA-binding specificities. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):240–245. doi: 10.1126/science.3140377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckett D., Uhlenbeck O. C. Ribonucleoprotein complexes of R17 coat protein and a translational operator analog. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 20;204(4):927–938. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi A., Spahr P. F. Nucleotide sequence at the binding site for coat protein on RNA of bacteriophage R17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):3033–3037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.3033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht M. H., Hehir K. M., Nelson H. C., Sturtevant J. M., Sauer R. T. Increasing and decreasing protein stability: effects of revertant substitutions on the thermal denaturation of phage lambda repressor. J Cell Biochem. 1985;29(3):217–224. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240290306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentze M. W., Rouault T. A., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Oxidation-reduction and the molecular mechanism of a regulatory RNA-protein interaction. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):357–359. doi: 10.1126/science.2711187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakula A. A., Young V. B., Sauer R. T. Bacteriophage lambda cro mutations: effects on activity and intracellular degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8829–8833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Profy A. T., Schimmel P. A sulfhydryl presumed essential is not required for catalysis by an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15474–15479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J., Lowary P., Wu H. N., Stormo G., Uhlenbeck O. C. RNA binding site of R17 coat protein. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 24;26(6):1563–1568. doi: 10.1021/bi00380a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J., Uhlenbeck O. C. Nucleoside and nucleotide inactivation of R17 coat protein: evidence for a transient covalent RNA-protein bond. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 16;24(15):4239–4244. doi: 10.1021/bi00336a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzyk R. M., Koontz S. W., Schimmel P. A covalent adduct between the uracil ring and the active site of an aminoacyl tRNA synthetase. Nature. 1982 Jul 8;298(5870):136–140. doi: 10.1038/298136a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



