Abstract
Automated fluorescence-based DNA sequence analysis offers the possibility to undertake very large scale sequencing projects. Directed strategies, such as the specific-primer-directed sequencing approach ('gene walking'), should prove useful in such projects. Described herein is a study involving the use of this approach in conjunction with automated fluorescence detection on a commercial instrument (ABI 370A DNA sequencer). This includes procedures for the rapid chemical synthesis and purification of labeled primers, the design of primer sequences that are compatible with the commercial analysis software, and automated DNA sequence analysis using such primers. A set of four fluorophore-labeled primers can be reliably synthesized in a twenty-four hour period, and greater than 300 nucleotides of analyzed new sequence obtained using this set in an additional twenty-four hours. Scale-up of these procedures to take advantage of the full capabilities of the sequencer is, at present, too slow and costly to be suitable for routine sequencing, and therefore the use of specific-primers is best suited to the closure of gaps in extended sequence produced using random cloning and sequencing strategies.
Full text
PDF




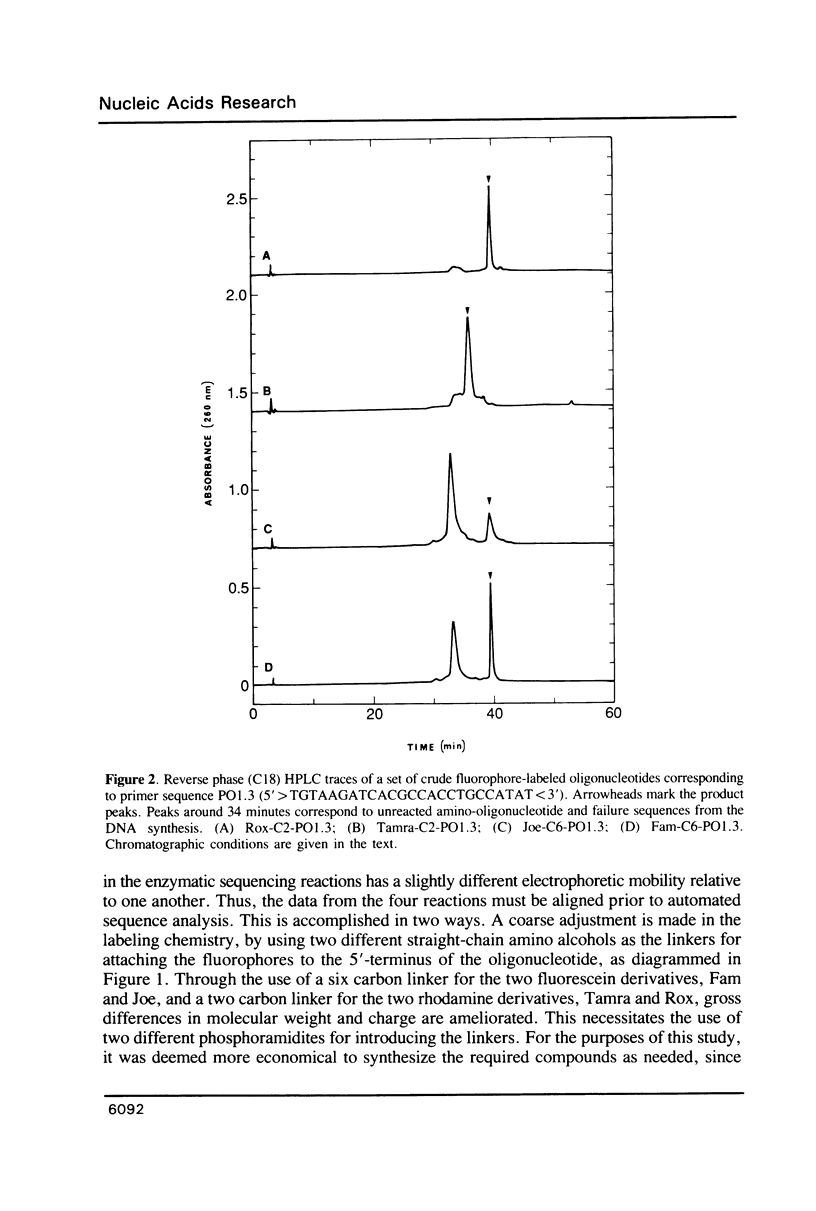
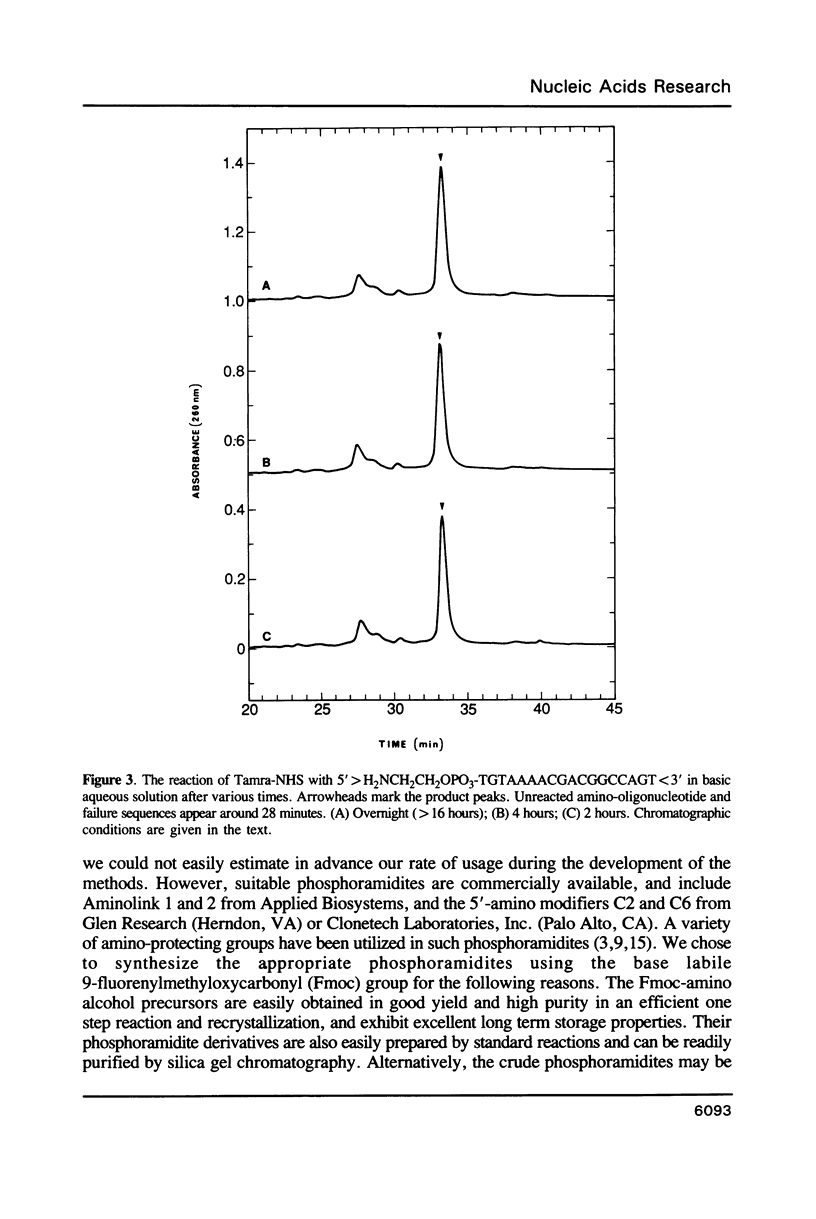


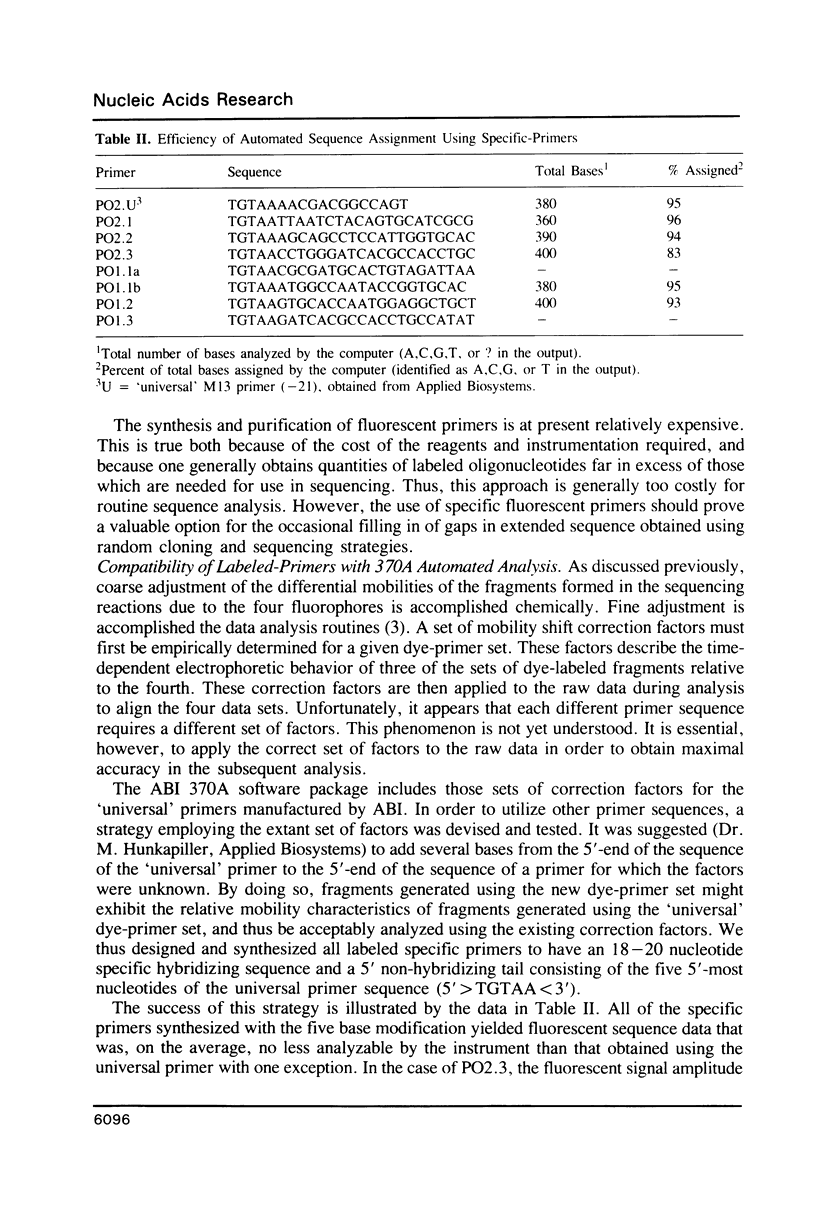

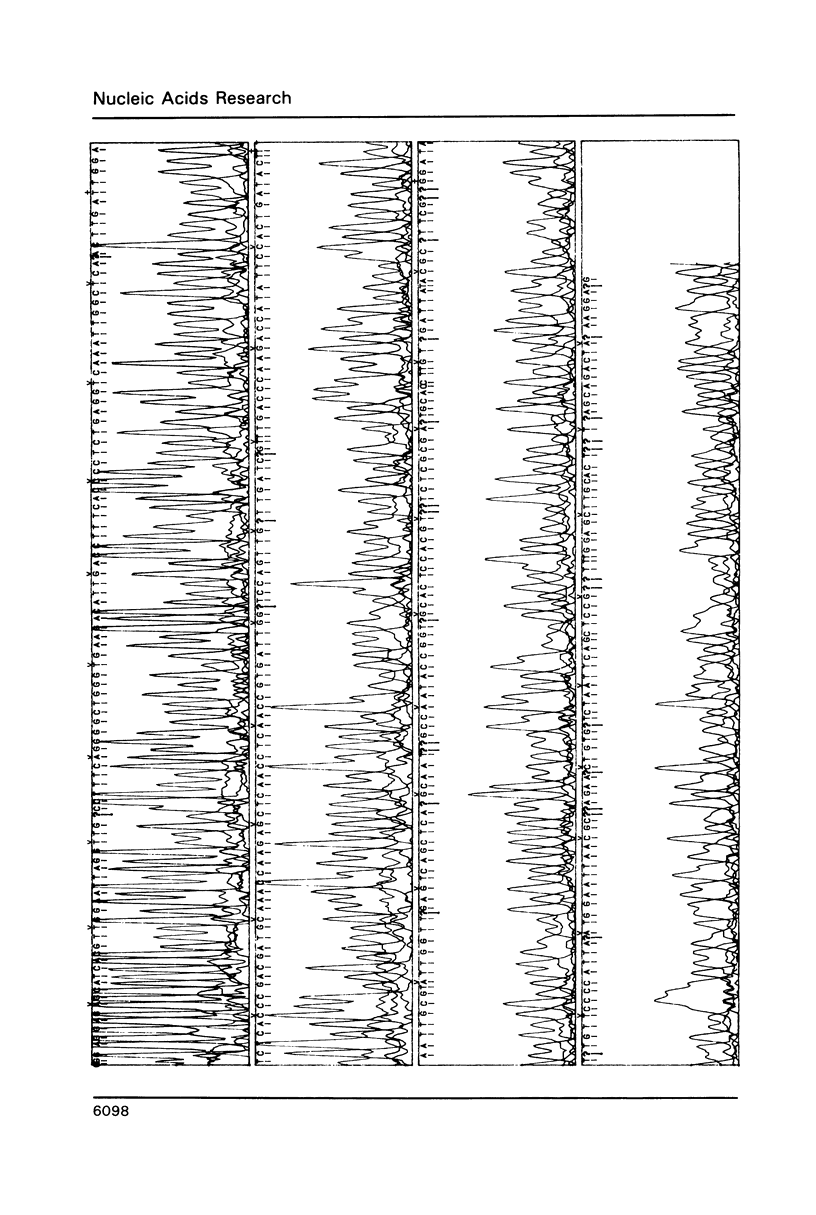




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal S., Christodoulou C., Gait M. J. Efficient methods for attaching non-radioactive labels to the 5' ends of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6227–6245. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansorge W., Sproat B., Stegemann J., Schwager C., Zenke M. Automated DNA sequencing: ultrasensitive detection of fluorescent bands during electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4593–4602. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes W. M. Sequencing DNA with dideoxyribonucleotides as chain terminators: hints and strategies for big projects. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:538–556. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumbaugh J. A., Middendorf L. R., Grone D. L., Ruth J. L. Continuous, on-line DNA sequencing using oligodeoxynucleotide primers with multiple fluorophores. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5610–5614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly B. A. The synthesis of oligonucleotides containing a primary amino group at the 5'-terminus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):3131–3139. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.3131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prober J. M., Trainor G. L., Dam R. J., Hobbs F. W., Robertson C. W., Zagursky R. J., Cocuzza A. J., Jensen M. A., Baumeister K. A system for rapid DNA sequencing with fluorescent chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides. Science. 1987 Oct 16;238(4825):336–341. doi: 10.1126/science.2443975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulhof J. C., Molko D., Teoule R. The final deprotection step in oligonucleotide synthesis is reduced to a mild and rapid ammonia treatment by using labile base-protecting groups. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):397–416. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha N. D., Biernat J., McManus J., Köster H. Polymer support oligonucleotide synthesis XVIII: use of beta-cyanoethyl-N,N-dialkylamino-/N-morpholino phosphoramidite of deoxynucleosides for the synthesis of DNA fragments simplifying deprotection and isolation of the final product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4539–4557. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. M., Sanders J. Z., Kaiser R. J., Hughes P., Dodd C., Connell C. R., Heiner C., Kent S. B., Hood L. E. Fluorescence detection in automated DNA sequence analysis. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):674–679. doi: 10.1038/321674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. C., Kobori J. A., Siu G., Hood L. E. Specific-primer-directed DNA sequencing. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):353–360. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90536-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



