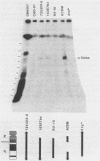
Abstract
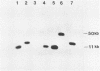
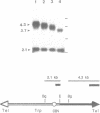
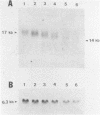
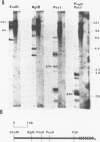
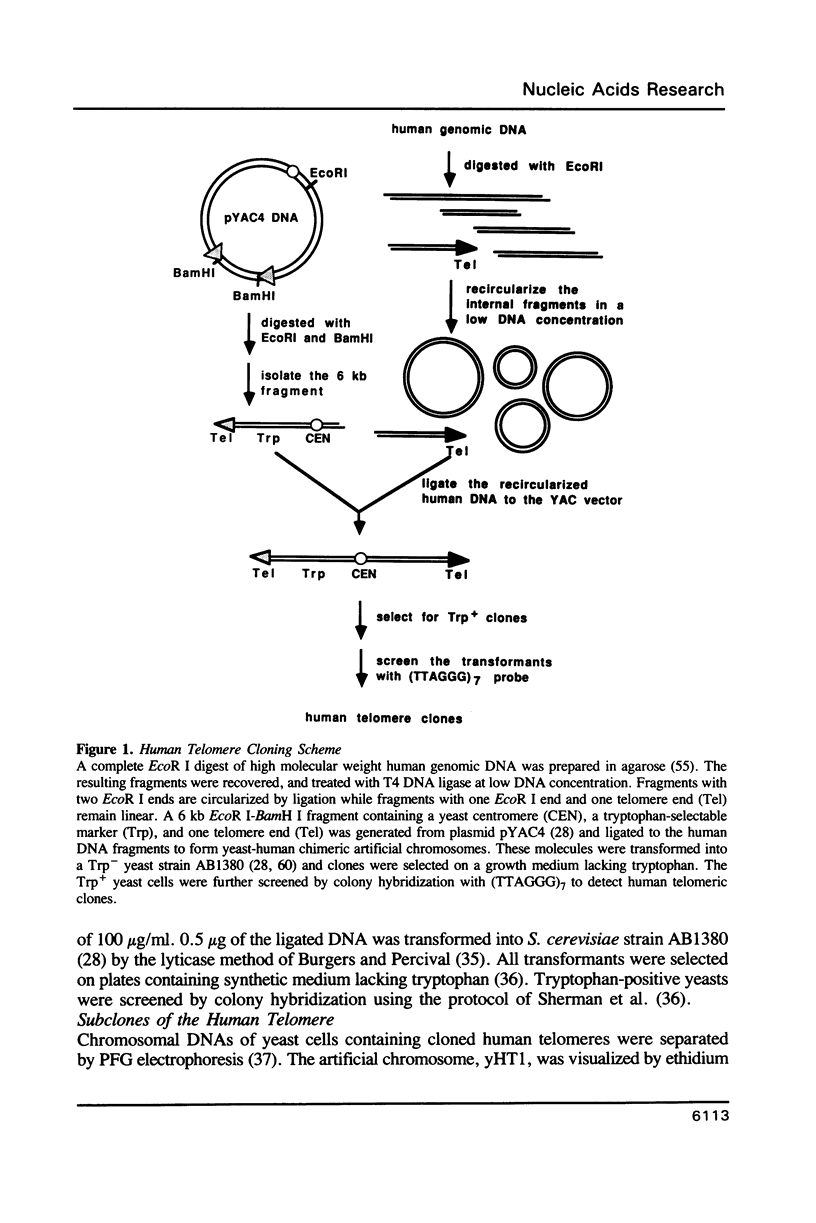
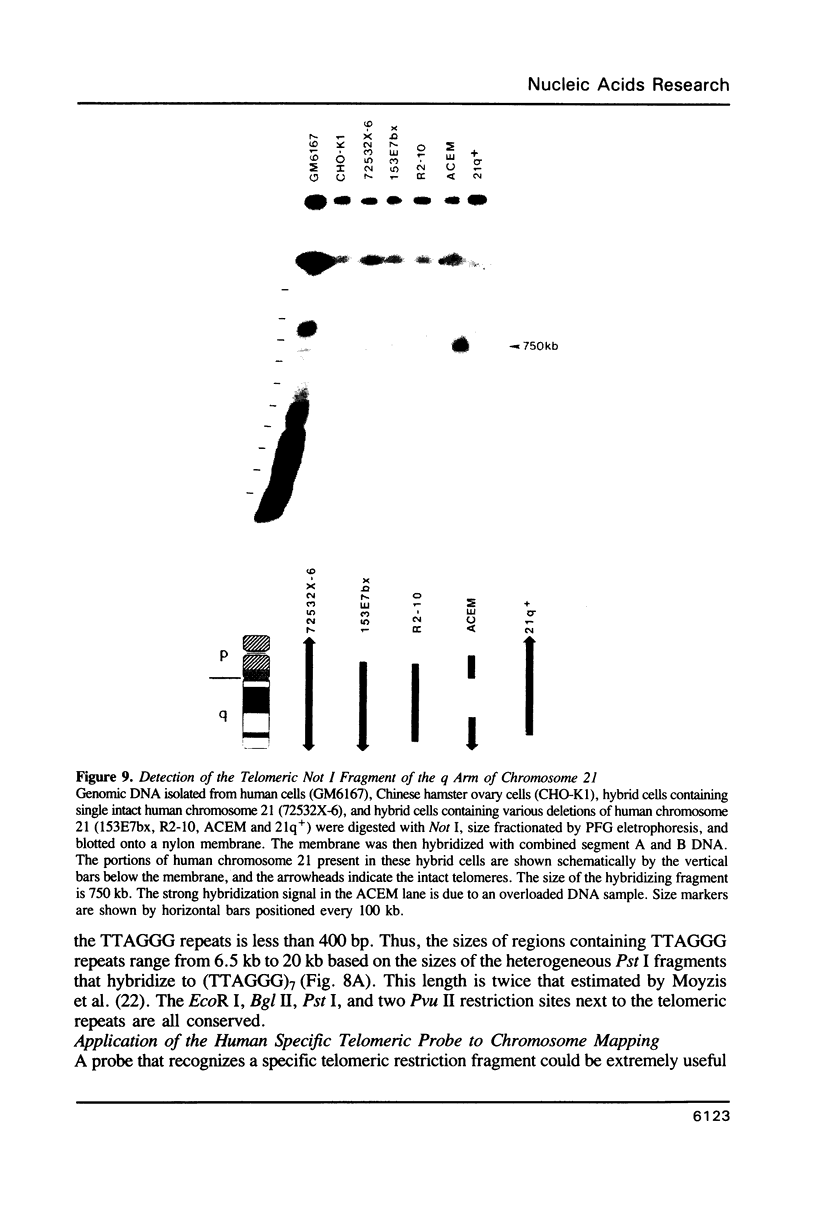
A method is described that allows cloning of human telomeres in S. cerevisiae by joining human telomeric restriction fragments to yeast artificial chromosome halves. The resulting chimeric yeast-human chromosomes propagate as true linear chromosomes, demonstrating that the human telomere structure is capable of functioning in yeast and suggesting that telomere functions are evolutionarily conserved between yeast and human. One cloned human telomere, yHT1, contains 4 kb of human genomic DNA sequence next to the tandemly repeating TTAGGG hexanucleotide. Genomic hybridizations using both cloned DNA and TTAGGG repeats have revealed a common structural organization of human telomeres. This 4 kb of genomic DNA sequence is present in most, but not all, human telomeres, suggesting that the region is not involved in crucial chromosome-specific functions. However, the extent of common features among the human telomeres and possible similarities in organization with yeast telomeres suggest that this region may play a role in general chromosome behavior such as telomere-telomere interactions. Unlike the simple telomeric TTAGGG repeats, our cloned human genomic DNA sequence does not cross-hybridize with rodent DNA. Thus, this clone allows the identifications of the terminal restriction fragments of specific human chromosomes in human-rodent hybrid cells.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allshire R. C., Gosden J. R., Cross S. H., Cranston G., Rout D., Sugawara N., Szostak J. W., Fantes P. A., Hastie N. D. Telomeric repeat from T. thermophila cross hybridizes with human telomeres. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):656–659. doi: 10.1038/332656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley T. Specific end-to-end attachment of chromosomes in Ornithogalum virens. J Cell Sci. 1979 Aug;38:357–367. doi: 10.1242/jcs.38.1.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
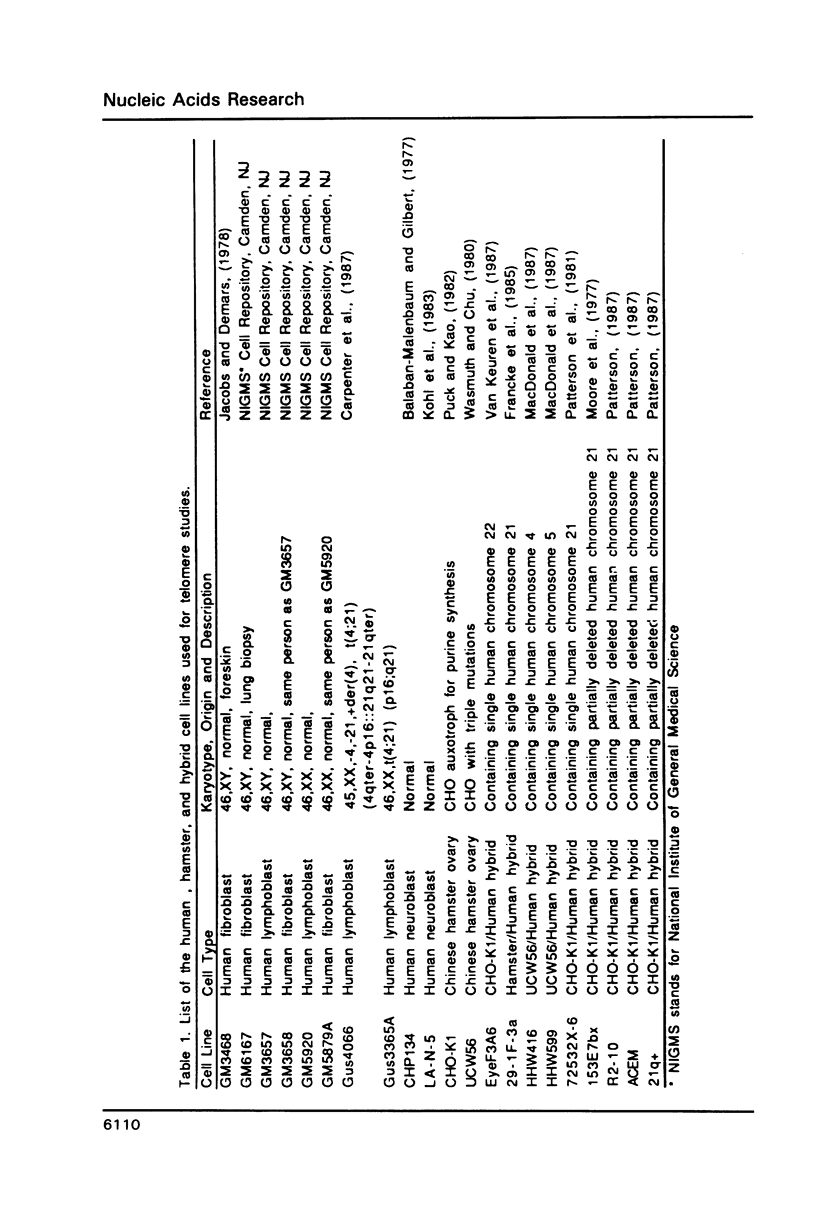
- Balaban-Malenbaum G., Gilbert F. Double minute chromosomes and the homogeneously staining regions in chromosomes of a human neuroblastoma cell line. Science. 1977 Nov 18;198(4318):739–741. doi: 10.1126/science.71759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman A. J. Letter: Simplification of palindromic telomere theory. Nature. 1975 Jan 31;253(5490):379–380. doi: 10.1038/253379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedbrook J. R., Jones J., O'Dell M., Thompson R. D., Flavell R. B. A molecular description of telometic heterochromatin in secale species. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):545–560. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90529-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards A., Michels P. A., Lincke C. R., Borst P. Growth of chromosome ends in multiplying trypanosomes. Nature. 1983 Jun 16;303(5918):592–597. doi: 10.1038/303592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H., Challoner P. B. Identification of a telomeric DNA sequence in Trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90238-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Telomeres: do the ends justify the means? Cell. 1984 May;37(1):7–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90295-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. The molecular structure of centromeres and telomeres. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:163–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boswell R. E., Klobutcher L. A., Prescott D. M. Inverted terminal repeats are added to genes during macronuclear development in Oxytricha nova. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3255–3259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgers P. M., Percival K. J. Transformation of yeast spheroplasts without cell fusion. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jun;163(2):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. T., Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):806–812. doi: 10.1126/science.3033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter N. J., Mayes J. S., Say B., Wilson D. P. Partial deletion 21: case report with biochemical studies and review. J Med Genet. 1987 Nov;24(11):706–709. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.11.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalier-Smith T. Palindromic base sequences and replication of eukaryote chromosome ends. Nature. 1974 Aug 9;250(5466):467–470. doi: 10.1038/250467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. S., Tye B. K. Organization of DNA sequences and replication origins at yeast telomeres. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E. Replicative heterogeneity of mammalian DNA. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Mar;71(1):106–112. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossen P. E., Pathak S., Arrighi F. E. A high resolution study of the DNA replication patterns of chinese hamster chromosomes using sister chromatid differential staining technique. Chromosoma. 1975 Nov 11;52(4):339–347. doi: 10.1007/BF00364018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dancis B. M., Holmquist G. P. Telomere replication and fusion in eukaryotes. J Theor Biol. 1979 May 21;78(2):211–224. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(79)90265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N. V., Brown D. D. The nucleotide sequence of oocyte 5S DNA in Xenopus laevis. I. The AT-rich spacer. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):701–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flickinger R. A. Localization of AT-rich sequences at the nuclear matrix. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1986 Jun;10(6):415–420. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(86)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Ochs H. D., de Martinville B., Giacalone J., Lindgren V., Distèche C., Pagon R. A., Hofker M. H., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Minor Xp21 chromosome deletion in a male associated with expression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, chronic granulomatous disease, retinitis pigmentosa, and McLeod syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Mar;37(2):250–267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam T. C., Tanzi R. E., Haines J. L., Bonner T. I., Faryniarz A. G., Hobbs W. J., MacDonald M. E., Cheng S. V., Folstein S. E., Conneally P. M. Localization of the Huntington's disease gene to a small segment of chromosome 4 flanked by D4S10 and the telomere. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):565–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber J. E., Thorburn P. C., Rogers D. Meiotic and mitotic behavior of dicentric chromosomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1984 Feb;106(2):185–205. doi: 10.1093/genetics/106.2.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P., Lalande M., Stroh H., Bruns G., Flint A., Latt S. A. Construction of a chromosome 16-enriched phage library and characterization of several DNA segments from 16p. Hum Genet. 1987 Oct;77(2):95–103. doi: 10.1007/BF00272372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs L., Bean C. L., Marx J. A. Optimal phenotypic expression times for HPRT mutants induced in foreskin-, skin-, and lung-derived human diploid fibroblasts. Environ Mutagen. 1983;5(5):717–731. doi: 10.1002/em.2860050510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs L., Demars R. Quantification of chemical mutagenesis in diploid human fibroblasts: induction of azaguanine-resistant mutants by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. Mutat Res. 1978 Feb;53(1):29–53. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(78)90377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. D., Flavell R. B. Chromosomal structure and arrangement of repeated DNA sequences in the telomeric heterochromatin of Secale cereale and its relatives. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):1209–1213. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Kanda N., Schreck R. R., Bruns G., Latt S. A., Gilbert F., Alt F. W. Transposition and amplification of oncogene-related sequences in human neuroblastomas. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D. D., Spangler E. A., Blackburn E. H. Dynamics of telomere length variation in Tetrahymena thermophila. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):477–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90501-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Anderson M. A., Gilliam T. C., Tranejaerg L., Carpenter N. J., Magenis E., Hayden M. R., Healey S. T., Bonner T. I., Gusella J. F. A somatic cell hybrid panel for localizing DNA segments near the Huntington's disease gene. Genomics. 1987 Sep;1(1):29–34. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90101-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarroll R. M., Fangman W. L. Time of replication of yeast centromeres and telomeres. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):505–513. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90072-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClintock B. The Fusion of Broken Ends of Chromosomes Following Nuclear Fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1942 Nov;28(11):458–463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.28.11.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClintock B. The Stability of Broken Ends of Chromosomes in Zea Mays. Genetics. 1941 Mar;26(2):234–282. doi: 10.1093/genetics/26.2.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Mirault M. E., Laemmli U. K. Organization of the higher-order chromatin loop: specific DNA attachment sites on nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore E. E., Jones C., Kao F. T., Oates D. C. Synteny between glycinamide ribonucleotide synthetase and superoxide dismutase (soluble). Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Jul;29(4):389–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Birnstiel M. L. The putative promoter of a Xenopus laevis ribosomal gene is reduplicated. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 24;6(12):3733–3743. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.12.3733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyzis R. K., Buckingham J. M., Cram L. S., Dani M., Deaven L. L., Jones M. D., Meyne J., Ratliff R. L., Wu J. R. A highly conserved repetitive DNA sequence, (TTAGGG)n, present at the telomeres of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6622–6626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Claus T. E., Szostak J. W. Characterization of two telomeric DNA processing reactions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4642–4650. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Schultes N. P., Szostak J. W. Chromosome length controls mitotic chromosome segregation in yeast. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):529–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90284-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Szostak J. W. Construction of artificial chromosomes in yeast. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):189–193. doi: 10.1038/305189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson D., Graw S., Jones C. Demonstration, by somatic cell genetics, of coordinate regulation of genes for two enzymes of purine synthesis assigned to human chromosome 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):405–409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelan M. C., Morton C. C., Stevenson R. E., Tanzi R. E., Stewart G. D., Watkins P. C., Gusella J. F., Amos J. A. Molecular and cytogenetic characterization of a de novo t(5p;21q) in a patient previously diagnosed as monosomy 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Oct;43(4):511–519. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluta A. F., Dani G. M., Spear B. B., Zakian V. A. Elaboration of telomeres in yeast: recognition and modification of termini from Oxytricha macronuclear DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1475–1479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzi M., Pace T., Dore E., Frontali C. Identification of a telomeric DNA sequence in Plasmodium berghei. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2991–2995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck T. T., Kao F. T. Somatic cell genetics and its application to medicine. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:225–271. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.001301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards E. J., Ausubel F. M. Isolation of a higher eukaryotic telomere from Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90494-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M., Prescott D. M. DNA intermediates and telomere addition during genome reorganization in Euplotes crassus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):411–417. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. Isolation of a telomeric DNA sequence from Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):1041–1046. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Saffran W., Welsh J., Haas R., Goldenberg M., Cantor C. R. New techniques for purifying large DNAs and studying their properties and packaging. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):189–195. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shampay J., Szostak J. W., Blackburn E. H. DNA sequences of telomeres maintained in yeast. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):154–157. doi: 10.1038/310154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Purification, specific fragmentation, and separation of large DNA molecules. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:449–467. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. D., Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F. RFLPS at the D21S19 locus of human chromosome 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):7168–7168. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.7168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Blackburn E. H. Cloning yeast telomeres on linear plasmid vectors. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Haines J. L., Watkins P. C., Stewart G. D., Wallace M. R., Hallewell R., Wong C., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Gusella J. F. Genetic linkage map of human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Venegas A., Weinberg F., Bishop R., Rutter W. J. Structure of yeast phenylalanine-tRNA genes: an intervening DNA segment within the region coding for the tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):190–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Keuren M. L., Hart I. M., Kao F. T., Neve R. L., Bruns G. A., Kurnit D. M., Patterson D. A somatic cell hybrid with a single human chromosome 22 corrects the defect in the CHO mutant (Ade-I) lacking adenylosuccinase activity. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;44(2-3):142–147. doi: 10.1159/000132358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Liu A. Y., Borst P. Structure of the growing telomeres of Trypanosomes. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90239-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley R. M., Szostak J. W., Petes T. D. Is there left-handed DNA at the ends of yeast chromosomes? Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):84–86. doi: 10.1038/302084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley R. W., Chan C. S., Tye B. K., Petes T. D. Unusual DNA sequences associated with the ends of yeast chromosomes. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):157–160. doi: 10.1038/310157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasmuth J. J., Chu L. Y. Linkage in cultured Chinese hamster cells of two genes, emtB and leuS, involved in protein synthesis and isolation of cell lines with mutations in three linked genes. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):697–702. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasmuth J. J., Hewitt J., Smith B., Allard D., Haines J. L., Skarecky D., Partlow E., Hayden M. R. A highly polymorphic locus very tightly linked to the Huntington's disease gene. Nature. 1988 Apr 21;332(6166):734–736. doi: 10.1038/332734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C., Yao C. H. Repeated hexanucleotide C-C-C-C-A-A is present near free ends of macronuclear DNA of Tetrahymena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7436–7439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young B. S., Pession A., Traverse K. L., French C., Pardue M. L. Telomere regions in Drosophila share complex DNA sequences with pericentric heterochromatin. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A., Blanton H. M. Distribution of telomere-associated sequences on natural chromosomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2257–2260. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]