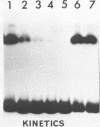
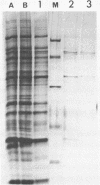
Abstract
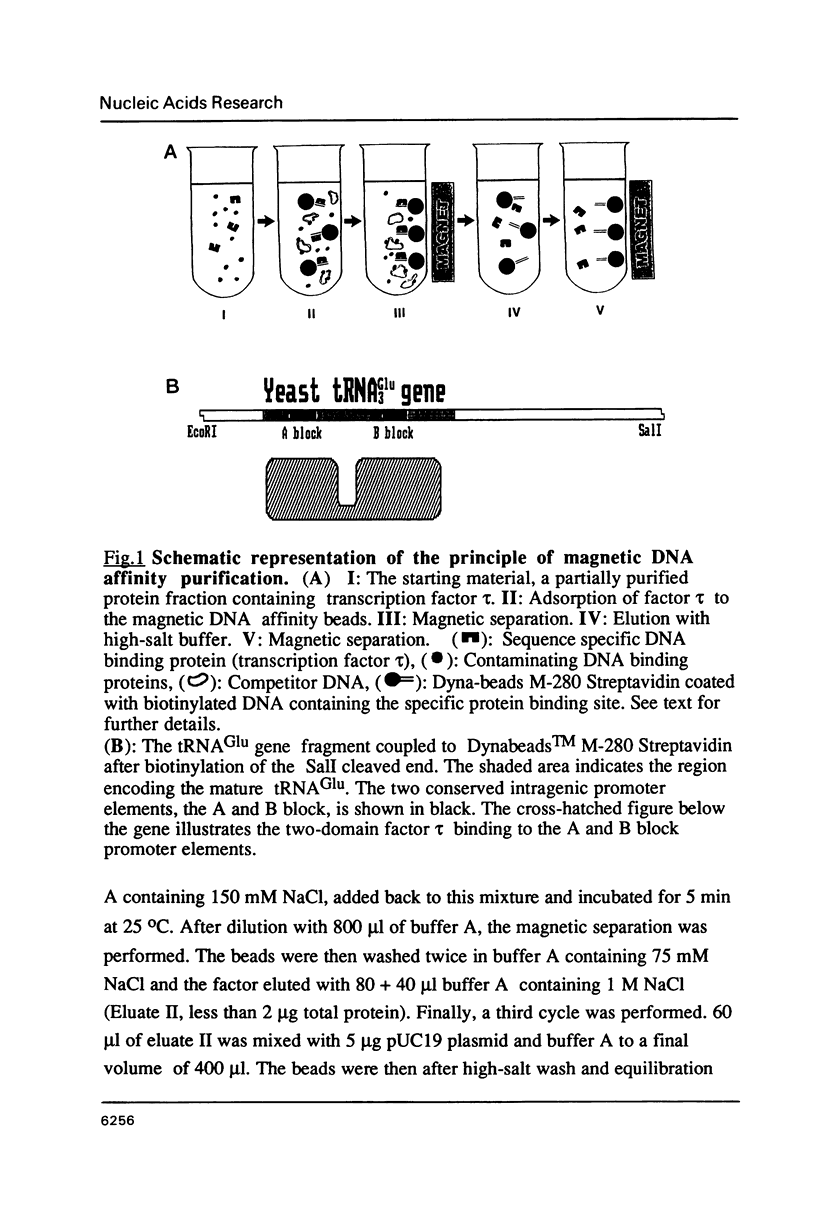
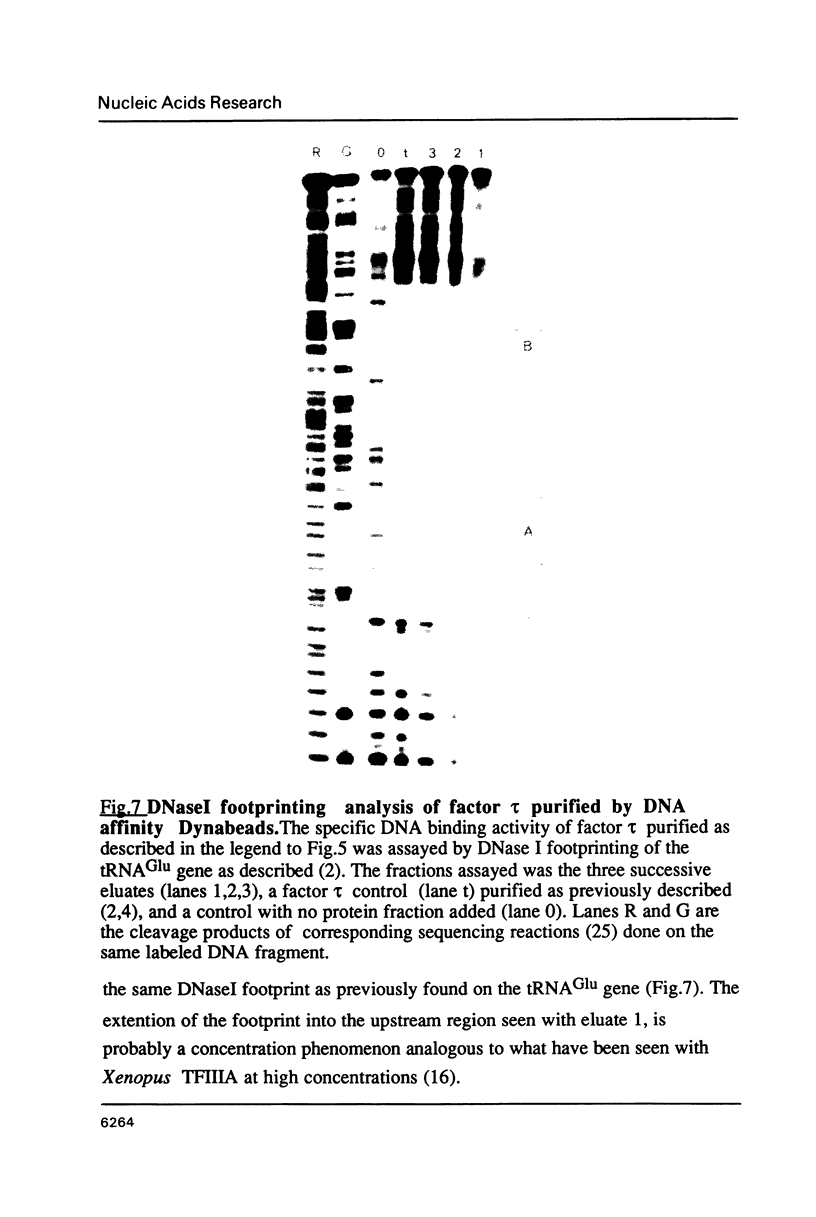
We present a new method for rapid purification to near homogeneity of sequence specific DNA binding proteins based on magnetic separation. The method is described for the purification of the yeast transcription factor tau. DNA affinity Dynabeads (monodisperse superparamagnetic particles) specifically bind the protein in the presence of competitor DNA. By magnetic separation, wash and elution, highly enriched transcription factor preparations are obtained within minutes. In less than an hour with three cycles of adsorption, nearly homogeneous factor tau was obtained. The factor preparation contained mainly two polypeptides of 100 and 140 kDa and was fully active in transcription and DNA binding assays. This procedure should work for any high-affinity sequence-specific DNA binding protein with only minor modifications.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker R. E., Camier S., Sentenac A., Hall B. D. Gene size differentially affects the binding of yeast transcription factor tau to two intragenic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8768–8772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. E., Gabrielsen O., Hall B. D. Effects of tRNATyr point mutations on the binding of yeast RNA polymerase III transcription factor C. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5275–5282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camier S., Gabrielsen O., Baker R., Sentenac A. A split binding site for transcription factor tau on the tRNA3Glu gene. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):491–500. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsen O. S., Andersen K. E., Oyen T. B. Yeast RNA polymerase III. Chromatographic, catalytic and DNA-binding properties are highly dependent on the type of anion. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 1;141(2):345–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsen O. S., Marzouki N., Ruet A., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Two polypeptide chains in yeast transcription factor tau interact with DNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7505–7511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsen O. S., Oyen T. B. The requirement for the A block promoter element in tRNA gene transcription in vitro depends on the ionic environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5699–5713. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lea T., Vartdal F., Nustad K., Funderud S., Berge A., Ellingsen T., Schmid R., Stenstad P., Ugelstad J. Monosized, magnetic polymer particles: their use in separation of cells and subcellular components, and in the study of lymphocyte function in vitro. J Mol Recognit. 1988 Feb;1(1):9–18. doi: 10.1002/jmr.300010104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzouki N., Camier S., Ruet A., Moenne A., Sentenac A. Selective proteolysis defines two DNA binding domains in yeast transcription factor tau. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):176–178. doi: 10.1038/323176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Bilezikjian L. M. Binding of a nuclear protein to the cyclic-AMP response element of the somatostatin gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):175–178. doi: 10.1038/328175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruet A., Camier S., Smagowicz W., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Isolation of a class C transcription factor which forms a stable complex with tRNA genes. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):343–350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J. Assembly of a yeast 5 S RNA gene transcription complex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11578–11584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman D. J., Caspers P., Geiduschek E. P. Effects of temperature and single-stranded DNA on the interaction of an RNA polymerase III transcription factor with a tRNA gene. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman D. J., Geiduschek E. P. Differential binding of a S. cerevisiae RNA polymerase III transcription factor to two promoter segments of a tRNA gene. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):847–853. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. J., Segall J. Characterization of factors and DNA sequences required for accurate transcription of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5 S RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4531–4540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldschmidt R., Jahn D., Seifart K. H. Purification of transcription factor IIIB from HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13350–13356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilchek M., Bayer E. A. The avidin-biotin complex in bioanalytical applications. Anal Biochem. 1988 May 15;171(1):1–32. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windsor W. T., Lee T. C., Daly T. J., Wu C. W. Xenopus transcription factor IIIA binds to the flanking regions of the 5 S RNA gene intragenic control region in a unique and highly ordered state. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10272–10277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]