Abstract
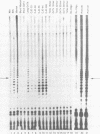
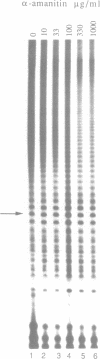
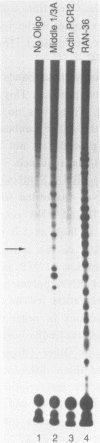
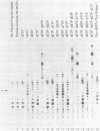
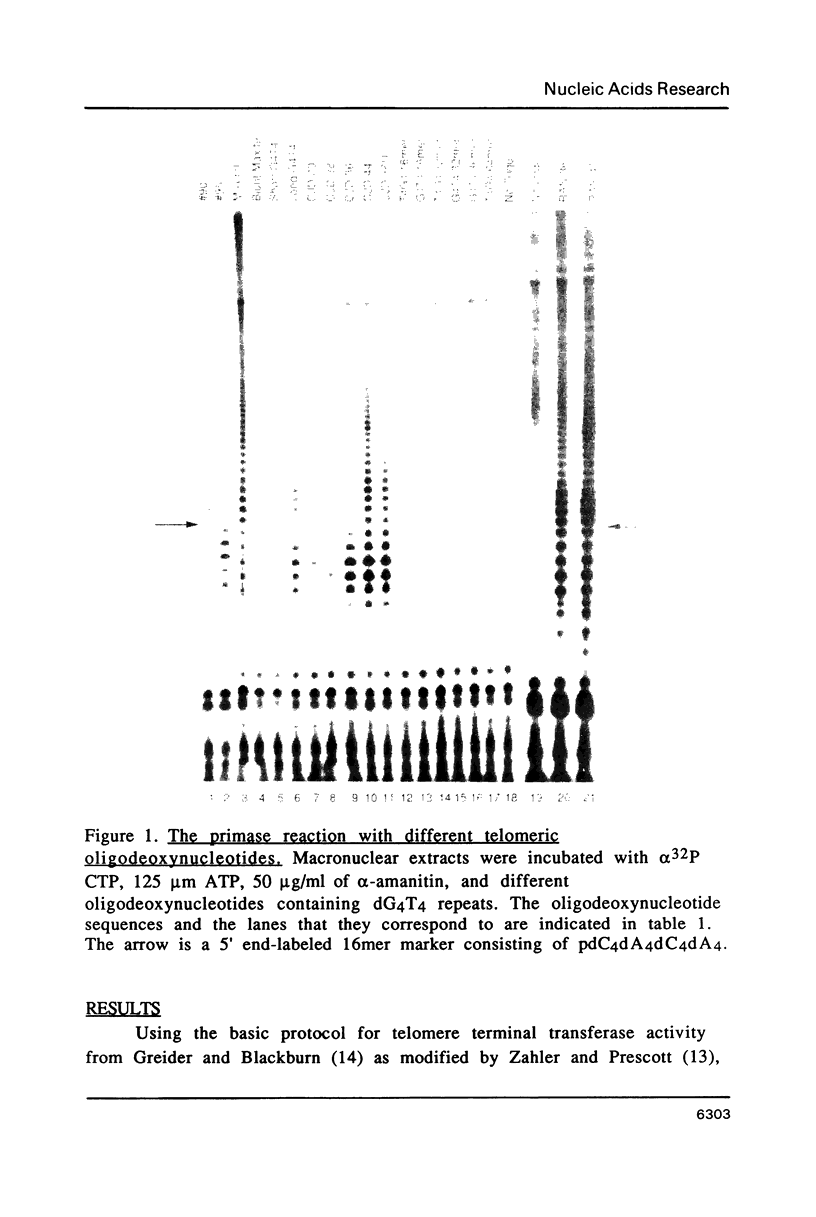
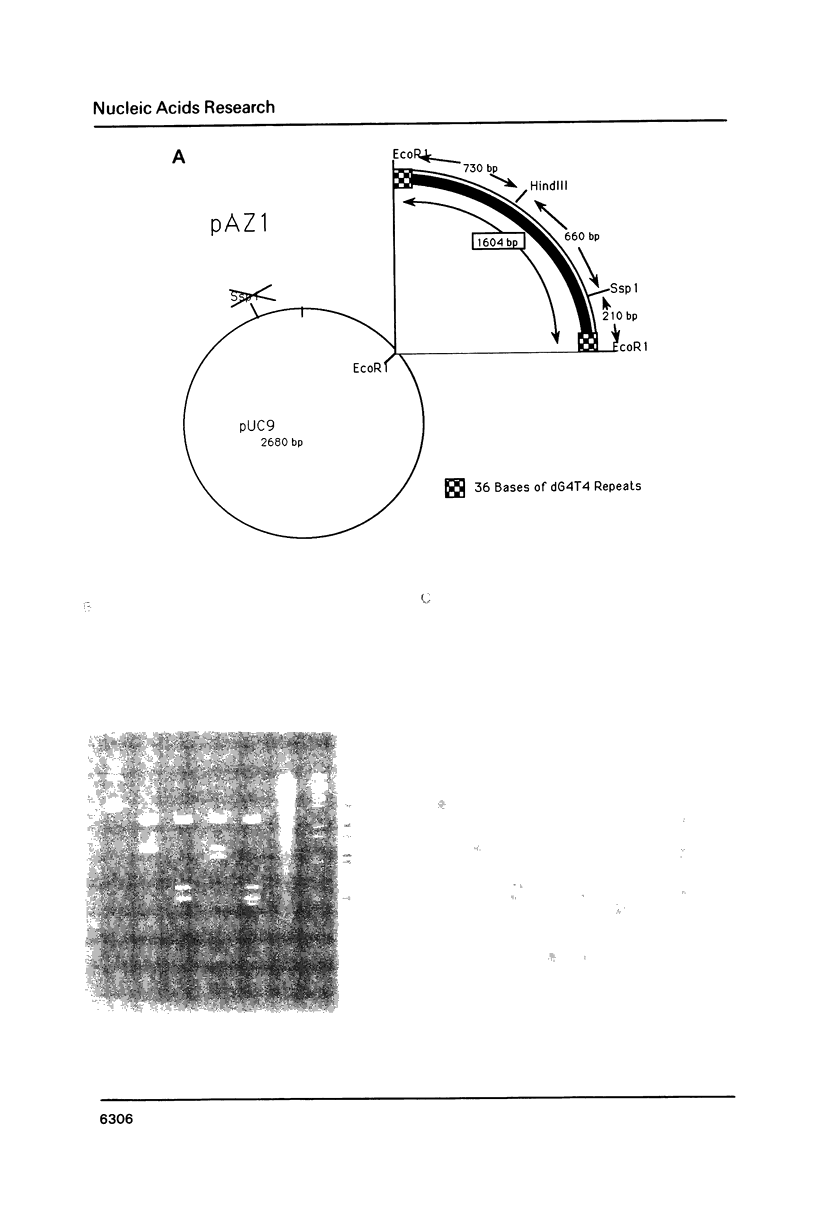
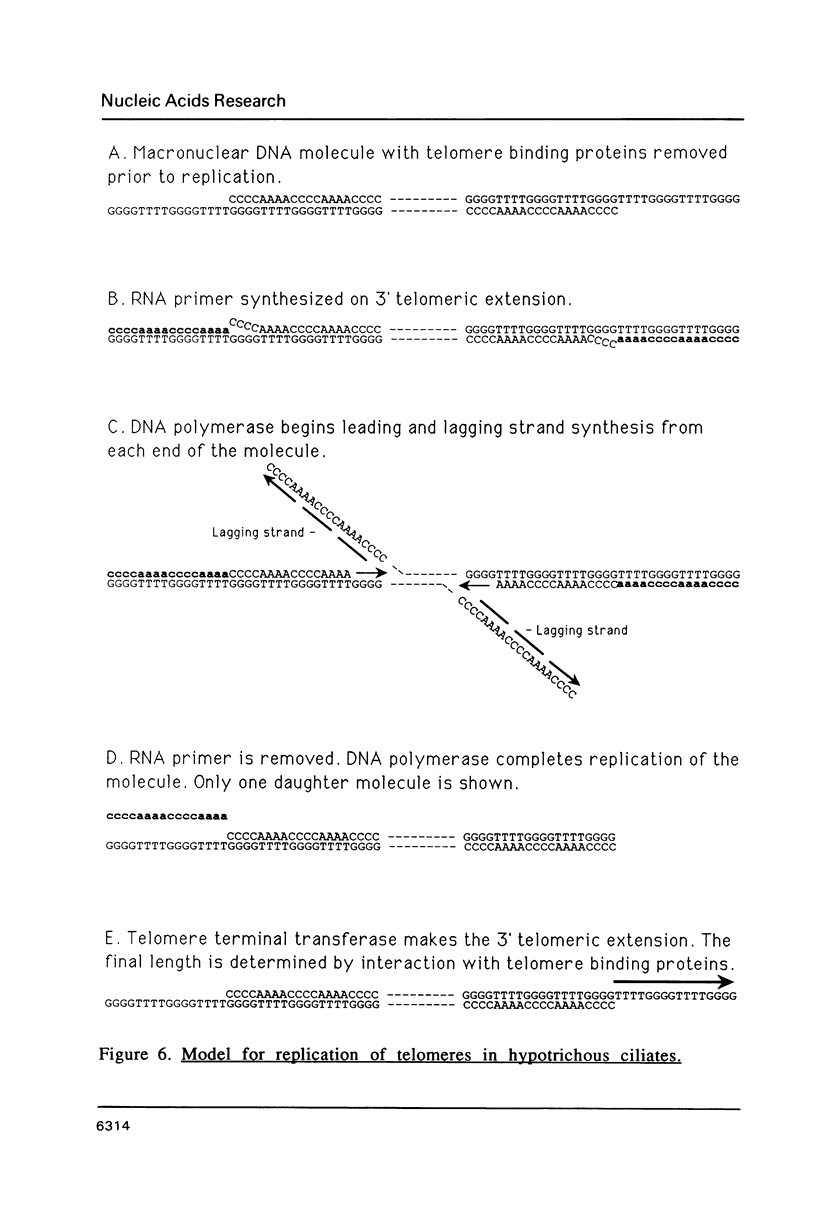
An enzymatic activity in crude extracts of macronuclei from the hypotrichous ciliate Oxytricha nova catalyzes the synthesis of RNA consisting of (C4A4)n using an oligodeoxynucleotide template of the telomeric sequence (dG4T4)n. Single-stranded (dG4T4)n is an effective template if it has a random sequence at its 5' end. The enzyme will not use a (dG4T4)n template of any length (up to 64 bases) if it lacks a random sequence at the 5' end. With a random, single-stranded sequence at the 5' end, the (dG4T4)n oligodeoxynucleotide must be at least 36 bases long to work as a template. A 16-base, single-stranded region of (dG4T4)2 is an effective template when joined to a 20-base double-stranded region of (dG4T4)n/(dA4dC4)n, a structural arrangement that is the same as the native telomere of Oxytricha macronuclear DNA. The RNA-synthesizing activity is unaffected by 1.0 mg/ml of alpha-amanitin. Macronuclear extracts have an alpha-amanitin-insensitive, RNA-polymerizing activity that can use a random 55mer oligodeoxynucleotide as a template. This enzyme activity may be the same one that uses (dG4T4)n templates to make (C4A4)n RNA. The (C4A4)n RNA made in the reaction can prime DNA synthesis by the E. coli DNA polymerase I Klenow fragment. Therefore, the RNA polymerase activity fulfills the requirements of the telomere DNA primase that we postulated for replication of telomeres in hypotrichs (Zahler and Prescott, 1988, Nucleic Acids Research 16, 6953-6972).
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blair D. G. Eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1988;89(4):647–670. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(88)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. L. Eukaryotic DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:733–771. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalier-Smith T. Palindromic base sequences and replication of eukaryote chromosome ends. Nature. 1974 Aug 9;250(5466):467–470. doi: 10.1038/250467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschling D. E., Zakian V. A. Telomere proteins: specific recognition and protection of the natural termini of Oxytricha macronuclear DNA. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):195–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90442-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. The telomere terminal transferase of Tetrahymena is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme with two kinds of primer specificity. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90576-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greslin A. F., Loukin S. H., Oka Y., Prescott D. M. An analysis of the macronuclear actin genes of Oxytricha. DNA. 1988 Oct;7(8):529–536. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1988.7.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E. R., Blackburn E. H. An overhanging 3' terminus is a conserved feature of telomeres. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):345–348. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaguni L. S., Lehman I. R. Eukaryotic DNA polymerase-primase: structure, mechanism and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jul 13;950(2):87–101. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobutcher L. A., Swanton M. T., Donini P., Prescott D. M. All gene-sized DNA molecules in four species of hypotrichs have the same terminal sequence and an unusual 3' terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3015–3019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyzis R. K., Buckingham J. M., Cram L. S., Dani M., Deaven L. L., Jones M. D., Meyne J., Ratliff R. L., Wu J. R. A highly conserved repetitive DNA sequence, (TTAGGG)n, present at the telomeres of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6622–6626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murti K. G., Prescott D. M. Replication forms of the gene-sized DNA molecules of hypotrichous ciliates. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;3(9):1562–1566. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.9.1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. M., Cech T. R. Properties of the telomeric DNA-binding protein from Oxytricha nova. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):769–774. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. M., Cech T. R. Telomeric DNA-protein interactions of Oxytricha macronuclear DNA. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):783–793. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards E. J., Ausubel F. M. Isolation of a higher eukaryotic telomere from Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90494-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. D. Origin of concatemeric T7 DNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 18;239(94):197–201. doi: 10.1038/newbio239197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Prescott D. M. Telomere terminal transferase activity in the hypotrichous ciliate Oxytricha nova and a model for replication of the ends of linear DNA molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):6953–6972. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]