Abstract
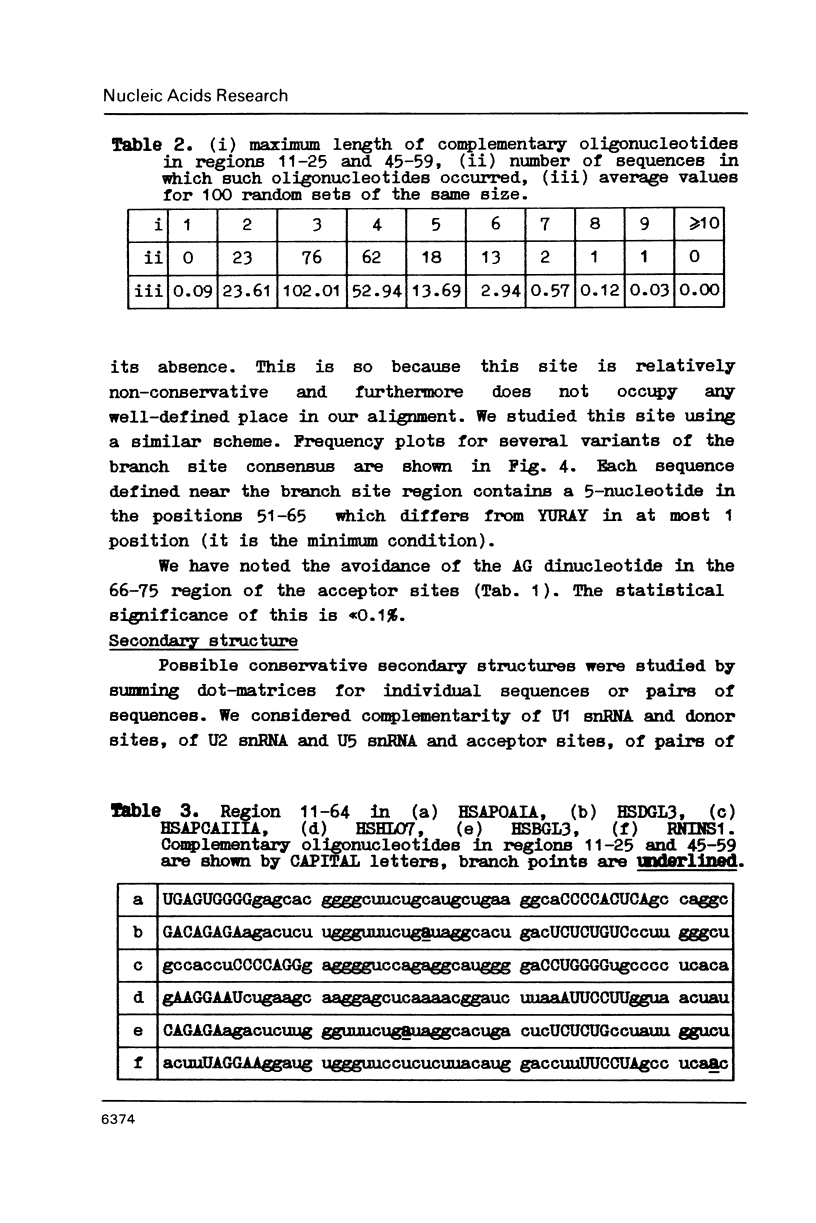
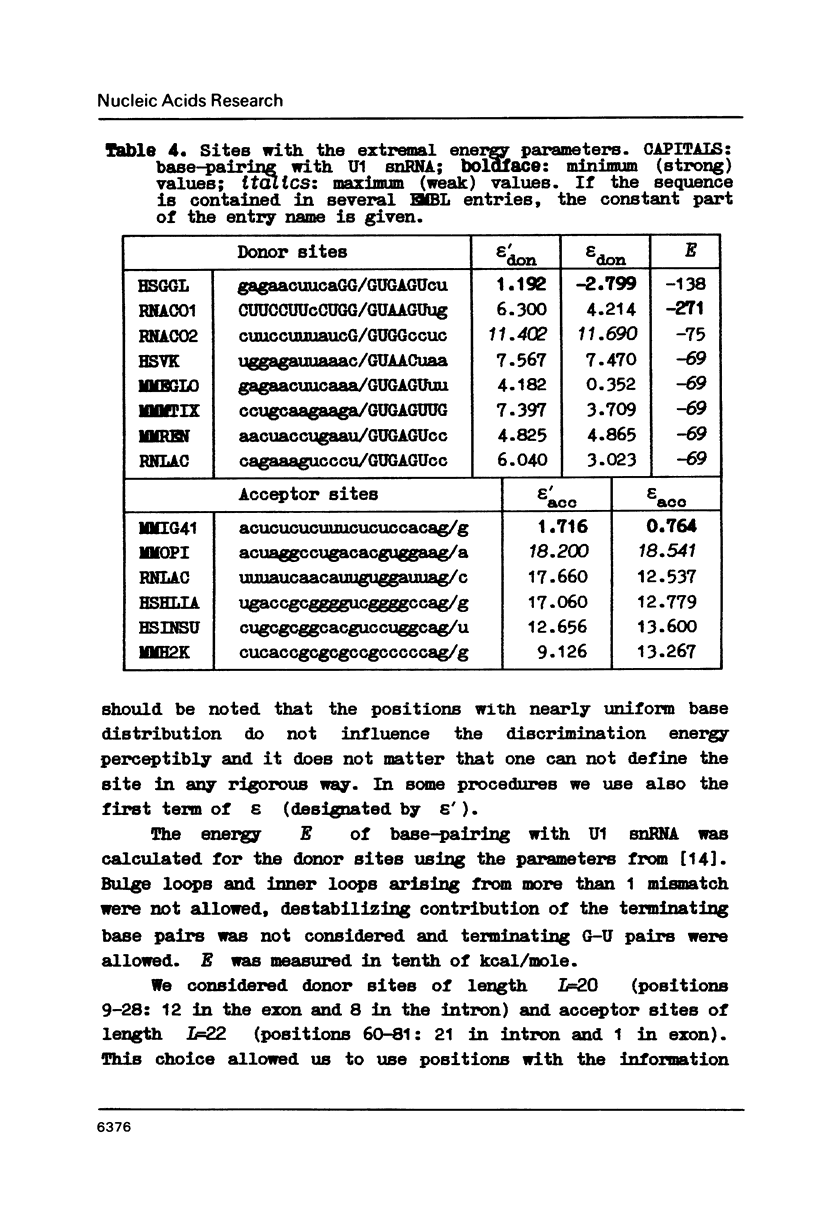
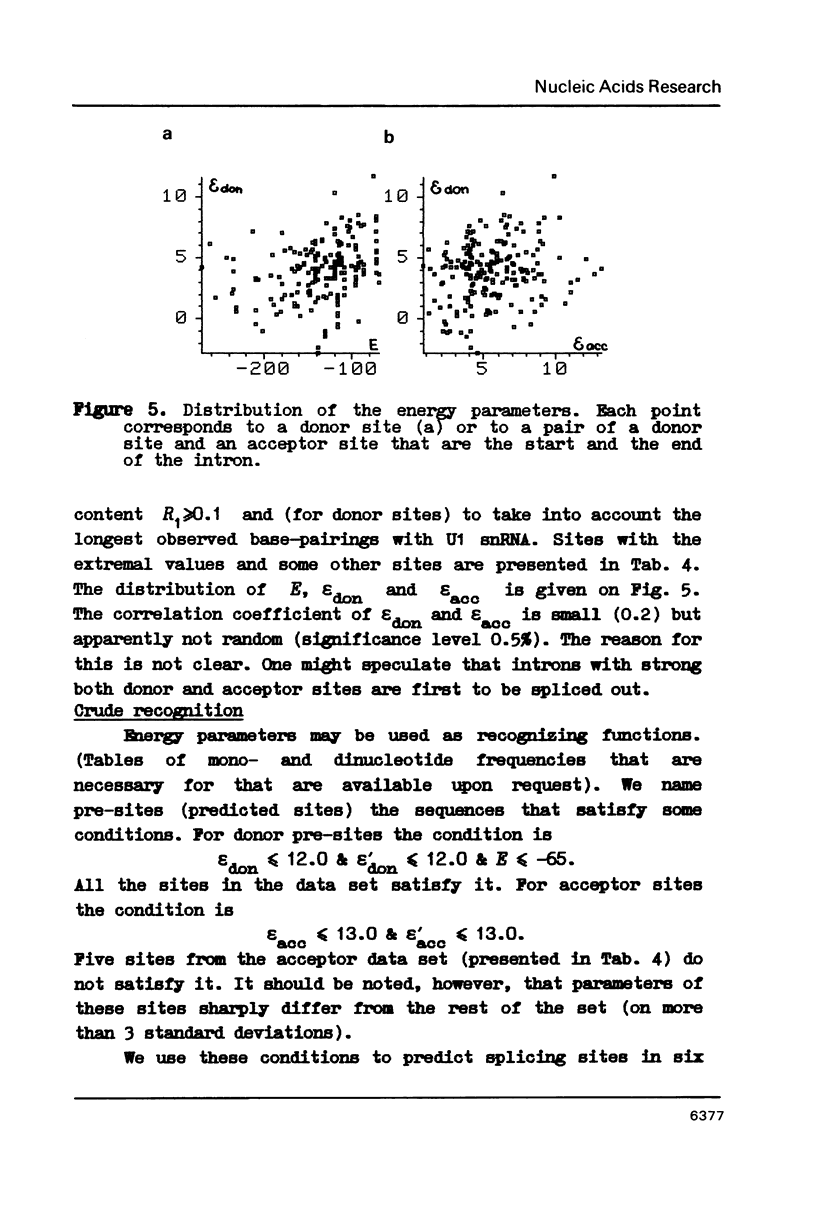
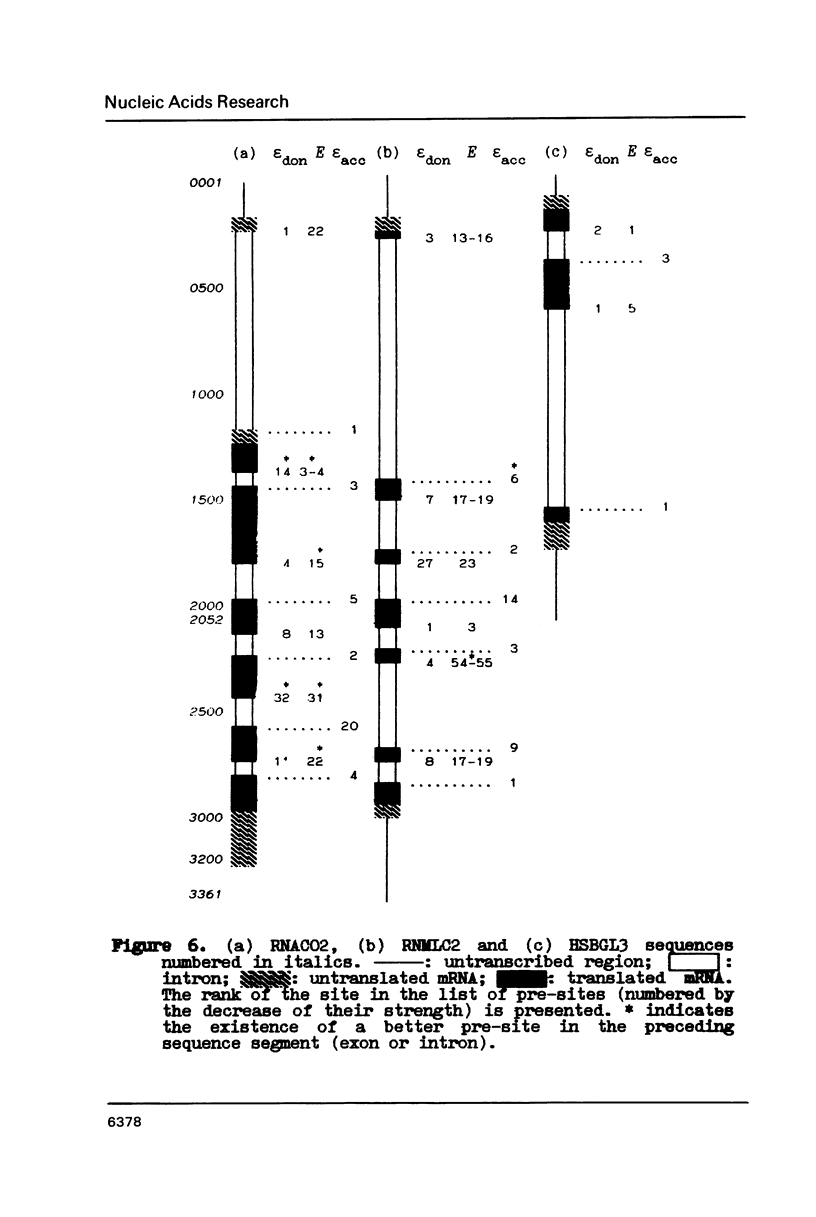
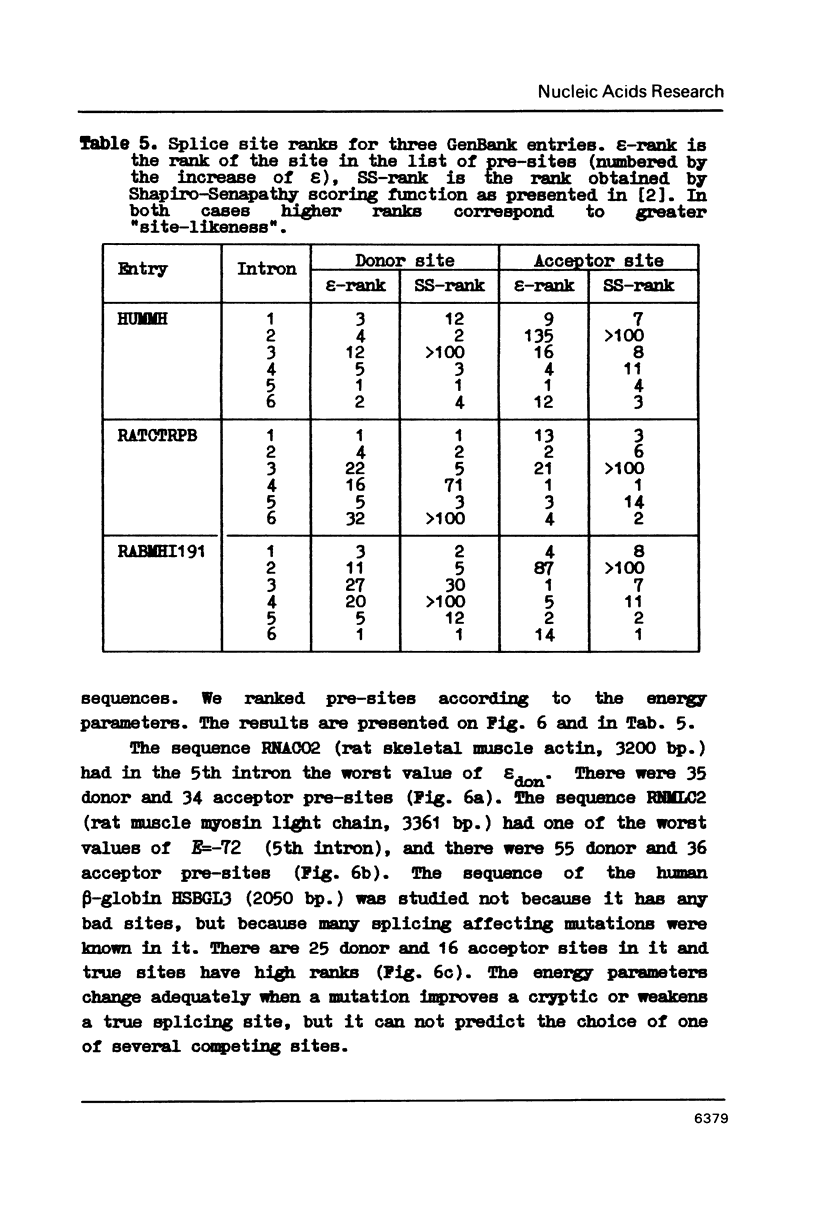
222 donor and 222 acceptor (including 206 pairs) non-homologous splicing sites were studied. Well known features of these were confirmed and some novel observations were made. It is (1) cCAGGGag signal in (-60)-(-58) region of acceptor sites; (2) strong complementarity between regions (-69)-(-55) and (-36)-(-22) of some of the acceptor sites, and (3) small but statistically significant correlation between discrimination energies of corresponding donor and acceptor sites.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg O. G., von Hippel P. H. Selection of DNA binding sites by regulatory proteins. Statistical-mechanical theory and application to operators and promoters. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 20;193(4):723–750. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90354-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fickett J. W. Recognition of protein coding regions in DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5303–5318. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:671–708. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo M., Iida Y., Shimbo M. Syntactic pattern analysis of 5'-splice site sequences of mRNA precursors in higher eukaryote genes. Comput Appl Biosci. 1987 Nov;3(4):319–324. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/3.4.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lida Y. DNA sequences and multivariate statistical analysis. Categorical discrimination approach to 5' splice site signals of mRNA precursors in higher eukaryotes' genes. Comput Appl Biosci. 1987 Jun;3(2):93–98. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/3.2.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Reed R. The role of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):673–678. doi: 10.1038/325673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata K., Kanehisa M., DeLisi C. Prediction of splice junctions in mRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5327–5340. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima Y., Gotoh Y. Signals for the selection of a splice site in pre-mRNA. Computer analysis of splice junction sequences and like sequences. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):247–259. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90647-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent A., Zeitlin S., Efstratiadis A. Minimal exon sequence requirements for efficient in vitro splicing of mono-intronic nuclear pre-mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11284–11291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinqueton J., Moreau J. Application of learning techniques to splicing site recognition. Biochimie. 1985 May;67(5):541–547. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(85)80274-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. A role for exon sequences and splice-site proximity in splice-site selection. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W. Globin mRNA sequences: analysis of base pairing and evolutionary implications. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):985–1002. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider T. D., Stormo G. D., Gold L., Ehrenfeucht A. Information content of binding sites on nucleotide sequences. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):415–431. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Hofer E., Weissmann C. A minimal intron length but no specific internal sequence is required for splicing the large rabbit beta-globin intron. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):915–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90426-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



