Abstract
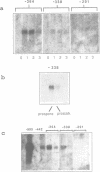
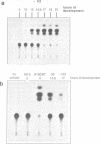
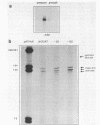
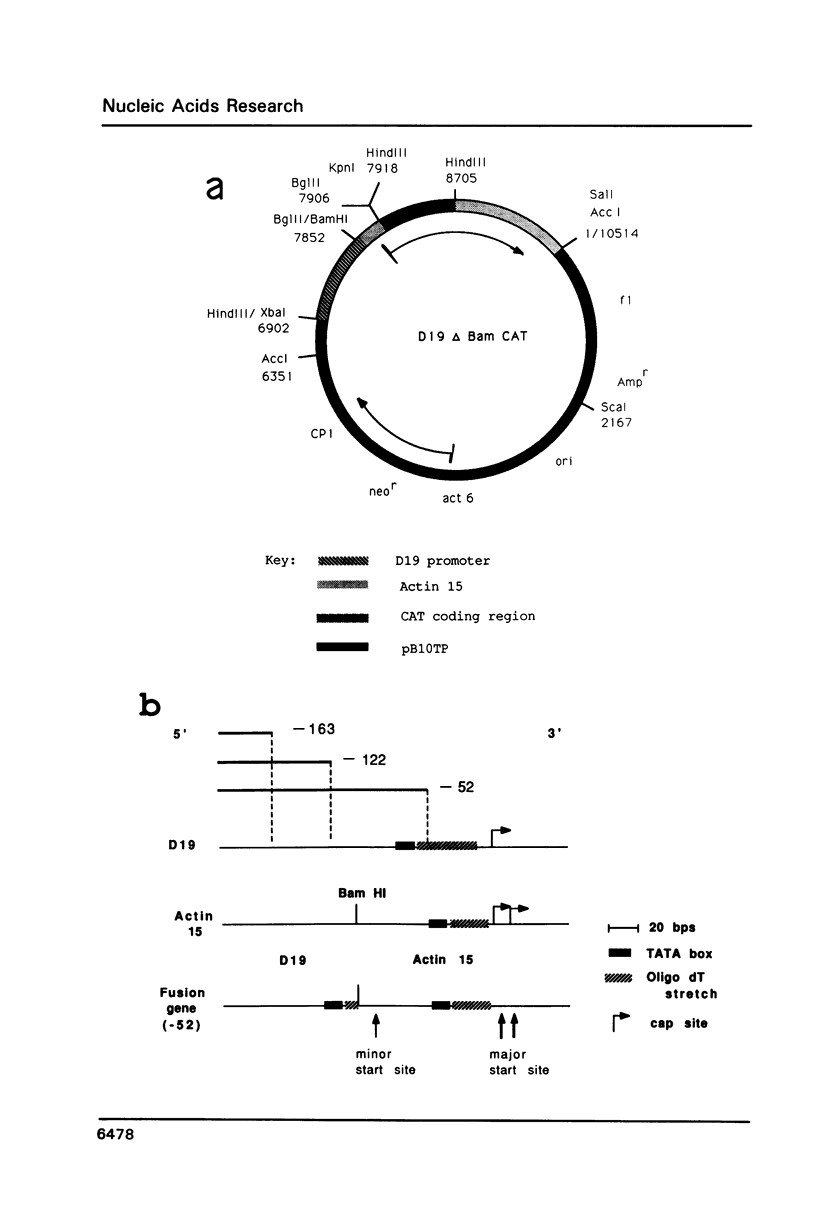
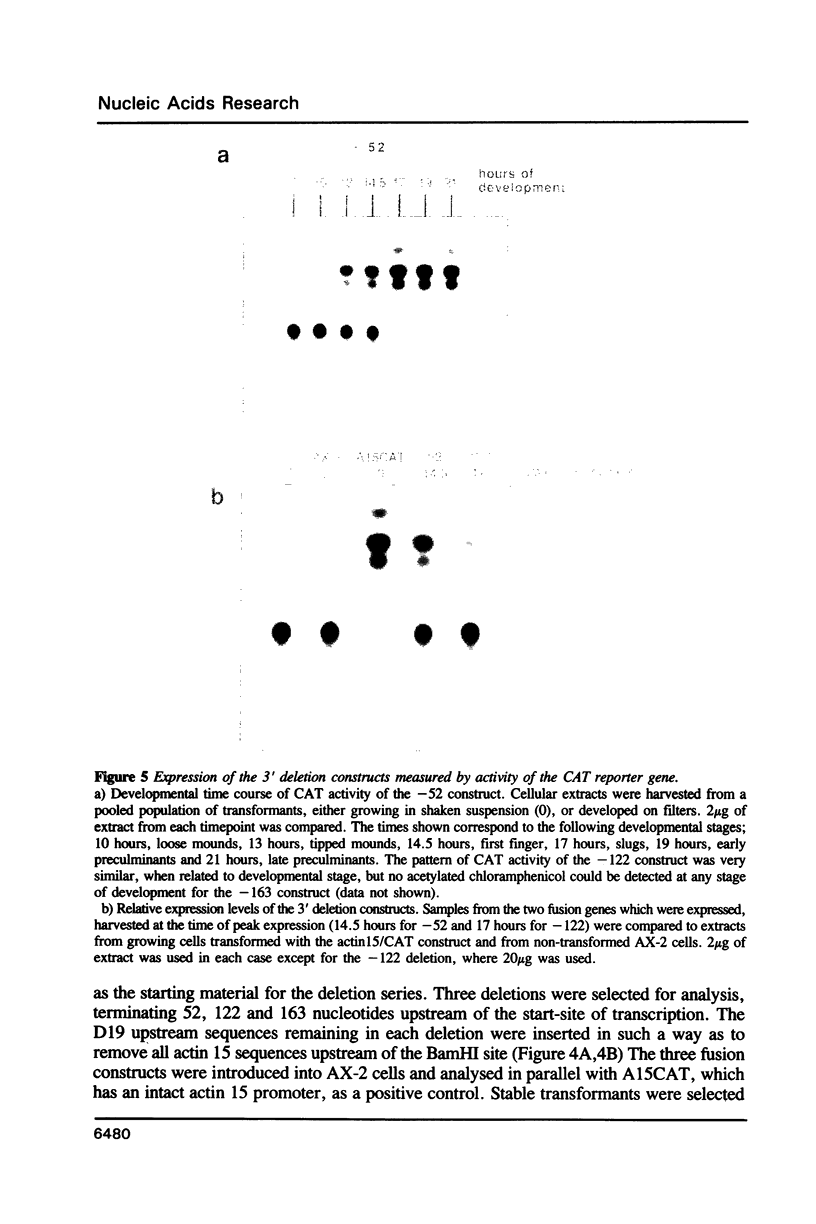
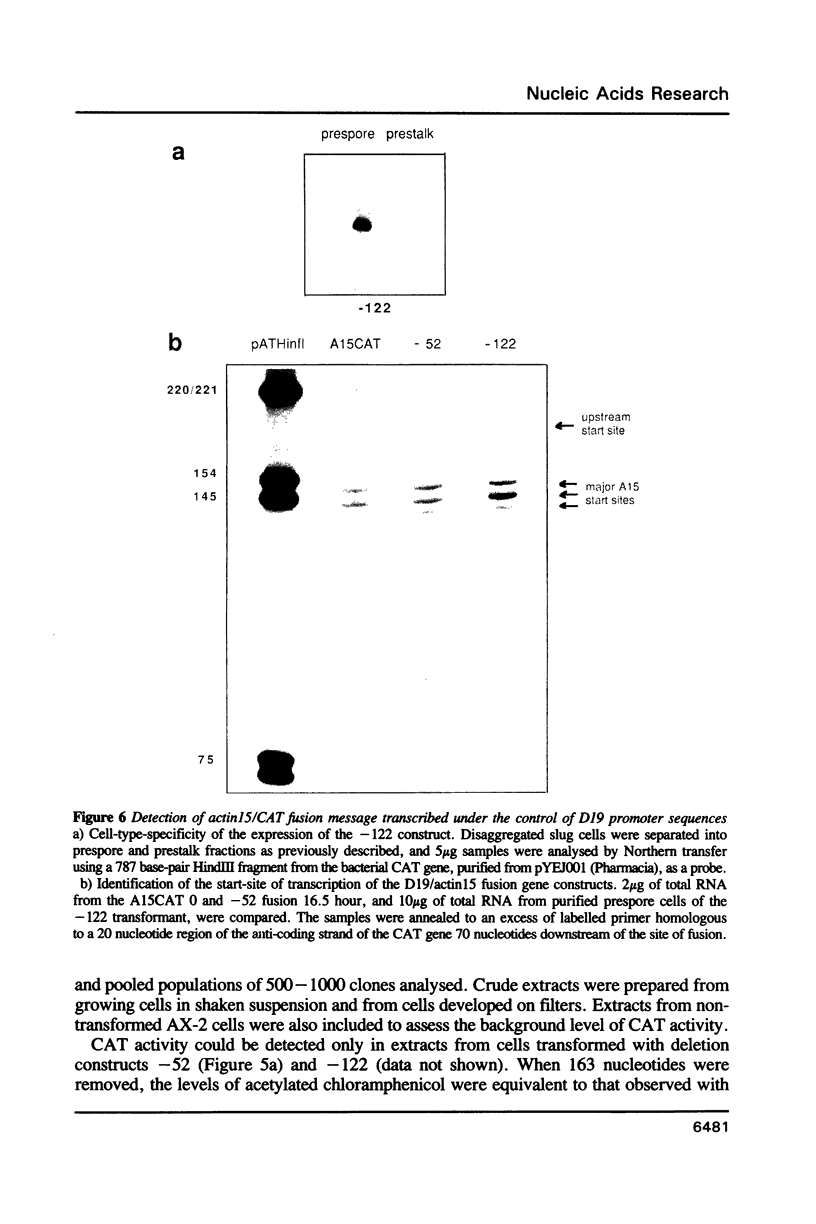
There has been considerable debate about the relative contributions of transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms to the regulation of prespore gene expression in Dictyostelium. We have determined the DNA sequence upstream of D19, the Dictyostelium gene encoding PsA, a prespore-specific, cell surface protein of unknown function. Our analysis of gene fusions, in which D19 upstream sequences are placed adjacent to a heterologous reporter gene, indicates that transcriptional signals alone are sufficient for the correct temporal and cell-type specific expression of this gene. We also show that the 5' and 3' boundaries of the minimal sequences necessary for correct developmental regulation lie within the region 338 to 122 nucleotides upstream of the start site of transcription but that flanking sequences seem to be necessary for optimal expression.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barklis E., Lodish H. F. Regulation of dictyostelium discoideum mRNAs specific for prespore or prestalk cells. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1139–1148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90297-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey L., Palatnik C. M., Jacobson A. Messenger RNA half-life in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1983 Jan;95(1):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M., Knecht D., Lodish H. F., Loomis W. F. DNA sequences required for expression of a Dictyostelium actin gene. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3361–3366. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04651.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta S., Firtel R. A. An 80-bp cis-acting regulatory region controls cAMP and development regulation of a prestalk gene in Dictyostelium. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):294–304. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta S., Firtel R. A. Identification of the sequences controlling cyclic AMP regulation and cell-type-specific expression of a prestalk-specific gene in Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):149–159. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. M., Pears C. J., Williams J. G. Characterization of two divergently transcribed Dictyostelium gene pairs and identification of G-rich sequence element lying between them with the characteristics of a basal promoter element. Dev Genet. 1988;9(4-5):455–468. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020090423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early A. E., Williams J. G., Meyer H. E., Por S. B., Smith E., Williams K. L., Gooley A. A. Structural characterization of Dictyostelium discoideum prespore-specific gene D19 and of its product, cell surface glycoprotein PsA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3458–3466. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early A. E., Williams J. G. Two vectors which facilitate gene manipulation and a simplified transformation procedure for Dictyostelium discoideum. Gene. 1987;59(1):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jermyn K. A., Berks M., Kay R. R., Williams J. G. Two distinct classes of prestalk-enriched mRNA sequences in Dictyostelium discoideum. Development. 1987 Aug;100(4):745–755. doi: 10.1242/dev.100.4.745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krefft M., Voet L., Gregg J. H., Mairhofer H., Williams K. L. Evidence that positional information is used to establish the prestalk-prespore pattern in Dictyostelium discoideum aggregates. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):201–206. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01784.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krefft M., Voet L., Gregg J. H., Williams K. L. Use of a monoclonal antibody recognizing a cell surface determinant to distinguish prestalk and prespore cells of Dictyostelium discoideum slugs. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Aug;88:15–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiarotti G., Ceccarelli A., Lodish H. F. Cyclic AMP stabilizes a class of developmentally regulated Dictyostelium discoideum mRNAs. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):616–618. doi: 10.1038/301616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiarotti G., Giorda R., Ceccarelli A., Perlo C. mRNA stabilization controls the expression of a class of developmentally regulated genes in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5786–5790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiarotti G., Lefebvre P., Lodish H. F. Differences in the stability of developmentally regulated mRNAs in aggregated and disaggregated Dictyostelium discoideum cells. Dev Biol. 1982 Jan;89(1):82–91. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90296-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manrow R. E., Jacobson A. mRNA decay rates in late-developing Dictyostelium discoideum cells are heterogeneous, and cyclic AMP does not act directly to stabilize cell-type-specific mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4088–4097. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehdy M. C., Ratner D., Firtel R. A. Induction and modulation of cell-type-specific gene expression in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):763–771. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nellen W., Silan C., Saur U., Firtel R. A. Regulatory sequences in the promoter of the Dictyostelium Actin 6 gene. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3367–3372. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04652.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyama M., Blumberg D. D. Changes during differentiation in requirements for cAMP for expression of cell-type-specific mRNAs in the cellular slime mold, Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1986 Oct;117(2):550–556. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pears C. J., Williams J. G. Identification of a DNA sequence element required for efficient expression of a developmentally regulated and cAMP-inducible gene of Dictyostelium discoideum. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):195–200. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04738.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pears C. J., Williams J. G. Multiple copies of a G-rich element upstream of a cAMP-inducible Dictyostelium gene are necessary but not sufficient for efficient gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8467–8486. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole S. J., Firtel R. A. Conserved structural features are found upstream from the three co-ordinately regulated discoidin I genes of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jan 15;172(2):203–220. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner D., Borth W. Comparison of differentiating Dictyostelium discoideum cell types separated by an improved method of density gradient centrifugation. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Jan;143(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap P., Van Lookeren Campagne M. M., Van Driel R., Spek W., Van Haastert P. J., Pinas J. Postaggregative differentiation induction by cyclic AMP in Dictyostelium: intracellular transduction pathway and requirement for additional stimuli. Dev Biol. 1986 Nov;118(1):52–63. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Town C., Gross J. The role of cyclic nucleotides and cell agglomeration in postaggregative enzyme synthesis in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1978 Apr;63(2):412–420. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang A., Bradbury J. M. Separation and properties of prestalk and prespore cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Apr;132(2):433–441. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts D. J., Ashworth J. M. Growth of myxameobae of the cellular slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum in axenic culture. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):171–174. doi: 10.1042/bj1190171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]