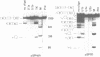Abstract
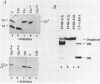
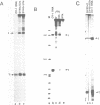
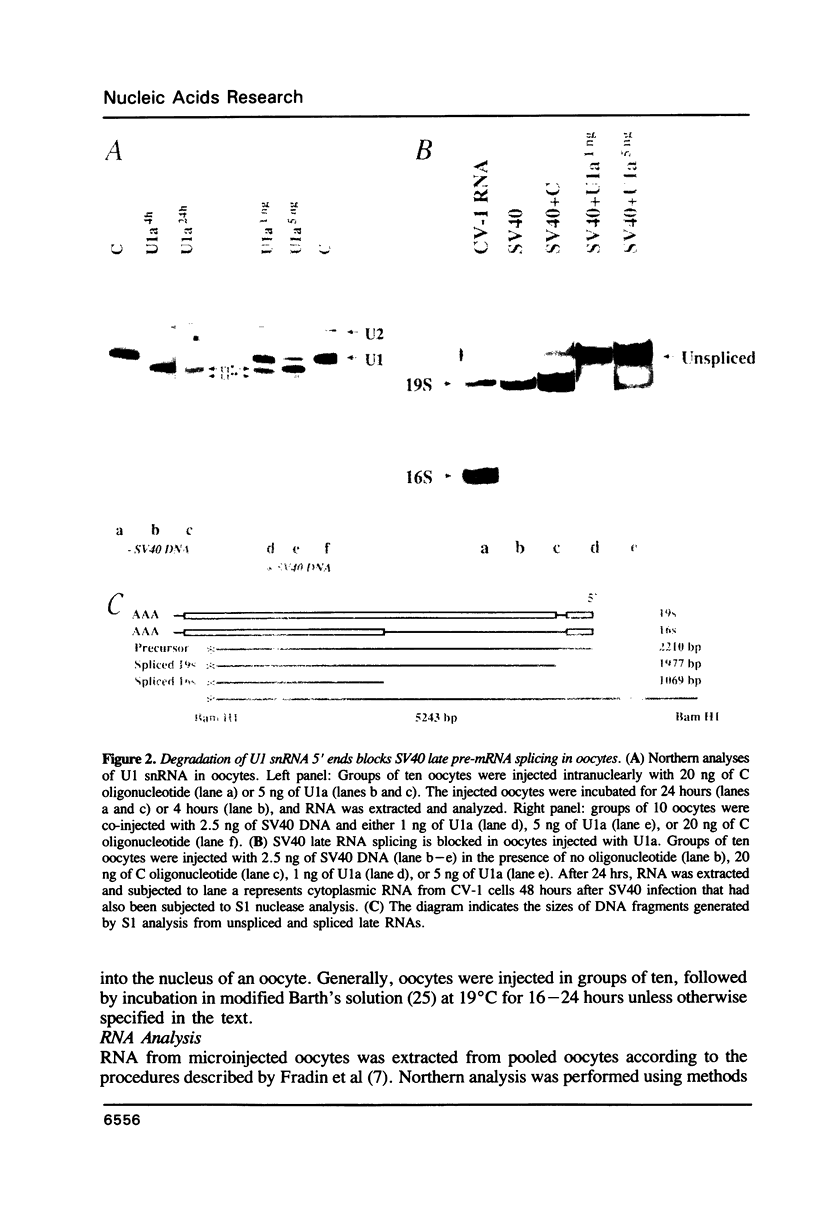
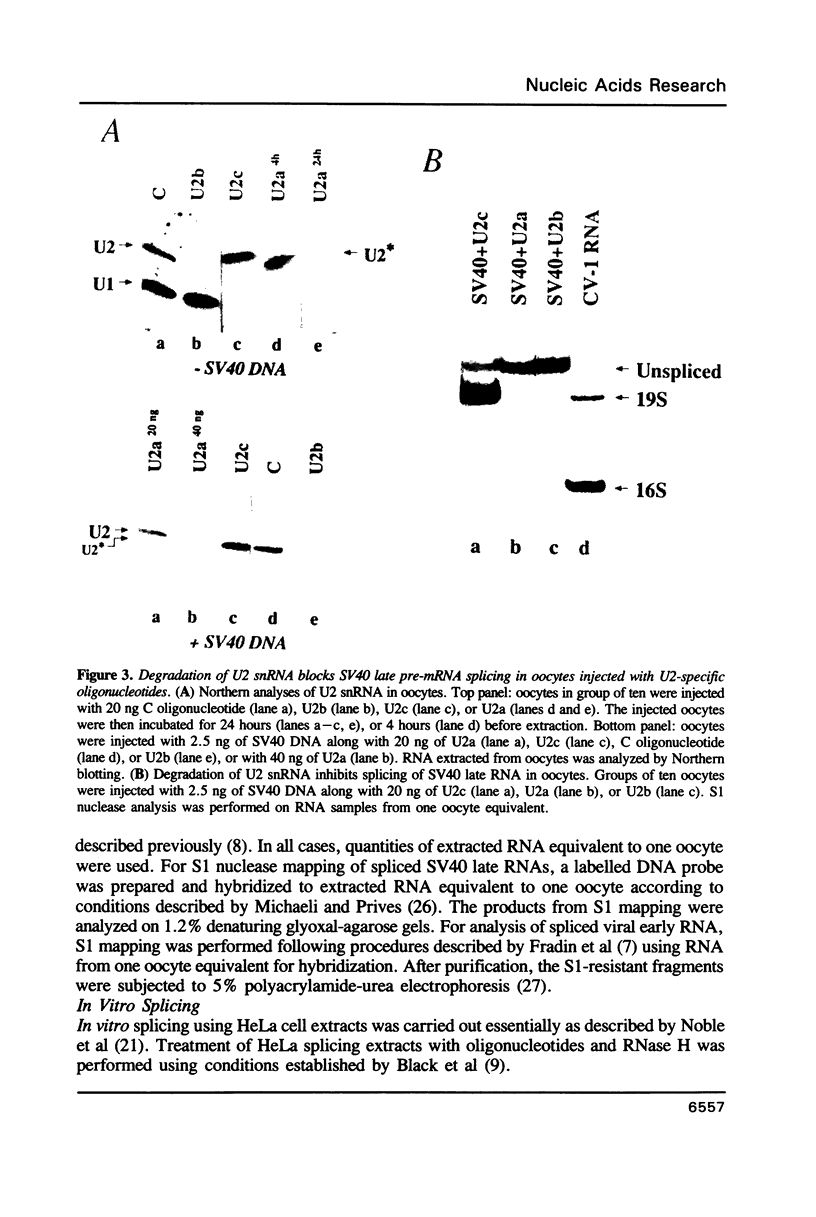
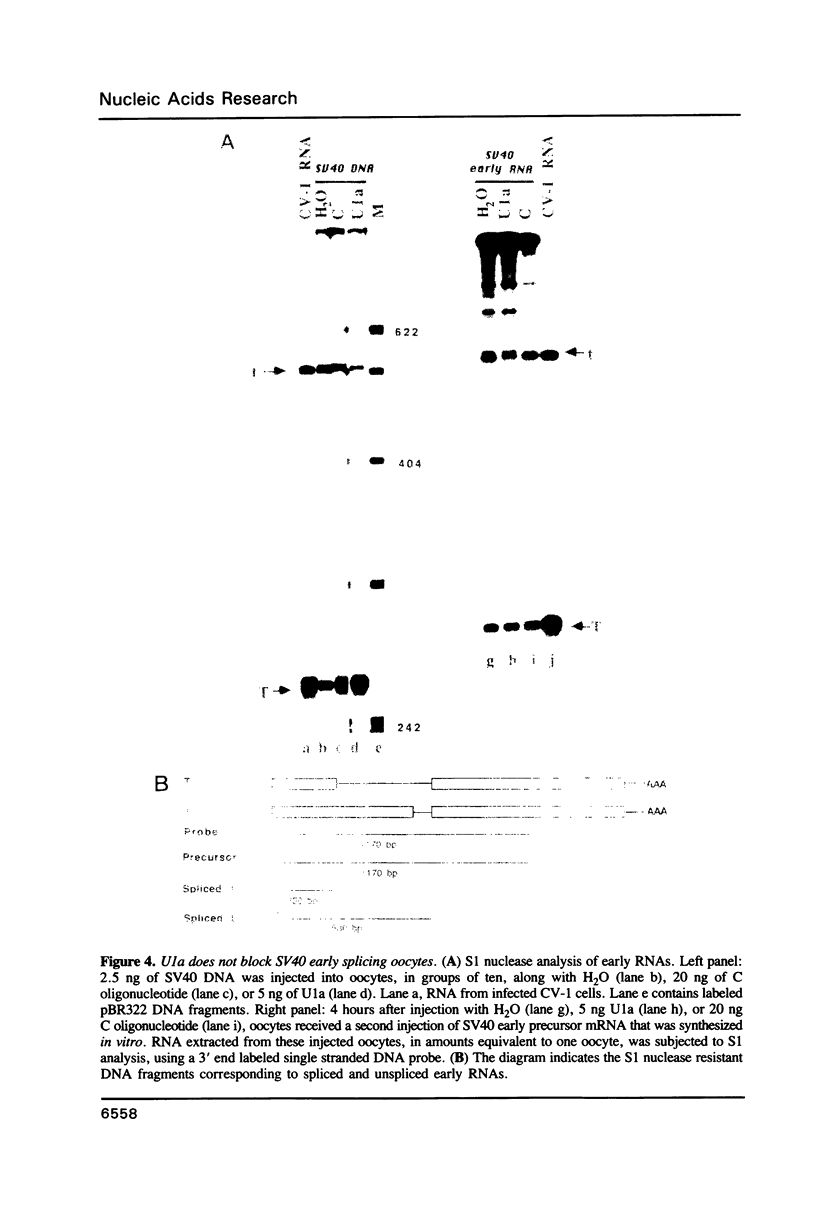
We have investigated the roles of U1 and U2 snRNP particles in SV40 pre-mRNA splicing by oligonucleotide-targeted degradation of U1 or U2 snRNAs in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Microinjection of oligonucleotides complementary to regions of U1 or U2 RNAs either in the presence or absence of SV40 DNA resulted in specific cleavage of the corresponding snRNA. Unexpectedly, degradation of U1 or U2 snRNA was far more extensive when the oligonucleotide was injected without, or prior to, introduction of viral DNA. In either co-injected or pre-injected oocytes, these oligonucleotides caused a dramatic reduction in the accumulation of spliced SV40 mRNA expressed from the viral late region, and a commensurate increase in unspliced late RNA. When pre-injected, two different U2 specific oligonucleotides also inhibited the formation of both large and small tumor antigen spliced early mRNAs. However, even when, by pre-injection of a U1 5' end-specific oligonucleotide, greater than 95% degradation of the U1 snRNA 5' ends occurred in oocytes, no reduction in early pre-mRNA splicing was observed. In contrast, the same U1 5' end oligonucleotide, when added to HeLa splicing extracts, substantially inhibited the splicing of SV40 early pre-mRNA, indicating that U1 mRNP is not totally dispensable for early splicing. These findings confirm and extend our earlier observations which suggested that different pre-mRNAs vary in their requirements for snRNPs.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berget S. M., Robberson B. L. U1, U2, and U4/U6 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins are required for in vitro splicing but not polyadenylation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):691–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90344-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindereif A., Green M. R. An ordered pathway of snRNP binding during mammalian pre-mRNA splicing complex assembly. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2415–2424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L., Chabot B., Steitz J. A. U2 as well as U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins are involved in premessenger RNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):737–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L., Steitz J. A. Pre-mRNA splicing in vitro requires intact U4/U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):697–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90345-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave C., Chevrier M., Nguyen T. T., Hélène C. Rate of degradation of [alpha]- and [beta]-oligodeoxynucleotides in Xenopus oocytes. Implications for anti-messenger strategies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10507–10521. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Black D. L., LeMaster D. M., Steitz J. A. The 3' splice site of pre-messenger RNA is recognized by a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1344–1349. doi: 10.1126/science.2933810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Leser G., Martin T. E. Ultrastructural distribution of nuclear ribonucleoproteins as visualized by immunocytochemistry on thin sections. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):358–363. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes D. J., Kirschner M. W., Caput D., Dahlberg J. E., Lund E. Differential expression of multiple U1 small nuclear RNAs in oocytes and embryos of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):681–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes D. J., Kornberg T. B., Kirschner M. W. Small nuclear RNA transcription and ribonucleoprotein assembly in early Xenopus development. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):62–72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fradin A., Jove R., Hemenway C., Keiser H. D., Manley J. L., Prives C. Splicing pathways of SV40 mRNAs in X. laevis oocytes differ in their requirements for snRNPs. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):927–936. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90427-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Manley J. L. Factors influencing alternative splice site utilization in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):738–748. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good P. J., Welch R. C., Barkan A., Somasekhar M. B., Mertz J. E. Both VP2 and VP3 are synthesized from each of the alternative spliced late 19S RNA species of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):944–953. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.944-953.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Maniatis T., Melton D. A. Human beta-globin pre-mRNA synthesized in vitro is accurately spliced in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B. Changes in somatic cell nuclei inserted into growing and maturing amphibian oocytes. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1968 Nov;20(3):401–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T. Multiple factors including the small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1 and U2 are necessary for pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):725–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Keller W., Appel B., Lührmann R. The 5' terminus of the RNA moiety of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles is required for the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90551-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. True genes for human U1 small nuclear RNA. Copy number, polymorphism, and methylation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):2013–2021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Reed R. The role of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):673–678. doi: 10.1038/325673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Zeller R. Xenopus laevis U2 snRNA genes: tandemly repeated transcription units sharing 5' and 3' flanking homology with other RNA polymerase II transcribed genes. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1883–1891. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01675.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E. Linear DNA does not form chromatin containing regularly spaced nucleosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1608–1618. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaeli T., Pan Z. Q., Prives C. An excised SV40 intron accumulates and is stable in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):1012–1020. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaeli T., Prives C. Regulation of simian virus 40 gene expression in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2019–2028. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaeli T., Prives C. pBR322 DNA inhibits simian virus 40 gene expression in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1579–1594. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. J., Stephens D. L., Mertz J. E. Kinetics of accumulation and processing of simian virus 40 RNA in Xenopus laevis oocytes injected with simian virus 40 DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1581–1594. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottram J., Perry K. L., Lizardi P. M., Lührmann R., Agabian N., Nelson R. G. Isolation and sequence of four small nuclear U RNA genes of Trypanosoma brucei subsp. brucei: identification of the U2, U4, and U6 RNA analogs. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1212–1223. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Pettersson I., Hinterberger M., Karmas A., Steitz J. A. The U1 small nuclear RNA-protein complex selectively binds a 5' splice site in vitro. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):509–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90432-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble J. C., Pan Z. Q., Prives C., Manley J. L. Splicing of SV40 early pre-mRNA to large T and small t mRNAs utilizes different patterns of lariat branch sites. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90218-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble J. C., Prives C., Manley J. L. In vitro splicing of simian virus 40 early pre mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1219–1235. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Mount S. M., Steitz J. A., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors is inhibited by antisera to small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90212-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Z. Q., Prives C. Assembly of functional U1 and U2 human-amphibian hybrid snRNPs in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1328–1331. doi: 10.1126/science.2970672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Siliciano P. G., Guthrie C. Recognition of the TACTAAC box during mRNA splicing in yeast involves base pairing to the U2-like snRNA. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90564-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles C. L., Perlman P. S., Mecklenburg K. L., Petrillo M. L., Tabor J. H., Jarrell K. A., Cheng H. L. A self-splicing RNA excises an intron lariat. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90755-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby S. W., Abelson J. An early hierarchic role of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein in spliceosome assembly. Science. 1988 Nov 18;242(4881):1028–1035. doi: 10.1126/science.2973660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Zamore P. D., Green M. R. A factor, U2AF, is required for U2 snRNP binding and splicing complex assembly. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90509-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1987 Feb 13;235(4790):766–771. doi: 10.1126/science.3544217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Lund E., Murphy J. T., Pettersson U., Dahlberg J. E. Human U2 and U1 RNA genes use similar transcription signals. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3295–3301. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02293.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Laskey R. A., Finch J., Gurdon J. B. Selective DNA conservation and chromatin assembly after injection of SV40 DNA into Xenopus oocytes. Dev Biol. 1978 May;64(1):178–188. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Weiner A. M. A compensatory base change in U1 snRNA suppresses a 5' splice site mutation. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Krol A. R., Mol J. N., Stuitje A. R. Modulation of eukaryotic gene expression by complementary RNA or DNA sequences. Biotechniques. 1988 Nov-Dec;6(10):958–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Veen R., Arnberg A. C., van der Horst G., Bonen L., Tabak H. F., Grivell L. A. Excised group II introns in yeast mitochondria are lariats and can be formed by self-splicing in vitro. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90756-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]