Abstract
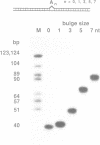
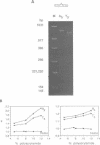
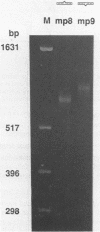
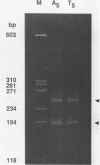
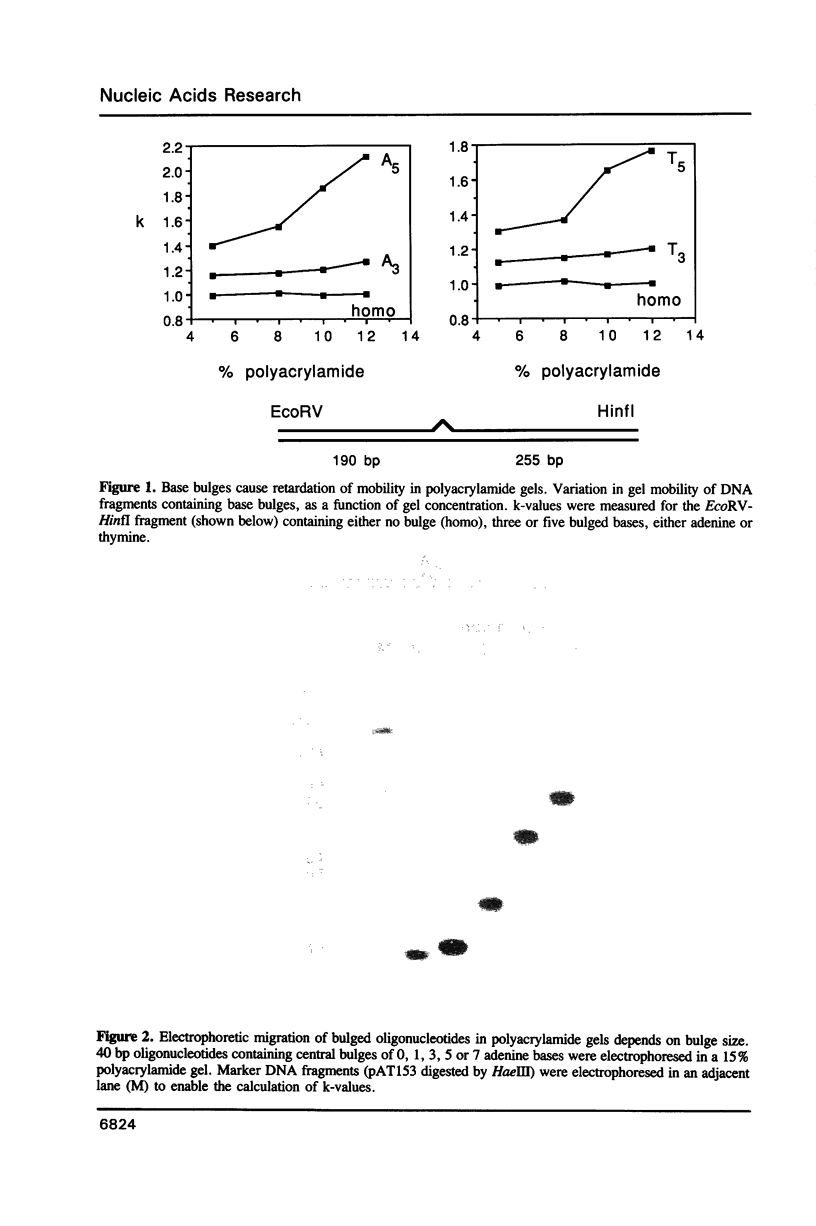
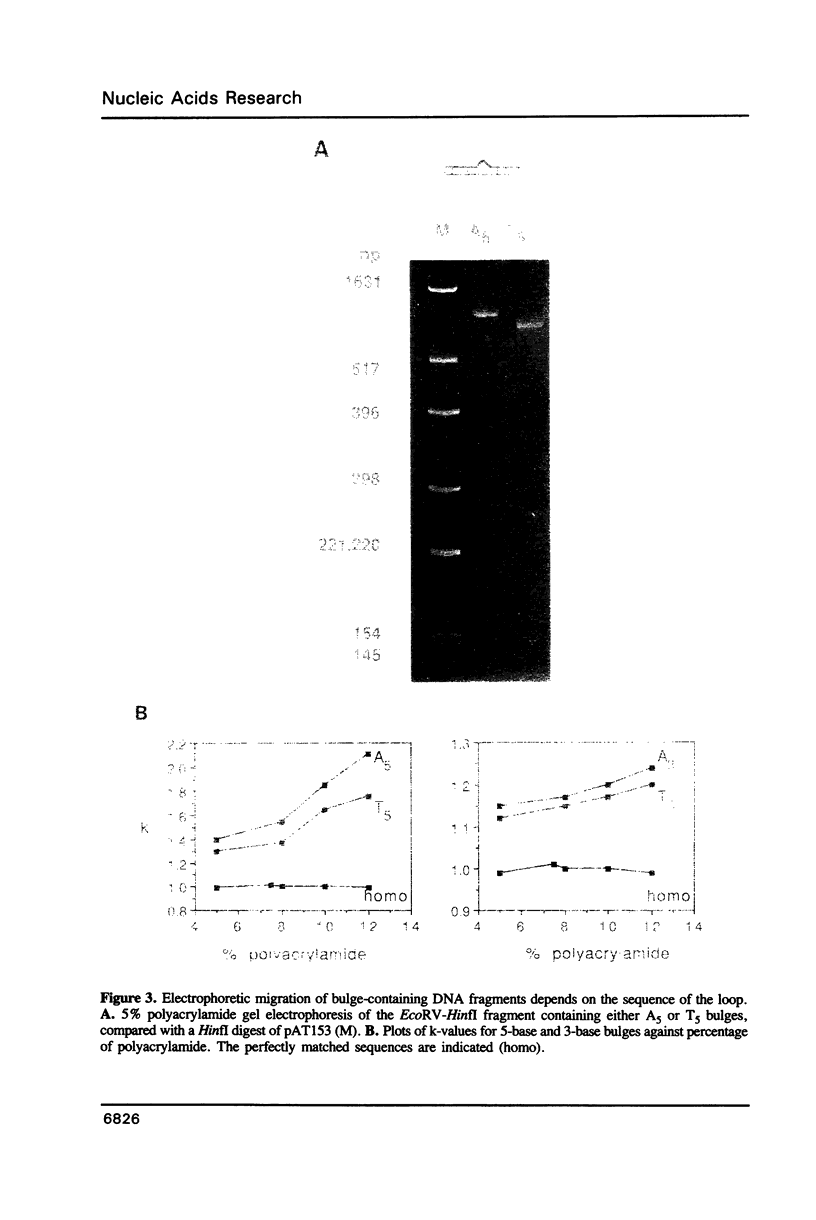
We have studied the structure and reactivities of two kinds of mismatched DNA sequences--unopposed bases, or bulges, and multiple mismatched pairs of bases. These were generated in a constant sequence environment, in relatively long DNA fragments, using a technique based on heteroduplex formation between sequences cloned into single-stranded M13 phage. The mismatched sequences were studied from two points of view, viz 1. The mobility of the fragments on gel electrophoresis in polyacrylamide was studied in order to examine possible bending of the DNA due to the presence of the mismatch defect. Such bending would constitute a global effect on the conformation of the molecule. 2. Sequences in and around the mismatches were studied using enzyme and chemical probes of DNA structure. This would reveal more local structural effects of the mismatched sequences. We observed that the structures of the bulges and the multiple mismatches appear to be fundamentally different. The bulged sequences exhibited a large gel retardation, consistent with a significant bending of the DNA at the bulge, and whose magnitude depends on the number of mismatched bases. The larger bulges were sensitive to cleavage by single-strand specific nucleases, and modified by diethyl pyrocarbonate (adenines) or osmium tetroxide (thymines) in a non-uniform way, suggesting that the bulges have a precise structure that leads to exposure of some, but not all, of the bases. In contrast the multiple mismatches ('bubbles') cause very much less bending of the DNA fragment in which they occur, and uniform patterns of chemical reactivity along the length of the mismatched sequences, suggesting a less well defined, and possibly flexible, structure. The precise structure of the bulges suggests that such features may be especially significant for recognition by proteins.
Full text
PDF



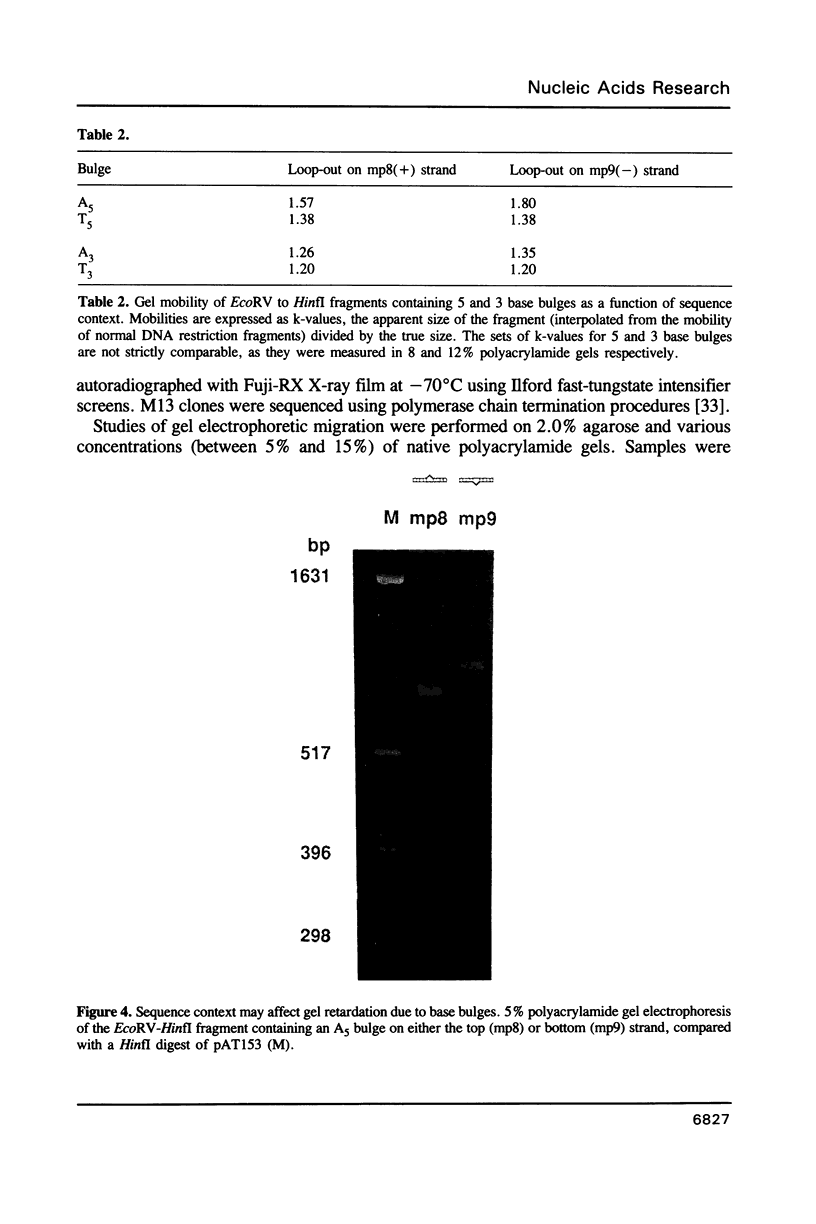
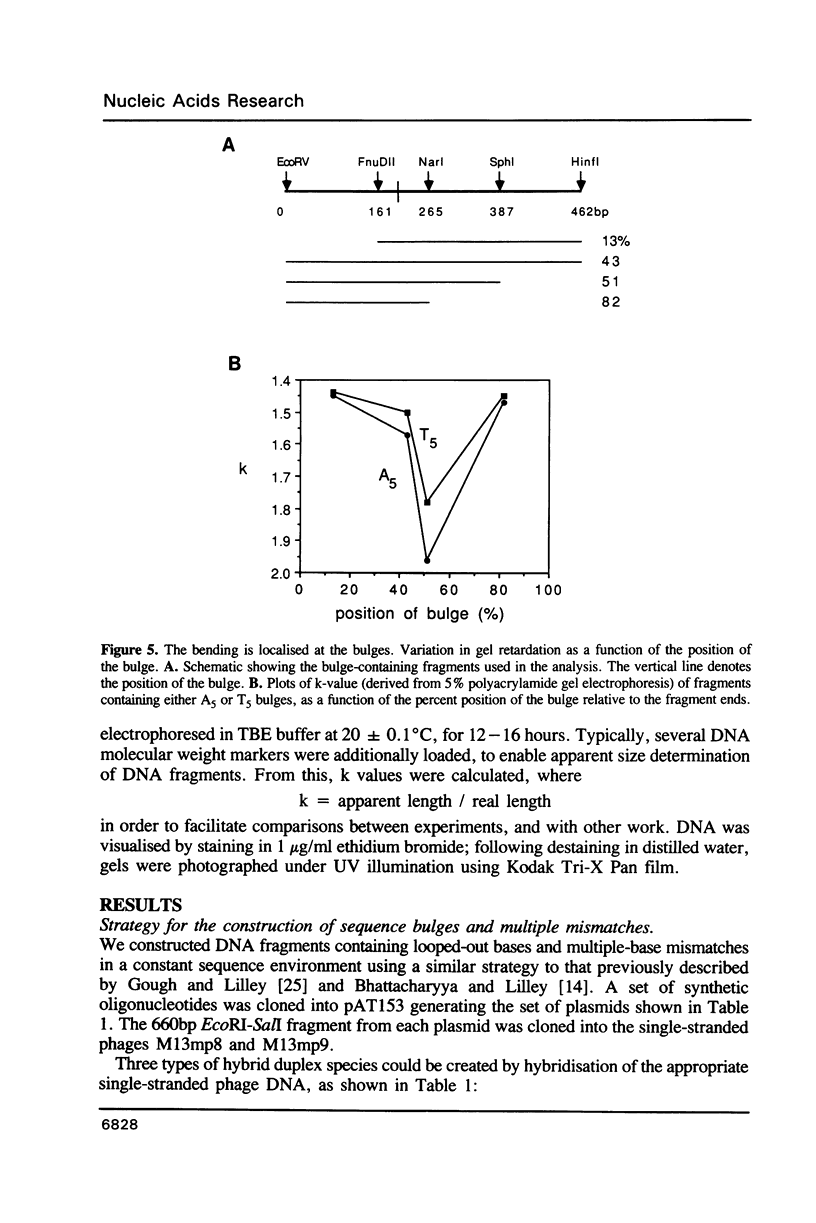





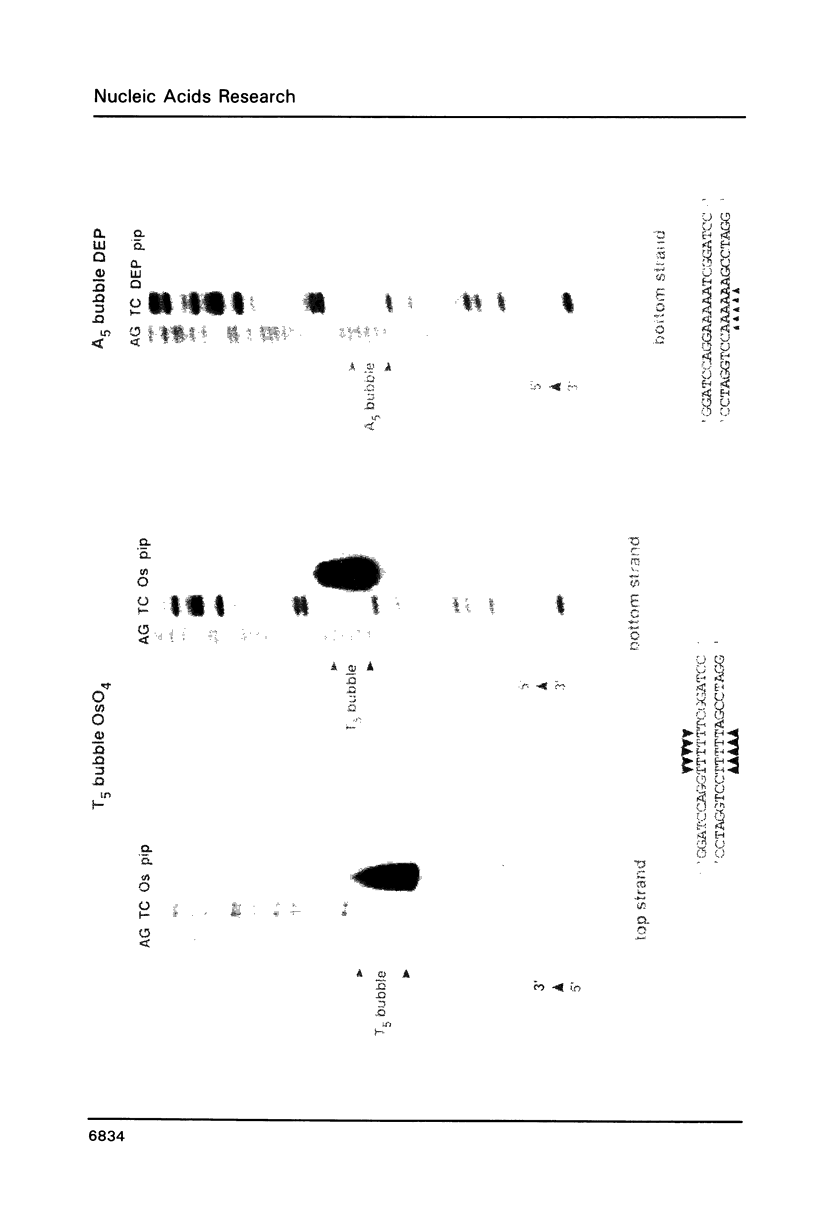






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold F. H., Wolk S., Cruz P., Tinoco I., Jr Structure, dynamics, and thermodynamics of mismatched DNA oligonucleotide duplexes d(CCCAGGG)2 and d(CCCTGGG)2. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 30;26(13):4068–4075. doi: 10.1021/bi00387a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkner K. L., Folk W. R. Polynucleotide kinase exchange reaction: quantitave assay for restriction endonuclease-generated 5'-phosphoroyl termini in DNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3176–3184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckle M., Buc H. Fine mapping of DNA single-stranded regions using base-specific chemical probes: study of an open complex formed between RNA polymerase and the lac UV5 promoter. Biochemistry. 1989 May 16;28(10):4388–4396. doi: 10.1021/bi00436a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline S. W., Yarus M., Wier P. Construction of a systematic set of tRNA mutants by ligation of synthetic oligonucleotides into defined single-stranded gaps. DNA. 1986 Feb;5(1):37–51. doi: 10.1089/dna.1986.5.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis A. G., Haasnoot J. H., den Hartog J. F., de Rooij M., van Boom J. H., Cornelis A. Local destabilisation of a DNA double helix by a T--T wobble pair. Nature. 1979 Sep 20;281(5728):235–236. doi: 10.1038/281235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton R. G., Rodrigues N. R., Campbell R. D. Reactivity of cytosine and thymine in single-base-pair mismatches with hydroxylamine and osmium tetroxide and its application to the study of mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4397–4401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S., Wang J. C. On the sequence determinants and flexibility of the kinetoplast DNA fragment with abnormal gel electrophoretic mobilities. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Lomonossoff G. P., Laskey R. A. High sequence specificity of micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2659–2673. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodgson J. B., Wells R. D. Synthesis and thermal melting behavior of oligomer-polymer complexes containing defined lengths of mismatched dA-dG and dG-dG nucleotides. Biochemistry. 1977 May 31;16(11):2367–2374. doi: 10.1021/bi00630a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlong J. C., Lilley D. M. Highly selective chemical modification of cruciform loops by diethyl pyrocarbonate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 27;14(10):3995–4007. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.10.3995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough G. W., Lilley D. M. DNA bending induced by cruciform formation. Nature. 1985 Jan 10;313(5998):154–156. doi: 10.1038/313154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Sequence dependence of the curvature of DNA: a test of the phasing hypothesis. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7033–7037. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hare D., Shapiro L., Patel D. J. Extrahelical adenosine stacks into right-handed DNA: solution conformation of the d(C-G-C-A-G-A-G-C-T-C-G-C-G) duplex deduced from distance geometry analysis of nuclear Overhauser effect spectra. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7456–7464. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W. Diethyl pyrocarbonate: a chemical probe for secondary structure in negatively supercoiled DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8009–8013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh C. H., Griffith J. D. Deletions of bases in one strand of duplex DNA, in contrast to single-base mismatches, produce highly kinked molecules: possible relevance to the folding of single-stranded nucleic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4833–4837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston B. H., Rich A. Chemical probes of DNA conformation: detection of Z-DNA at nucleotide resolution. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):713–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshua-Tor L., Rabinovich D., Hope H., Frolow F., Appella E., Sussman J. L. The three-dimensional structure of a DNA duplex containing looped-out bases. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):82–84. doi: 10.1038/334082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleff S., Kemper B. Initiation of heteroduplex-loop repair by T4-encoded endonuclease VII in vitro. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1527–1535. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02972.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouchakdjian M., Li B. F., Swann P. F., Patel D. J. Pyrimidine.pyrimidine base-pair mismatches in DNA. A nuclear magnetic resonance study of T.T pairing at neutral pH and C.C pairing at acidic pH in dodecanucleotide duplexes. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 5;202(1):139–155. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90526-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard N. J., McDonald J. J., Henderson R. E., Reichmann M. E. Reaction of diethyl pyrocarbonate with nucleic acid components. Adenosine. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 31;10(18):3335–3342. doi: 10.1021/bi00794a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. Dynamic, sequence-dependent DNA structure as exemplified by cruciform extrusion from inverted repeats in negatively supercoiled DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):101–112. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Palecek E. The supercoil-stabilised cruciform of ColE1 is hyper-reactive to osmium tetroxide. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1187–1192. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01949.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. The inverted repeat as a recognizable structural feature in supercoiled DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6468–6472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V. I., Mirkin S. M., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. A pH-dependent structural transition in the homopurine-homopyrimidine tract in superhelical DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Oct;3(2):327–338. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10508420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace H. A., Pelham H. R., Travers A. A. Association of an S1 nuclease-sensitive structure with short direct repeats 5' of Drosophila heat shock genes. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):555–557. doi: 10.1038/304555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini J. C., Levene S. D., Crothers D. M., Englund P. T. Bent helical structure in kinetoplast DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7664–7668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClellan J. A., Palecek E., Lilley D. M. (A-T)n tracts embedded in random sequence DNA--formation of a structure which is chemically reactive and torsionally deformable. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 9;14(23):9291–9309. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.23.9291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M., Harrison R. W., Wlodawer A., Appella E., Sussman J. L. Crystal structure of 15-mer DNA duplex containing unpaired bases. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):85–86. doi: 10.1038/334085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrich P. DNA mismatch correction. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:435–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Lumelsky N., Lerman L. S., Maniatis T. Detection of single base substitutions in total genomic DNA. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):495–498. doi: 10.1038/313495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Wells R. D. Cruciform structures in supercoiled DNA. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):466–470. doi: 10.1038/289466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardi A., Morden K. M., Patel D. J., Tinoco I., Jr Kinetics for exchange of imino protons in the d(C-G-C-G-A-A-T-T-C-G-C-G) double helix and in two similar helices that contain a G . T base pair, d(C-G-T-G-A-A-T-T-C-G-C-G), and an extra adenine, d(C-G-C-A-G-A-A-T-T-C-G-C-G). Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 7;21(25):6567–6574. doi: 10.1021/bi00268a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Marky L. A., Rice J. A., Broka C., Itakura K., Breslauer K. J. Extra adenosine stacks into the self-complementary d(CGCAGAATTCGCG) duplex in solution. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 2;21(3):445–451. doi: 10.1021/bi00532a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Haniford D. B., Morgan A. R. A structural basis for S1 nuclease sensitivity of double-stranded DNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):271–280. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice J. A., Crothers D. M. DNA bending by the bulge defect. Biochemistry. 1989 May 16;28(10):4512–4516. doi: 10.1021/bi00436a058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripley L. S. Model for the participation of quasi-palindromic DNA sequences in frameshift mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4128–4132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J., Lowary P., Wu H. N., Stormo G., Uhlenbeck O. C. RNA binding site of R17 coat protein. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 24;26(6):1563–1568. doi: 10.1021/bi00380a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Sklenar V., Appella E., Cohen J. S. Conformational perturbation due to an extra adenosine in a self-complementary oligodeoxynucleotide duplex. Biopolymers. 1987 Dec;26(12):2041–2052. doi: 10.1002/bip.360261206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholten P. M., Nordheim A. Diethyl pyrocarbonate: a chemical probe for DNA cruciforms. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 27;14(10):3981–3993. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.10.3981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha N. D., Biernat J., McManus J., Köster H. Polymer support oligonucleotide synthesis XVIII: use of beta-cyanoethyl-N,N-dialkylamino-/N-morpholino phosphoramidite of deoxynucleosides for the synthesis of DNA fragments simplifying deprotection and isolation of the final product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4539–4557. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincze A., Henderson R. E., McDonald J. J., Leonard N. J. Reaction of diethyl pyrocarbonate with nucleic acid components. Bases and nucleosides derived from guanine, cytosine, and uracil. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Apr 18;95(8):2677–2682. doi: 10.1021/ja00789a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodson S. A., Crothers D. M. Structural model for an oligonucleotide containing a bulged guanosine by NMR and energy minimization. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3130–3141. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]