Abstract
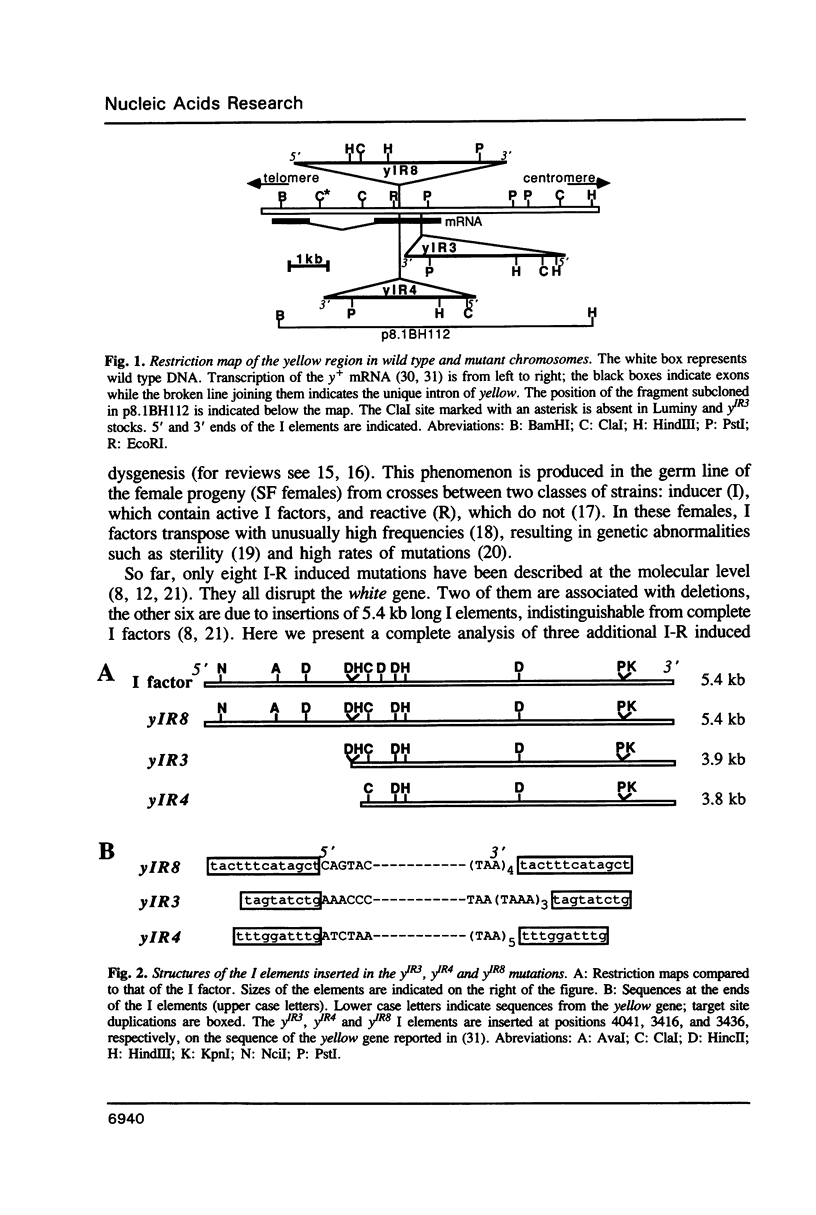
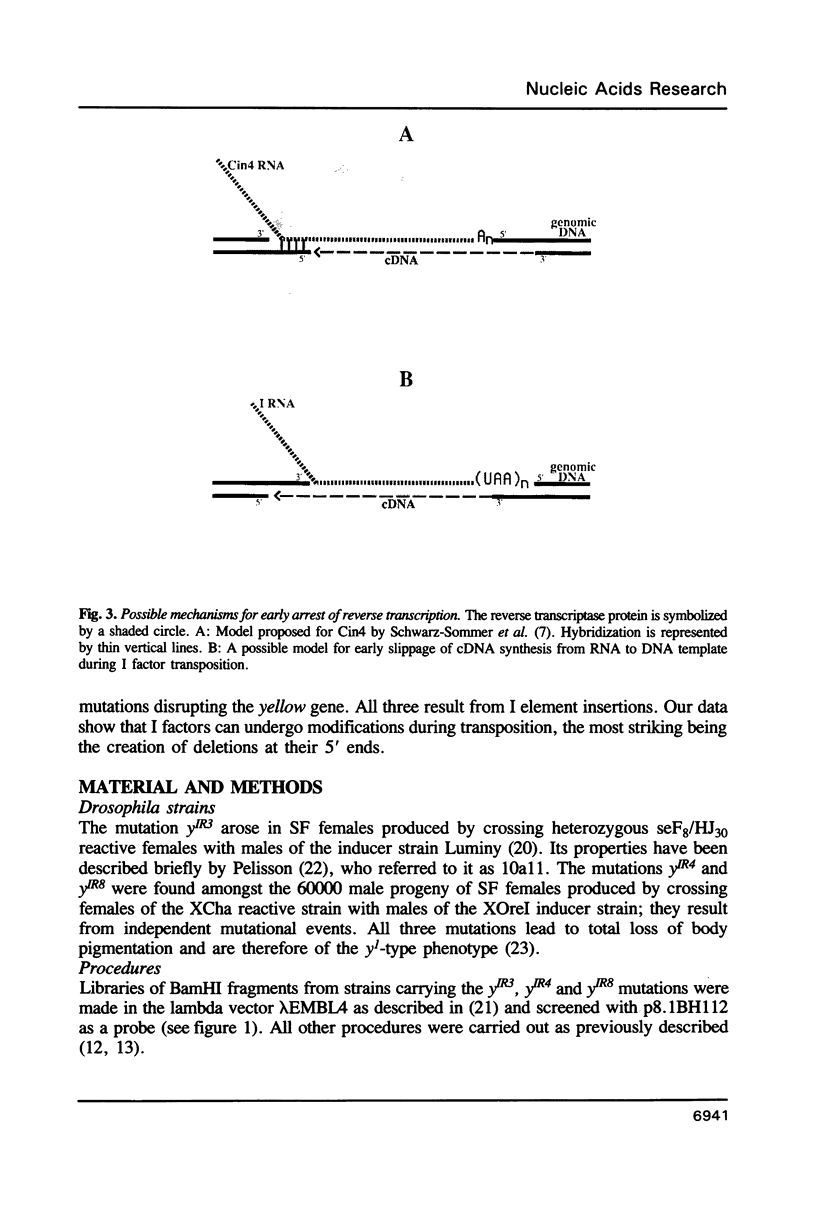
I factors in Drosophila melanogaster are transposable elements structurally related to Mammalian LINEs. Their transposition is activated at high frequencies during I-R hybrid dysgenesis and is associated with the production of mutations of various sorts. Very few of these mutations have been studied at the molecular level; those reported so far result either from chromosomal rearrangements or from insertions of complete I factors. We have analysed three I-R induced yellow mutations and have found that one of them is due to the insertion of an I element very similar to the complete I factor, whereas the other two are due to insertions of I elements that are truncated at their 5' ends; one of them exhibits an unusual 3' end. We discuss possible mechanisms of production of such modified I elements.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bucheton A., Paro R., Sang H. M., Pelisson A., Finnegan D. J. The molecular basis of I-R hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: identification, cloning, and properties of the I factor. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90536-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campuzano S., Carramolino L., Cabrera C. V., Ruíz-Gómez M., Villares R., Boronat A., Modolell J. Molecular genetics of the achaete-scute gene complex of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):327–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chia W., Howes G., Martin M., Meng Y. B., Moses K., Tsubota S. Molecular analysis of the yellow locus of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3597–3605. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04688.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crozatier M., Vaury C., Busseau I., Pelisson A., Bucheton A. Structure and genomic organization of I elements involved in I-R hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9199–9213. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ambrosio E., Waitzkin S. D., Witney F. R., Salemme A., Furano A. V. Structure of the highly repeated, long interspersed DNA family (LINE or L1Rn) of the rat. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):411–424. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Casari G. Related polypeptides are encoded by Drosophila F elements, I factors, and mammalian L1 sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5843–5847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Digan M. E., Dawid I. B. A family of oligo-adenylate-terminated transposable sequences in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 25;168(4):715–727. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T. G., Singer M. F. LINE-1: a mammalian transposable element. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 8;910(3):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. H., Lister C. K., Kellett E., Finnegan D. J. Transposable elements controlling I-R hybrid dysgenesis in D. melanogaster are similar to mammalian LINEs. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90815-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN M. M. Complementation at the yellow locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1961 Nov;46:1385–1388. doi: 10.1093/genetics/46.11.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer P. K., Spana C., Corces V. G. On the molecular mechanism of gypsy-induced mutations at the yellow locus of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2657–2662. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04548.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Kuhara S., Takenaka O., Sakaki Y. L1 family of repetitive DNA sequences in primates may be derived from a sequence encoding a reverse transcriptase-related protein. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):625–628. doi: 10.1038/321625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian H. H., Jr, Wong C., Youssoufian H., Scott A. F., Phillips D. G., Antonarakis S. E. Haemophilia A resulting from de novo insertion of L1 sequences represents a novel mechanism for mutation in man. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):164–166. doi: 10.1038/332164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel B. E., ole-MoiYoi O. K., Young J. R. Ingi, a 5.2-kb dispersed sequence element from Trypanosoma brucei that carries half of a smaller mobile element at either end and has homology with mammalian LINEs. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1465–1475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. D., Padgett R. W., Hardies S. C., Shehee W. R., Comer M. B., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd The sequence of a large L1Md element reveals a tandemly repeated 5' end and several features found in retrotransposons. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):168–182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrokhi L. J., Georgieva S. G., Ilyin Y. V. jockey, a mobile Drosophila element similar to mammalian LINEs, is transcribed from the internal promoter by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):685–691. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Green M. M., Rubin G. M. Partial revertants of the transposable element-associated suppressible allele white-apricot in Drosophila melanogaster: structures and responsiveness to genetic modifiers. Genetics. 1988 Feb;118(2):221–234. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard G., Bregliano J. C., Bucheton A., Lavige J. M., Pelisson A., Kidwell M. G. Non-mendelian female sterility and hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Genet Res. 1978 Nov;32(3):275–287. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300018772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard G. Non-mendelian female sterility in Drosophila melanogaster: hereditary transmission of I factor. Genetics. 1976 May;83(1):107–123. doi: 10.1093/genetics/83.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priimägi A. F., Mizrokhi L. J., Ilyin Y. V. The Drosophila mobile element jockey belongs to LINEs and contains coding sequences homologous to some retroviral proteins. Gene. 1988 Oct 30;70(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard M. A., Dura J. M., Pélisson A., Bucheton A., Finnegan D. J. A cloned I-factor is fully functional in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Nov;214(3):533–540. doi: 10.1007/BF00330491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pélisson A. The I--R system of hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: are I factor insertions responsible for the mutator effect of the I--R interaction? Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(1):123–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00270149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sang H. M., Pélisson A., Bucheton A., Finnegan D. J. Molecular lesions associated with white gene mutations induced by I-R hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3079–3085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02262.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Leclercq L., Göbel E., Saedler H. Cin4, an insert altering the structure of the A1 gene in Zea mays, exhibits properties of nonviral retrotransposons. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3873–3880. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02727.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]