Abstract
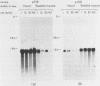
Several types of evidence indicate that the gene coding for the skeletal muscle actin is expressed in the rat heart: 1) A recombinant plasmid containing an insert with a nucleotide sequence identical to that of the homologous region of skeletal muscle actin gene was isolated from a cDNA library prepared on rat cardiac mRNA template. 2) Using specific probes it was found that the hearts of newborn rats contain a significant amount of skeletal muscle actin mRNA. The quantity of this mRNA in the heart decreases during development. 3) The skeletal muscle actin gene is DNAase I sensitive in nuclei from rat heart tissue. A plasmid containing a cDNA insert homologous to a part of the cardiac actin mRNA was isolated and sequenced. It was found that in spite of the great similarity between the amino acid sequence of the skeletal muscle and cardiac actins, the nucleotide sequences of the two mRNAs are considerably divergent. There is only limited sequence homology between the 3' untranslated regions of the two mRNAs. However, there is an extensive sequence homology between the 3' untranslated regions of the rat and human cardiac mRNAs, suggesting a functional role for this region of the gene or mRNA.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Nageotte R., Chambraud B., Rougeon F. Mouse immunoglobulin genes: a bacterial plasmid containing the entire coding sequence for a pre-gamma 2a heavy chain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1231–1241. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Pictet R. L., Rutter W. J., Cordell B., Tischer E., Goodman H. M. Sequence of the human insulin gene. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):26–32. doi: 10.1038/284026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellard M., Gannon F., Chambon P. Nucleosome structure III: the structure and transcriptional activity of the chromatin containing the ovalbumin and globin genes in chick oviduct nuclei. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):779–791. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmon Y., Czosnek H., Nudel U., Shani M., Yaffe D. DNAase I sensitivity of genes expressed during myogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3085–3098. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chizzonite R. A., Everett A. W., Clark W. A., Jakovcic S., Rabinowitz M., Zak R. Isolation and characterization of two molecular variants of myosin heavy chain from rabbit ventricle. Change in their content during normal growth and after treatment with thyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):2056–2065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke N. E., Coit D., Shine J., Baxter J. D., Martial J. A. Human prolactin. cDNA structural analysis and evolutionary comparisons. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):4007–4016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke N. E., Coit D., Weiner R. I., Baxter J. D., Martial J. A. Structure of cloned DNA complementary to rat prolactin messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6502–6510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeNoto F. M., Moore D. D., Goodman H. M. Human growth hormone DNA sequence and mRNA structure: possible alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3719–3730. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornwald J. A., Kuncio G., Peng I., Ordahl C. P. The complete nucleotide sequence of the chick a-actin gene and its evolutionary relationship to the actin gene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):3861–3876. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.3861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garel A., Axel R. Selective digestion of transcriptionally active ovalbumin genes from oviduct nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3966–3970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I., Gibson W. Identification and characterization of multiple forms of actin. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):793–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A. Isolation and partial characterization of the Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Petrino M. G., Kakunaga T. Molecular structure and evolutionary origin of human cardiac muscle actin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5901–5905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Tanese N., Fuchs E. Complementary DNA sequence of a human cytoplasmic actin. Interspecies divergence of 3' non-coding regions. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 5;163(4):673–678. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90117-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P., Rosenthal N., Efstratidadis A., Gilbert W., Kolodner R., Tizard R. The structure and evolution of the two nonallelic rat preproinsulin genes. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):545–558. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon I., Bhorjee J. S. Isolation and characterization of nuclei and purification of chromatin from differentiating cultures of rat skeletal muscle. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Jan;137(1):141–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A. J., Alonso S., Caravatti M., Buckingham M. E. A fetal skeletal muscle actin mRNA in the mouse and its identity with cardiac actin mRNA. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Katcoff D., Zakut R., Shani M., Carmon Y., Finer M., Czosnek H., Ginsburg I., Yaffe D. Isolation and characterization of rat skeletal muscle and cytoplasmic actin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2763–2767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Zakut R., Shani M., Neuman S., Levy Z., Yaffe D. The nucleotide sequence of the rat cytoplasmic beta-actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1759–1771. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordahl C. P., Cooper T. A. Strong homology in promoter and 3'-untranslated regions of chick and rat alpha-actin genes. Nature. 1983 May 26;303(5915):348–349. doi: 10.1038/303348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page G. S., Smith S., Goodman H. M. DNA sequence of the rat growth hormone gene: location of the 5' terminus of the growth hormone mRNA and identification of an internal transposon-like element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 11;9(9):2087–2104. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.9.2087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perler F., Efstratiadis A., Lomedico P., Gilbert W., Kolodner R., Dodgson J. The evolution of genes: the chicken preproinsulin gene. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90641-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shani M., Nudel U., Zevin-Sonkin D., Zakut R., Givol D., Katcoff D., Carmon Y., Reiter J., Frischauf A. M., Yaffe D. Skeletal muscle actin mRNA. Characterization of the 3' untranslated region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):579–589. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storti R. V., Rich A. Chick cytoplasmic actin and muscle actin have different structural genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2346–2350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Groudine M. Chromosomal subunits in active genes have an altered conformation. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):848–856. doi: 10.1126/science.948749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Butler-Browne G. S., Gros F. Identification of a novel form of myosin light chain present in embryonic muscle tissue and cultured muscle cells. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):415–431. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Butler-Browne G. S., Gros F. Protein synthesis and actin heterogeneity in calf muscle cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2018–2022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Sell S. M., Butler-Browne G. S., Schwartz K., Bouveret P., Pinset-Härstöm I. Three myosin heavy-chain isozymes appear sequentially in rat muscle development. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):805–809. doi: 10.1038/292805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Sell S. M., Eriksson A., Thornell L. E. Myosin subunit types in skeletal and cardiac tissues and their developmental distribution. Dev Biol. 1982 Jun;91(2):478–484. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Sell S. M. Myosin from fetal hearts contains the skeletal muscle embryonic light chain. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):731–733. doi: 10.1038/286731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Bingham P. M., Livak K. J., Holmgren R., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: I. Evidence for higher order domains of defined DNA sequence. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakut R., Shani M., Givol D., Neuman S., Yaffe D., Nudel U. Nucleotide sequence of the rat skeletal muscle actin gene. Nature. 1982 Aug 26;298(5877):857–859. doi: 10.1038/298857a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]