Abstract
cDNA libraries have been constructed from mRNAs isolated from mature male DBA/2 mouse submaxillary glands. Several recombinant plasmids have been assigned to particular mRNA species and their in vitro translation products by HART and hybrid selection. Clones containing copies of two abundant mRNA species that showed no sexual dimorphism were selected for detailed characterisation. Nucleotide sequences determined from one series of clones define an 850 nucleotide mRNA encoding a polypeptide of 16.5 kd having an N-terminal signal sequence, an acidic core and four glycosylation sites. A second family of clones correspond to an mRNA of 800 nucleotides, the sequence of which can be interpreted as coding for an intracellular protein of 14.7 kd. Computer searches of protein and nucleic acid sequences have not revealed the identity of either of these submaxillary gland products.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barka T. Biologically active polypeptides in submandibular glands. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Aug;28(8):836–859. doi: 10.1177/28.8.7003006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catanzaro D. F., Mullins J. J., Morris B. J. The biosynthetic pathway of renin in mouse submandibular gland. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7364–7368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin W. W., Kronenberg H. M., Dee P. C., Maloof F., Habener J. F. Nucleotide sequence of the mRNA encoding the pre-alpha-subunit of mouse thyrotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5329–5333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Similar amino acid sequences: chance or common ancestry? Science. 1981 Oct 9;214(4517):149–159. doi: 10.1126/science.7280687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray A., Dull T. J., Ullrich A. Nucleotide sequence of epidermal growth factor cDNA predicts a 128,000-molecular weight protein precursor. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):722–725. doi: 10.1038/303722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
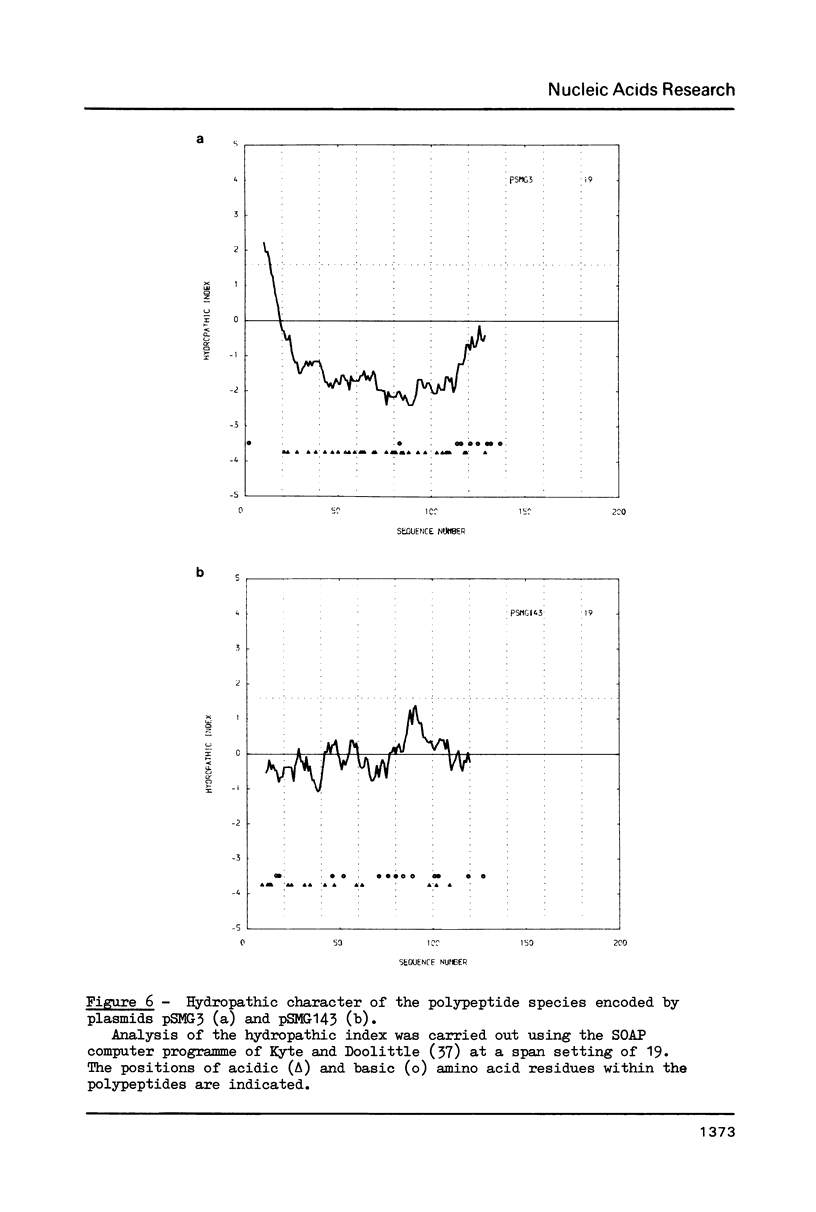
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Grez M., Hauser H., Lindenmaier W., Schütz G. 5'-Terminal sequences of eucaryotic mRNA can be cloned with high efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2251–2266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason A. J., Evans B. A., Cox D. R., Shine J., Richards R. I. Structure of mouse kallikrein gene family suggests a role in specific processing of biologically active peptides. Nature. 1983 May 26;303(5915):300–307. doi: 10.1038/303300a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. J., Burt D. W., Windass J. D., McTurk P., George H., Brammar W. J. Molecular cloning of two distinct renin genes from the DBA/2 mouse. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1461–1466. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01338.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyes B. E., Mevarech M., Stein R., Agarwal K. L. Detection and partial sequence analysis of gastrin mRNA by using an oligodeoxynucleotide probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1770–1774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccini N., Knopf J. L., Gross K. W. A DNA polymorphism, consistent with gene duplication, correlates with high renin levels in the mouse submaxillary gland. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):205–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt R. E., Dzau V. J., Ouellette A. J. Abundant androgen regulated mRNAs in mouse submandibular gland: cell-free translation of renin precursor mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3433–3449. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronne H., Lundgren S., Severinsson L., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Growth factor-binding proteases in the murine submaxillary gland: isolation of a cDNA clone. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1561–1564. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01624.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougeon F., Chambraud B., Foote S., Panthier J. J., Nageotte R., Corvol P. Molecular cloning of a mouse submaxillary gland renin cDNA fragment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6367–6371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roukema P. A., Oderkerk C. H., Salkinoga-Salonen M. S. The murine sublingual and submandibular mucins. Their isolation and characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 23;428(2):432–440. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Selby M., Urdea M., Quiroga M., Bell G. I., Rutter W. J. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the precursor of mouse nerve growth factor. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):538–540. doi: 10.1038/302538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Urdea M., Quiroga M., Sanchez-Pescador R., Fong N., Selby M., Rutter W. J., Bell G. I. Structure of a mouse submaxillary messenger RNA encoding epidermal growth factor and seven related proteins. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):236–240. doi: 10.1126/science.6602382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiness D., Darnell J. E. Polyadenylic acid segment in mRNA becomes shorter with age. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 28;241(113):265–268. doi: 10.1038/newbio241265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skup D., Windass J. D., Sor F., George H., Williams B. R., Fukuhara H., De Maeyer-Guignard J., De Maeyer E. Molecular cloning of partial cDNA copies of two distinct mouse IFN-beta mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3069–3084. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Berman C., Dull T. J. Human beta-nerve growth factor gene sequence highly homologous to that of mouse. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):821–825. doi: 10.1038/303821a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. M., Cherry M., Taylor B. A., Wilson J. D. Genetic and endocrine control of renin activity in the submaxillary gland of the mouse. Biochem Genet. 1981 Jun;19(5-6):509–523. doi: 10.1007/BF00484623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. M., Erdös E. G., Wilson J. D., Taylor B. A. Location on chromosome 1 of Rnr, a gene that regulates renin in the submaxillary gland of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5623–5626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windass J. D., Brammar W. J. Aberrant immunity behaviour of hybrid lambda imm21 phages containing the DNA of ColE1-type plasmids. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;172(3):329–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00271733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D., Blanchetot A., Jeffreys A. J. Molecular cloning of seal myoglobin mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7133–7144. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]