Abstract
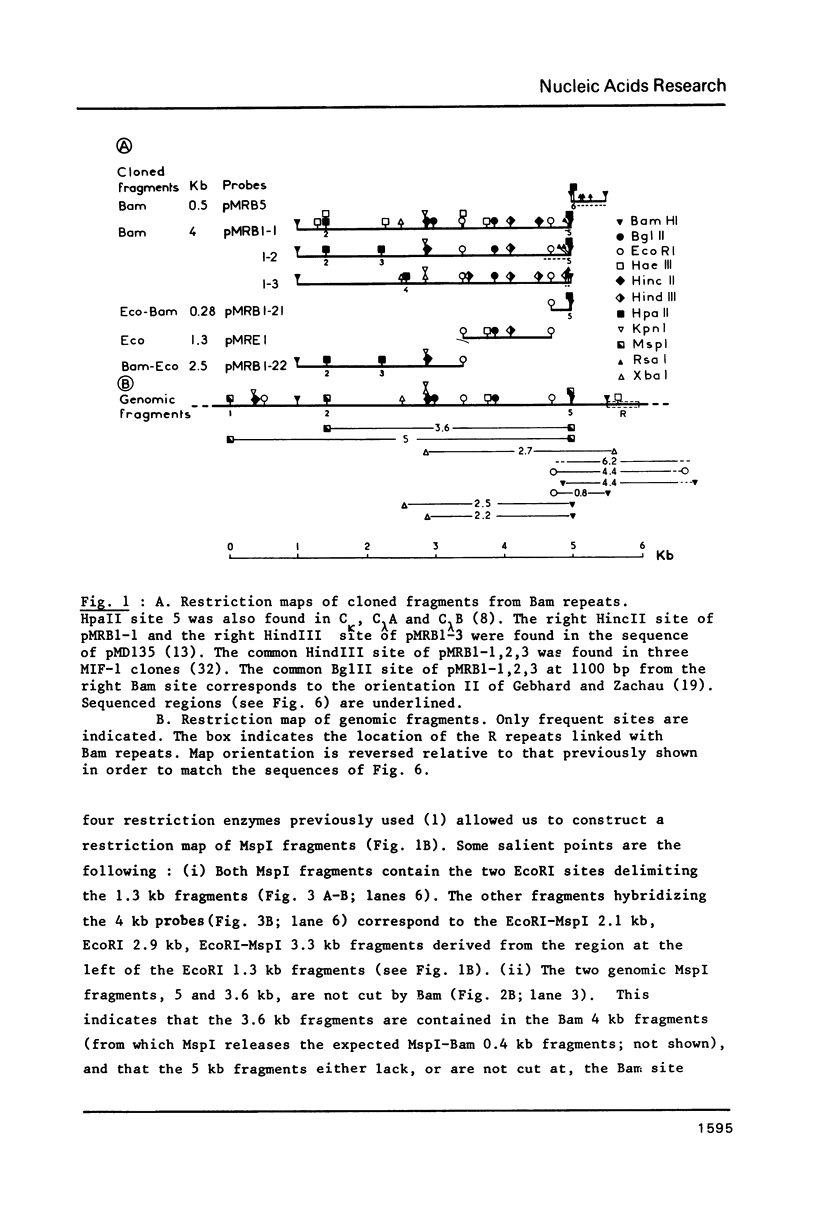
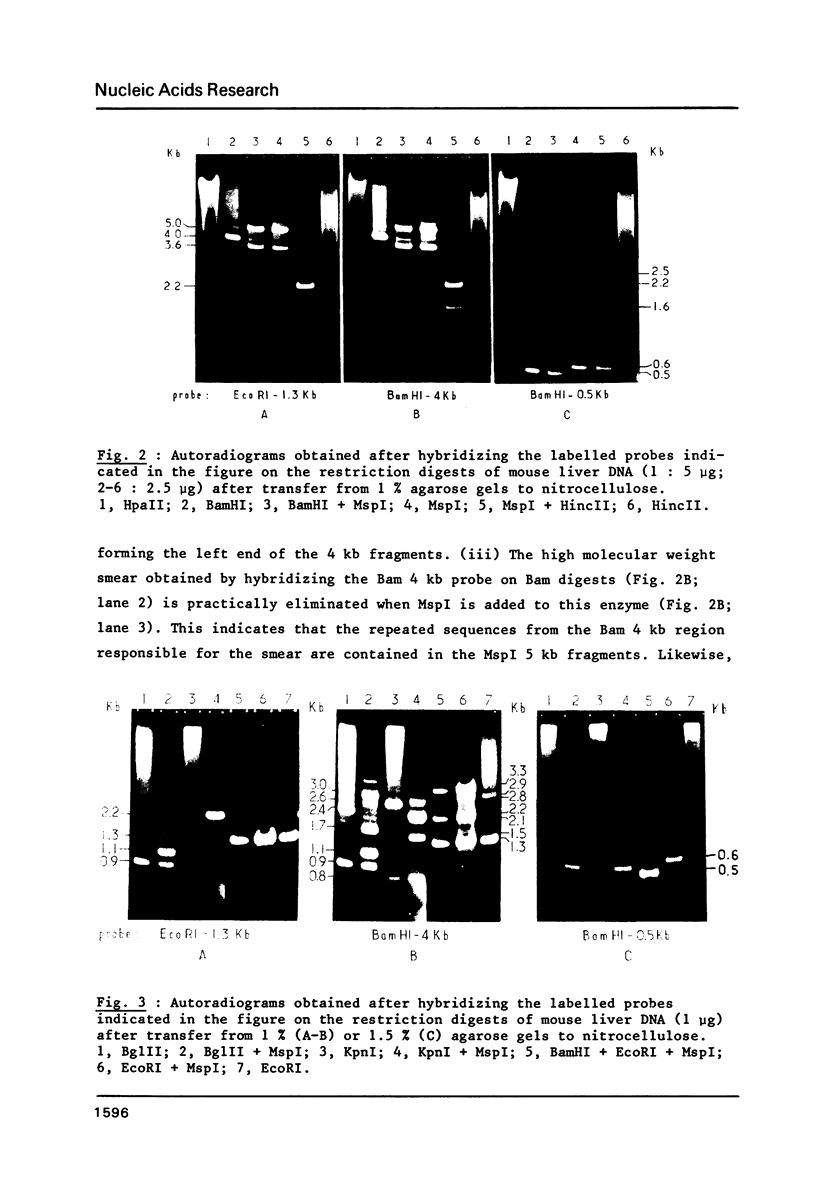
Mouse DNA contains two equally abundant, homologous subfamilies of MspI 3.6 and 5 kb repeated fragments. The first subfamily corresponds to the previously described (1) Bam 4 kb repeats, the second one to Bam repeated fragments of higher molecular weight. These subfamilies account for the vast majority of long Bam repeats and are linked with contiguous short Bam 0.5 kb repeats. A minority of these composite Bam repeats extend, on the 0.5 kb side, into R repeats. In turn, a fraction of the composite Bam/R repeats extend further, for at least 3 kb, into other repeated sequences contiguous to the R repeats. The long Bam repeats belong, therefore, in at least three superfamilies of repeats, the longest one being over 9 kb in size. Some general properties of these superfamilies are discussed.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown A., Huang R. C. Mouse EcoRI satellite DNA contains a sequence homologous to the long terminal repeat of the intracisternal A particle gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6123–6127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. D., Dover G. Organization and evolutionary progress of a dispersed repetitive family of sequences in widely separated rodent genomes. J Mol Biol. 1981 Aug 25;150(4):441–466. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90374-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. D., Piechaczyk M. Insertion sequences and tandem repetitions as sources of variation in a dispersed repeat family. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 5;165(2):249–256. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80256-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. M., Schildkraut C. L. A family of moderately repetitive sequences in mouse DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4075–4090. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuny G., Soriano P., Macaya G., Bernardi G. The major components of the mouse and human genomes. 1. Preparation, basic properties and compositional heterogeneity. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(2):227–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05227.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T. G. Characterization of a highly repetitive family of DNA sequences in the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):5003–5013. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.5003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T. G. Size and structure of the highly repetitive BAM HI element in mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5073–5091. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhard W., Meitinger T., Höchtl J., Zachau H. G. A new family of interspersed repetitive DNA sequences in the mouse genome. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 25;157(3):453–471. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90471-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhard W., Zachau H. G. Organization of the R family and other interspersed repetitive DNA sequences in the mouse genome. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 25;170(2):255–270. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80147-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigwood N. L., Jahn C. L., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. Locations of three repetitive sequence families found in BALB/c adult beta-globin clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1133–1150. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller R., Arnheim N. Structure and organization of the highly repeated and interspersed 1.3 kb EcoRI-Bg1II sequence family in mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 11;8(21):5031–5042. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.21.5031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Hess I., Zachau H. G. Highly regular arrangement of a restriction-nuclease-sensitive site in rodent satellite DNAs. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 15;45(2):501–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerman M. I., Thayer R. E., Singer M. F. Kpn I family of long interspersed repeated DNA sequences in primates: polymorphism of family members and evidence for transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3966–3970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. Intracisternal A-particle genes: identification in the genome of Mus musculus and comparison of multiple isolates from a mouse gene library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3571–3575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueders K. K., Paterson B. M. A short interspersed repetitive element found near some mouse structural genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7715–7729. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Novel classes of mouse repeated DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 11;8(15):3247–3258. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.15.3247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier-Rotival M., Cortadas J., Macaya G., Bernardi G. Isolation and organization of calf ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;6(6):2109–2123. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.6.2109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier-Rotival M., Soriano P., Cuny G., Strauss F., Bernardi G. Sequence organization and genomic distribution of the major family of interspersed repeats of mouse DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):355–359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A. J., Alonso S., Guénet J. L., Buckingham M. E. Number and organization of actin-related sequences in the mouse genome. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 15;167(1):77–101. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson B., Bernardi G. The distribution of CR1, and Alu-like family of interspersed repeats, in the chicken genome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 2;740(3):339–341. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafit-Zagardo B., Brown F. L., Zavodny P. J., Maio J. J. Transcription of the KpnI families of long interspersed DNAs in human cells. Nature. 1983 Jul 21;304(5923):277–280. doi: 10.1038/304277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;76:67–112. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61789-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F., Thayer R. E., Grimaldi G., Lerman M. I., Fanning T. G. Homology between the KpnI primate and BamH1 (M1F-1) rodent families of long interspersed repeated sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5739–5745. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P., Meunier-Rotival M., Bernardi G. The distribution of interspersed repeats is nonuniform and conserved in the mouse and human genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1816–1820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P., Szabo P., Bernardi G. The scattered distribution of actin genes in the mouse and human genomes. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):579–583. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R., Storb U. Association of two different repetitive DNA elements near immunoglobulin light chain genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1803–1817. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]