Abstract
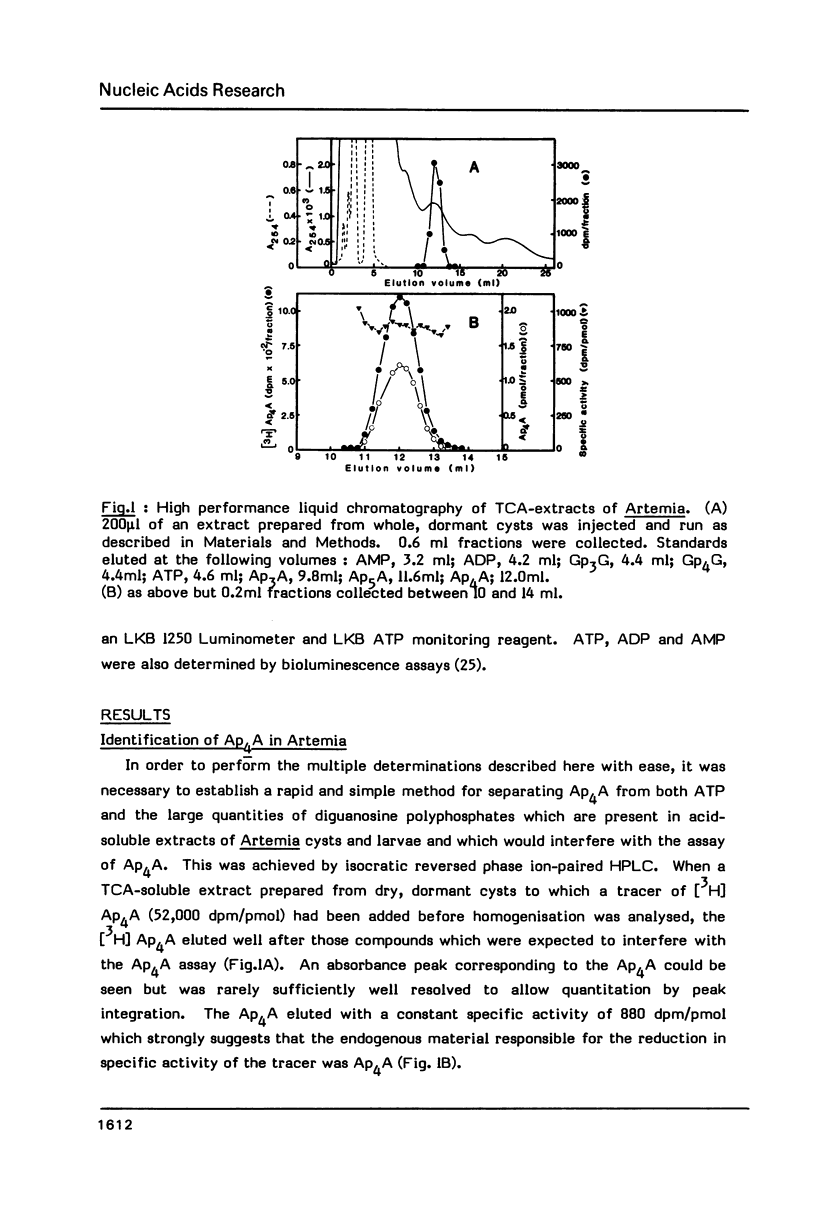
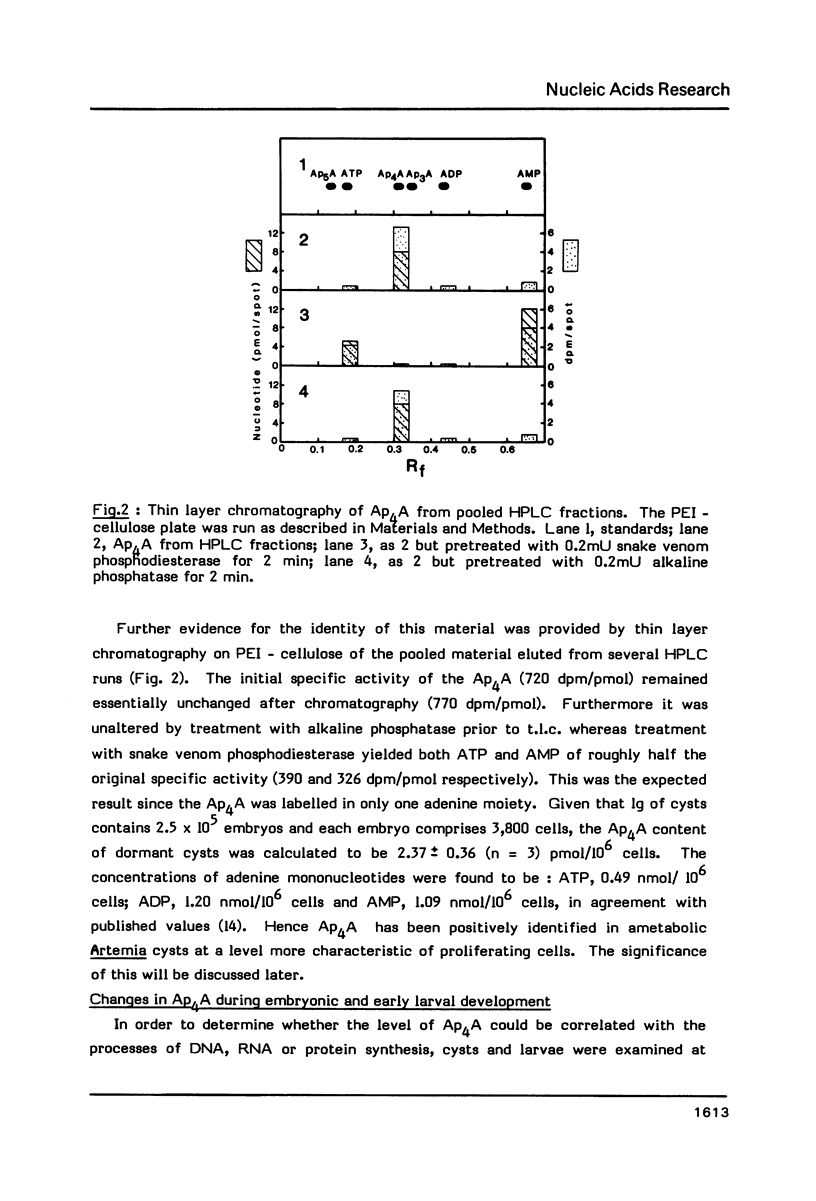
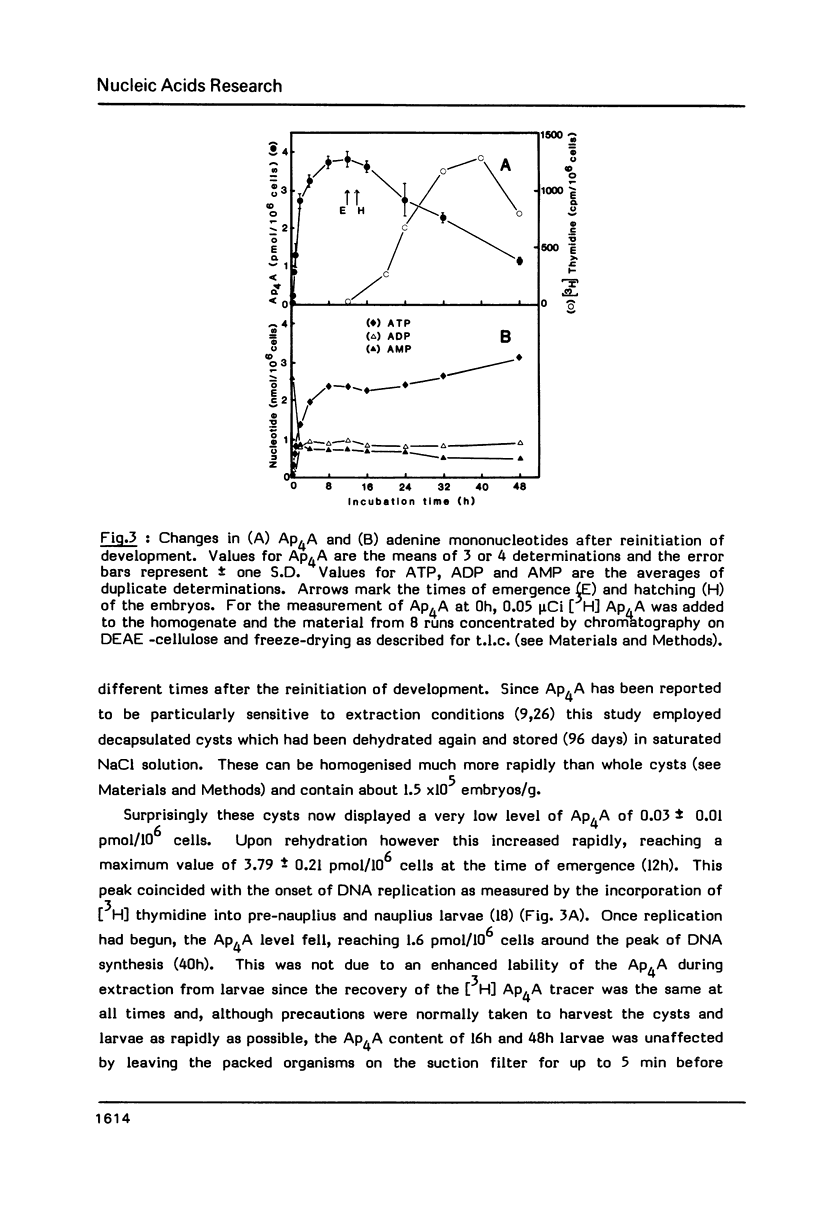
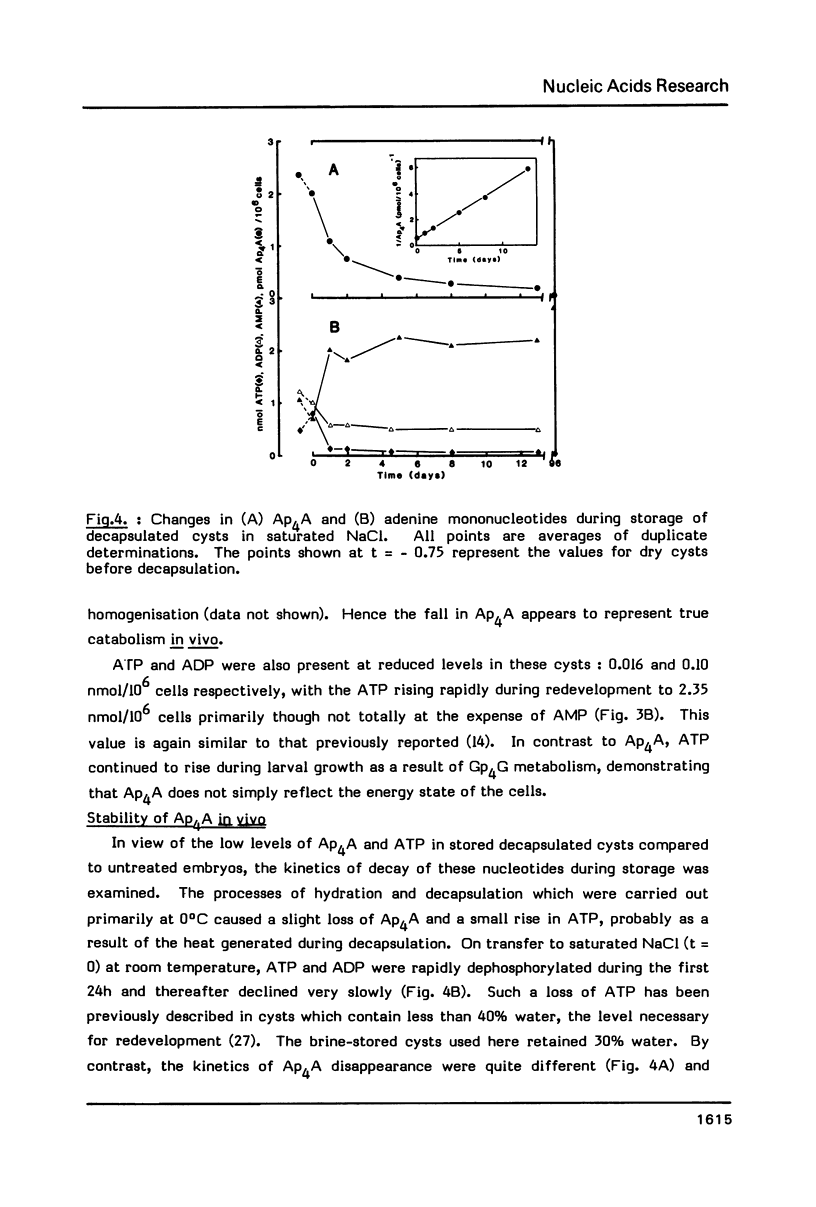
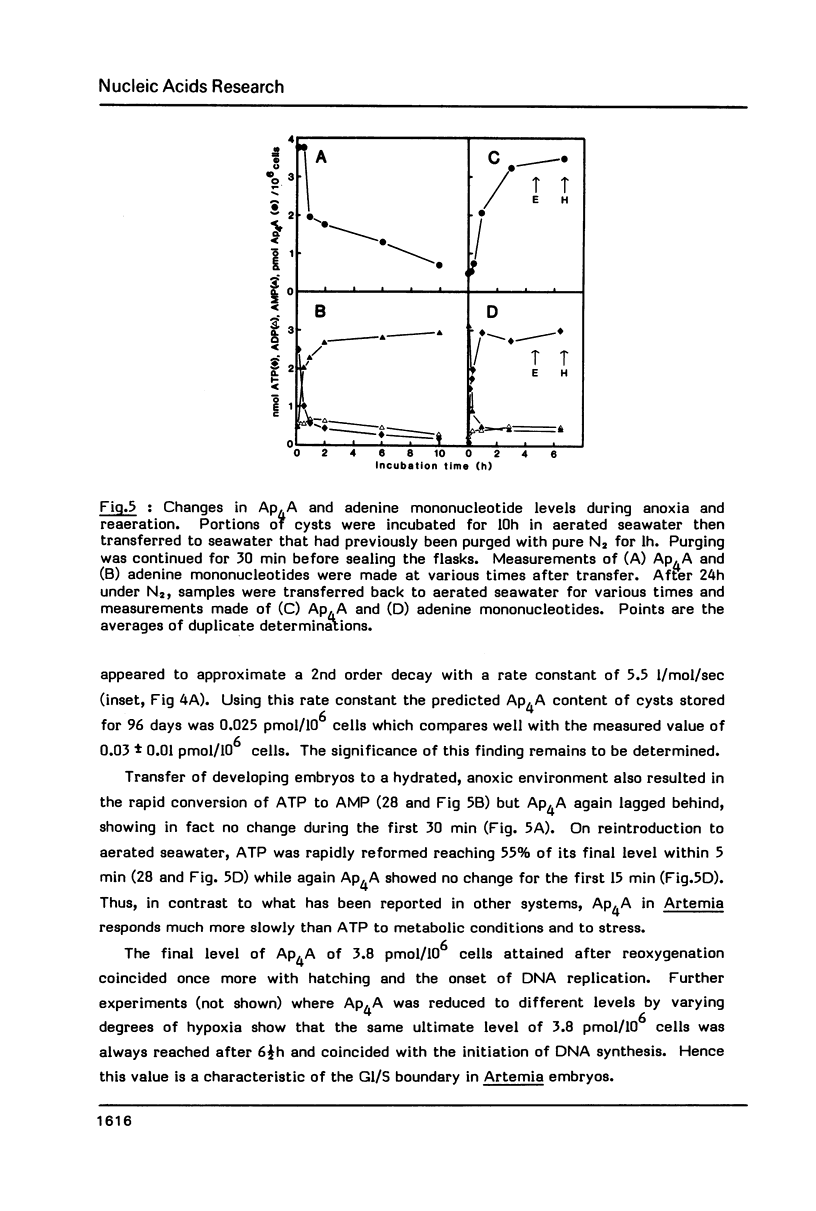
Diadenosine 5',5'"-P1,P4-tetraphosphate (Ap4A) has been detected in cysts and developing embryos of the brine shrimp Artemia in amounts 10(4)-10(6) times lower than that of the guanine analogue, Gp4G. The unexpectedly high level of Ap4A in dormant cysts of 2.37 pmol/10(6) cells can be reduced to 0.03 pmol/10(6) cells by decapsulation and storage in saturated NaCl. When development is reinitiated, the Ap4A content of the decapsulated embryos undergoes a rapid 125 -fold increase, reaching a maximum of 3.79 pmol/10(6) cells at the point of emergence when DNA replication begins. If replication is delayed by hypoxia, the Ap4A level is adjusted in order to reach the same maximum value when replication finally begins. As replication proceeds, the level of Ap4A declines again. Unlike mammalian cells, Ap4A in Artemia is less metabolically labile than ATP. These results are consistent with the suggested role of Ap4A in the initiation of DNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baril E., Bonin P., Burstein D., Mara K., Zamecnik P. Resolution of the diadenosine 5',5"'-P1,P4-tetraphosphate binding subunit from a multiprotein form of HeLa cell DNA polymerase alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4931–4935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes L. D., Culver C. A. Isolation and characterization of diadenosine 5',5"'-P1,P4-tetraphosphate pyrophosphohydrolase from Physarum polycephalum. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6123–6128. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameselle J. C., Costas M. J., Sillero M. A., Sillero A. Bis-(5'-guanosyl) tetraphosphatase in rat tissues. Biochem J. 1982 Feb 1;201(2):405–410. doi: 10.1042/bj2010405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. S., Cavagnaro J. Interrelationships between water and cellular metabolism in Artemia cysts. IV. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate and cyst hydration. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Jun;88(2):159–166. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040880205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flodgaard H., Klenow H. Abundant amounts of diadenosine 5',5"'-P1,P4-tetraphosphate are present and releasable, but metabolically inactive, in human platelets. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 15;208(3):737–742. doi: 10.1042/bj2080737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goerlich O., Foeckler R., Holler E. Mechanism of synthesis of adenosine(5')tetraphospho(5')adenosine (AppppA) by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(1):135–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau V. P., Sillero M. A., Sillero A. Binding of P1,P4-bis(5'-guanosyl)tetraphosphate to brain. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):11848–11851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt F. Diadenosine 5',5'''-P1,P4-tetraphosphate triggers initiation of in vitro DNA replication in baby hamster kidney cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):371–375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt F. Diadenosine tetraphosphate triggers in vitro DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):649–653. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt F., Waltl G., Jantzen H. M., Hamprecht K., Huebscher U., Kuenzle C. C. Diadenosine 5',5'''-P1,P4-tetraphosphate, a ligand of the 57-kilodalton subunit of DNA polymerase alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6081–6085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höhn M., Albert W., Grummt F. Diadenosine tetraphosphate hydrolase from mouse liver. Purification to homogeneity and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3003–3006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubowski H., Guranowski A. Enzymes hydrolyzing ApppA and/or AppppA in higher plants. Purification and some properties of diadenosine triphosphatase, diadenosine tetraphosphatase, and phosphodiesterase from yellow lupin (Lupinus luteus) seeds. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9982–9989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khym J. X. An analytical system for rapid separation of tissue nucleotides at low pressures on conventional anion exchangers. Clin Chem. 1975 Aug;21(9):1245–1252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthje J., Ogilvie A. The presence of diadenosine 5',5'''-P1,P3-triphosphate (Ap3A) in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 30;115(1):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90997-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClean D. K., Warner A. H. Aspects of nucleic acid metabolism during development of the brine shrimp Artemia salina. Dev Biol. 1971 Jan;24(1):88–105. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie A., Antl W. Diadenosine tetraphosphatase from human leukemia cells. Purification to homogeneity and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4105–4109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie A. Determination of diadenosine tetraphosphate (Ap4A) levels in subpicomole quantities by a phosphodiesterase luciferin--luciferase coupled assay: application as a specific assay for diadenosine tetraphosphatase. Anal Biochem. 1981 Aug;115(2):302–307. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardoll D. M., Vogelstein B., Coffey D. S. A fixed site of DNA replication in eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90527-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plateau P., Mayaux J. F., Blanquet S. Zinc(II)-dependent synthesis of diadenosine 5', 5"' -P(1) ,P(4) -tetraphosphate by Escherichia coli and yeast phenylalanyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetases. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 4;20(16):4654–4662. doi: 10.1021/bi00519a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst H., Hamprecht K., Gekeler V. Replicon initiation frequency and intracellular levels of ATP, ADP, AMP and of diadenosine 5',5'''-P1,P4-tetraphosphate in ehrlich ascites cells cultured aerobically and anaerobically. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 27;110(2):688–693. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91204-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport E., Zamecnik P. C. Presence of diadenosine 5',5''' -P1, P4-tetraphosphate (Ap4A) in mamalian cells in levels varying widely with proliferative activity of the tissue: a possible positive "pleiotypic activator". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3984–3988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss J. R., Moffatt J. G. Dismutation reactions of nucleoside polyphosphates. 3. The synthesis of alpha, omega-dinucleoside 5'-polyphosphates. J Org Chem. 1965 Oct;30(10):3381–3387. doi: 10.1021/jo01021a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater J. M., McLennan A. G. DNA polymerases alpha and gamma during pre-emergence and early larval development of Artemia. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec 15;129(2):415–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocco D. M., Beers P. C., Warner A. H. Effect of anoxia on nucleotide metabolism in encysted embryos of the brine shrimp. Dev Biol. 1972 Apr;27(4):479–493. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90187-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Matsunami N., Itaya A., Yoshihara K. Histone-dependent ADP-ribosylation of low molecular nucleotide by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. J Biochem. 1981 Oct;90(4):1131–1139. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallejo C. G., Sillero M. A., Sillero A. Diguanosinetetraphosphate guanylohydrolase in Artemia salina. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 17;358(1):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90264-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Denbos G., Finamore F. J. An unusual pathway for the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate by the purine-requiring organism Artemia salina. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2816–2818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner A. H., Finamore F. J. Nucleotide metabolism during brine shrimp embryogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1933–1937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner A. H., MacRae T. H., Wahba A. J. The use of Artemia salina for developmental studies: preparation of embryos, tRNA, ribosomes and initiation factor 2. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:298–311. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamecnik P. C., Rapaport E., Baril E. F. Priming of DNA synthesis by diadenosine 5',5"'-P1,P4-tetraphosphate with a double-stranded octadecamer as a template and DNA polymerase alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1791–1794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamecnik P. C., Stephenson M. L., Janeway C. M., Randerath K. Enzymatic synthesis of diadenosine tetraphosphate and diadenosine triphosphate with a purified lysyl-sRNA synthetase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jul 6;24(1):91–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90415-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



