Abstract
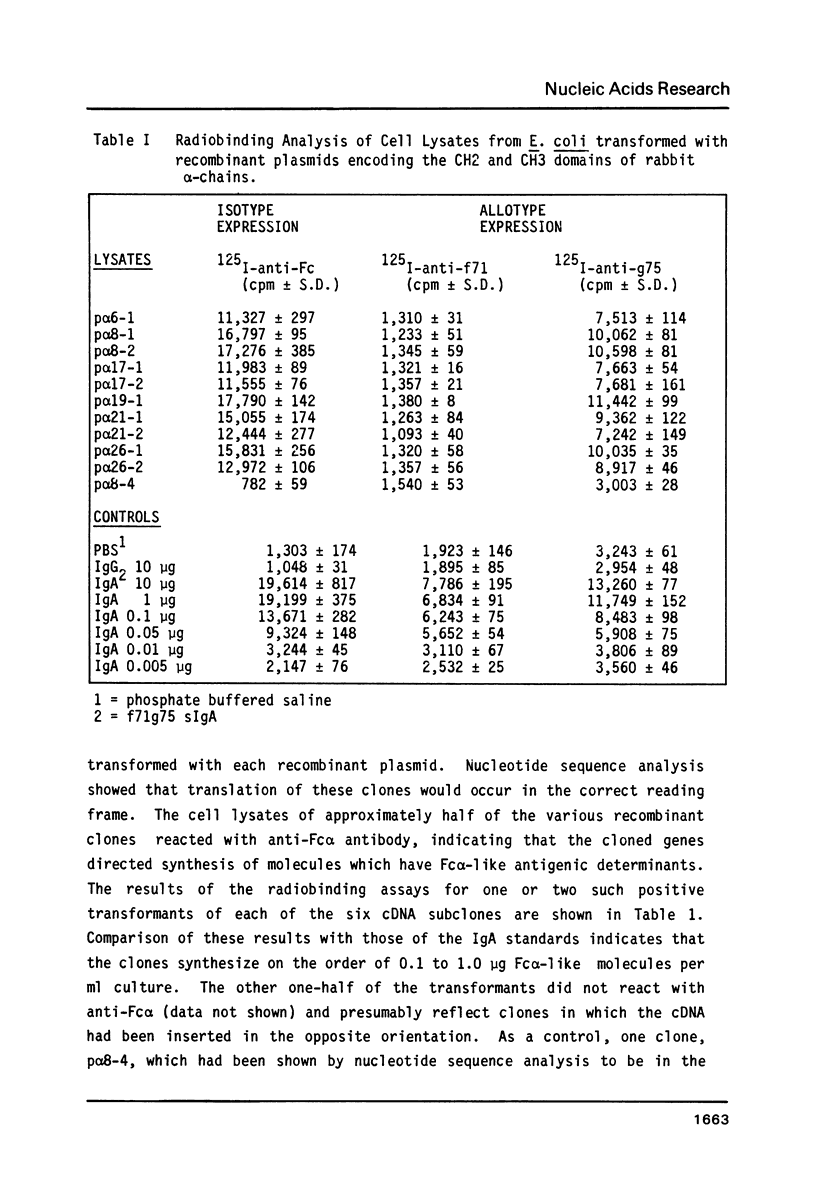
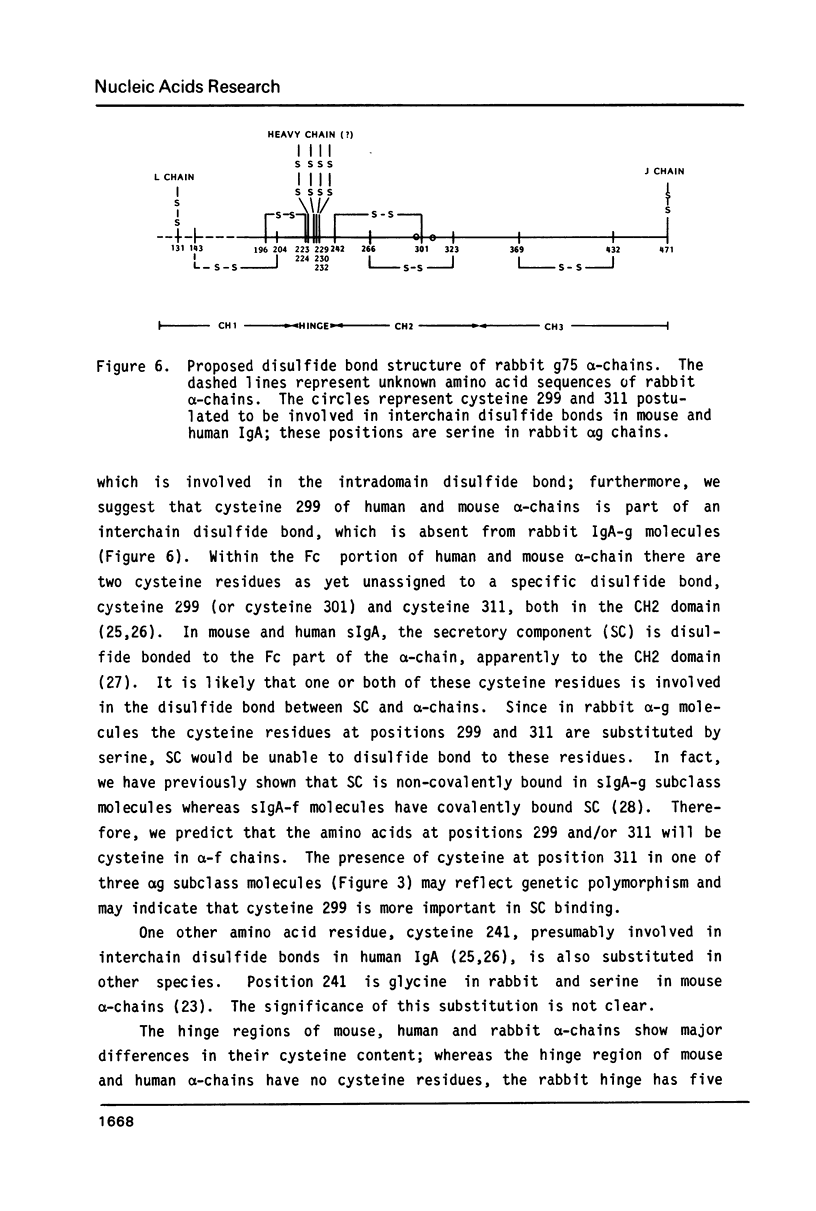
cDNA molecules encoding rabbit IgA alpha-heavy chains have been synthesized and six of these have been characterized. The complete nucleotide sequence of one cDNA, p 19 (942bp), showed that it encoded all but the N-terminal 57 amino acid residues of the constant region of alpha-chains. The cDNA molecules were subcloned into the expression vector pUC8 and E. coli were transformed. Radioimmunoassay of the molecules synthesized by these clones showed that all six cDNA molecules encoded alpha-chains of the IgA-g subclass. Comparison of the amino acids encoded by the alpha-cDNA with the amino acid sequence of mouse and human alpha-chains showed that although all of the intradomain disulfide bonds appear to be conserved, some positions, probably involved in interchain disulfide bonds, are not conserved. We propose that secretory component is covalently bound to cysteine 299 and/or cysteine 301 of the CH2 domain of mouse and human alpha-chains. The results from Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA with 32P-cDNA suggests that the rabbit genome has multiple C alpha genes.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Nageotte R., Sikorav J. L., Heidmann O., Rougeon F. Mouse immunoglobulin A: nucleotide sequence of the structural gene for the alpha heavy chain derived from cloned cDNAs. Gene. 1981 May;13(4):365–374. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Maniatis T., Kafatos F. C., Jeffrey A., Vournakis J. N. Full length and discrete partial reverse transcripts of globin and chorion mRNAs. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott B. W., Jr, Friedenson B., Knight K. L. Free sulfhydryl groups of rabbit secretory IgA. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1611–1617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Rabbitts T. H. Arrangement of human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes implies evolutionary duplication of a segment containing gamma, epsilon and alpha genes. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):709–713. doi: 10.1038/300709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Kindle K. L., Davidson N., Kindle K. L. The actin genes of Drosophila: a dispersed multigene family. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):365–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90511-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanly W. C., Knight K. L., Gilman-Sachs A., Dray S., Lichter E. A. Close linkage of the genes for rabbit IgA allotypes, Af71 to Af75, to the chromosomal region controlling immunoglobulin heavy chain allotypes. J Immunol. 1972 Jun;108(6):1723–1725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanly W. C., Lichter E. A., Dray S., Knight K. L. Rabbit immunoglobulin A allotypic specificities. Localization to two papain fragments, fab 2 and fc 2 , of secretory immunoglobulin A. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):733–741. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joho R., Weissman I. L., Early P., Cole J., Hood L. Organization of kappa light chain genes in germ-line and somatic tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1106–1110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight K. L., Vetter M. L., Malek T. R. Distribution of covalently bound and non-covalently bound secretory component on sbuclasses of rabbit secretory IgA. J Immunol. 1975 Aug;115(2):595–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. S., Low T. L., Infante A., Putnam F. W. Complete covalent structure of a human IgA1 immunoglobulin. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1017–1020. doi: 10.1126/science.821146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malek T. R., Hanly W. C., Knight K. L. Papain-resistant (f) and papain-sensitive (g) subclasses of rabbit sLgA. Allotypic specificities on different domains of the g subclass of alpha-chains (alpha g). Eur J Immunol. 1974 Oct;4(10):692–697. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830041011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malek T. R., Knight K. L. Digestion of the "proteolytic resistant" f-subclass of rabbit secretory IgA. Localization of f-subclass allotypic specificities to the Fc2alpha fragment. Immunochemistry. 1977 Jul;14(7):493–496. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(77)90301-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malek T. R., Peterson B. E., Hanly W. C., Knight K. L., Friedenson B. Structural studies of rabbit IgA allotypes: partial amino acid sequences of alpha-chain allotypes controlled by allelic genes at the Calphag locus. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):950–954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J., Kulhavy R., Wright G. P., Tomana M. Studies on human secretory immunoglobulin A. VI. Cyanogen bromide cleavage. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):404–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Wu R. Terminal transferase-catalyzed addition of nucleotides to the 3' termini of DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):43–62. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Takahashi N., Yaoita Y., Honjo T. Organization of the constant-region gene family of the mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):499–506. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Frelinger J. G., Fisher D., Hunkapiller T., Pereira D., Weissman S. M., Uehara H., Nathenson S., Hood L. Three cDNA clones encoding mouse transplantation antigens: homology to immunoglobulin genes. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90508-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker P. W., Slightom J. L., Blattner F. R. Mouse IgA heavy chain gene sequence: implications for evolution of immunoglobulin hinge axons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7684–7688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenstein-Todel C., Prelli F., Frangione B., Franklin E. C. Immunoglobulin A. Arrangement of disulfide bridges in the "hinge" region of an immunoglobulin lin A-1 human myeloma protein. Biochemistry. 1973 Dec 4;12(25):5195–5197. doi: 10.1021/bi00749a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]