Abstract
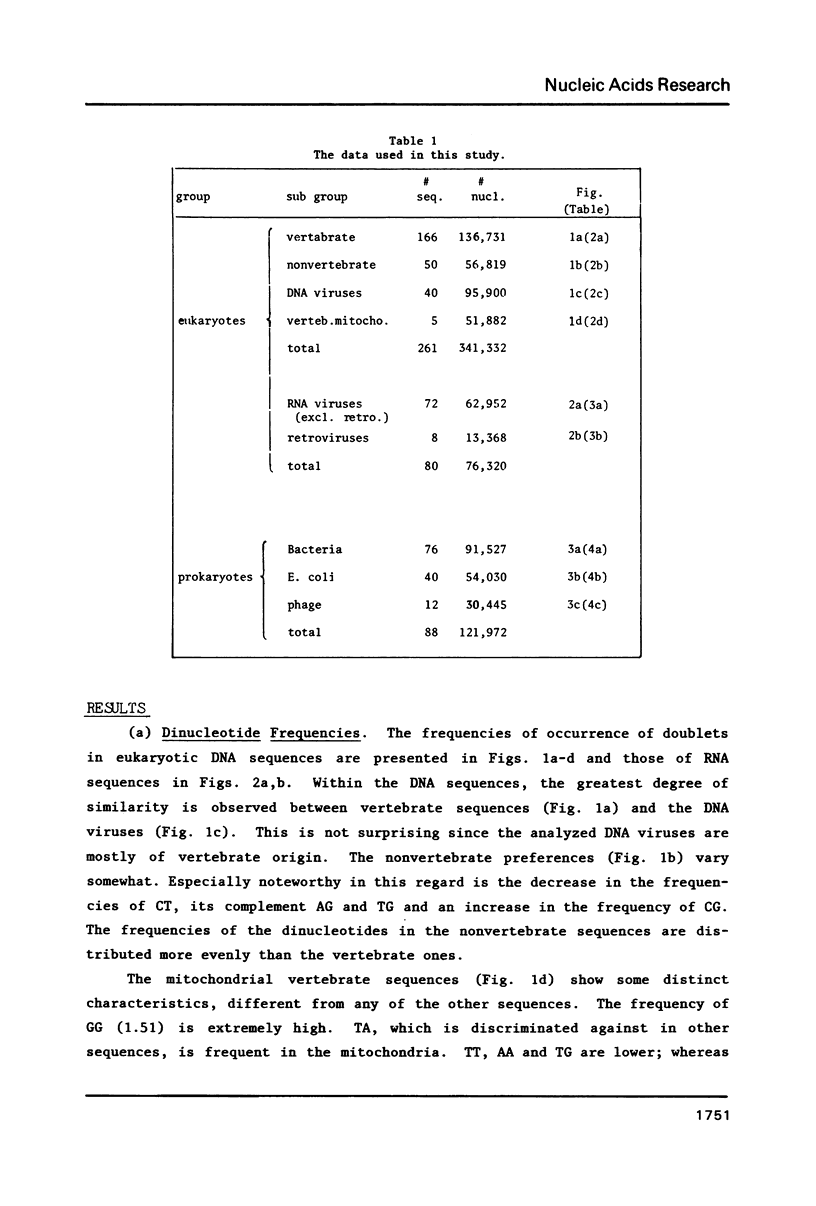
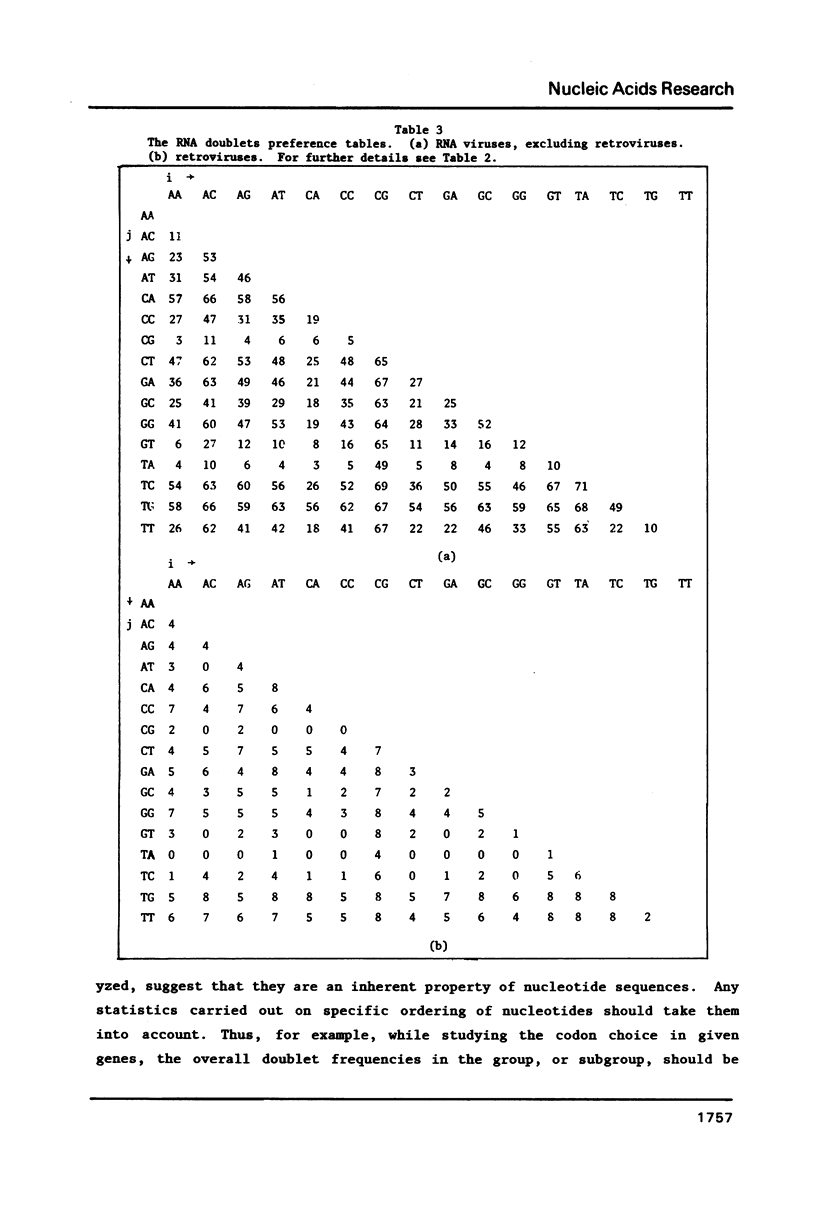
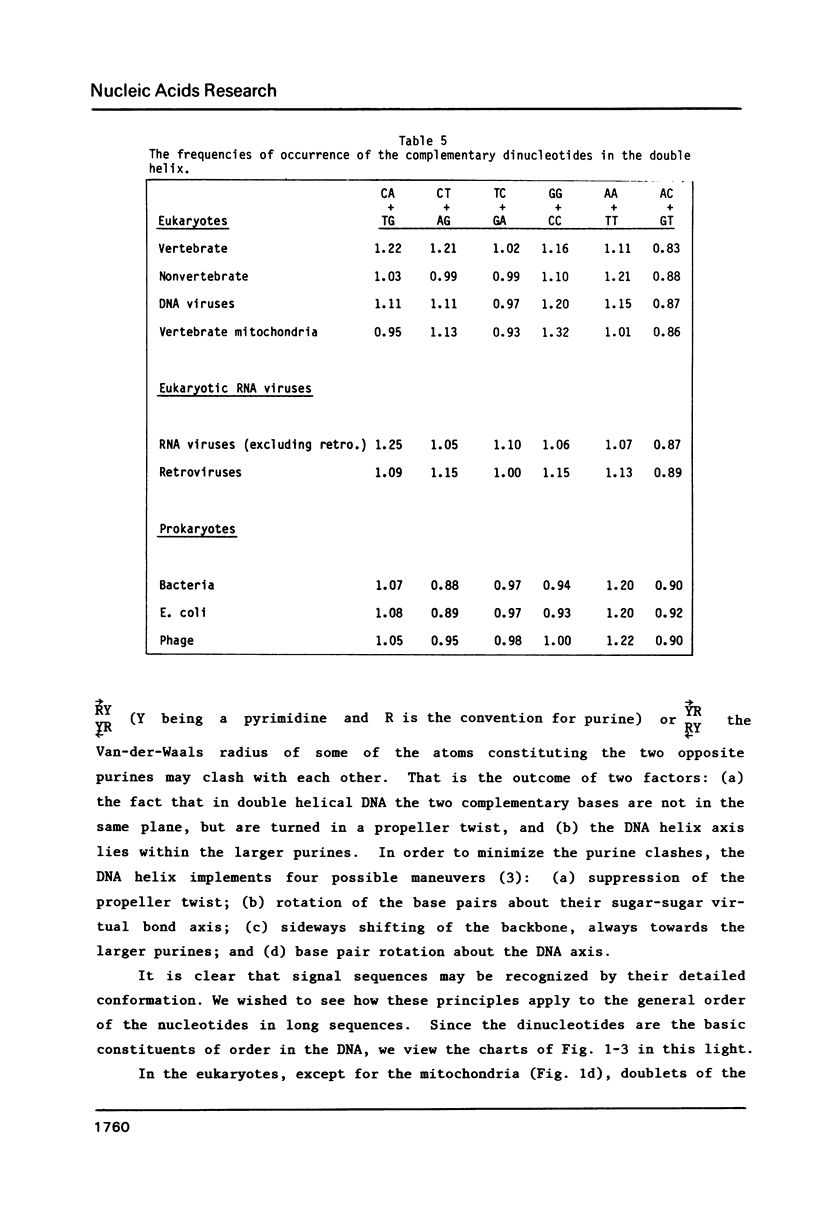
We analyze the dinucleotide frequencies of occurrence and preferences separately within the vertebrates, nonvertebrates, DNA viruses, mitochondria, RNA viruses, bacteria and phage sequences. Over half a million nucleotides from more than 400 sequences were used in this study. Distinct patterns are observed. Some of the patterns are common to all sequences, some to either eukaryotes or prokaryotes and others to the subgroups within them. Doublets are the most basic ingredient of order in nucleotide sequences. We suggest that their preferences and the arrangement of nucleotides in the DNA in general is determined to a large extent by the conformational and packaging considerations of the double helix. Some principles of DNA conformation are viewed in light of our results.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almagor H. A Markov analysis of DNA sequences. J Theor Biol. 1983 Oct 21;104(4):633–645. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(83)90251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calladine C. R. Mechanics of sequence-dependent stacking of bases in B-DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 25;161(2):343–352. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R. Kinematic model for B-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7318–7322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. II. Influence of base sequence on helix structure. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):761–786. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Dickerson R. E. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. III. Geometry of hydration. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):535–556. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Wing R. M., Takano T., Broka C., Tanaka S., Itakura K., Dickerson R. E. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer: conformation and dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2179–2183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M. How many base-pairs per turn does DNA have in solution and in chromatin? Some theoretical calculations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):640–644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussinov R. Eukaryotic dinucleotide preference rules and their implications for degenerate codon usage. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 15;149(1):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90264-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussinov R. Nearest neighbor nucleotide patterns. Structural and biological implications. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8458–8462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussinov R. Some indications for inverse DNA duplication. J Theor Biol. 1982 Apr 21;95(4):783–791. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(82)90353-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussinov R. Some rules in the ordering of nucleotides in the DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 10;8(19):4545–4562. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Blakesley R. W., Hardies S. C., Horn G. T., Larson J. E., Selsing E., Burd J. F., Chan H. W., Dodgson J. B., Jensen K. F. The role of DNA structure in genetic regulation. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1977;4(3):305–340. doi: 10.3109/10409237709102561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


