Abstract
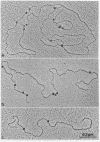
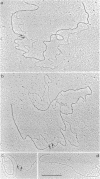
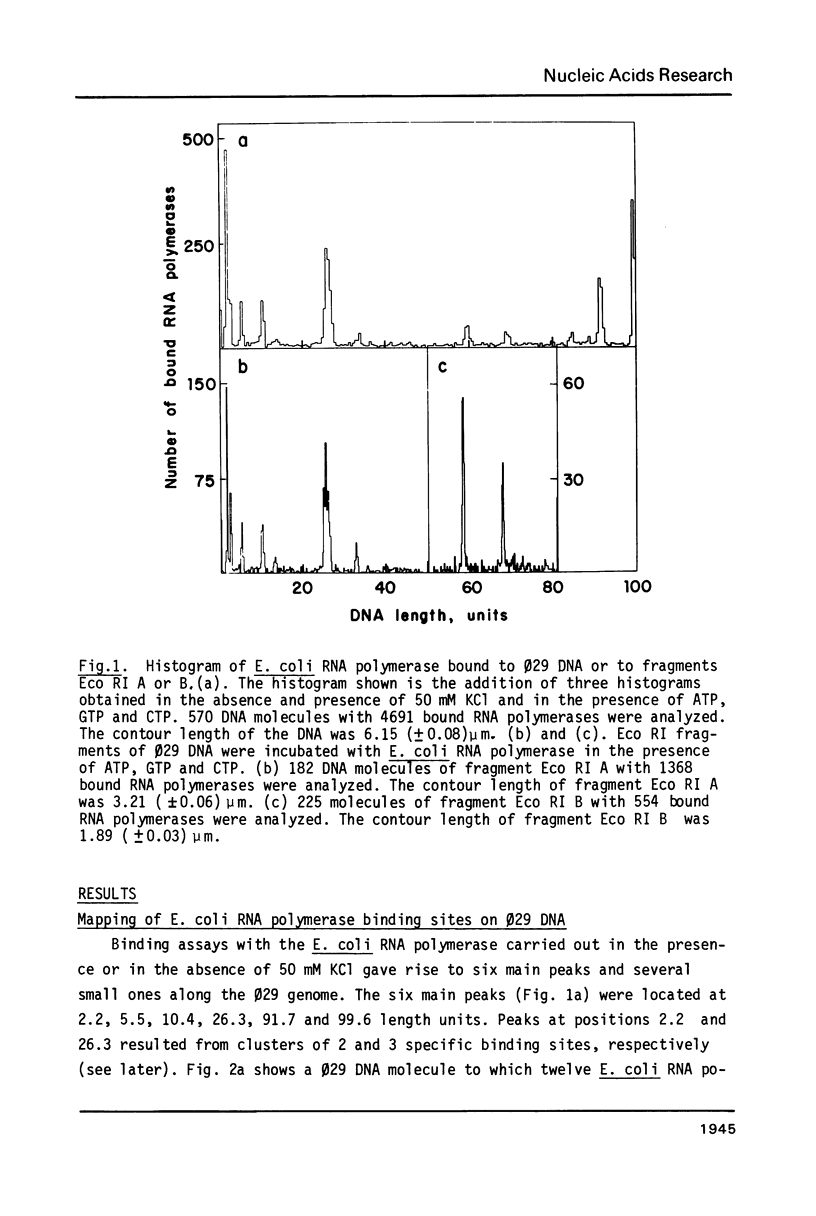
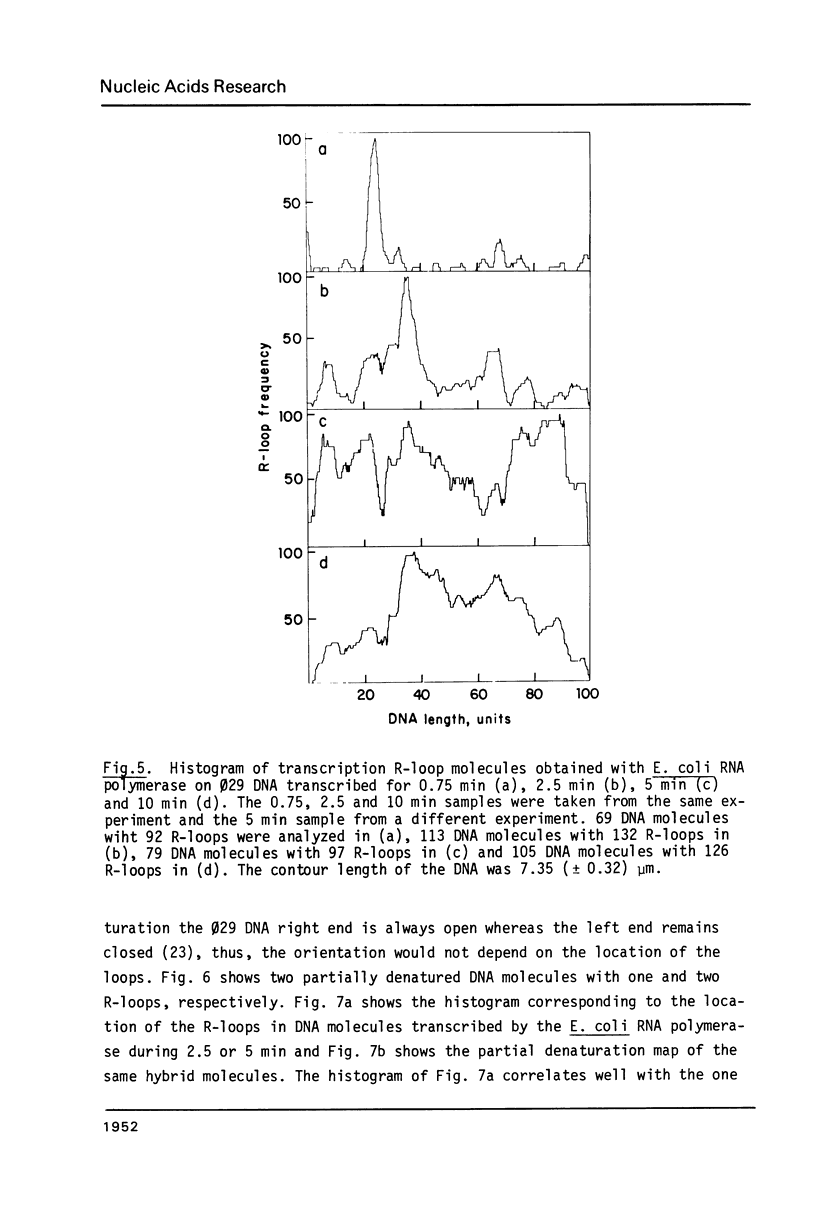
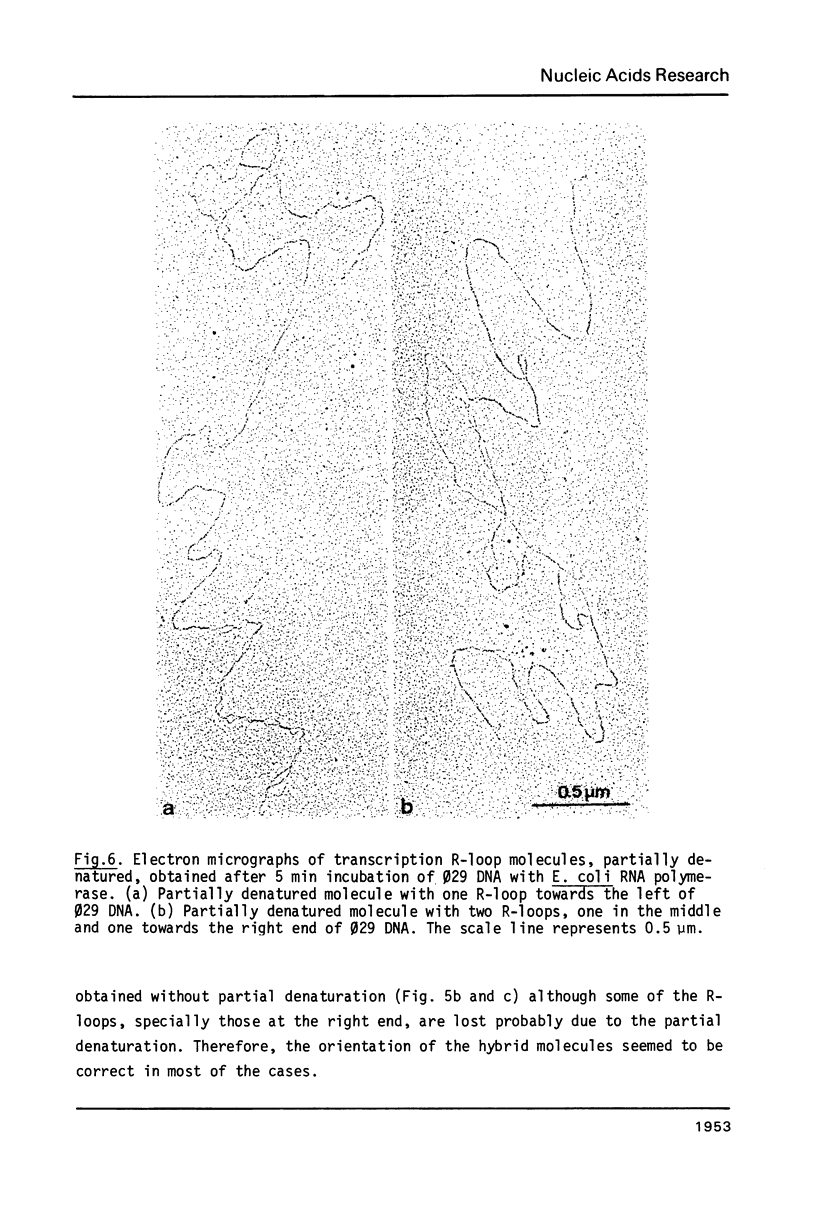
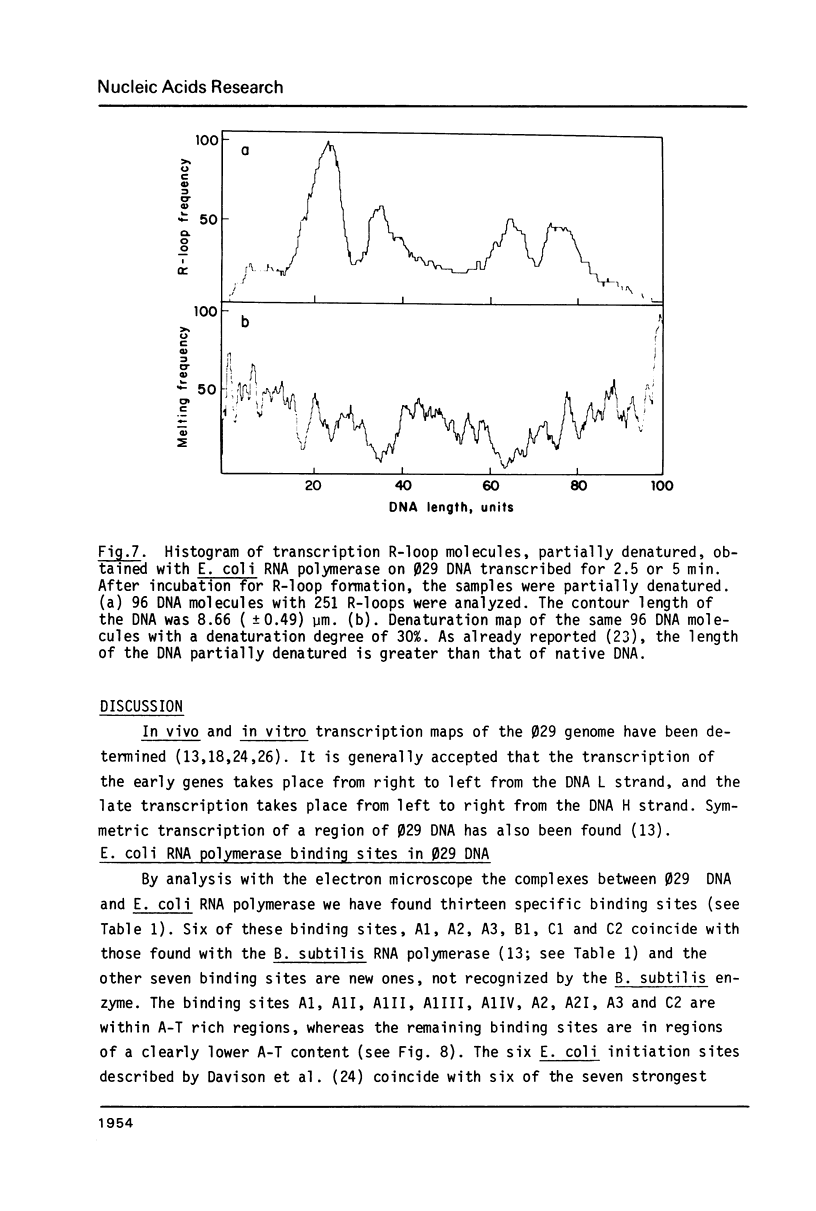
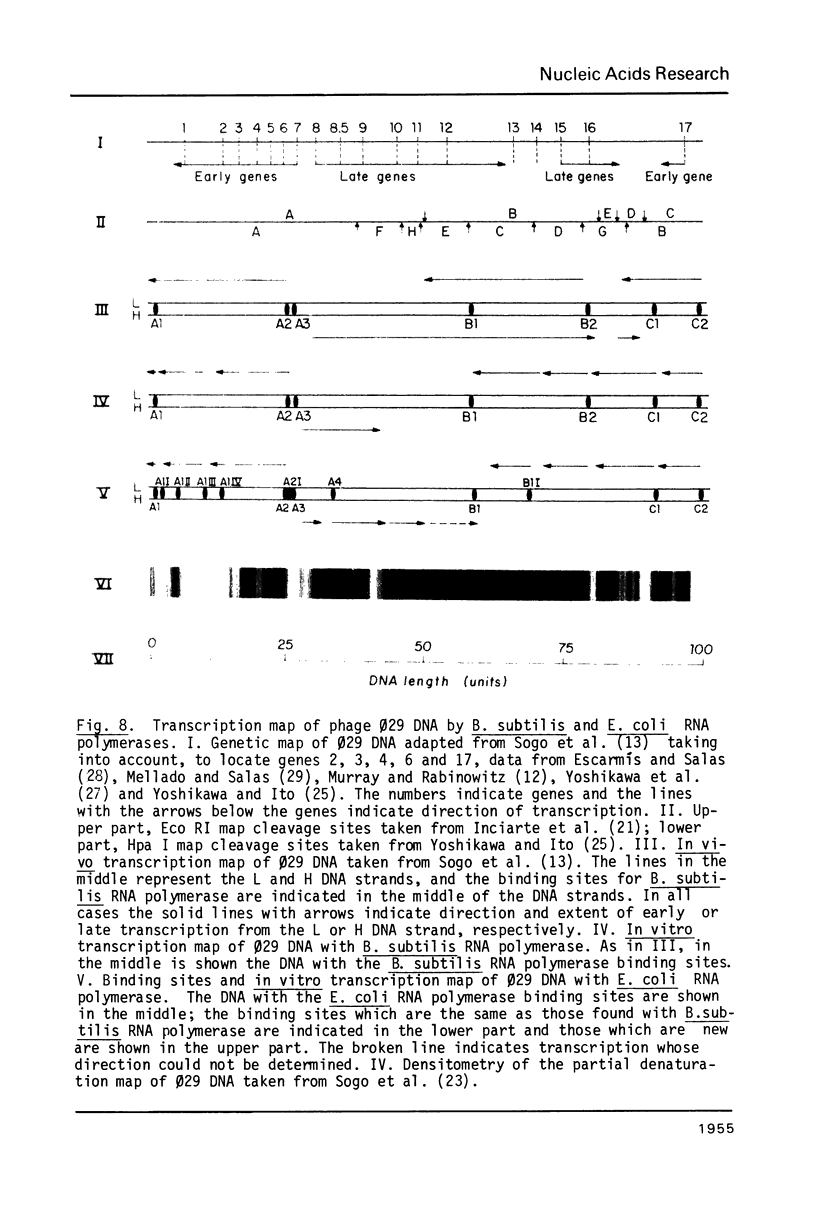
The Escherichia coli RNA polymerase bound to phage phi 29 DNA has been visualized by electron microscopy. Thirteen specific binding sites have been observed at 1.7,2.6,5.5,10.4,13.7,25.2,25.7,26.3,33.5,59.5,69.2,91.7 and 99.6 DNA length units and they have been named A1,A1I,A1II,A1III,A1IV,A2,A2I, A3, A4,B1,B1I,C1 and C2, respectively. The binding sites A1,A2,A3,B1,C1 and C2 coincide with those found with Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase. The transcription of phage phi 29 DNA with B. subtilis or E. coli RNA polymerases has been studied. With the B. subtilis RNA polymerase eight transcripts were found, starting at positions corresponding to the binding sites A1, A1III, A2,A3,B1I,B2,C1 and C2, respectively. With the E. coli RNA polymerase the same transcripts were found and a new one starting at position corresponding to the A4 binding site. The RNAs starting at binding sites A1,A1III,A2,B1I, B2,C1 and C2 are transcribed from right to left, as expected for early RNA. The RNAs which initiate at positions A3 and A4 are transcribed from left to right and probably correspond to late RNAs.
Full text
PDF

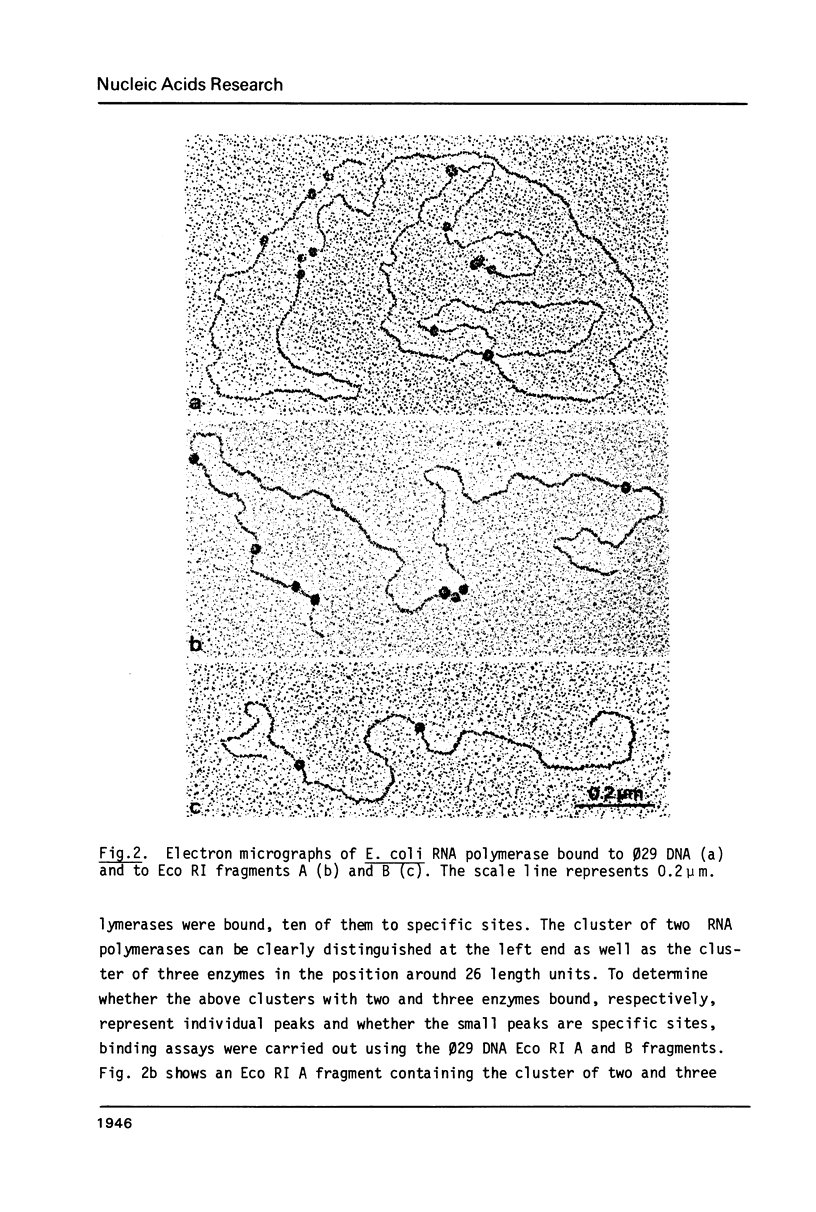

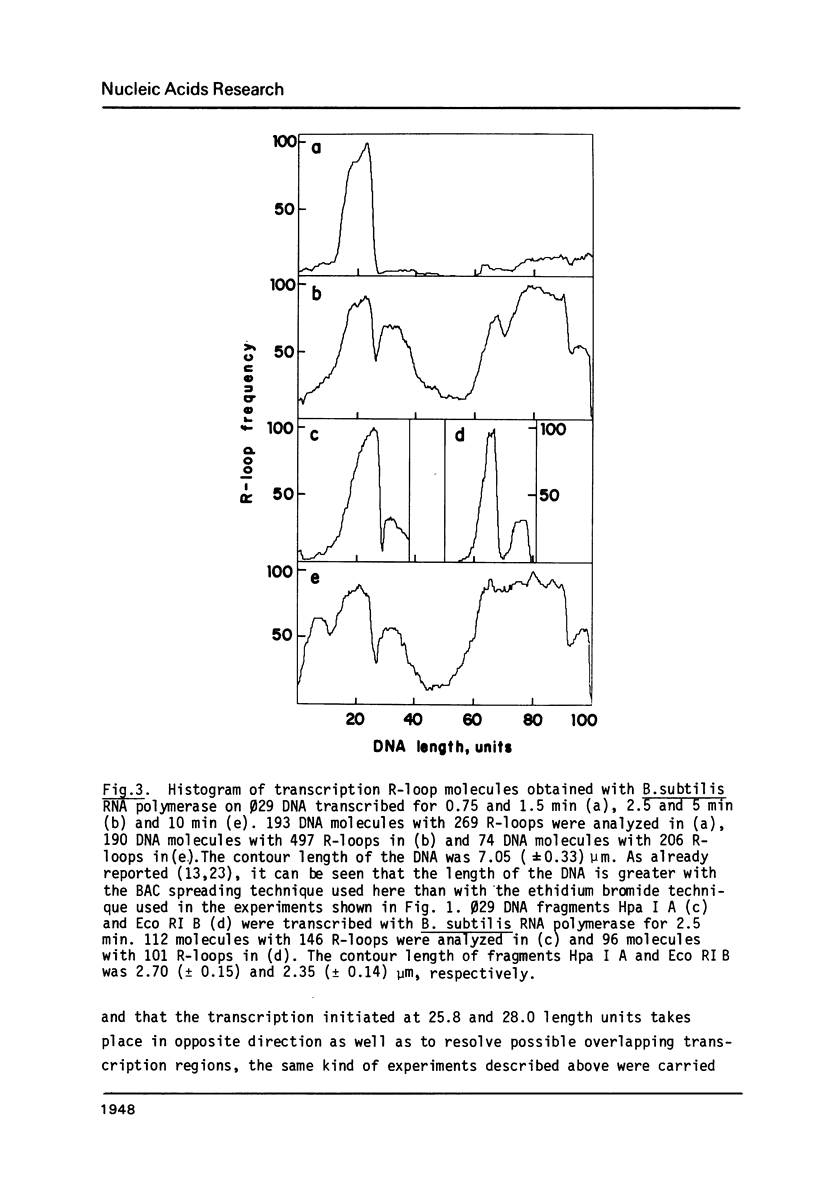
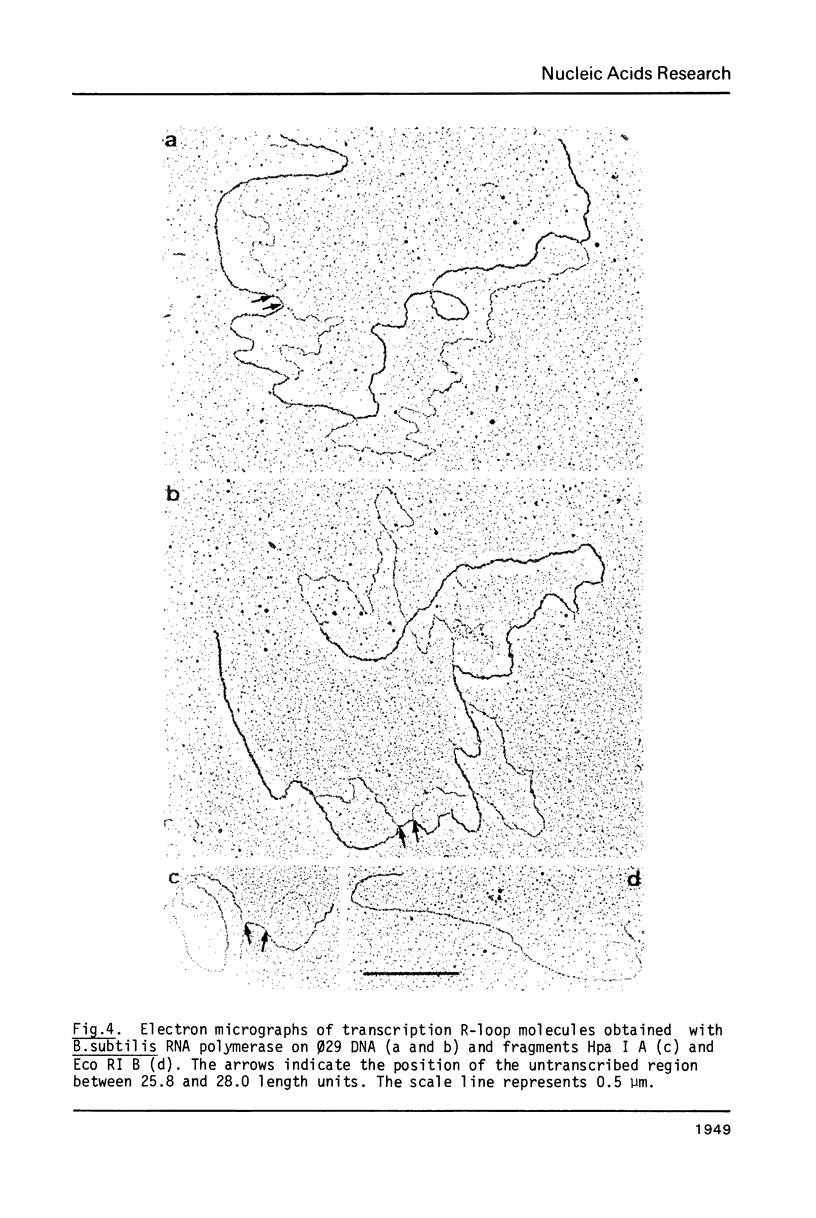
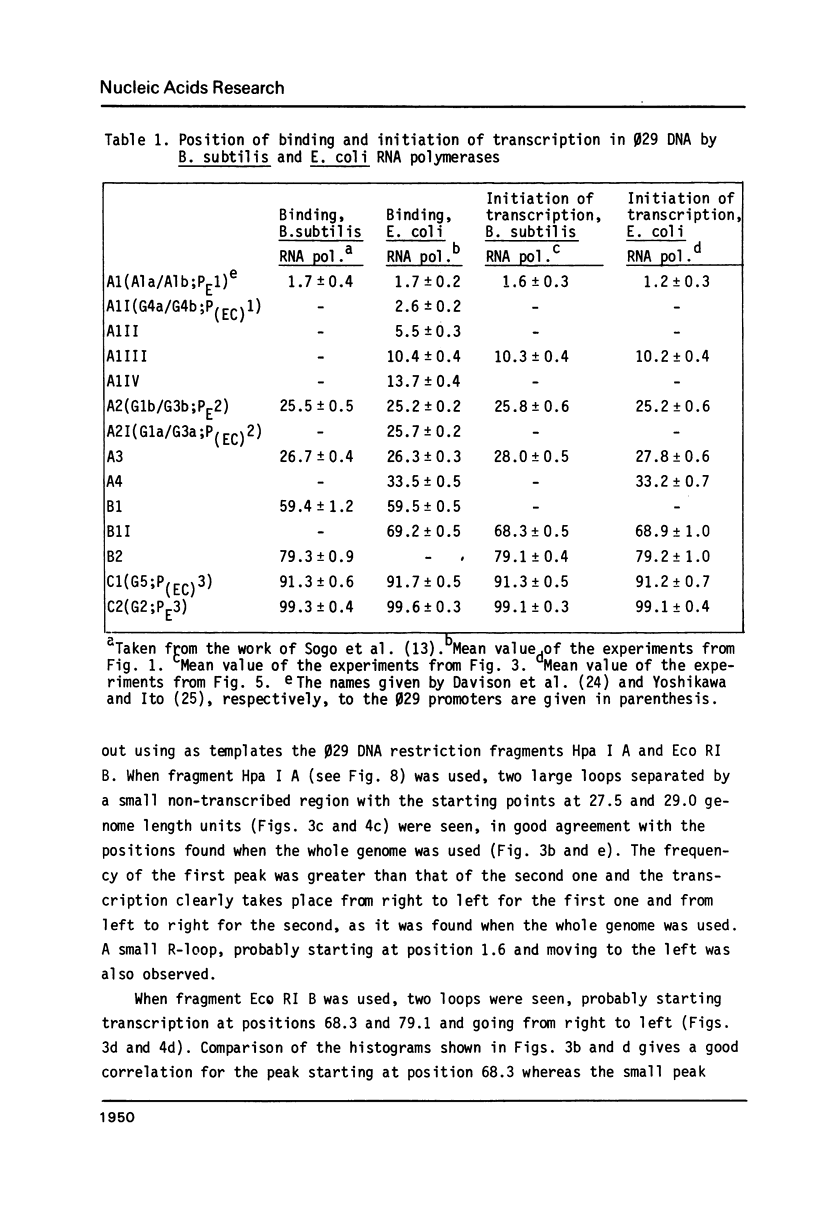






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avila J., Hermoso J. M., Viñuela E., Salas M. Subunit composition of B. subtilis RNA polymerase. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1244–1245. doi: 10.1038/2261244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C. Electron microscopic analysis of transcription: mapping of initiation sites and direction of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3164–3168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Travers A. A., Dunn J. J., Bautz E. K. Factor stimulating transcription by RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Jan 4;221(5175):43–46. doi: 10.1038/221043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., Camacho A., Moreno F., Jiménez F., Mellado R. P., Viñuela E., Salas M. Bacillus subtilis phage phi29. Characterization of gene products and functions. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 1;66(2):229–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Specificity of promoter site utilization in vitro by bacterial RNA polymerases on Bacillus phage phi 29 DNA. Transcription mapping with exonuclease III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8819–8830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi R. H. Multiple RNA polymerase holoenzymes exert transcriptional specificity in Bacillus subtilis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Apr 1;214(2):772–781. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escarmís C., Salas M. Nucleotide sequence of the early genes 3 and 4 of bacteriophage phi 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5785–5798. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldenwang W. G., Lang N., Losick R. A sporulation-induced sigma-like regulatory protein from B. subtilis. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):615–624. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldenwang W. G., Losick R. Novel RNA polymerase sigma factor from Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7000–7004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding N. E., Ito J., David G. S. Identification of the protein firmly bound to the ends of bacteriophage phi 29 DNA. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90248-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito J. Bacteriophage phi29 terminal protein: its association with the 5' termini of the phi29 genome. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):895–904. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.895-904.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura F., Ito J. Transcription of the genome of bacteriophage phi 29: isolation and mapping of the major early mRNA synthesized in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):562–577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.562-577.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller T., Kübler O., Portmann R., Sogo J. M. High resolution physical mapping of specific binding sites of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase on the DNA of bacteriophage T7 . J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90298-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Shorenstein R. G., Sonenshein A. L. Structural alteration of RNA polymerase during sporulation. Nature. 1970 Aug 29;227(5261):910–913. doi: 10.1038/227910a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellado R. P., Salas M. High level synthesis in Escherichia coli of the Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29 proteins p3 and p4 under the control of phage lambda PL promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5773–5784. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Nucleotide sequences of transcription and translation initiation regions in Bacillus phage phi 29 early genes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):1053–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas M., Mellado R. P., Viñuela E. Characterization of a protein covalently linked to the 5' termini of the DNA of Bacillus subtilis phage phi29. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 25;119(2):269–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90438-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F., De Sain C. V., Anderson D. L. Transcription during the development of bacteriophage phi29: definition of "early" and "late" phi29 ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1973 Jan;11(1):9–16. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.1.9-16.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogo J. M., Inciarte M. R., Corral J., Viñuela E., Salas M. RNA polymerase binding sites and transcription map of the DNA of Bacillus subtilis phage phi29. J Mol Biol. 1979 Feb 5;127(4):411–436. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90230-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogo J. M., Rodeño P., Koller T., Viñuela E., Salas M. Comparison of the A-T rich regions and the Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase binding sites in phage phi 29 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 11;7(1):107–120. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggs J. L., Gilman M. Z., Chamberlin M. J. Heterogeneity of RNA polymerase in Bacillus subtilis: evidence for an additional sigma factor in vegetative cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2762–2766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yehle C. O. Genome-linked protein associated with the 5' termini of bacteriophage phi29 DNA. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):776–783. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.776-783.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa H., Friedmann T., Ito J. Nucleotide sequences at the termini of phi 29 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1336–1340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa H., Ito J. Nucleotide sequence of the major early region of bacteriophage phi 29. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90149-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]