Abstract
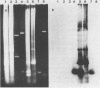
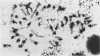
Cleavage of sheep DNA with the restriction endonuclease EcoR I yields three discrete size classes (370, 435 and 800bp) of highly repetitive DNA. The 435bp long fragment was cloned and its nucleotide sequence determined. All three classes of repetitive DNA are related to each other as seen by cross-hybridisation. They are tandemly arranged in the genome and in situ hybridisation to sheep lymphocyte chromosomes show their location mainly in the centromere region of all chromosomes. The primary sequence of the repetitive DNA shows a close structural similarity to the bovine 1.715 satellite DNA, however only poor cross-hybridisation between the sheep and cattle repetitive DNA could be shown.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appels R., Peacock W. J. The arrangement and evolution of highly repeated (satellite) DNA sequences with special reference to Drosophila. Int Rev Cytol Suppl. 1978;Suppl 8:69–126. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60472-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D. L. Molecular arrangement and evolution of heterochromatic DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:121–144. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtain C. C., Pascoe G., Hayman R. Satellite DNA in the sheep and goat. Biochem Genet. 1973 Nov;10(3):253–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00485703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans H. J., Buckland R. A., Sumner A. T. Chromosome homology and heterochromatin in goat, sheep and ox studied by banding techniques. Chromosoma. 1973 Jul 18;42(4):383–402. doi: 10.1007/BF00399407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch I. R., Morton C. C., Nakahara K., Leder P. Human immunoglobulin heavy chain genes map to a region of translocations in malignant B lymphocytes. Science. 1982 Apr 16;216(4543):301–303. doi: 10.1126/science.6801764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurnit D. M., Brown F. L., Maio J. J. Mammalian repetitive DNA sequences in a stable Robertsonian system. Characterization, in situ hybridizations, and cross-species hybridizations of repetitive DNAs in calf, sheep, and goat chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;21(3):145–167. doi: 10.1159/000130888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pech M., Streeck R. E., Zachau H. G. Patchwork structure of a bovine satellite DNA. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):883–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90140-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Płucienniczak A., Skowroński J., Jaworski J. Nucleotide sequence of bovine 1.715 satellite DNA and its relation to other bovine satellite sequences. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 25;158(2):293–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90434-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizes G. A possible structure for calf satellite DNA I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2677–2696. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeck R. E. Inserted sequences in bovine satellite DNA's. Science. 1981 Jul 24;213(4506):443–445. doi: 10.1126/science.6264600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]