Abstract
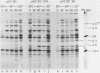
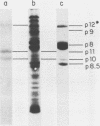
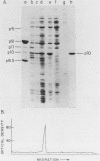
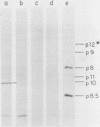
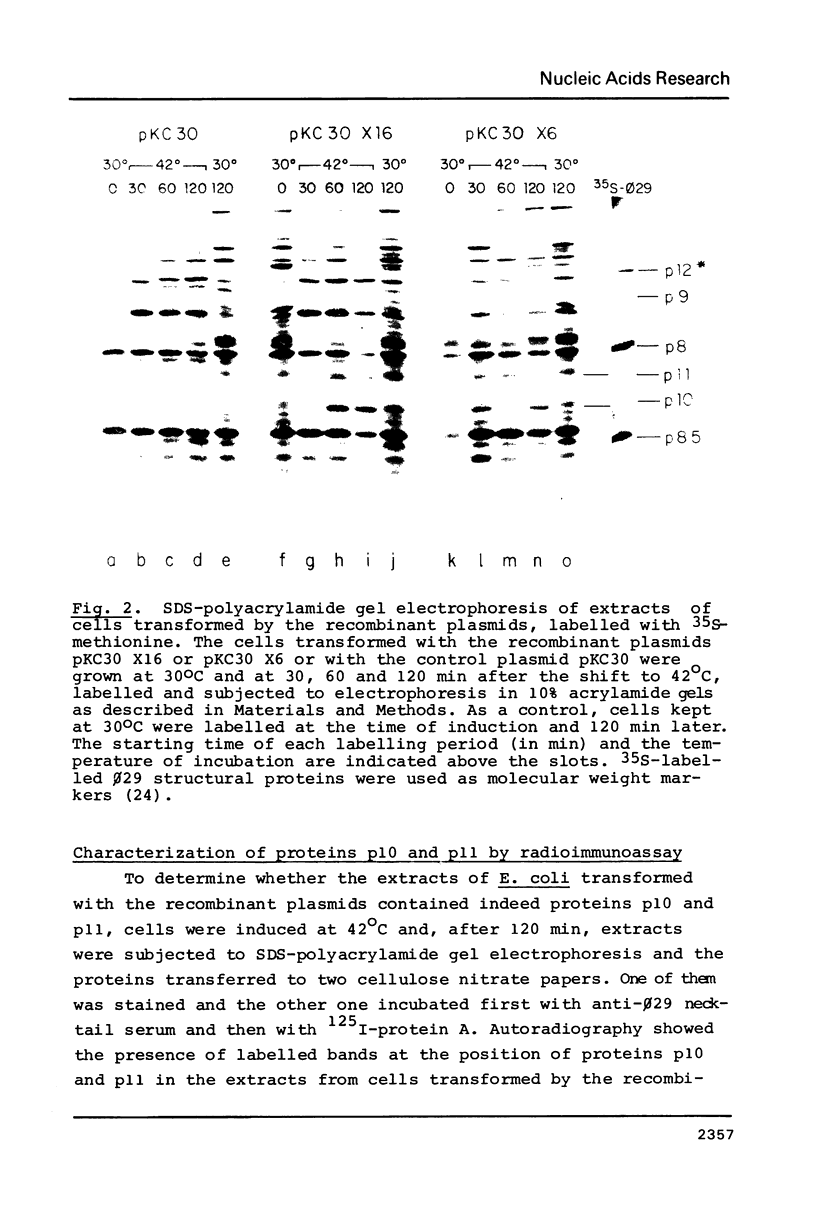
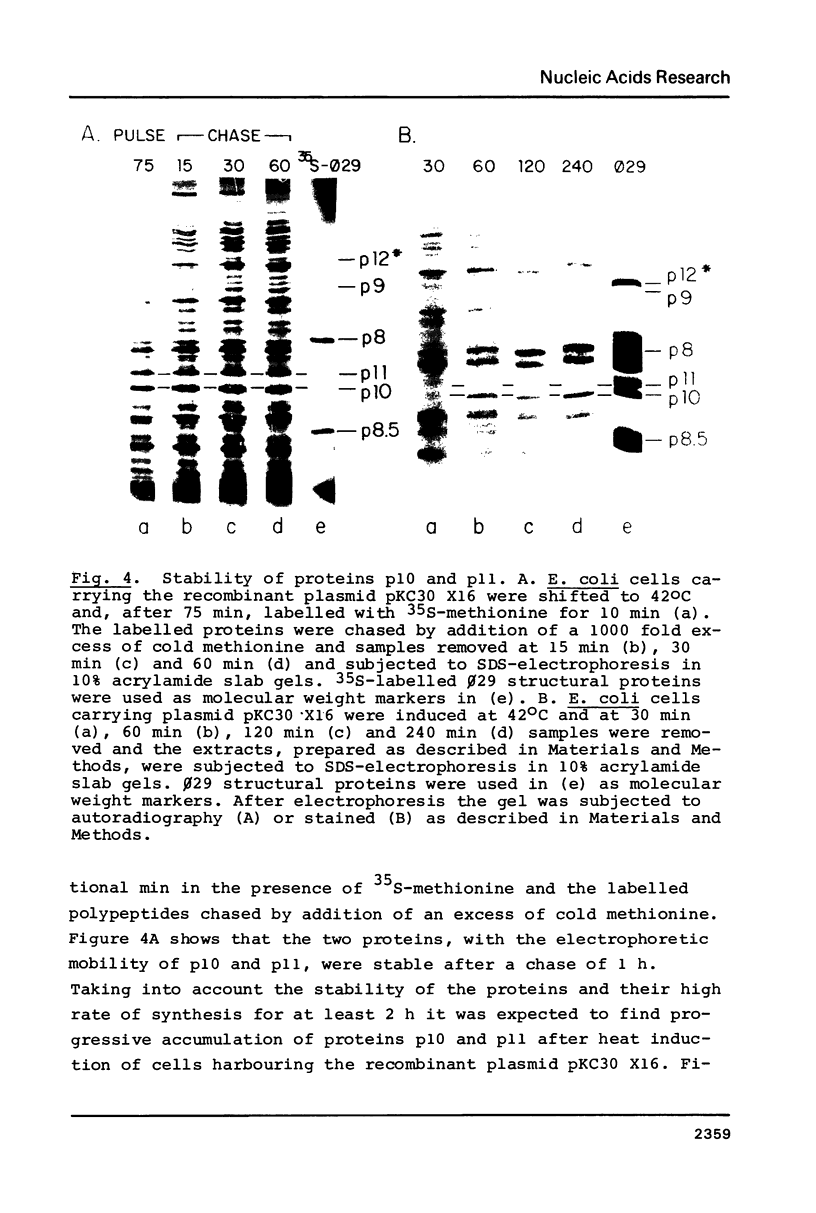
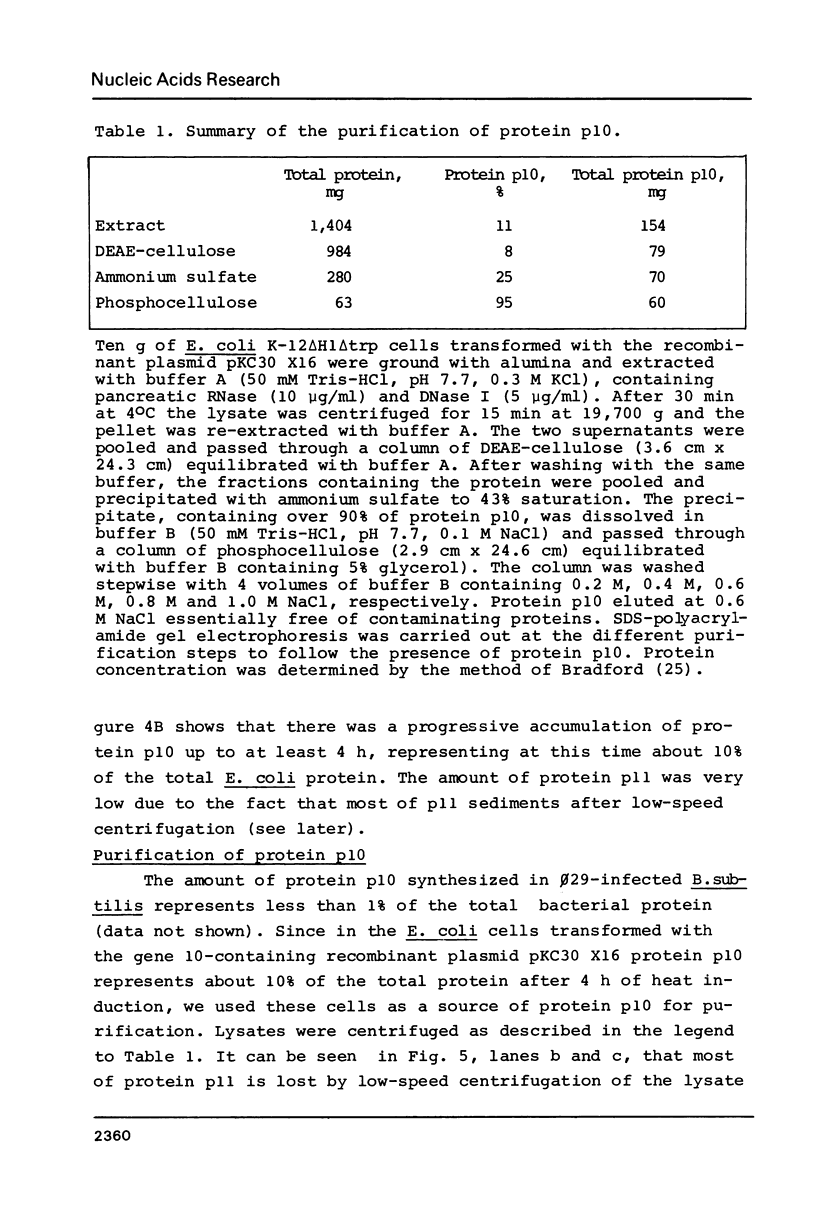
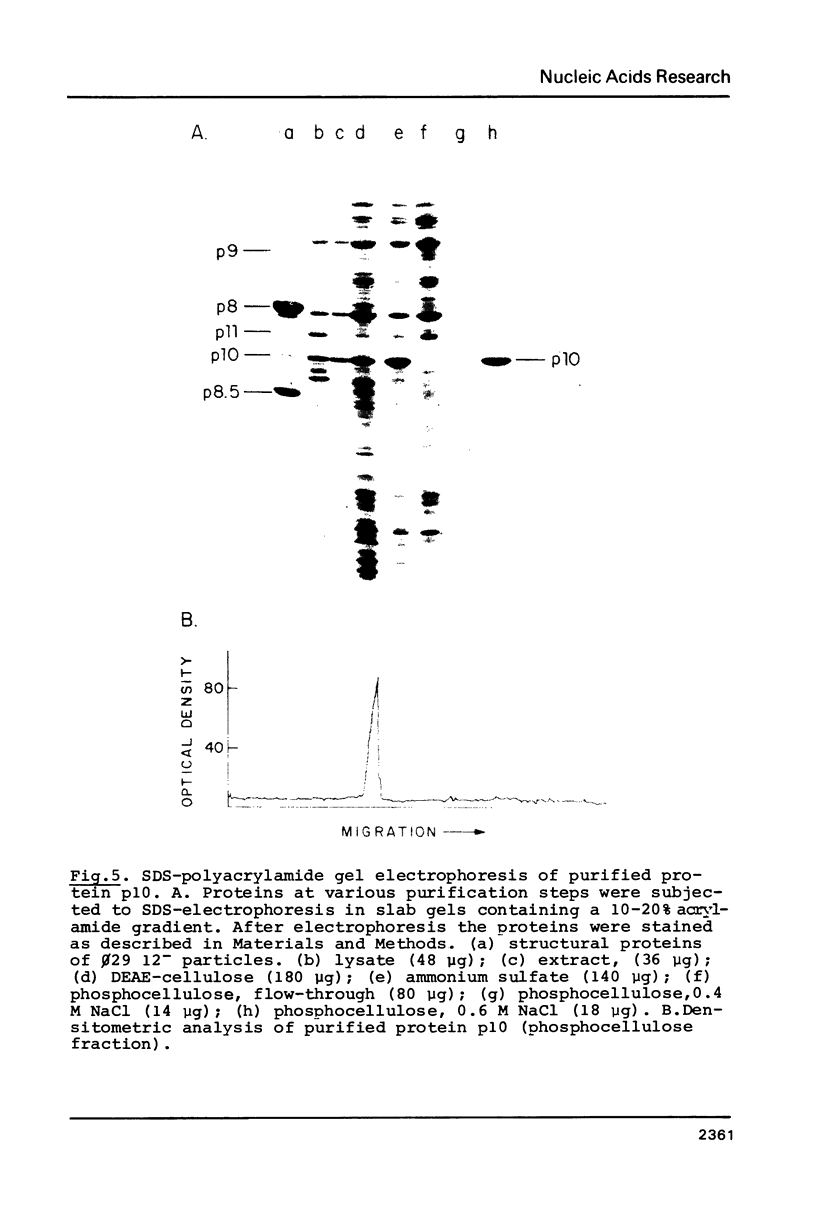
A phi 29 DNA fragment containing genes 10 and 11, coding for the connector protein and the lower collar protein, respectively, has been cloned in the pBR322 derivative plasmid pKC30 under the control of the PL promoter of phage lambda. Two polypeptides with the electrophoretic mobility of proteins p10 and p11 were labelled with 35S-methionine after heat induction. The proteins were characterized as p10 and p11 by radioimmunoassay and they represented about 10% and 7%, respectively, of the total E. coli protein after 4 hours of induction. These proteins represent less than 1% of the B. subtilis protein in phi 29-infected cells. Protein p10 has been highly purified from the E. coli cells carrying the recombinant plasmid. Antibodies raised against the purified protein p10 reacted with the connector protein produced in phi 29-infected B. subtilis.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernard H. U., Remaut E., Hershfield M. V., Das H. K., Helinski D. R., Yanofsky C., Franklin N. Construction of plasmid cloning vehicles that promote gene expression from the bacteriophage lambda pL promoter. Gene. 1979 Jan;5(1):59–76. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camacho A., Jiménez F., De La Torre J., Carrascosa J. L., Mellado R. P., Vásquez C., Viñuela E., Salas M. Assembly of Bacillus subtilis phage phi29. 1. Mutants in the cistrons coding for the structural proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb 15;73(1):39–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camacho A., Jiménez F., Viñuela E., Salas M. Order of assembly of the lower collar and the tail proteins of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):540–545. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.540-545.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., Camacho A., Moreno F., Jiménez F., Mellado R. P., Viñuela E., Salas M. Bacillus subtilis phage phi29. Characterization of gene products and functions. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 1;66(2):229–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., Carazo J. M., García N. Structural localization of the proteins of the head to tail connecting region of bacteriophage phi 29. Virology. 1983 Jan 15;124(1):133–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., Viñuela E., García N., Santisteban A. Structure of the head-tail connector of bacteriophage phi 29. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 15;154(2):311–324. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4428–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derom C., Gheysen D., Fiers W. High-level synthesis in Escherichia coli of the SV40 small-t antigen under control of the bacteriophage lambda pL promoter. Gene. 1982 Jan;17(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90099-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driedonks R. A., Engel A., tenHeggeler B., van Driel Gene 20 product of bacteriophage T4 its purification and structure. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 15;152(4):641–662. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García J. A., Carrascosa J. L., Salas M. Assembly of the tail protein of the Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):18–30. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García J. A., Pastrana R., Prieto I., Salas M. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene coding for the protein linked to the ends of Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29 DNA. Gene. 1983 Jan-Feb;21(1-2):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90148-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen E. W., Reilly B. E., Tosi M. E., Anderson D. L. Analysis of gene function of bacteriophage phi 29 of Bacillus subtilis: identification of cistrons essential for viral assembly. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):501–517. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.501-517.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix R. W. Symmetry mismatch and DNA packaging in large bacteriophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4779–4783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inciarte M. R., Lázaro J. M., Salas M., Vińuela E. Physical map of bacteriophage phi29 DNA. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):314–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellado R. P., Moreno F., Viñuela E., Salas M., Reilly B. E., Anderson D. L. Genetic analysis of bacteriophage phi 29 of Bacillus subtilis: integration and mapping of reference mutants of two collections. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):495–500. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.495-500.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno F. Suppressor-sensitive mutants and genetic map of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29. Virology. 1974 Nov;62(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90298-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas M., Mellado R. P., Viñuela E. Characterization of a protein covalently linked to the 5' termini of the DNA of Bacillus subtilis phage phi29. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 25;119(2):269–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90438-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simatake H., Rosenberg M. Purified lambda regulatory protein cII positively activates promoters for lysogenic development. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):128–132. doi: 10.1038/292128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogo J. M., Inciarte M. R., Corral J., Viñuela E., Salas M. RNA polymerase binding sites and transcription map of the DNA of Bacillus subtilis phage phi29. J Mol Biol. 1979 Feb 5;127(4):411–436. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90230-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa H., Ito J. Nucleotide sequence of the major early region of bacteriophage phi 29. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90149-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]