Abstract
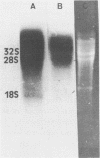
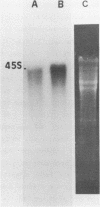
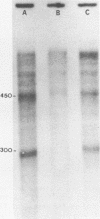
The synthesis of preribosomal RNA is inhibited "in vivo" and "in vitro" by the protease inhibitor leupeptin. "In vivo" leupeptin decreases by 74% the incorporation of labeled uridine into 45S pre rRNA while the synthesis of other RNA species is only slightly decreased. "In vitro", the elongation of already initiated pre rRNA chains that is achieved by incubation of isolated nucleoli is blocked by leupeptin. On the other hand, "in vitro" leupeptin has no direct effect on RNA polymerase I, tested in a nonspecific transcriptional system with Calf thymus DNA as template and in run off experiments with a cloned DNA containing the initiation site of the rDNA gene. A 100 kDa nucleolar protein which has been shown to be endoproteolytic cleaved "in vivo" (1) acts as an inhibitor of rDNA transcription in presence of leupeptin but produces little effect on the nonspecific transcription. In absence of the drug, the 100 kDa protein is processed in specific peptides which appeared to be similar to the "in vivo" maturation products. The possible role of the 100 kDa maturation process in the regulation of rDNA transcription is discussed.
Full text
PDF



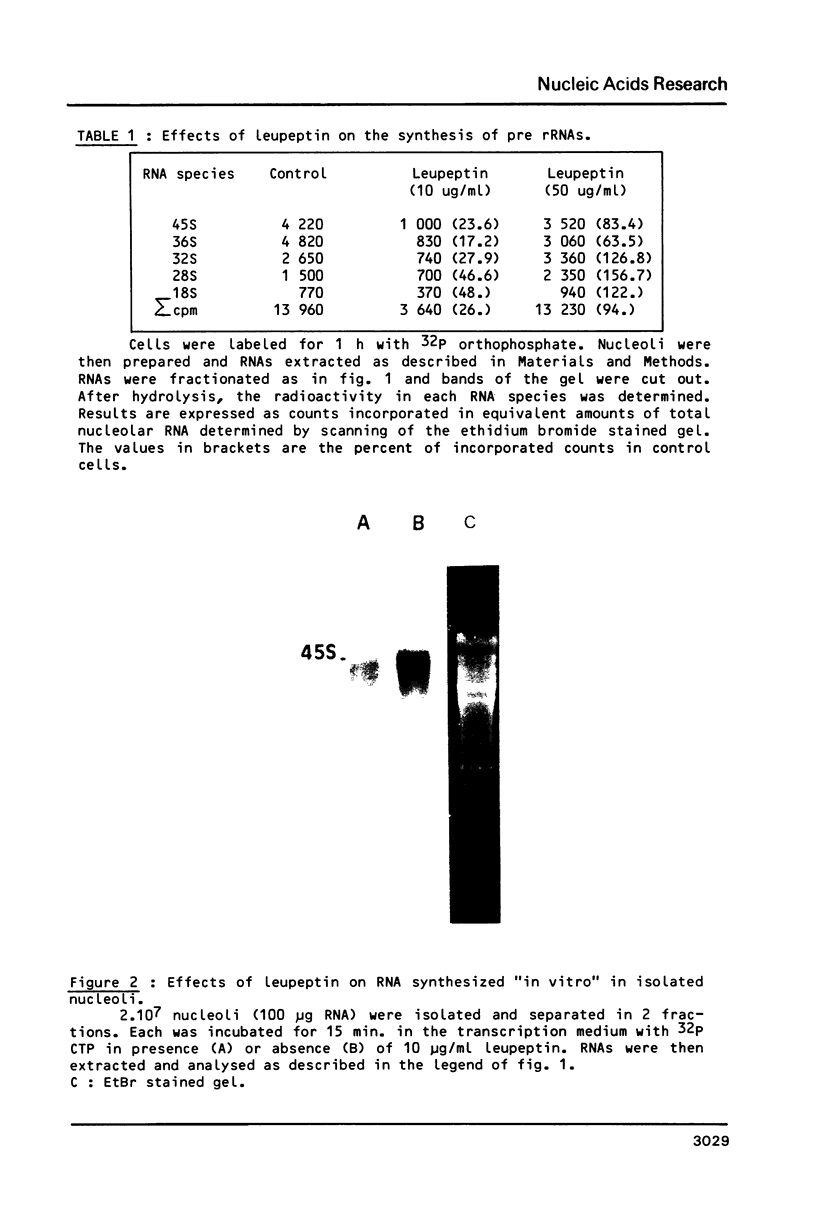






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachellerie J. P., Nicoloso M., Zalta J. P. Nucleolar chromatin in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Topographical distribution of ribosomal DNA sequences and isolation of ribosomal transcription complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep 15;79(1):23–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11779.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballal N. R., Kang Y. J., Olson M. O., Busch H. Changes in nucleolar proteins and their phosphorylation patterns during liver regeneration. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):5921–5925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourbon H. M., Bugler B., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Amalric F., Zalta J. P. Maturation of a 100 kDa protein associated with preribosomes in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Biol Rep. 1983 May;9(1-2):39–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00777472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugler B., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Bouche G., Bourbon H., Amalric F. Detection and localization of a class of proteins immunologically related to a 100-kDa nucleolar protein. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov 15;128(2-3):475–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhler J. M., Huet J., Davies K. E., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Immunological studies of yeast nuclear RNA polymerases at the subunit level. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9949–9954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caboche M., Bachellerie J. P. RNA methylation and control of eukaryotic RNA biosynthesis. Effects of cycloleucine, a specific inhibitor of methylation, on ribosomal RNA maturation. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Mar 15;74(1):19–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chooi W. Y., Leiby K. R. An electron microscopic method for localization of ribosomal proteins during transcription of ribosomal DNA: a method for studying protein assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4823–4827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franze-Fernández M. T., Pogo A. O. Regulation of the nucleolar DNA-dependent RNA polymerase by amino acids in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3040–3044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuno K., Ishikawa T., Kato K. Appearance of autolysosomes in rat liver after leupeptin treatment. J Biochem. 1982 May;91(5):1485–1494. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Grummt F. Control of nucleolar RNA synthesis by the intracellular pool sizes of ATP and GTP. Cell. 1976 Mar;7(3):447–453. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Roth E., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro is species specific. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):173–174. doi: 10.1038/296173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Specific transcription of mouse ribosomal DNA in a cell-free system that mimics control in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn G. D., Affolter H. U., Atmar V. J., Seebeck T., Gubler U., Braun R. Polyamine-mediated phosphorylation of a nucleolar protein from Physarum polycephalum that stimulates rRNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2541–2545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Warner J. R. Characterization of ribosomal precursor particles from HeLa cell nucleoli. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jan 28;63(2):233–246. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90372-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMeur M., Glanville N., Mandel J. L., Gerlinger P., Palmiter R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene family: hormonal control of X and Y gene transcription and mRNA accumulation. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):561–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90152-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamrack M. D., Olson M. O., Busch H. Amino acid sequence and sites of phosphorylation in a highly acidic region of nucleolar nonhistone protein C23. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 24;18(15):3381–3386. doi: 10.1021/bi00582a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Financsek I., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Fractionation and reconstitution of factors required for accurate transcription of mammalian ribosomal RNA genes: identification of a species-dependent initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M., Shimada N., Higashinakagawa T. Effect of cycloheximide on the nucleolar RNA synthesis in rat liver. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):91–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. O., Rivers Z. M., Thompson B. A., Kao W. Y., Case S. T. Interaction of nucleolar phosphoprotein C23 with cloned segments of rat ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 5;22(14):3345–3351. doi: 10.1021/bi00283a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific nucleolar and nucleoplasmic RNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):675–682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. H. Microinjection of purified ornithine decarboxylase into Xenopus oocytes selectively stimulates ribosomal RNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1318–1321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland J. H., Greenbaum L. M. Paradoxical effect of leupeptin in vivo on cathepsin B activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 14;110(1):332–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91300-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsui K., Tsutsui K., Oda T. Isolation and characterization of a high-molecular-weight acid-soluble nuclear protein from mouse ascites-sarcoma cells. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jul;108(2):497–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04747.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandelt C., Grummt I. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes is a prerequisite for ribosomal DNA transcription in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3795–3809. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalta J., Zalta J. P., Simard R. Isolation of nucleoli. A method that combines high yield, structural integrity, and biochemical preservation. J Cell Biol. 1971 Nov;51(21):563–568. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.2.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]