Abstract
Passive transfer of neutralizing antibodies is effective in protecting rhesus macaques against simian/human immunodeficiency virus (SHIV) challenge. In addition to neutralization, effector functions of the crystallizable fragment (Fc) of antibodies are involved in antibody-mediated protection against a number of viruses. We recently showed that interaction between the Fc fragment of the broadly neutralizing antibody IgG1 b12 and cellular Fcγ receptors (FcγRs) plays an important role in protection against SHIV infection in rhesus macaques. The specific nature of this Fc-dependent protection is largely unknown. To investigate, we generated a panel of 11 IgG1 b12 antibody variants with selectively diminished or enhanced affinity for the two main activating FcγRs, FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa. All 11 antibody variants bind gp120 and neutralize virus as effectively as does wild-type b12. Binding studies using monomeric (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay [ELISA] and surface plasmon resonance [SPR]) and cellularly expressed Fcγ receptors show decreased (up to 5-fold) and increased (up to 90-fold) binding to FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa with this newly generated panel of antibodies. In addition, there was generally a good correlation between b12 variant affinity for Fcγ receptor and variant function in antibody-dependent cell-mediated virus inhibition (ADCVI), phagocytosis, NK cell activation assays, and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) assays. In future studies, these b12 variants will enable the investigation of the protective role of individual FcγRs in HIV infection.
INTRODUCTION
Most effective viral vaccines elicit neutralizing antibodies, and extensive studies carried out in rhesus macaques show that neutralizing antibodies are efficient in protecting against simian immunodeficiency virus/human immunodeficiency virus (SIV/HIV) challenge (17–19, 29, 30, 36, 47). Effector functions mediated by the crystallizable fragment (Fc) of antibodies, such as complement activation, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), phagocytosis, and release of antiviral cytokines and chemokines, contribute to protection against a number of viruses (5, 21, 35). We recently demonstrated that the Fc part of the broadly neutralizing antibody IgG1 b12 plays a crucial role in protection against simian-human immunodeficiency virus (SHIV) infection in rhesus macaques (17, 18). In these studies, using b12 variants deficient in Fcγ receptor (FcγR) interaction and complement activation, or complement activation only, we showed that complement activation alone was unimportant but that interaction with Fcγ receptors was required to obtain the full protective potential of the b12 antibody (17, 18).
The human Fcγ receptor family consists of three classes with six members: FcγRI, FcγRII (FcγRIIa, FcγRIIb, and FcγRIIc), and FcγRIII (FcγRIIIa and FcγRIIIb). The FcγRs are expressed on a wide variety of immune cells, the most potent effector cells being NK cells, macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells. NK cells almost exclusively express the activating FcγRIIIa and are thought to be the main cell type involved in ADCC. Macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells all express FcγRIIa and are phagocytic. However, they also express a mixture of other activating (FcγRI and FcγRIIIa) and inhibitory (FcγRIIb) receptors and can exhibit multiple effector functions, including ADCC (9, 34). FcγRI binds monomeric IgG with high affinity and, therefore, given the high concentration of serum IgG, is thought to be saturated under physiological conditions. In contrast, FcγRIIa, FcγRIIb, and FcγRIIIa bind monomeric IgG with low affinity and under physiological conditions probably require the formation of immune complexes for efficient IgG binding, consistent with a role for such FcγRs in pathogen clearance and immunoregulation (9, 34).
The FcγRs bind IgG antibodies in the lower hinge region mainly through interaction with a common set of residues. However, residues outside this common footprint also influence the strength of binding and are specific for the individual receptors (43). Manipulating the binding affinities between antibodies and FcγRs is a growing area of interest, especially in cancer research and the development of therapeutic antibodies. Antibody binding to FcγRIIIa, and to some extent also to FcγRIIa, has been the focus of this research. Two main approaches, deglycosylation and site-specific mutagenesis, have been used to engineer antibodies with greatly enhanced binding to FcγRIIIa and/or FcγRIIa, with corresponding increases in the potency of effector functions (22, 25, 41, 43). These studies provide insight into the antibody residues that need to be altered to generate antibodies with specific affinities for individual FcγRs.
Here, we describe the generation of a panel of b12 variant antibodies with selectively diminished or enhanced affinity for FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa. Binding to both monomeric and cellularly expressed FcγRs was characterized for all new variants and compared to wild-type (wt) b12. In addition, all variants were evaluated for effector function potency in viral inhibition, phagocytosis, NK cell activation, and ADCC assays. We believe that these variants will be valuable tools in future studies investigating the protective role of individual FcγRs in HIV infection.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Generation of IgG1 b12 variants.
Nucleic acid substitutions were introduced into pDR12 (7, 20) by QuikChange II XL site-directed mutagenesis (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA). All constructs were verified by sequence analysis (Eton Bioscience, San Diego, CA). Antibodies were expressed in CHO-K1 cells and purified using affinity chromatography (protein A Sepharose Fast Flow; GE Healthcare, United Kingdom).
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), gp120, and FcγRs.
Binding to gp120 was measured by coating microtiter plates (Corning Life Sciences, Lowell, MA) with 5 μg/ml JR-FL gp120 (Progenics, Tarrytown, NY) overnight at 4°C. Plates were blocked with 4% nonfat milk before serial dilutions of antibodies in 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA)-phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)-0.02% Tween were incubated for 1 h at room temperature. Binding was detected with alkaline phosphatase (AP)-labeled anti-human F(ab′)2 (1:1,000; Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, PA) and a phosphatase substrate (Sigma).
Binding of antibodies to recombinant FcγRs (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN) was performed as previously described (17). Binding was measured by capturing the FcγRs with an anti-penta-His antibody (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) applied as a coating to a microtiter plate. Serial dilutions of b12 or variants were then added. A horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled F(ab′)2 fragment of goat anti-human F(ab′)2 (1:100,000; Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, PA) was used as the detection antibody, and the results were visualized with tetramethylbenzidine (TMB).
SPR measurements.
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) measurements using a Biacore 2000 system were performed as previously described (41). Briefly, antibodies were captured (10 μl/min for 5 min) onto an amine-coupled protein A (Pierce, Rockford, IL) CM5 biosensor chip (Biacore, Piscataway, NJ). FcγRs (0.5 μM, 2-fold serial dilutions, 5 dilutions in total) were injected over the antibody-bound protein A surface at 30 μl/min for 3 min followed by an 8-min dissociation phase. Background binding obtained by injection of FcγRs onto the protein A CM5 biosensor chip (without antibody) was subtracted from the experiment traces. To account for baseline drift caused by IgG dissociation, all measurements were preceded by injection of buffer alone, which was later subtracted from all tracings (33). Binding curves were fitted to a 1:1 binding model using GraphPad Prism (GraphPad, San Diego, CA), and kinetic variables were used to calculate equilibrium dissociation constants (KDs).
Antibody binding to cellularly expressed FcγRs.
Binding of antibodies to cellularly expressed FcγRs was evaluated using the TZM-bl Fcγ cell lines (38). Cells (2 × 105/well) were stained with serial dilutions of b12 or variants for 1 h at room temperature (RT) in 96-well plates and washed twice with 2% fetal calf serum (FCS)-PBS, before being stained with a phycoerythrin (PE)-labeled F(ab′)2 fragment goat anti-human IgG F(ab′)2 for 30 min at RT (1:200 dilution; Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, PA). The double-stained cells were washed twice with 2% FCS-PBS before flow cytometry (Acurri C6; Acurri Cytometers, Ann Arbor, MI). All antibodies were diluted in 2% FCS-PBS. Data analysis was performed using FlowJo (Tree Star, Ashland, OR) and GraphPad Prism.
Virus neutralization assay.
Replication-incompetent HIV-1 enveloped pseudovirus was generated by cotransfection of 293T cells with HIV-1 Env-expressing plasmid (pSVIII) and pSG3ΔEnv as previously described (27). Serial dilutions of wt b12, b12 variants, and an isotype control antibody, DEN3, were preincubated with pseudovirus for 1 h at 37°C before being added to TZM-bl cells. Luciferase reporter gene expression was evaluated 2 days postinfection. The antibody dilution causing 50% reduction (50% inhibitory concentration [IC50]) was calculated by regression analysis using GraphPad Prism.
ADCVI.
Infectious virus was produced by transfection of 293T cells with pLAI-JRFL (26). Antibody-dependent cell-mediated viral inhibition (ADCVI) was performed as previously described (13, 17), except that target cells were human CD4 cells (activated for 3 days with 1 μg/ml phytohemagglutinin [PHA] and 50 units/ml interleukin-2 [IL-2]). Target cells were infected with a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.1 for 4 h (resulting in approximately 10% infection of target cells 48 h postinfection, measured by intracellular p24 staining). Forty-eight hours postinfection, target cells were washed and incubated with serial dilutions of antibodies (wt b12, b12 variants, and DEN3) and freshly isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) (effector-to-target ratio, 20:1). After 7 days, the supernatant was assayed for p24 by a p24-specific ELISA (Aalto Bio Reagents Ltd., Dublin, Ireland). Viral inhibition was calculated based on the p24 amount from a no-antibody control. CD4 cells were purified from whole blood using the RosetteSep human CD4+ T cell enrichment kit (Stemcell Technologies Inc., Vancouver, Canada). PBMCs were from the same donor and purified from whole blood by Ficoll-Paque centrifugation.
Phagocytosis.
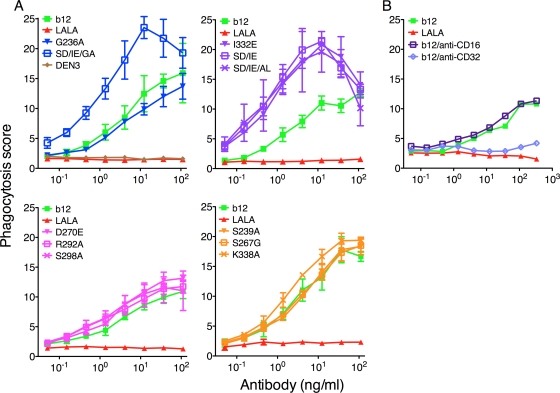
The phagocytosis assay was based on the monocytic cell line THP-1 (H131-FcγRIIa) and performed as previously described (2). Briefly, biotinylated JR-CSF gp120 was incubated with 1-μm fluorescent neutravidin beads (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) overnight at 4°C. Beads were subsequently washed to remove excess antigen. Washed beads (9 × 105/well) were placed in round-bottomed 96-well plates, and serial dilutions of wt b12, b12 variants, and DEN3 were added and incubated for 2 h at 37°C before THP-1 cells were added and incubated overnight at 37°C. Cells were washed and fixed (4% paraformaldehyde) before analysis by flow cytometry (BD LSR II; BD Bioscience, San Jose, CA). Flow data were analyzed using FlowJo (Tree Star, Ashland, OR), and a phagocytic score was determined by multiplying the percentage of cells positive for beads with the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of the same cell population (scores divided by 105 for ease of presentation). Fcγ receptor blocking experiments were done with the addition of an anti-CD32 antibody (Abcam, Cambridge, MA) or an anti-CD16 antibody (BD Pharmingen, San Diego, CA) together with the cells.
In vitro NK activation assay.
NK cells were purified using RosetteSep human NK cell enrichment (routinely resulting in >70% CD56-positive cells) (Stemcell Technologies Inc., Vancouver, Canada). Microtiter plates were coated with serial dilutions of b12 and b12 variants for 2 h at 37°C and washed with PBS, and 5 × 104 NK cells were added together with an anti-CD107a-PE antibody (BD Pharmingen, San Diego, CA). The NK cells were incubated for 4 h at 37°C and washed with 2% FCS-PBS before CD107a expression was determined by flow cytometry (Acurri C6; Acurri Cytometers, Ann Arbor, MI). Data analysis was performed using FlowJo (Tree Star, Ashland, OR) and GraphPad Prism.
ADCC.
An NK cell line derived from KHYG-1 cells (Japan Health Sciences Foundation) (48) that stably expresses human V158-FcγIIIa served as effector cells for the ADCC assay. NKR.CEM-CCR5 cells (46), which were modified to express firefly luciferase upon infection, served as targets. These cells were infected with HIV NL4-3 4 days prior to use. Effector and target cells were incubated at a 10:1 ratio in the presence of triplicate serial 2-fold dilutions of the IgG1 b12 variants. After 8 h, luciferase activity was measured using BriteLite Plus luciferase substrate (Perkin-Elmer, San Jose, CA). The luciferase signal in wells containing effectors and uninfected targets was subtracted out and thereby defined as 0% relative light units (RLU), whereas wells containing effectors and infected targets without serum or plasma were defined as 100% RLU. To calculate 50% ADCC titers, the percent RLU values above and below 50% were used to estimate the b12 concentration at 50% activity. Area under the curve (AUC) values for ADCC activity were calculated from the sum over all b12 dilutions for log10 100 − log10 % RLU. This sum was multiplied by the dilution factor of log10 2 to find an area. A Spearman correlation was calculated using GraphPad Prism.
RESULTS
Generation of IgG1 b12 variants.
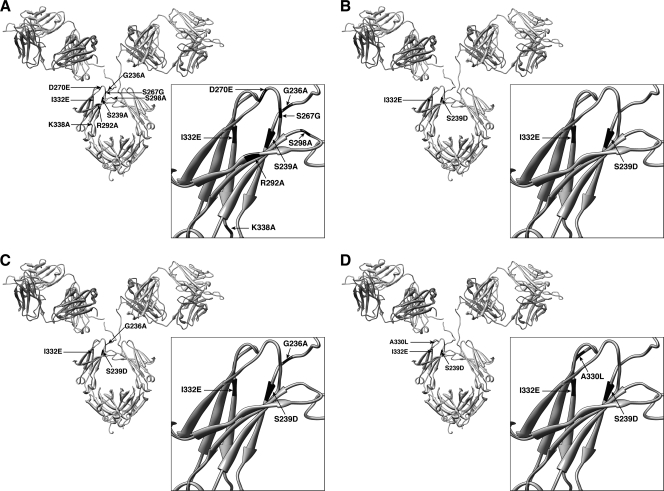
To enable us to investigate the importance of specific FcγRs in the protection against HIV infection, 11 IgG1 b12 variants were generated (Fig. 1). The 11 variants contain substitutions previously described in large-scale mutagenesis screening of IgG1 binding to human FcγRs (25, 41, 43). The substitutions introduced into the new variants were chosen to focus on the antibody interaction with FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa, which are the main activating receptors and are important in protection against a number of viruses in animal models (6, 9, 16, 31, 32). The new b12 variants can roughly be divided into four groups: decreased FcγRIIa binding (FcγRIIa down-variants; D270E, R292A, and S298A), decreased FcγRIIIa binding (FcγRIIIa down-variants; S239A, S267G, and K338A), increased FcγRIIa binding (FcγRIIa up-variants; G236A and S239D/I332E/G236A), and increased FcγRIIIa binding (FcγRIIIa up-variants; I332E, S239D/I332E, and S239D/I332E/A330L).
Fig. 1.
Location of substitutions introduced into the b12 antibody molecule. (A) Single substitutions (G236A, S239A, S267G, D270E, R292A, S298A, I332E, and K338A). (B) Double substitutions (S239D/I332E). (C) Triple substitutions (S239D/I332E/G236A). (D) Triple substitutions (S239D/I332E/A330L). The structure of b12 is described in the work of Saphire et al. (42) (PDB accession code 1HZH).
gp120 binding and neutralization of pseudovirus.
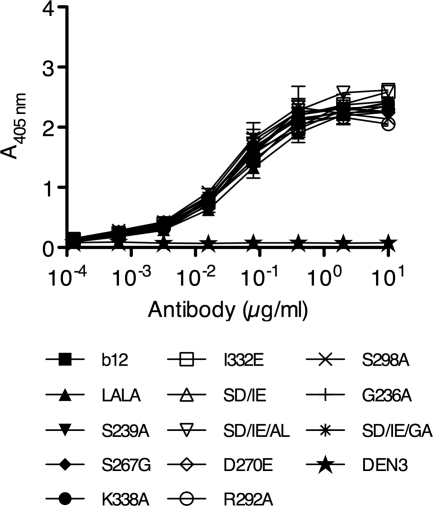
The introduced substitutions are all located in the Fc part of the antibody and as such should not interfere with Fab recognition. All 11 b12 variants were tested in a gp120-specific ELISA, and as expected, all bound JR-FL gp120 with an apparent affinity close to that of wt b12 (50% effective concentration [EC50] between 0.029 and 0.053 μg/ml) (Fig. 2). A 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test showed no significant difference between the EC50s (P=0.9735). In addition, we tested all b12 variants in a pseudovirus neutralization assay and showed that all variants neutralized HIV JR-FL, HIV JR-CSF, and SHIVSF162P3 with potency similar to that of wt b12 (Table 1).
Fig. 2.
Binding of wild-type b12, b12 variants, and negative IgG1 control anti-dengue virus antibody DEN3 to HIV-1 JR-FL gp120. ELISA plates were coated with JR-FL gp120, and serial dilutions of b12 or b12 variants were added. An AP-anti-human F(ab′)2 antibody was used as secondary antibody. wt b12 and variants bind gp120 with similar apparent affinities. Values are means and standard deviations of duplicate wells. The assay was performed twice with similar results.
Table 1.
b12 variant pseudovirus neutralization
| Variant | IC50a (μg/ml) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| JR-FL | JR-CSF | SHIVSF162P3 | |
| wt b12 | 0.023 | 0.88 | 0.13 |
| S239A | 0.026 | 0.77 | 0.09 |
| S267G | 0.024 | 0.37 | 0.11 |
| K338A | 0.028 | 0.16 | 0.15 |
| I332E | 0.027 | 0.64 | 0.10 |
| SD/IE | 0.029 | 0.46 | 0.05 |
| SD/IE/AL | 0.027 | 0.39 | 0.06 |
| D270E | 0.028 | 0.42 | 0.09 |
| R292A | 0.027 | 0.28 | 0.10 |
| S298A | 0.028 | 0.63 | 0.07 |
| G236A | 0.028 | 0.66 | 0.16 |
| SD/IE/GA | 0.059 | 0.45 | 0.11 |
The antibody dilution causing 50% reduction (IC50) in luciferase reporter gene expression was calculated by regression analysis (n=2).
Binding to human FcγRs.
To explore the Fcγ receptor binding specificities of the b12 variants, we carried out ELISAs specific for FcγRI, H131-FcγRIIa, and F158-FcγRIIIa. Binding to FcγRI was equal to that of wt b12 for all variants except G236A, for which a minor decrease in apparent affinity was observed (Table 2 ). The variants designed to decrease affinity for FcγRIIIa (FcγRIIIa down-variants) showed a 2- to 5-fold decrease in apparent affinity of binding to FcγRIIIa compared to wt b12, whereas binding to FcγRIIa was fairly similar to wt b12 (Table 2). The variants designed to increase binding to FcγRIIa (FcγRIIa up-variants) and FcγRIIIa (FcγRIIIa up-variants) showed highly increased apparent affinity, an 8- to 49-fold increase for FcγRIIa and a 7- to 90-fold increase for FcγRIIIa, compared to wt b12 (Table 2). The FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa up-variants showed variable binding to the nontargeted receptor (i.e., 0.9- to 66-fold increase in apparent affinity of FcγRIIa up-variants to FcγRIIIa compared to wt b12 and 3- to 6-fold increase for FcγRIIIa up-variants to FcγRIIa compared to wt b12) (Table 2). The b12 variants generated to show a decreased affinity for FcγRIIa (FcγRIIa down-variants) seemed less potent than previously reported (43), as only a 2-fold decrease in apparent affinity relative to wt b12 was observed (Table 2). The b12 variants with increased affinity for FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa were further evaluated in SPR experiments to measure binding to the two receptors. KDs were calculated based on the generated sensorgrams, and the binding affinities obtained were comparable to previously reported data (Table 3) (25, 41). Importantly, the SPR data also showed binding affinities (fold relative to wt b12) comparable to those obtained with the ELISA (Tables 2 and 3).
Table 2.
Relative binding affinities determined by ELISA
| Group and variant | Binding relative to wt b12a |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| FcγRI | FcγRIIa | FcγRIIIa | |
| FcγRIIIa down-variants | |||
| S239A | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.22 |
| S267G | 1.05 | 2.99 | 0.21 |
| K338A | 1.21 | 1.50 | 0.41 |
| FcγRIIIa up-variants | |||
| I332E | 1.21 | 3.19 | 7.32 |
| SD/IE | 1.29 | 5.99 | 31 |
| SD/IE/AL | 1.06 | 3.41 | 90 |
| FcγRIIa down-variants | |||
| D270E | 0.71 | 0.42 | 0.69 |
| R292A | 0.91 | 0.43 | 0.65 |
| S298A | 0.84 | 0.52 | 1.31 |
| FcγRIIa up-variants | |||
| G236A | 0.44 | 8.63 | 0.93 |
| SD/IE/GA | 0.91 | 49 | 66 |
Numbers represent the EC50 of wt b12/EC50s of b12 variants. EC50s (half-maximal effective concentrations) were calculated by fitting binding curves generated by plotting A450 of FcγR binding as a function of antibody concentration (n=2).
Table 3.
Binding affinities for b12 variants to FcγRs determined by SPR
| Group and variant | FcγRIIa |
FcγRIIIa |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KDa (μM) | Foldb | KDa (μM) | Foldb | |
| Wild-type b12 | 0.735 | 1 | 0.200 | 1 |
| FcγRIIIa up-variants | ||||
| I332E | 0.220 | 3.3 | 0.038 | 5.3 |
| SD/IE | 0.147 | 5.0 | 0.005 | 40 |
| SD/IE/AL | 0.246 | 3.0 | 0.002 | 100 |
| FcγRIIa up-variants | ||||
| G236A | 0.125 | 5.9 | 0.180 | 1.1 |
| SD/IE/GA | 0.036 | 20 | 0.011 | 18 |
KDs were obtained from global fits of Biacore sensorgrams (n=2).
Fold is relative to wt b12 (KD of b12/KD of variant).
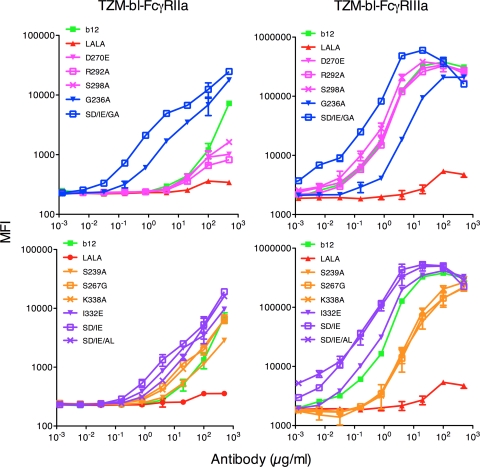
To evaluate the interaction between the b12 variants and cellularly expressed Fcγ receptors, we used the TZM-bl cell lines engineered to constitutively express either H131-FcγRIIa or F158-FcγRIIIa (38). Binding measurements using the TZM-bl-FcγRIIa cells showed a minor decrease in apparent binding affinity relative to wt b12 for the FcγRIIa down-variants, a large increase for the FcγRIIa up-variants, similar relative affinity or a minor increase for the FcγRIIIa down-variants, and a minor increase for the FcγRIIIa up-variants (Fig. 3, left column). The TZM-bl-FcγRIIIa cell line showed a decrease in apparent binding affinity relative to wt b12 for the FcγRIIIa down-variants, an increase for the FcγRIIIa up-variants, similar relative affinity for the FcγRIIa down-variants, and a decrease for G236A and an increase for S239D/I332E/G236A (FcγRIIa up-variants) (Fig. 3, right column). Overall, the patterns of binding to the cellularly expressed FcγRs mimic closely that which was observed in the ELISA and SPR assays.
Fig. 3.
Binding of wt b12 and b12 variants to FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa expressed on the surface of TZM-bl cells. Cells were stained with serially diluted b12 or variants. A secondary antibody was added [PE-anti-human F(ab′)2 antibody] before analysis by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Binding curves were generated by plotting mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of FcγR binding as a function of antibody concentration. Left plots are TZM-bl-FcγRIIa cells; right plots are TZM-bl-FcγRIIIa cells. FcγRIIa up-variants are shown in blue, FcγRIIa down-variants are shown in pink, FcγRIIIa up-variants are shown in purple, and FcγRIIIa down-variants are shown in yellow. Values are means and standard deviations of triplicate wells. The assay was performed twice with similar results.
These combined studies (using monomeric and cellularly expressed FcγRs) demonstrate that we have generated a panel of IgG1 b12 variants with a range of selectively diminished or enhanced affinities for the main activating receptors FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa.
Viral inhibition.
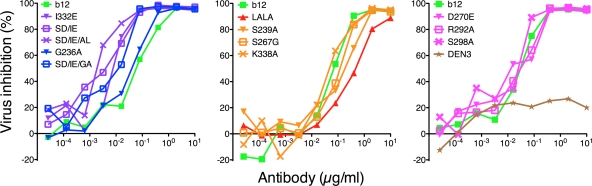
To measure the antiviral effects of the altered FcγR affinities of the generated b12 variants, we first carried out an ADCVI assay. The ADCVI assay is a measurement of the ability of the antibody, in the presence of effector cells, to inhibit viral replication in infected cells. Using autologous PBMC and CD4 cells as effector and target cells, we observed that all variants with increased affinity for either of the main activating receptors (FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa) also showed an increase in viral inhibition of HIV-1 JR-FL compared to wt b12 (Fig. 4). The variants with decreased affinity for FcγRIIIa resulted in a minor decrease in viral inhibition, whereas the variants with decreased affinity for FcγRIIa showed viral inhibition similar to that of wt b12 (Fig. 4). However, the non-FcγR-interacting variant (LALA) still mediated inhibition (albeit lower), indicating that neutralization is an important factor in the observed inhibition (Fig. 4). To investigate the role of FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa in ADCVI further, we calculated the IC50 for the b12 variants and performed a Spearman correlation test between IC50 and FcγR affinity (from Table 2). A significant correlation was obtained for FcγRIIIa (r=0.7622, P=0.0055), and no correlation could be shown between IC50 and FcγRIIa affinity (r=0.4685, P=0.1275).
Fig. 4.
ADCVI with wt b12, b12 variants, and DEN3 as an IgG1 control antibody. Human CD4 cells were infected with HIV-1 JR-FL (MOI of 0.1). Forty-eight hours postinfection, cells were washed and incubated with serial dilutions of antibodies (wt b12, b12 variants, and DEN3) and freshly isolated autologous PBMCs. Viral inhibition was measured by analyzing supernatant in a p24-specific ELISA 9 days postinfection. Increased or decreased affinity for FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa results in a corresponding increase or decrease in viral inhibition, respectively. FcγRIIa up-variants are shown in blue, FcγRIIa down-variants are shown in pink, FcγRIIIa up-variants are shown in purple, and FcγRIIIa down-variants are shown in yellow. Values are means of triplicate wells. The assay was performed twice with similar results.
Phagocytosis.
To further investigate the effector function specificity of the b12 variants, we used a newly developed phagocytosis assay (2). The assay is based on the cellular uptake of gp120-coated fluorescence beads by the monocytic cell line THP-1 (H131-FcγRIIa) (44). Hence, the THP-1 cells become more fluorescent in proportion to the amount of beads that they internalize. As seen in Fig. 5 A, wt b12 increases phagocytosis compared to IgG1 controls (LALA and DEN3). All variants with increased FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa (I332E, S239D/I332E, S239D/I332E/G236A, and S239D/I332E/A330L) binding showed higher phagocytosis than did wt b12, except the G236A variant, which showed phagocytosis similar to that of wt b12. The variants designed to decrease FcγRIIa (but which did so by only 2-fold) and FcγRIIIa binding showed phagocytic potency similar to wt b12. To evaluate the importance of the different receptors, we added a CD16 or CD32 blocking antibody together with wt b12. As expected, blocking FcγRIIa also abolished all phagocytosis, whereas blocking FcγRIIIa showed no effect (Fig. 5B), demonstrating that the observed internalization was FcγRIIa dependent. We calculated the EC50 (based on the phagocytosis score) for the b12 variants. However, no significant correlation could be shown between EC50 and FcγRIIa affinity (Spearman correlation, r=−0.3217, P=0.3085) despite the FcγRIIa dependency.
Fig. 5.
Phagocytosis of gp120-coated beads with wt b12, b12 variants, and DEN3. (A) Fluorescent gp120-coated beads were opsonized with antibodies for 2 h before the addition of THP-1 cells. Phagocytosis was evaluated after 24 h of coincubation of cells and bead-antibody complexes using flow cytometry. A phagocytosis score was calculated by multiplying the percentage of cells positive for beads with the mean fluorescence intensity of the same cell population. Applying both values ensures that the number of active phagocytic cells as well as the phagocytic efficiency of the individual cell is added to the experimental read-out. FcγRIIa up-variants are shown in blue, FcγRIIa down-variants are shown in pink, FcγRIIIa up-variants are shown in purple, and FcγRIIIa down-variants are shown in yellow. Values are means and standard deviations of triplicate wells. The assay was repeated twice. (B) As in panel A, except that an anti-CD16 or anti-CD32 antibody was added together with wt b12 to determine the FcγR (IIa or IIIa) that mediated phagocytosis of the beads. The assay was performed twice with similar results.
NK cell activation.
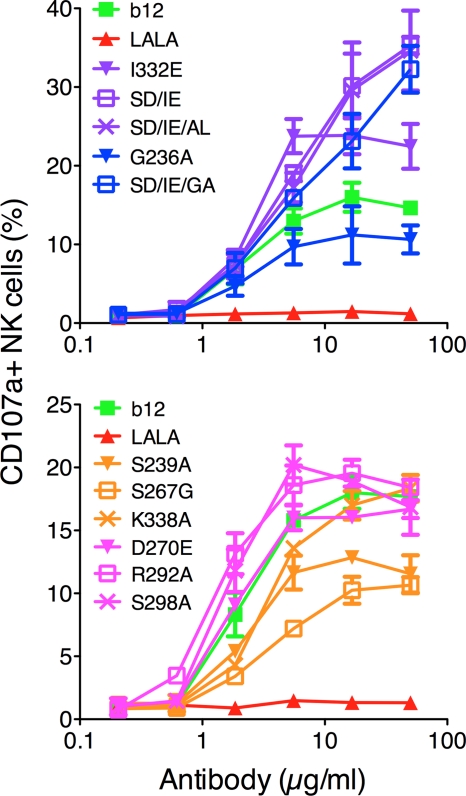
NK-mediated effector functions (ADCC, gamma interferon [IFN-γ], and tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-α] secretion) are closely linked to cell activation (3, 4). To evaluate the potency of b12 variants to activate NK cells, 96-microtiter plates were coated with wt b12 or b12 variants to mimic antibody aggregation before adding freshly purified human NK cells. After a 4-hour incubation period, the cells were analyzed for the expression of the well-characterized marker for NK cell activation, CD107a. All variants with increased affinity for FcγRIIIa showed a corresponding increase in NK cell activation compared to wt b12, with the double (S239D/I332E) and triple (S239D/I332E/A330L and S239D/I332E/G236A) variants showing the highest potency (Fig. 6). As expected, the FcγRIIa down-variants (D270E, R292A, and S298A) had activation potentials similar to that of wt b12 (Fig. 6). The FcγRIIIa down-variants (S239A, S267G, and K338A) and G236A all showed a substantially lower ability to activate NK cells than did wt b12 (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6.
In vitro NK cell activation using wt b12 and b12 variants. Microtiter plates were coated with antibody. Freshly isolated NK cells were incubated for 4 h before evaluation for CD107a expression by flow cytometry. Curves were generated by plotting percent NK cell expression as a function of coating antibody concentration. FcγRIIa up-variants are shown in blue, FcγRIIa down-variants are shown in pink, FcγRIIIa up-variants are shown in purple, and FcγRIIIa down-variants are shown in yellow. Values are means and standard deviations of triplicate wells. The assay was performed twice with similar results.
ADCC.
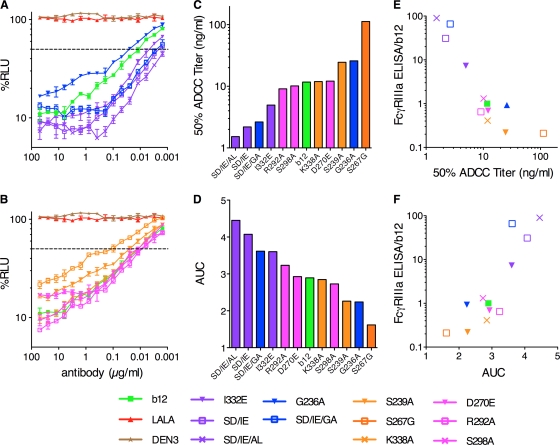
ADCC has been shown to be a key effector function in antibody-based treatment of certain cancers (8) and could therefore also be an important factor in protection against HIV. To investigate the ADCC potency of the b12 variants, we infected a CEM.NKR-CCR5 cell line containing a Tat-inducible luciferase reporter gene with HIV NL4-3. The infected CEM cells were coincubated for 8 h with an NK cell line constitutively expressing CD16 and serial dilutions of antibodies before being evaluated for luciferase activity. All b12 variants with higher affinity for FcγRIIIa (SD/IE/AL, SD/IE, I332E, and SD/IE/GA) showed a marked increase in the ability to mediate ADCC compared to wt b12 (seen as a decrease in luciferase expression) whereas the variants with lower affinity for FcγRIIIa (S239A and S267G, except K338A) showed the reverse (Fig. 7 A). The 50% ADCC titers and areas under the curve (AUC) for all the variants and wt b12 were calculated and display a broad range of ADCC potencies (Fig. 7B and C). In addition, plotting of the relative affinities of b12 and b12 variants for FcγRIIIa (Table 2) as a function of 50% ADCC titer and AUC demonstrates a strong positive correlation between FcγRIIIa affinity and ADCC (Fig. 7D and E) (Spearman correlation, r=−0.85, P=0.0008, and r=0.79, P=0.0033, respectively).
Fig. 7.
ADCC by b12, b12 variants, and DEN3 using target cells infected with HIV-1 NL4-3. (A and B) Variants of b12 were titrated for ADCC activity against target cells infected with HIV-1 NL4-3, starting at a concentration of 50 μg/ml, and using an NK cell line expressing human CD16 (FcγRIIIa) as the effector cells. The killing of virus-infected cells by ADCC is indicated by a loss of relative light units (RLU). The dashed line indicates 50% activity. DEN3 and LALA served as negative controls. (C and D) For each monoclonal antibody, 50% ADCC titers (C) and area under the curve (AUC) (D) values for ADCC are shown. The minimum SD/IE/AL concentration tested, 1.5 ng/ml, is reported in lieu of a 50% titer. (E and F) Fold differences in binding of FcγRIIIa relative to b12 are plotted as a function of 50% ADCC titers (E) and AUC values for ADCC (F). FcγRIIa up-variants are shown in blue, FcγRIIa down-variants are shown in pink, FcγRIIIa up-variants are shown in purple, and FcγRIIIa down-variants are shown in yellow. Values are means and standard deviations of triplicate wells.
DISCUSSION
An increasing number of studies suggest that in addition to neutralization, recruitment of innate effector cells through interaction with FcγRs plays an important role in antibody-mediated protection against HIV (11, 15, 17, 18). However, the FcγR-based mechanism of protection remains unknown.
To investigate the role of specific FcγRs in the context of HIV infection, we have engineered a panel of 11 IgG1 b12 variants with a broad range of affinities for FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa. We have shown a potent increase in affinity for both FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa for b12 up-variants compared to wild-type b12, displaying binding profiles very similar to those reported previously (25, 41). Surprisingly, the generated b12 down-variants, in particular the FcγRIIa subset, did not display a reduction in binding of the magnitude reported by Shields et al. (43). The reason for this discrepancy is at this time unknown, but differences in the binding assays could play a role, or possibly factors intrinsic to the b12 antibody could account for the difference.
While most antibody-based therapies are cancer focused (39), other diseases such as viral infections could potentially benefit from antibody treatment, as demonstrated in a human trial where a cocktail of broadly neutralizing antibodies was administered to HIV-infected individuals (45). The antibody regime resulted in a delay in viral rebound during interruption of antiviral treatment, attributed solely to the presence of the broadly neutralizing antibody IgG 2G12 in the cocktail (45). Interestingly, we recently reported that 2G12 protects rhesus macaques against SHIV challenges with higher potency than would be expected from its neutralization ability in vitro, which indicates that other mechanisms may contribute to protection in vivo (19). In treatment of HIV-1 infection, continuous administration of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) alone would be insufficient because of the emergence of escape variants (1, 28, 45). However, in specific cases such as strategies aimed at reactivating latent viral reservoirs where enhanced killing of infected cells would be a key component in clearing the infection, antibodies with enhanced effector functions could be useful.
Large-scale IgG mutagenesis screens have identified sets of residues critical for the interaction between IgG1 and different FcγRs and have allowed for the design of antibodies with specific FcγR binding profiles (25, 41, 43). FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa are considered the two main receptors for antiviral effector functions such as phagocytosis and ADCC (9, 14). We have shown that interaction with FcγRs is important for antibody-dependent protection against mucosal SHIV challenge in rhesus macaques (17, 18). ADCVI is a commonly used assay to investigate antibody-dependent inhibition of viral replication and measures the cumulative effect of multiple effector functions such as ADCC, phagocytosis, and the release of antiviral cytokines and chemokines. In this report we have demonstrated that increased affinity for FcγRIIIa resulted in an increase in viral inhibition (10). Additionally, we also showed that enhanced FcγRIIa affinity leads to increased viral inhibition, confirming the importance of FcγRIIa-bearing effector cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells in this regard (12, 37). Variants with lower affinity for both receptors (including LALA) showed only a small decrease in viral inhibition, indicating that the ADCVI assay is strongly influenced by non-FcγR-mediated functions such as neutralization.
In contrast to ADCVI, phagocytosis is mainly dependent on FcγRIIa since inhibiting the interaction with this receptor abolishes all phagocytic activity (2, 41). Surprisingly, we were unable to see any difference in phagocytosis for variants with increased affinity for FcγRIIa despite the broad range of enhancements (3- to 49-fold greater than wt b12). Yet, the same amino acid substitutions used here have been shown to induce a stratified increase in phagocytosis of cancer cells. However, the assay used in the cancer studies differs in term of effector cells, target, and endpoint read-out as well as the duration of the assay, and this may be responsible for the differences between those observations and these presented here (41). It would be of interest to explore the effects of varying some of these parameters on phagocytosis. Interestingly, HIV-infected individuals carrying the low-affinity allele of FcγRIIa have a faster disease progression than those with either mixed or high-affinity alleles, indicating a possible role for phagocytosis in in vivo viral control (14a).
Most of the focus on effector functions in protection against HIV has been on ADCC. Several studies, including the recent RV144 trial, suggest that ADCC or other extra neutralizing functions may contribute to protection against infection (11, 23, 40). In addition, ADCC-specific antibodies were shown to be present at a higher level in elite controllers than in HIV-infected individuals with low natural control of viremia. Our results show that the level of NK activation corresponds very well with the observed affinity for FcγRIIIa as well as with the ADCC potencies of the b12 variants. This emphasizes the previously observed strong link between these three phenomena (4, 24, 25, 41). The broad range of ADCC potencies for our panel of b12 variants should render them useful as control antibodies in future in vitro evaluations of new HIV-specific monoclonal antibodies or serum samples from infected/vaccinated study subjects.
Different approaches have been developed for optimizing antibody immune engagement. In this study, we have taken advantage of the large body of knowledge generated by amino acid substitutions in cancer antibody research (25, 41, 43). An alternative approach to changing the antibody-FcγR interface is to manipulate the glycosylation pattern of the antibody (22). A nonfucosylated humanized anti-epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) antibody showed an approximately 10-fold increase in affinity for FcγRIIIa relative to the fucosylated form (41). This antibody was also better able to mediate ADCC in the nonfucosylated form, albeit to a lesser magnitude (41). We have generated a nonfucosylated b12 antibody (D. R. Burton, unpublished data) that shows 5-fold-higher affinity for FcγRIIIa and is more potent at antiviral activity in vitro than is wt b12. However, the anti-HIV antibody 2G12, engineered to be nonfucosylated, showed only a minor increase in ADCVI relative to wt 2G12, suggesting that the increase in FcγRIIIa affinity may have been modest (10). In contrast, a 2G12 antibody carrying the SD/IE substitutions has been shown to induce a 10-fold increase in ADCC (24). Together, these in vitro results indicate that amino acid substitutions may provide more pronounced effects than glycosylation modifications for certain antibody functions but that the effects may differ between antibodies. The extent to which differences in in vitro potency of engineered antibodies are reflected in differences in activity in vivo remains to be seen, as very few studies have been performed. This will be an important aspect of future validation (9). The studies that have been done show promising results, at least in cancer models, as potent B-cell depletion was observed in monkeys after administration of either a nonfucosylated or an amino acid-modified antibody (7a, 25). Future in vivo studies in HIV protection models will be a pertinent opportunity to show whether treatment of infectious diseases can benefit accordingly.
In summary, we have generated a panel of IgG1 b12s with a broad range of affinities for human FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa while retaining wt b12 neutralization potency. We plan to use a selection of the newly generated b12 antibodies for passive transfer/SHIV challenge studies in rhesus macaques. Such in vivo evaluation of b12 variants with various binding profiles to FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa will contribute to defining the interplay between the humoral and innate immune system and to clarifying the role of specific effector functions such as ADCC and phagocytosis in protection against HIV.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Christina Corbaci for assistance with graphics. The following reagents were obtained through the AIDS Research and Reference Reagent Program, Division of AIDS, NIAID, NIH: CEM.NKR-CCR5 from Alexandra Trkola and TZM-bl/FcγRs from David Montefiori and Gabriel Perez.
This work was funded by a fellowship to B.M. from the Alfred Benzon Foundation and grants from NIH (AI055332), the International AIDS Vaccine Initiative through the Neutralizing Antibody Consortium, and the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT, and Harvard to D.R.B.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 17 August 2011.
REFERENCES
- 1. Abela I. A., Reynell L., Trkola A. 2010. Therapeutic antibodies in HIV treatment—classical approaches to novel advances. Curr. Pharm. Des. 16: 3754–3766 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Ackerman M. E., et al. 2011. A robust, high-throughput assay to determine the phagocytic activity of clinical antibody samples. J. Immunol. Methods 366: 8–19 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Alter G., Malenfant J. M., Altfeld M. 2004. CD107a as a functional marker for the identification of natural killer cell activity. J. Immunol. Methods 294: 15–22 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Awan F. T., et al. 2010. CD19 targeting of chronic lymphocytic leukemia with a novel Fc-domain-engineered monoclonal antibody. Blood 115: 1204–1213 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Baldridge J. R., Buchmeier M. J. 1992. Mechanisms of antibody-mediated protection against lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection: mother-to-baby transfer of humoral protection. J. Virol. 66: 4252–4257 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Banks N. D., Kinsey N., Clements J., Hildreth J. E. 2002. Sustained antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) in SIV-infected macaques correlates with delayed progression to AIDS. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 18: 1197–1205 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Burton D. R., et al. 1994. Efficient neutralization of primary isolates of HIV-1 by a recombinant human monoclonal antibody. Science 266: 1024–1027 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7a. Cardarelli P. M., et al. 2010. A nonfucosylated human antibody to CD19 with potent B-cell depletive activity for therapy of B-cell malignancies. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 59: 257–265 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Cartron G., et al. 2002. Therapeutic activity of humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and polymorphism in IgG Fc receptor FcgammaRIIIa gene. Blood 99: 754–758 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Desjarlais J. R., Lazar G. A., Zhukovsky E. A., Chu S. Y. 2007. Optimizing engagement of the immune system by anti-tumor antibodies: an engineer's perspective. Drug Discov. Today 12: 898–910 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Forthal D. N., et al. 2010. Fc-glycosylation influences Fcgamma receptor binding and cell-mediated anti-HIV activity of monoclonal antibody 2G12. J. Immunol. 185: 6876–6882 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Forthal D. N., Gilbert P. B., Landucci G., Phan T. 2007. Recombinant gp120 vaccine-induced antibodies inhibit clinical strains of HIV-1 in the presence of Fc receptor-bearing effector cells and correlate inversely with HIV infection rate. J. Immunol. 178: 6596–6603 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Forthal D. N., et al. 2006. Rhesus macaque polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies inhibit simian immunodeficiency virus in the presence of human or autologous rhesus effector cells. J. Virol. 80: 9217–9225 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Forthal D. N., Landucci G., Daar E. S. 2001. Antibody from patients with acute human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection inhibits primary strains of HIV type 1 in the presence of natural-killer effector cells. J. Virol. 75: 6953–6961 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Forthal D. N., Moog C. 2009. Fc receptor-mediated antiviral antibodies. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 4: 388–393 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14a. Forthal D. N., et al. 2007. FcγRIIa genotype predicts progression of HIV infection. J. Immunol. 179: 7916–7923 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Gomez-Roman V. R., et al. 2005. Vaccine-elicited antibodies mediate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity correlated with significantly reduced acute viremia in rhesus macaques challenged with SIVmac251. J. Immunol. 174: 2185–2189 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Hayashida I., et al. 1982. Mechanism of antibody-mediated protection against herpes simplex virus infection in athymic nude mice: requirement of Fc portion of antibody. Microbiol. Immunol. 26: 497–509 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Hessell A. J., et al. 2007. Fc receptor but not complement binding is important in antibody protection against HIV. Nature 449: 101–104 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Hessell A. J., et al. 2009. Effective, low-titer antibody protection against low-dose repeated mucosal SHIV challenge in macaques. Nat. Med. 15: 951–954 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Hessell A. J., et al. 2009. Broadly neutralizing human anti-HIV antibody 2G12 is effective in protection against mucosal SHIV challenge even at low serum neutralizing titers. PLoS Pathog. 5: e1000433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Hezareh M., Hessell A. J., Jensen R. C., van de Winkel J. G., Parren P. W. 2001. Effector function activities of a panel of mutants of a broadly neutralizing antibody against human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 75: 12161–12168 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Huber V. C., Lynch J. M., Bucher D. J., Le J., Metzger D. W. 2001. Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis makes a significant contribution to clearance of influenza virus infections. J. Immunol. 166: 7381–7388 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Jefferis R. 2009. Glycosylation as a strategy to improve antibody-based therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 8: 226–234 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Karnasuta C., et al. 2005. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic responses in participants enrolled in a phase I/II ALVAC-HIV/AIDSVAX B/E prime-boost HIV-1 vaccine trial in Thailand. Vaccine 23: 2522–2529 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Klein J. S., Webster A., Gnanapragasam P. N., Galimidi R. P., Bjorkman P. J. 2010. A dimeric form of the HIV-1 antibody 2G12 elicits potent antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. AIDS 24: 1633–1640 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Lazar G. A., et al. 2006. Engineered antibody Fc variants with enhanced effector function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103: 4005–4010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Leaman D. P., Kinkead H., Zwick M. B. 2010. In-solution virus capture assay helps deconstruct heterogeneous antibody recognition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 84: 3382–3395 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Li M., et al. 2005. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 env clones from acute and early subtype B infections for standardized assessments of vaccine-elicited neutralizing antibodies. J. Virol. 79: 10108–10125 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Mascola J. R. 2009. The cat and mouse of HIV-1 antibody escape. PLoS Pathog. 5: e1000592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Mascola J. R. 2002. Passive transfer studies to elucidate the role of antibody-mediated protection against HIV-1. Vaccine 20: 1922–1925 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Mascola J. R., et al. 2000. Protection of macaques against vaginal transmission of a pathogenic HIV-1/SIV chimeric virus by passive infusion of neutralizing antibodies. Nat. Med. 6: 207–210 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Mathews J. H., Roehrig J. T., Trent D. W. 1985. Role of complement and the Fc portion of immunoglobulin G in immunity to Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus infection with glycoprotein-specific monoclonal antibodies. J. Virol. 55: 594–600 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. McKendall R. R. 1985. IgG-mediated viral clearance in experimental infection with herpes simplex virus type 1: role for neutralization and Fc-dependent functions but not C' cytolysis and C5 chemotaxis. J. Infect. Dis. 151: 464–470 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Myszka D. G. 1999. Improving biosensor analysis. J. Mol. Recognit. 12: 279–284 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Nimmerjahn F., Ravetch J. V. 2008. Fcgamma receptors as regulators of immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8: 34–47 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Parren P. W., Burton D. R. 2001. The antiviral activity of antibodies in vitro and in vivo. Adv. Immunol. 77: 195–262 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Parren P. W., et al. 2001. Antibody protects macaques against vaginal challenge with a pathogenic R5 simian/human immunodeficiency virus at serum levels giving complete neutralization in vitro. J. Virol. 75: 8340–8347 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Peressin M., et al. 2011. HIV-1 replication in Langerhans and interstitial dendritic cells is inhibited by neutralizing and Fc-mediated inhibitory antibodies. J. Virol. 85: 1077–1085 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Perez L. G., Costa M. R., Todd C. A., Haynes B. F., Montefiori D. C. 2009. Utilization of immunoglobulin G Fc receptors by human immunodeficiency virus type 1: a specific role for antibodies against the membrane-proximal external region of gp41. J. Virol. 83: 7397–7410 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Reichert J. M. 2010. Antibodies to watch in 2010. MAbs 2: 84–100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Rerks-Ngarm S., et al. 2009. Vaccination with ALVAC and AIDSVAX to prevent HIV-1 infection in Thailand. N. Engl. J. Med. 361: 2209–2220 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Richards J. O., et al. 2008. Optimization of antibody binding to FcgammaRIIa enhances macrophage phagocytosis of tumor cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 7: 2517–2527 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Saphire E. O., et al. 2001. Crystal structure of a neutralizing human IGG against HIV-1: a template for vaccine design. Science 293: 1155–1159 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Shields R. L., et al. 2001. High resolution mapping of the binding site on human IgG1 for Fc gamma RI, Fc gamma RII, Fc gamma RIII, and FcRn and design of IgG1 variants with improved binding to the Fc gamma R. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 6591–6604 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Tebo A. E., Kremsner P. G., Luty A. J. 2002. Fcgamma receptor-mediated phagocytosis of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes in vitro. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 130: 300–306 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Trkola A., et al. 2005. Delay of HIV-1 rebound after cessation of antiretroviral therapy through passive transfer of human neutralizing antibodies. Nat. Med. 11: 615–622 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Trkola A., Matthews J., Gordon C., Ketas T., Moore J. P. 1999. A cell line-based neutralization assay for primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates that use either the CCR5 or the CXCR4 coreceptor. J. Virol. 73: 8966–8974 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Veazey R. S., et al. 2003. Prevention of virus transmission to macaque monkeys by a vaginally applied monoclonal antibody to HIV-1 gp120. Nat. Med. 9: 343–346 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Yagita M., et al. 2000. A novel natural killer cell line (KHYG-1) from a patient with aggressive natural killer cell leukemia carrying a p53 point mutation. Leukemia 14: 922–930 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]