Abstract
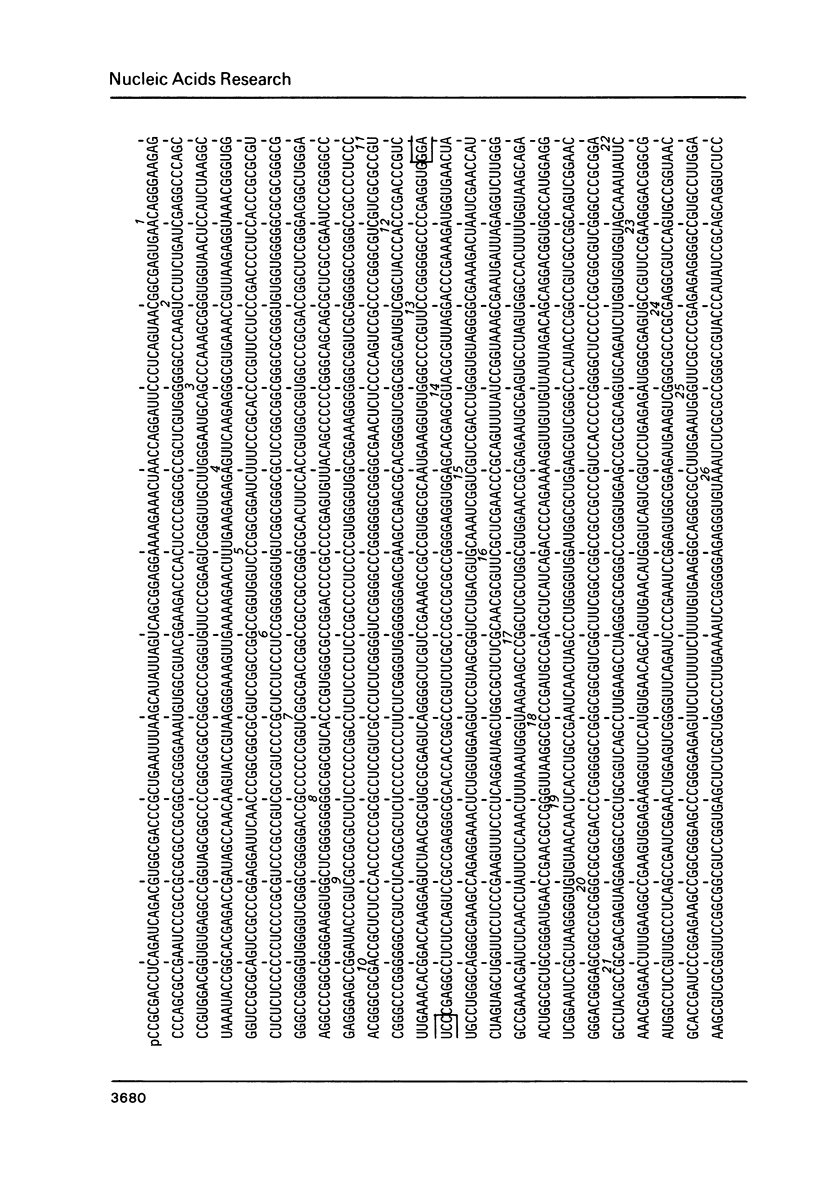
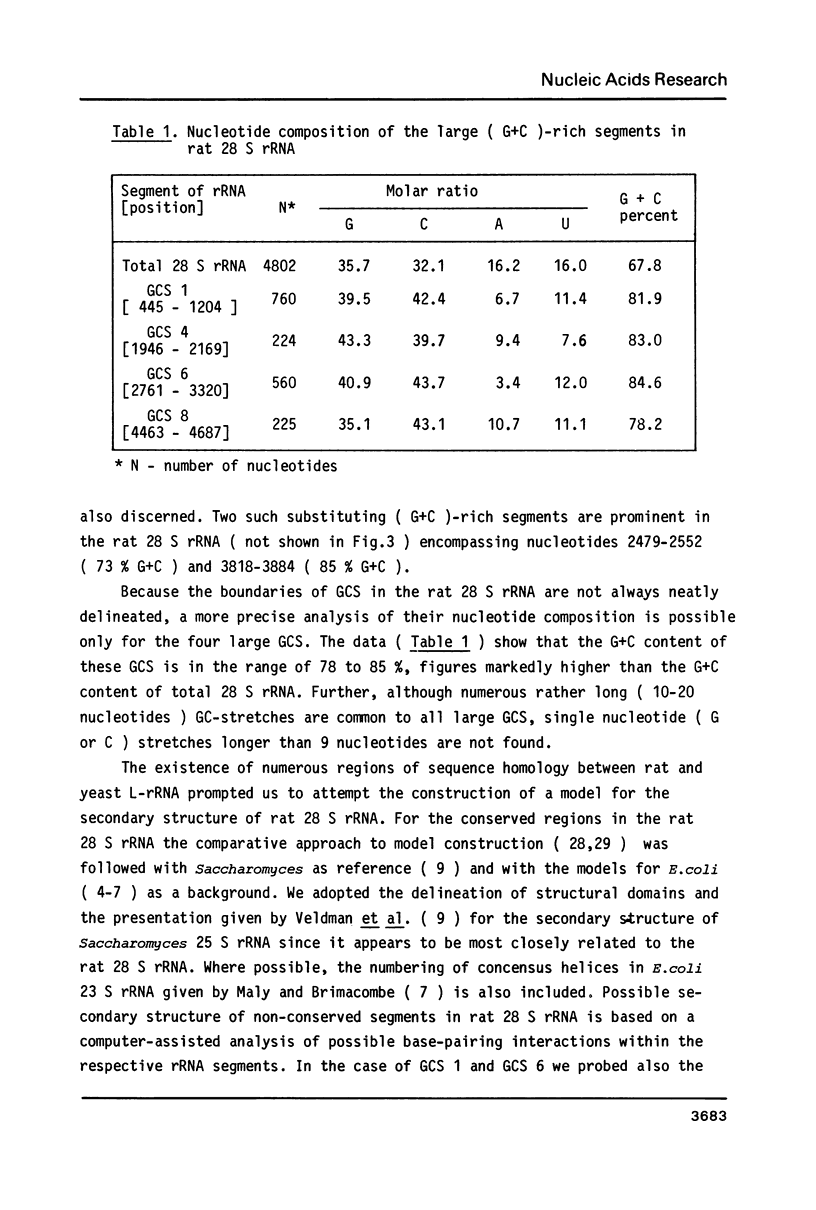
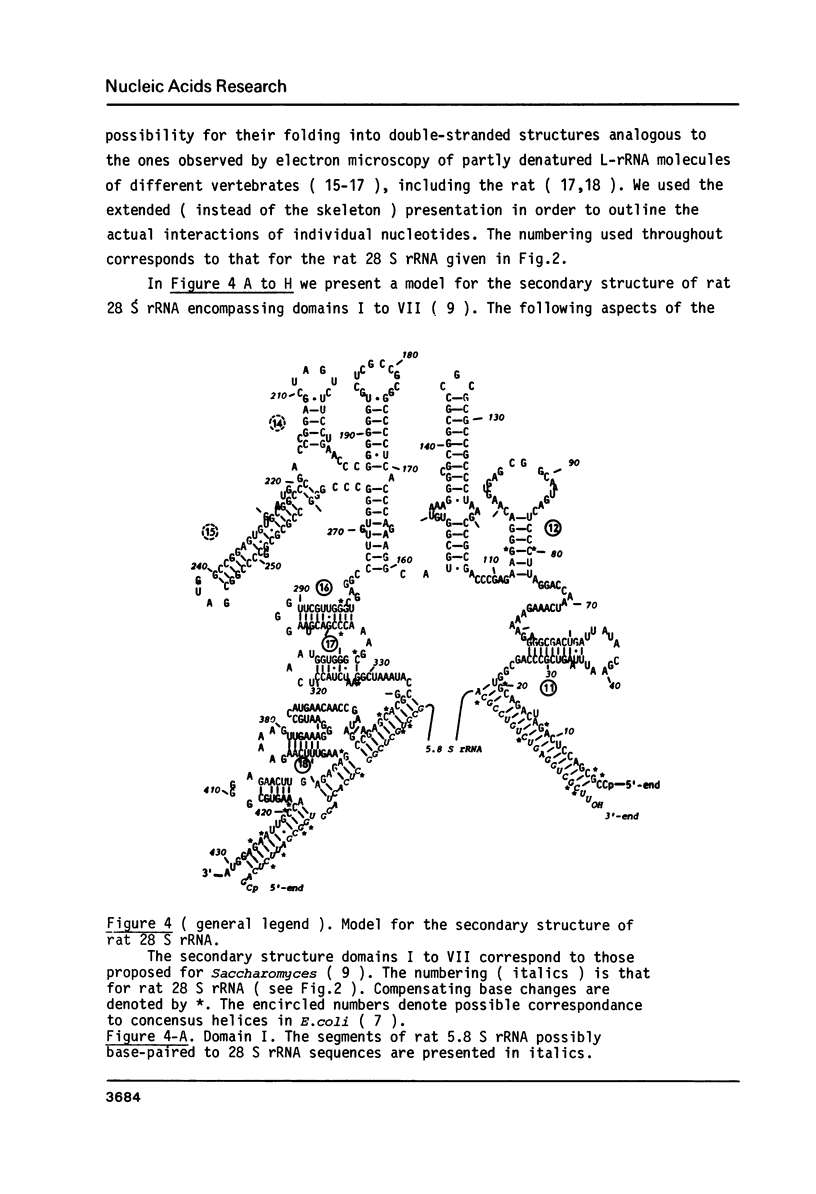
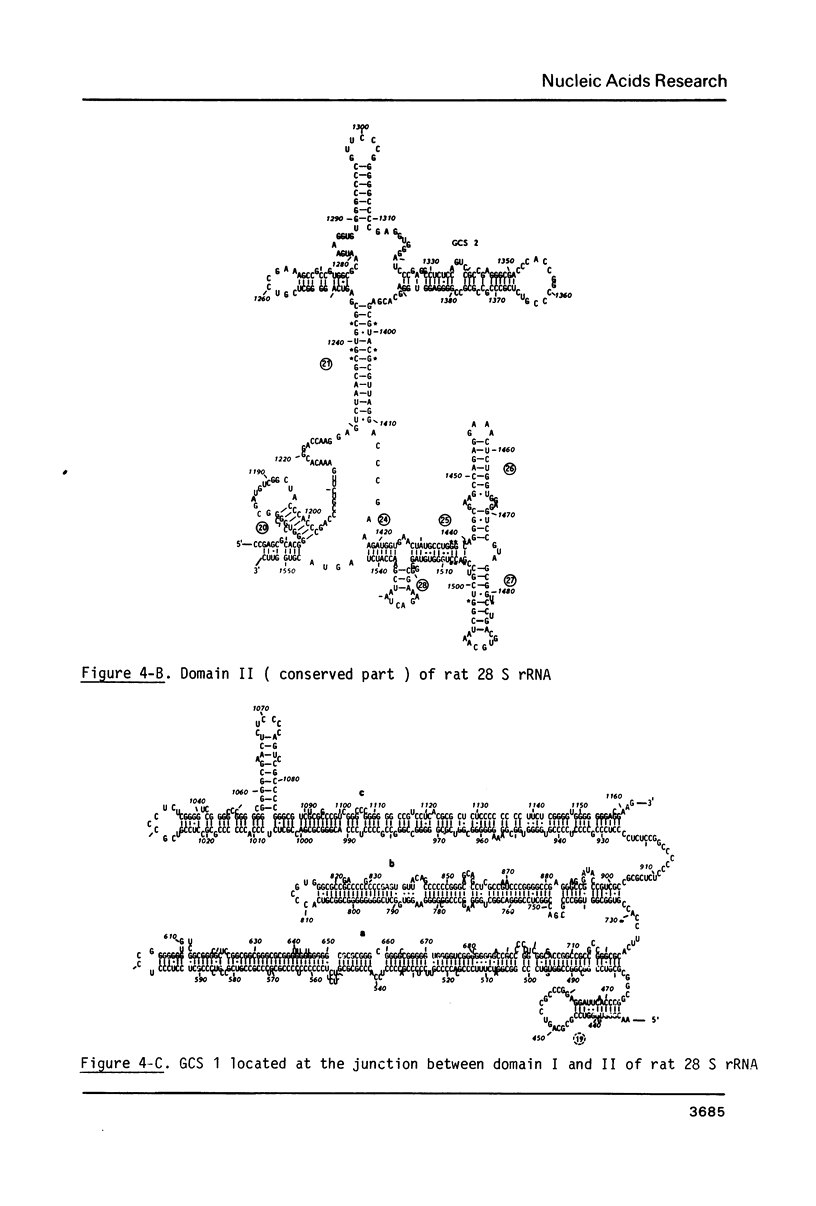
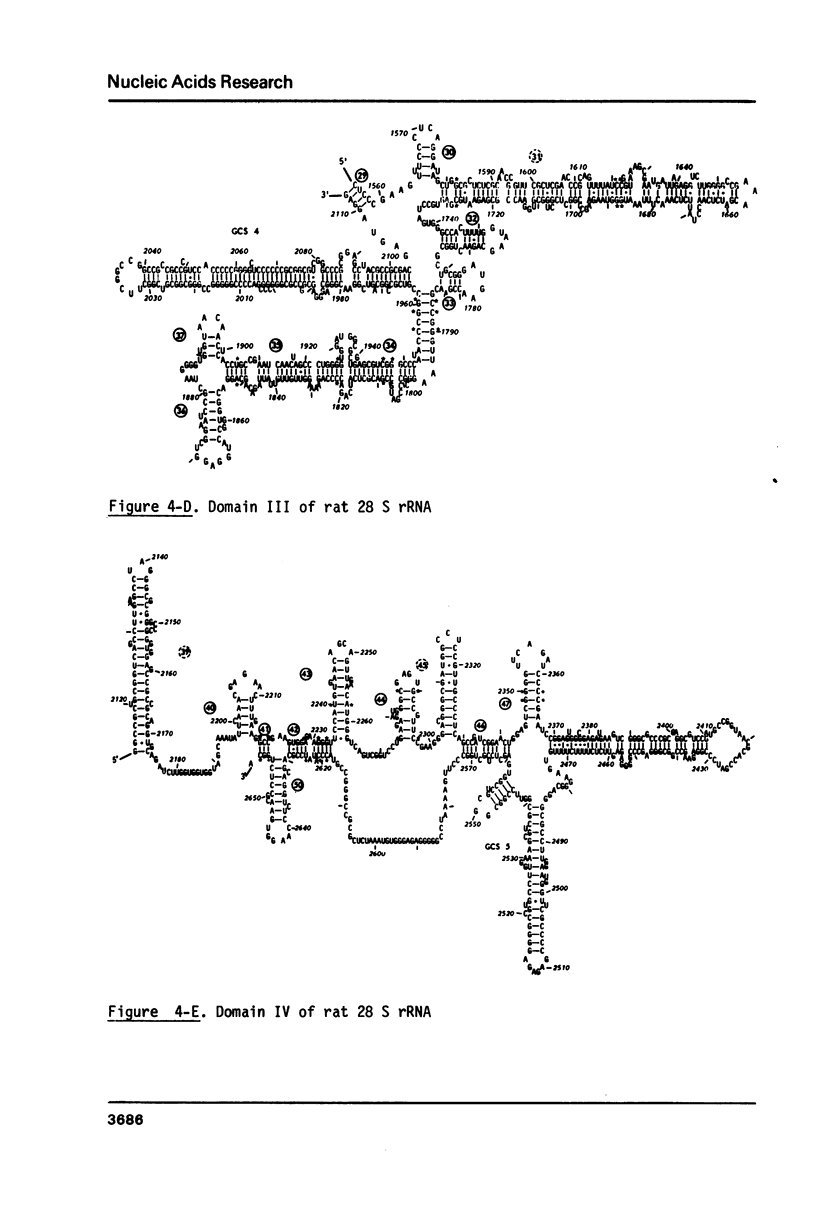
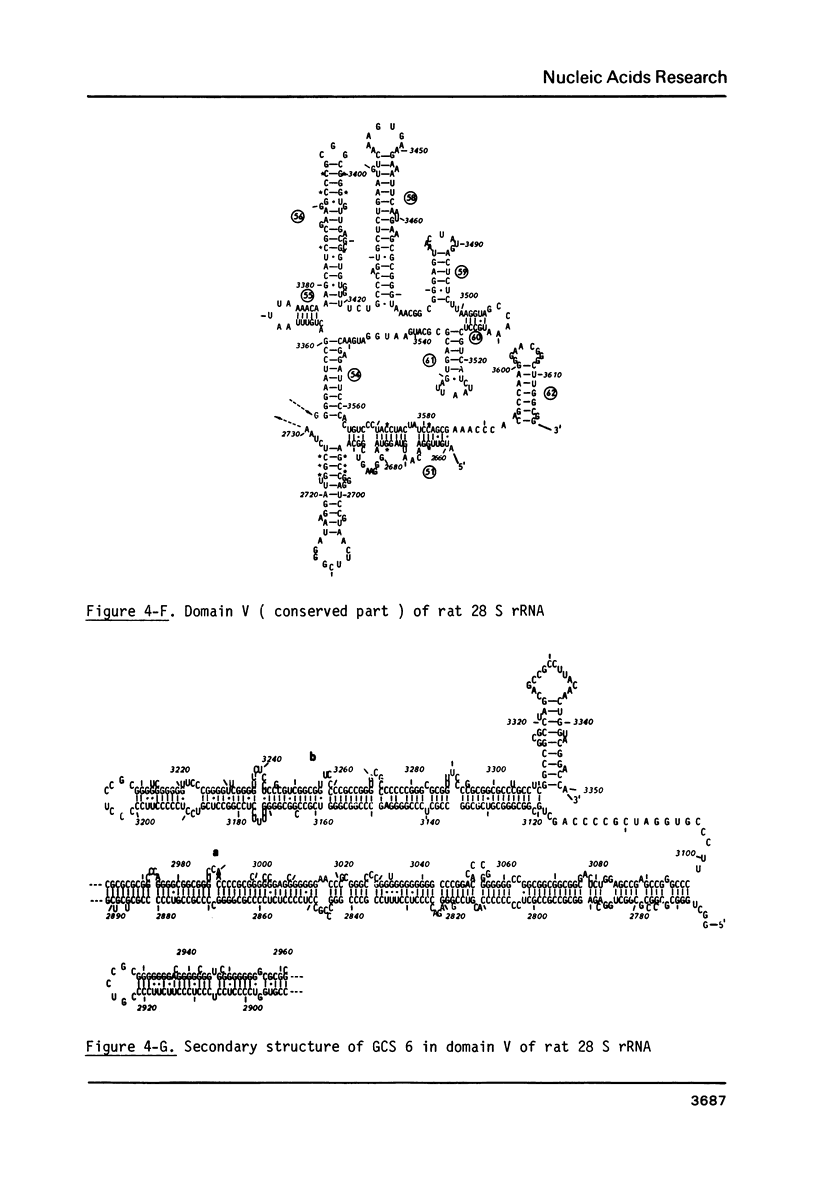
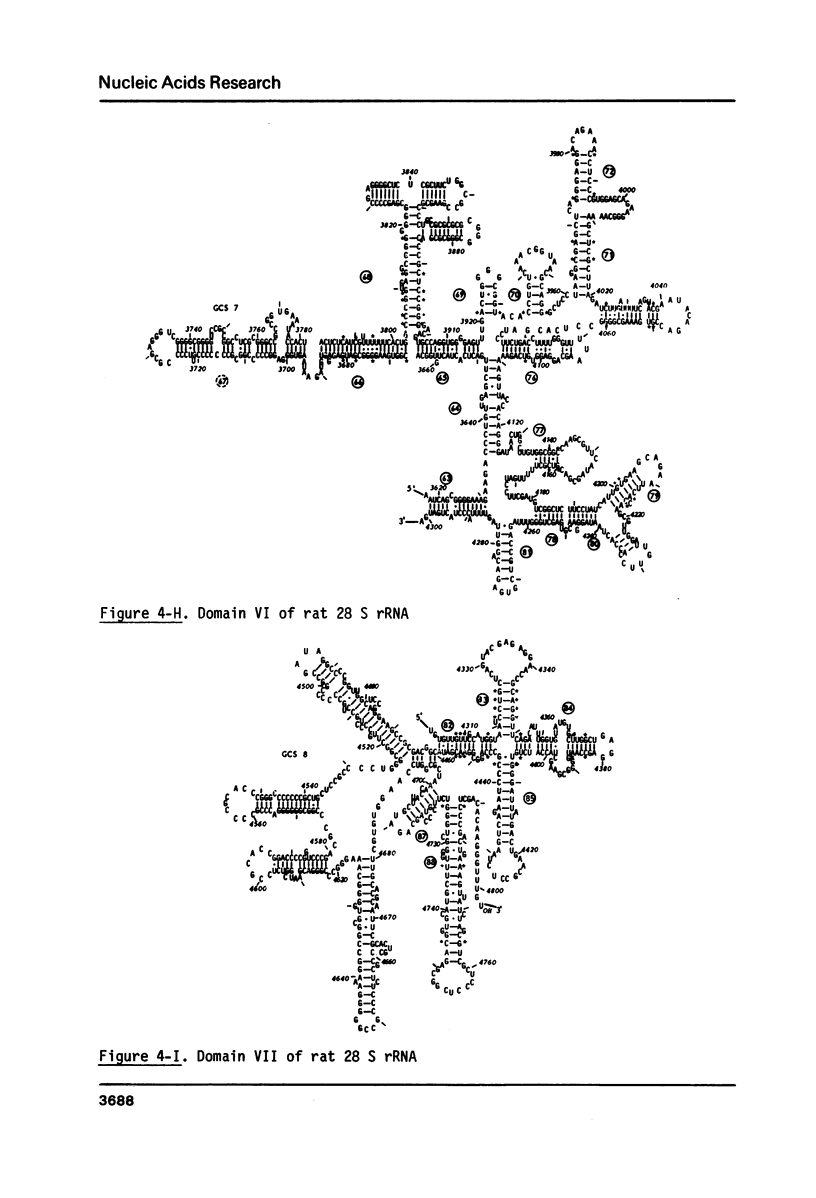
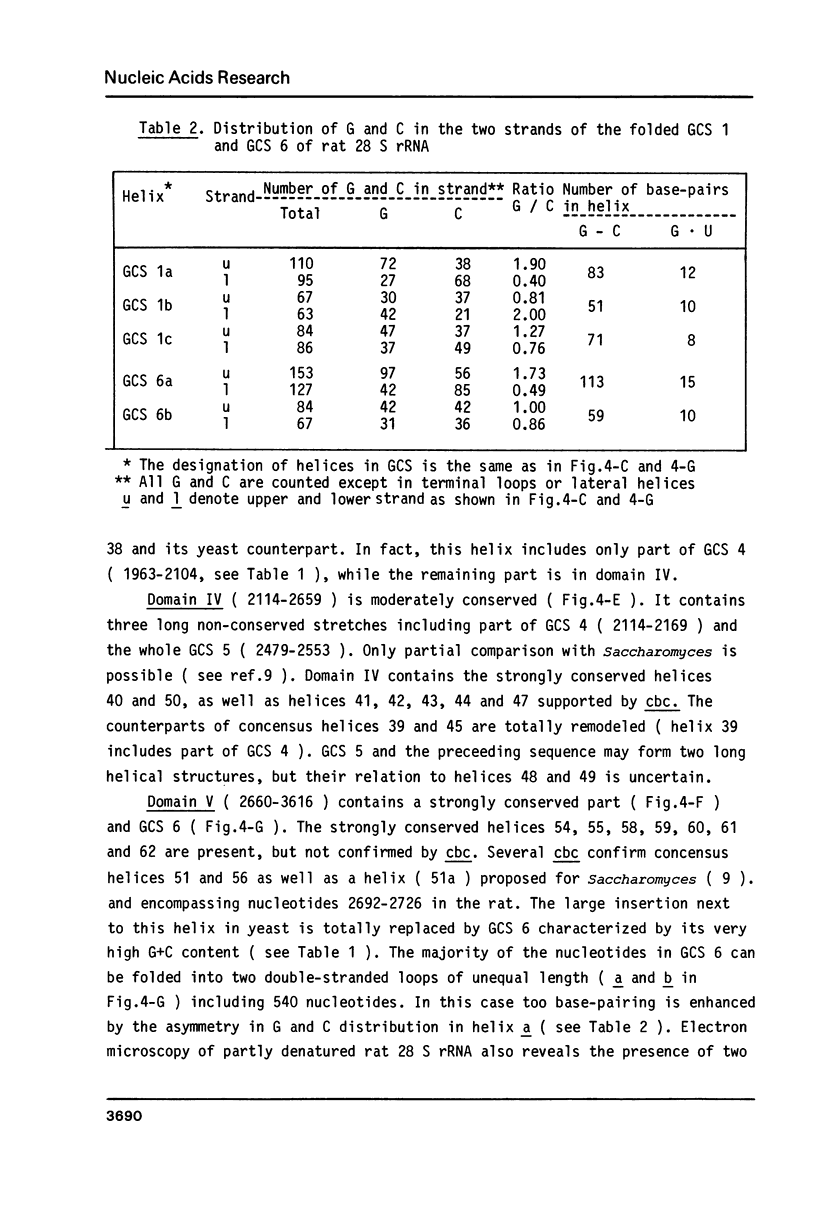
The primary structure of rat (Rattus norvegicus) 28 S rRNA is determined inferred from the sequence of cloned rDNA fragments. The rat 28 S rRNA contains 4802 nucleotides and has an estimated relative molecular mass (Mr, Na-salt) of 1.66 X 10(6). Several regions of high sequence homology with S. cerevisiae 25 S rRNA are present. These regions can be folded in characteristic base-paired structures homologous to those proposed for Saccharomyces and E. coli. The excess of about 1400 nucleotides in the rat 28 S rRNA (as compared to Saccharomyces 25 S rRNA) is accounted for mainly by the presence of eight distinct G+C-rich segments of different length inserted within the regions of high sequence homology. The G+C content of the four insertions, containing more than 200 nucleotides, is in the range of 78 to 85 percent. All G+C-rich segments appear to form strongly base-paired structures. The two largest G+C-rich segments (about 760 and 560 nucleotides, respectively) are located near the 5'-end and in the middle of the 28 S rRNA molecule. These two segments can be folded into long base-paired structures, corresponding to the ones observed previously by electron microscopy of partly denatured 28 S rRNA molecules.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braga E. A., Yussifov T. N., Nosikov V. V. Structural organization of rat ribosomal genes restriction endonuclease analysis of genomic and cloned ribosomal DNAs. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(2):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Machatt M. A., Pouyet J., Ebel J. P., Edwards K., Kössel H. Primary and secondary structures of Escherichia coli MRE 600 23S ribosomal RNA. Comparison with models of secondary structure for maize chloroplast 23S rRNA and for large portions of mouse and human 16S mitochondrial rRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4303–4324. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Dull T. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 23S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):201–204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammarano P., Pons S., Londei P. Discontinuity of the large ribosomal subunit RNA and rRNA molecular weights in eukaryote evolution. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1975;34(7):1123–1135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Olvera J., Wool I. G. The structure of rat 28S ribosomal ribonucleic acid inferred from the sequence of nucleotides in a gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7819–7831. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A. Structure and function of prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1977;32(3):193–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabeva M. D., Dudov K. P., Hadjiolov A. A., Emanuilov I., Todorov B. N. Intranuclear maturation pathways of rat liver ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 15;160(3):495–503. doi: 10.1042/bj1600495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delihas N. Liver ribosomal ribonucleic acid structural studies. Characterization of fragments from partial nuclease digestion. Biochemistry. 1967 Nov;6(11):3356–3362. doi: 10.1021/bi00863a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Wool I. G. The site of action of alpha-sarcin on eukaryotic ribosomes. The sequence at the alpha-sarcin cleavage site in 28 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9054–9060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Woese C. R. 5S RNA secondary structure. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):505–507. doi: 10.1038/256505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev O. I., Nikolaev N., Hadjiolov A. A., Skryabin K. G., Zakharyev V. M., Bayev A. A. The structure of the yeast ribosomal RNA genes. 4. Complete sequence of the 25 S rRNA gene from Saccharomyces cerevisae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6953–6958. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotz C., Zwieb C., Brimacombe R., Edwards K., Kössel H. Secondary structure of the large subunit ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli, Zea mays chloroplast, and human and mouse mitochondrial ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3287–3306. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjiolov A. A., Cox R. A., Huvos P. The presence of a high-molecular-weight (guanine-plus-cytosine)-rich segment at the 3' end of rabbit 28S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1975 Jun;147(3):625–628. doi: 10.1042/bj1470625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjiolov A. A., Milchev G. I. Mononucleotide composition of rat liver ribosomal ribonucleic acid fragments obtained by partial ribonuclease T1 digestion. C R Acad Bulg Sci. 1967;20(12):1333–1336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjiolov A. A., Venkov P. V., Dolapchiev L. B., Genchev D. D. The action of snake venom phosphodiesterase on liver ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 20;142(1):111–127. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90520-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami R., Mishima Y., Urano Y., Sakai M., Muramatsu M. Cloning and determination of the transcription termination site of ribosomal RNA gene of the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):1963–1979. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maly P., Brimacombe R. Refined secondary structure models for the 16S and 23S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7263–7286. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michot B., Bachellerie J. P., Raynal F. Sequence and secondary structure of mouse 28S rRNA 5'terminal domain. Organisation of the 5.8S-28S rRNA complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5273–5283. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Kop J., Wheaton V., Brosius J., Gutell R. R., Kopylov A. M., Dohme F., Herr W., Stahl D. A., Gupta R. Secondary structure model for 23S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6167–6189. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka T., Nomiyama H., Yoshida H., Kukita T., Kuhara S., Sakaki Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of the 26S rRNA gene of Physarum polycephalum: its significance in gene evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3163–3167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Wyler T., Hagenbüchle O. Changes in size and secondary structure of the ribosomal transcription unit during vertebrate evolution. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subrahmanyam C. S., Cassidy B., Busch H., Rothblum L. I. Nucleotide sequence of the region between the 18S rRNA sequence and the 28S rRNA sequence of rat ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 25;10(12):3667–3680. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.12.3667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Klootwijk J., de Regt V. C., Planta R. J., Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P. The primary and secondary structure of yeast 26S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6935–6952. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walseth T. F., Johnson R. A. The enzymatic preparation of [alpha-(32)P]nucleoside triphosphates, cyclic [32P] AMP, and cyclic [32P] GMP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 28;562(1):11–31. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90122-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Secondary structure maps of RNA: processing of HeLa ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2827–2831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Structure and processing of ribosomal RNA: a comparative electron microscopic study in three animals. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1975 Jul;(26):214–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



