Abstract
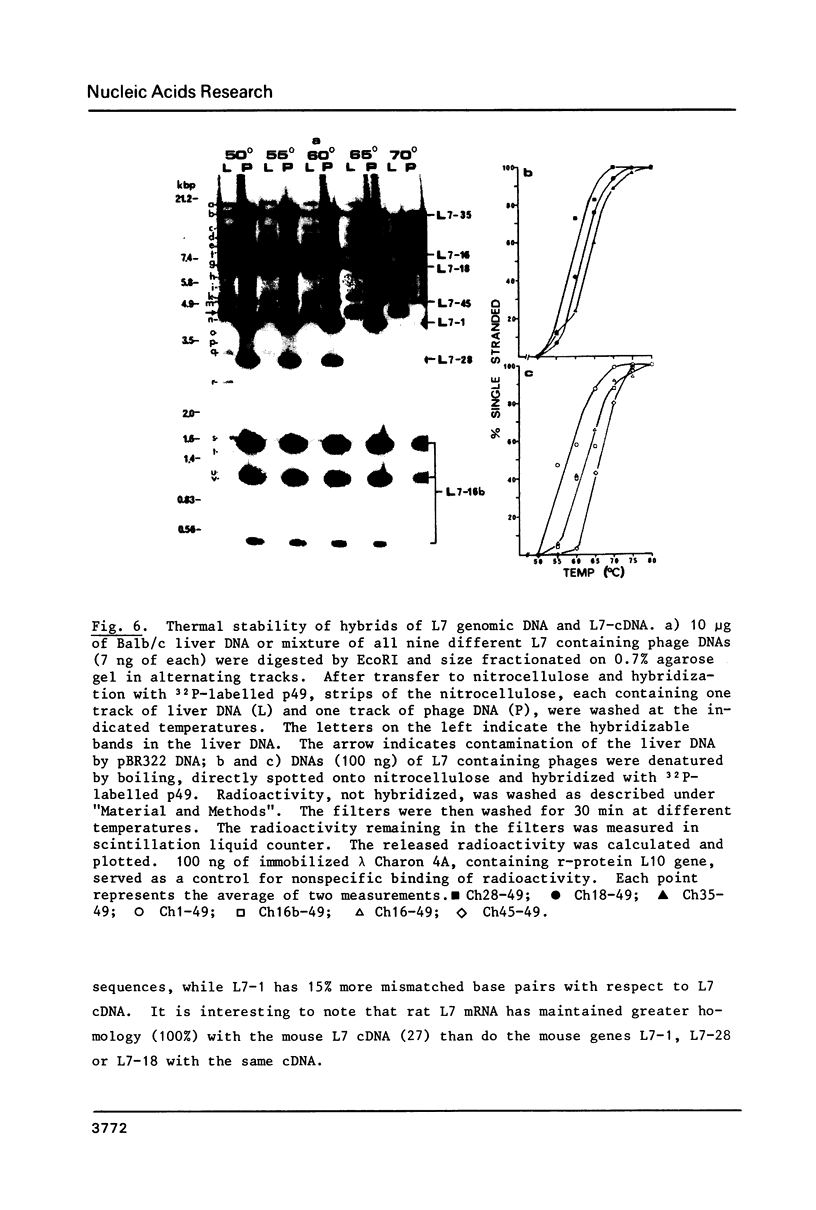
Mouse ribosomal protein L7 is encoded by a multigene family. Screening of two mouse genomic libraries with cloned L7 cDNA, has resulted in the isolation of nine independent lambda Charon 4A recombinant phages which include seven different L7 genes. Restriction enzyme mapping of six of these genes (L7-1, L7-16, L7-18, L7-28, L7-35 and L7- 16b ) reveals dissimilarity in sites within the L7 sequences as well as in the flanking regions. Electron microscopic analysis of heteroduplex and S1 nuclease mapping demonstrate that the first five genes contain the entire L7 mRNA sequence but lack introns. Based on these features we propose that these are processed genes. Of the L7 genes described here only one (L7- 16b ) exhibits a high degree of homology with L7 mRNA and contains introns. We discuss the possibility that this low representation of intron containing L7 genes may reflect the proportion of functional L7 genes in this multigene family.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Williams B. G., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Furlong L., Grunwald D. J., Kiefer D. O., Moore D. D., Schumm J. W. Charon phages: safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambda for DNA cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):161–169. doi: 10.1126/science.847462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollen G. H., Cohen L. H., Mager W. H., Klaassen A. W., Planta R. J. Isolation of cloned ribosomal protein genes from the yeast Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Gene. 1981 Sep;14(4):279–287. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90160-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzoni I., Beccari E., Luo Z. X., Amaldi F. Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein genes: isolation of recombinant cDNA clones and study of the genomic organization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1069–1086. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzoni I., Tognoni A., Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Beccari E., Buongiorno-Nardelli M., Amaldi F. Isolation and structural analysis of ribosomal protein genes in Xenopus laevis. Homology between sequences present in the gene and in several different messenger RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1982 Nov 5;161(3):353–371. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90244-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C. Recircularization and autonomous replication of a sheared R-factor DNA segment in Escherichia coli transformants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1293–1297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Eustachio P., Meyuhas O., Ruddle F., Perry R. P. Chromosomal distribution of ribosomal protein genes in the mouse. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):307–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90320-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faliks D., Meyuhas O. Coordinate regulation of ribosomal protein mRNA level in regenerating rat liver. Study with the corresponding mouse cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):789–801. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried H. M., Pearson N. J., Kim C. H., Warner J. R. The genes for fifteen ribosomal proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):10176–10183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis G. F., Hieter P. A., McBride O. W., Swan D., Leder P. Processed genes: a dispersed human immunoglobulin gene bearing evidence of RNA-type processing. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):321–325. doi: 10.1038/296321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. W., Rosenthal N., Rodakis G. C., Kafatos F. C. Evolution of two major chorion multigene families as inferred from cloned cDNA and protein sequences. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1317–1332. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90242-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Richards R. I. Human metallothionein genes--primary structure of the metallothionein-II gene and a related processed gene. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):797–802. doi: 10.1038/299797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käufer N. F., Fried H. M., Schwindinger W. F., Jasin M., Warner J. R. Cycloheximide resistance in yeast: the gene and its protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3123–3135. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Molenaar C. M., Cohen L. H., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. The structure of the gene coding for the phosphorylated ribosomal protein S10 in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5869–5878. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemischka I., Sharp P. A. The sequences of an expressed rat alpha-tubulin gene and a pseudogene with an inserted repetitive element. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):330–335. doi: 10.1038/300330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyuhas O., Perry R. P. Construction and identification of cDNA clones for mouse ribosomal proteins: application for the study of r-protein gene expression. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):113–129. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk R. J., Meyuhas O., Perry R. P. Mammals have multiple genes for individual ribosomal proteins. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90319-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mory Y. Y., Keshet E., Ram D., Kaminchik Y. Analysis of mouse embryonic gene library for the frequency of single and multiple copy genes. Mol Biol Rep. 1980 Dec 31;6(4):203–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00777525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Leder A., Leder P. Unusual alpha-globin-like gene that has cleanly lost both globin intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2806–2809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Morgan E. A. Genetics of bacterial ribosomes. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:297–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.001501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E., Schibler U., Huebner K., Croce C. M. Selective suppression of the transcription of ribosomal genes in mouse-human hybrid cells. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Mar;98(3):553–559. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040980313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosbash M., Harris P. K., Woolford J. L., Jr, Teem J. L. The effect of temperature-sensitive RNA mutants on the transcription products from cloned ribosomal protein genes of yeast. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):679–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Marcu K. B., Perry R. P. The synthesis and processing of the messenger RNAs specifying heavy and light chain immunoglobulins in MPC-11 cells. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1495–1509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Pittet A. C., Young R. A., Hagenbüchle O., Tosi M., Gellman S., Wellauer P. K. The mouse alpha-amylase multigene family. Sequence organization of members expressed in the pancreas, salivary gland and liver. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):247–266. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Tosi M., Pittet A. C., Fabiani L., Wellauer P. K. Tissue-specific expression of mouse alpha-amylase genes. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 5;142(1):93–116. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90208-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setzer D. R., McGrogan M., Schimke R. T. Nucleotide sequence surrounding multiple polyadenylation sites in the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5143–5147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. P., Munjaal R. P., Lagace L., Lai E. C., O'Malley B. W., Means A. R. Tissue-specific expression of a chicken calmodulin pseudogene lacking intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6485–6489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M., Young R. A., Hagenbüchle O., Schibler U. Multiple polyadenylation sites in a mouse alpha-amylase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2313–2323. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock R., Sweet R., Weiss M., Cedar H., Axel R. Intragenic DNA spacers interrupt the ovalbumin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1299–1303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
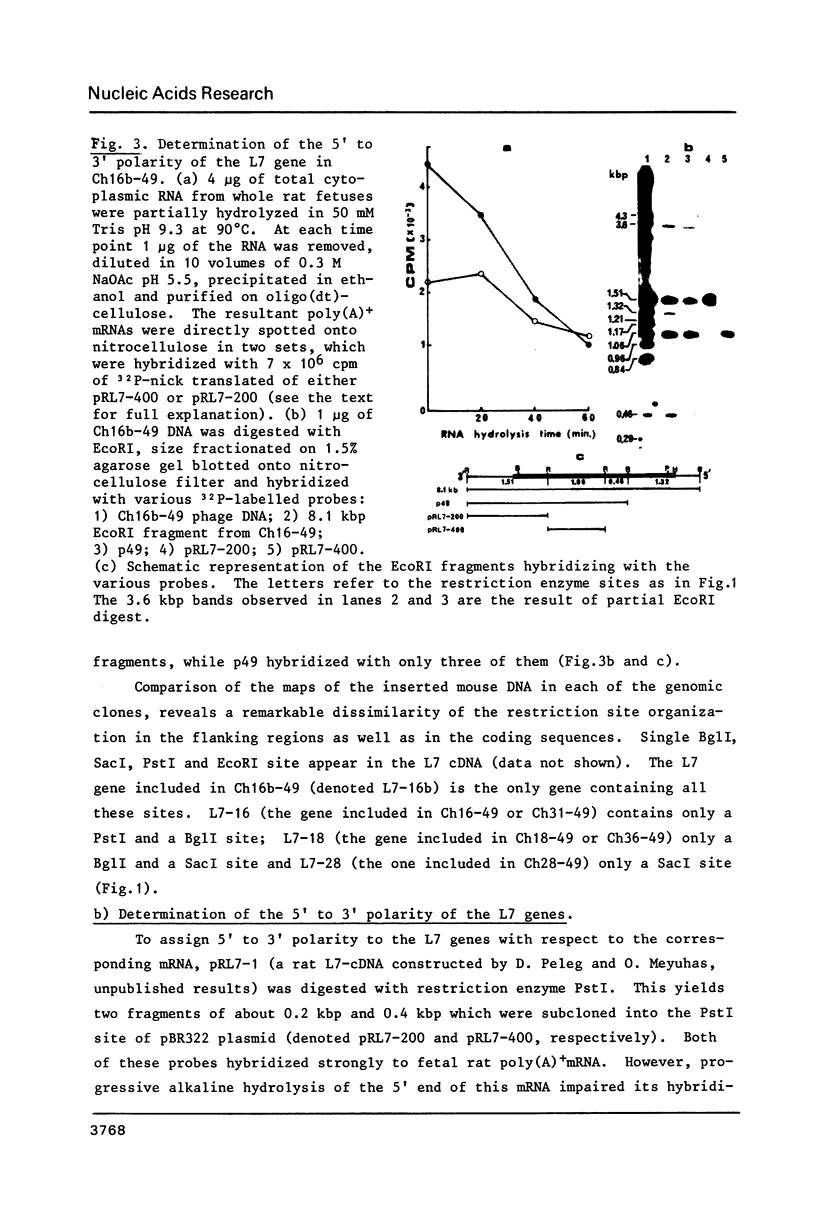
- Wilde C. D., Crowther C. E., Cowan N. J. Diverse mechanisms in the generation of human beta-tubulin pseudogenes. Science. 1982 Aug 6;217(4559):549–549. doi: 10.1126/science.6178164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]